一、gcc編譯過程示意圖?
?
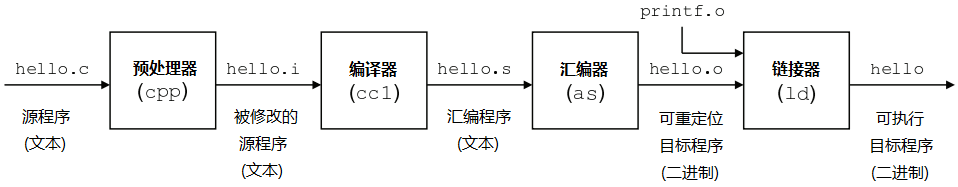
分析:
hello程序是一個高級C語言程序,這種形式容易被人讀懂。為了在系統上運行hello.c程序,每條C語句都必須轉化為低級機器指令。然后將這些指令打包成可執行目標文件格式,并以二進制形式存儲器于磁盤中。
?
gcc常用選項:
| 選項名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| ? -o | 產生目標(.i、.s、.o、可執行文件等) |
| ? -c | 通知gcc取消鏈接步驟,即編譯源碼并在最后生成目標文件 |
| ? -E | 只運行C預編譯器 |
| ? -S | 告訴編譯器產生匯編語言文件后停止編譯,產生的匯編語言文件擴展名為.s |
| -Wall | 使gcc對源文件的代碼有問題的地方發出警告 |
| -Idir | 將dir目錄加入搜索頭文件的目錄路徑 |
| -Ldir | 將dir目錄加入搜索庫的目錄路徑 |
| -llib | 鏈接lib庫 |
| -g | 在目標文件中嵌入調試信息,以便gdb之類的調試程序調試 |
?
舉例說明:
gcc -E hello.c -o hello.i(預處理)
gcc -S hello.i -o hello.s(編譯)
gcc -c hello.s -o hello.o(匯編)
gcc hello.o -o hello(鏈接)
gcc hello.c -o hello(直接編譯鏈接成可執行目標文件)
gcc -c hello.c或gcc -c hello.c -o hello.o(編譯生成可重定位目標文件)
?
二、gcc編譯多文件
文件:
hello_fn.h
hello_fn.c
main.c一次性編譯
gcc? hello_fn.c main.c –o newhello獨立編譯
gcc -Wall -c main.c -o main.o
gcc -Wall -c hello_fn.c -o hello_fn.o
gcc -Wall main.o hello_fn.o -o newhello
1. 測試代碼:
//hello_fn.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "hello_fn.h"void hello(const char* name)
{printf("hello %s!!!\n", name);
}//hello_fn.h
#ifndef _HELLO_FN_H
#define _HELLO_FN_Hvoid hello(const char* name);#endif//main.c
#include "hello_fn.h"int main(void)
{hello("everyone");return 0;
}輸出結果:
方法1:

方法二:
?











)




)


