數據類型-高級
4、復合類型
4.4、結構簡介
struct inflatable
{char name[20];float vol;double price;
};inflatable vincent; //C++
struct inflatable goose; //C
例子
// structur.cpp -- a simple structure
#include <iostream>
struct inflatable // structure declaration
{char name[20];float volume;double price;
};int main()
{using namespace std;inflatable guest ={"Glorious Gloria", // name value1.88, // volume value29.99 // price value}; // guest is a structure variable of type inflatable
// It's initialized to the indicated valuesinflatable pal ={"Audacious Arthur",3.12,32.99}; // pal is a second variable of type inflatable
// NOTE: some implementations require using
// static inflatable guest =cout << "Expand your guest list with " << guest.name;cout << " and " << pal.name << "!\n";
// pal.name is the name member of the pal variablecout << "You can have both for $";cout << guest.price + pal.price << "!\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Expand your guest list with Glorious Gloria and Audacious Arthur!
You can have both for $62.98!
*/
外部聲明可以被其后面的任何函數使用,而內部聲明只能被該聲明所屬的函數使用。通常使用外部聲明,這樣所有函數都可以使用這種類型的結構。

變量也可以在函數內部和外部定義,外部變量由所有的函數共享。C++不提倡使用外部變量,但提倡使用外部結構的聲明。
結構的賦值
可以使用賦值運算符(=)將結構A賦給另一個同類型的結構B。這樣結構中每個成員都將被設置成另一個結構中相應成員的值,即使成員是數組。這種賦值被稱為成員賦值。
// assgn_st.cpp -- assigning structures
#include <iostream>struct inflatable {char name[20];float volume;double price;
};int main() {using namespace std;inflatable bouquet = {"sunflowers",0.20,12.49};inflatable choice;cout << "bouquet: " << bouquet.name << " for $";cout << bouquet.price << endl;choice = bouquet; // assign one structure to anothercout << "choice: " << choice.name << " for $";cout << choice.price << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
bouquet: sunflowers for $12.49
choice: sunflowers for $12.49
*/
結構體數組
// arrstruc.cpp -- an array of structures
#include <iostream>struct inflatable {char name[20];float volume;double price;
};int main() {using namespace std;inflatable guests[2] = { // initializing an array of structs{"Bambi", 0.5, 21.99}, // first structure in array{"Godzilla", 2000, 565.99} // next structure in array};cout << "The guests " << guests[0].name << " and " << guests[1].name<< "\nhave a combined volume of "<< guests[0].volume + guests[1].volume << " cubic feet.\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
The guests Bambi and Godzilla
have a combined volume of 2000.5 cubic feet.
*/
結構中的位字段
與C語言一樣,C++也允許指定占用特定位數的結構成員,這使得創建于某個硬件設備上的寄存器對應的數據結構非常方便。
struct torgle_register
{unsigned int SN :4;unsigned int :4;bool goodIn:1bool goodTorgle:1;
}
4.5、共用體
共同體是一種數據格式,它能夠存儲不同的數據類型,但只能同時存儲其中的一種類型。也就是說,結構可以同時存儲int、long、double,共用體只能存儲int、long或double。
union one4all
{int int_val;long long_val;double double_val;
};struct widget
{char brand[20];int type;union id{long id_num;char id_char[20];}id_val;
};
widget prize;
if(prize.type==1)cin>>prize.id_val.id_num;
elsecin>>prize.id_val.id_char;//匿名共用體沒有名稱,其成員將成為位于相同地址處的變量
struct widget
{char brand[20];int type;union {long id_num;char id_char[20];};
};
widget prize;
if(prize.type==1)cin>>prize.id_num;
elsecin>>prize.id_char;
4.6、枚舉
enum spectnum{red, orange, yellow, green, blue, violet, indigo, yyuu};spectnum band;
band=blue; //valid
band=2000; //invalidband=orange; //valid
++band; //invalid
band=orange + red; //invalidint color =blue; //valid
band =3; //invalid
color=3+red; //valid, red converted to intband = spectnum(3); //強轉
枚舉的取值范圍
enum bits{one=1, two=2, four=4, eight=8};
bits myflag;
myflag=bits(6); //valid,because 6 is in bits range
范圍,最大值、最小值所對應的2次冪-1(負數:+1)
4.7、指針和自由存儲空間
// address.cpp -- using the & operator to find addresses
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int donuts = 6;double cups = 4.5;cout << "donuts value = " << donuts;cout << " and donuts address = " << &donuts << endl;
// NOTE: you may need to use unsigned (&donuts)
// and unsigned (&cups)cout << "cups value = " << cups;cout << " and cups address = " << &cups << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
donuts value = 6 and donuts address = 0x62fe1c
cups value = 4.5 and cups address = 0x62fe10
*/
指針與C++基本原理
面向對象編程與傳統的過程性編程的區別在于,OOP強調的是在運行階段(而不是編譯階段)進行決策。運行階段指的是程序正在運行時,編譯階段指的是編譯器將程序組合起來時。運行階段覺得就好比度假時,選擇參觀哪些景點取決于天氣和當時的心情;而編譯階段決策更像不管在什么條件下,都堅持預先設定的日程安排。總之,使用OOP時,可能在運行階段吧確定數組的長度。為使用這種方法,語言必須允許在程序運行時創建數組。C++采用的方法是,使用關鍵字new請求正確數量的農村以及使用指針來跟蹤新分配的內存的位置。在運行階段做決策并非OOP獨有的,但使用C++編寫這樣的代碼比使用C語言要簡單很多。
指針表示的是地址。*運算符被稱為間接值或解除引用運算符,將其應用與指針,可以得到該地址處存儲的值。
// pointer.cpp -- our first pointer variable
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int updates = 6; // declare a variableint *p_updates; // declare pointer to an intp_updates = &updates; // assign address of int to pointer// express values two wayscout << "Values: updates = " << updates;cout << ", *p_updates = " << *p_updates << endl;// express address two wayscout << "Addresses: &updates = " << &updates;cout << ", p_updates = " << p_updates << endl;// use pointer to change value*p_updates = *p_updates + 1;cout << "Now updates = " << updates << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Values: updates = 6, *p_updates = 6
Addresses: &updates = 0x62fe14, p_updates = 0x62fe14
Now updates = 7
*/
對于指針,&取地址運算符;*解除引用運算符。有以下的圖
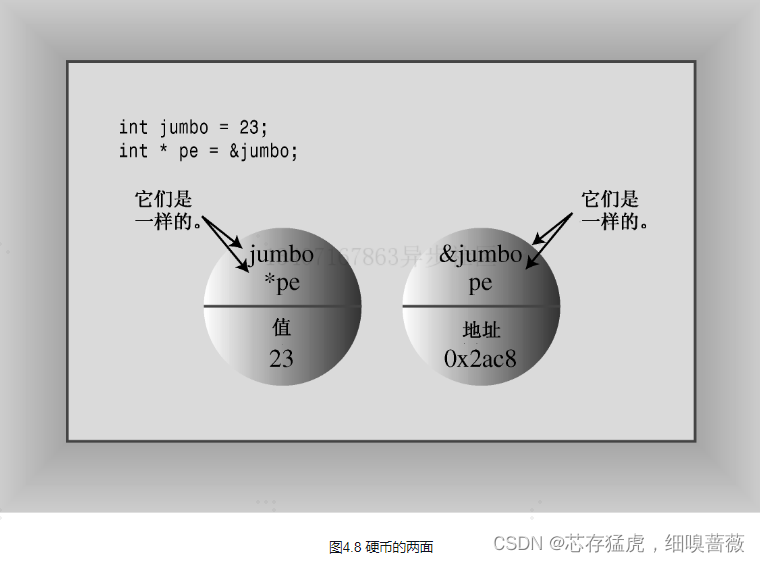
指針初始化
int * p_updates;int *ptr; //*ptr是一個int類型的值
int* ptr; //指針ptr指向int類型;ptr的類型是指針int的指針int* p1,p2; //一個指針(p1)和一個int變量(p2)double* tax_ptr;//指向double的指針
char* str; //指向char的指針
**注意:**在C++中,int*是一種復合類型,是指向int的指針
和數組一樣,指針都是基于其他類型的。雖然tax_ptr和str指向兩種長度不同的數據類型,但這兩個變量本身的長度通常是相同的。也就是說,char的地址和double的地址的長度相同。
可以在聲明語句中初始化指針。
//被初始化的是指針,而不是它指向的值
int higgens=5;
int* pt=&higgens;
// init_ptr.cpp -- initialize a pointer
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;int higgens = 5;int *pt = &higgens;cout << "Value of higgens = " << higgens<< "; Address of higgens = " << &higgens << endl;cout << "Value of *pt = " << *pt<< "; Value of pt = " << pt << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}/*
Value of higgens = 5; Address of higgens = 0x62fe14
Value of *pt = 5; Value of pt = 0x62fe14
*/
指針的危險
在C++中創建指針時,計算機將分配用來存儲地址的內存,但不會分配用來存儲指針所指向的數據的內存。為數據提供空間是一個獨立的步驟。
long *fwllow;
*fwllow=23455556; //invalid
警告
一定要在對指針應用解除引用運算符(*)之前,將指針初始化為一個確定的、適當的地址。
int* pt;
pt=0xB8000000; //type mismatch
//要將數字值作為地址來使用,應通過強制類型轉換將數字轉換為適當的地址類型
pt=(int*)0xB8000000; //type now match
new&delete
- 可以使用new來分配內存
//方式1
int* pn=new int;//方式2
int higgens;
int* pt=&higgens;
都是將一個int變量的地址賦給了指針。第2種情況下,可以通過名稱higgens來訪問該int,在第1種情況下,只能通過該指針進行訪問。
// use_new.cpp -- using the new operator
#include <iostream>
int main()
{using namespace std;int nights = 1001;int *pt = new int; // allocate space for an int*pt = 1001; // store a value therecout << "nights value = ";cout << nights << ": location " << &nights << endl;cout << "int ";cout << "value = " << *pt << ": location = " << pt << endl;double *pd = new double; // allocate space for a double*pd = 10000001.0; // store a double therecout << "double ";cout << "value = " << *pd << ": location = " << pd << endl;cout << "location of pointer pd: " << &pd << endl;cout << "size of pt = " << sizeof(pt);cout << ": size of *pt = " << sizeof(*pt) << endl;cout << "size of pd = " << sizeof pd;cout << ": size of *pd = " << sizeof(*pd) << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
nights value = 1001: location 0x62fe14
int value = 1001: location = 0x26d6710
double value = 1e+07: location = 0x26d6cf0
location of pointer pd: 0x62fe08
size of pt = 8: size of *pt = 4
size of pd = 8: size of *pd = 8
*/
- 使用delete釋放內存
int* ps= new int; //allocate memory with new
.... //use the memory
delete ps; //free memory with delete when done
這將釋放ps指向的內存,但不會刪除指針ps本身。例如,可以將ps重新指向另一個新分配的內存塊。一定要配對得使用new和delete。
不要嘗試釋放已經釋放的內存塊。另外,不能使用delete來釋放聲明變量所獲得的內存:
int *ps=new int;
delete ps;
delete ps; //not ok nowint jugs=5;
int* pi=&jugs; //ok
delete pi; //not allowed
警告:
智能用delete來釋放使用new分配的內存。然而,對空指針使用delete是安全的。
int* ps=new int;
int* pq=ps;
delete pq;
一般來說,不要創建兩個指向同一個內存塊的指針,因為這將增加錯誤地刪除同一個內存塊兩次的可能性。
- 使用new來創建動態數組
int* psome=new int[10];
delete [] psome;
//分配內存的通用格式
type_name* pointer_name =new type_name[size];
使用new和delete時,應遵守以下規則
- 不要使用delete來釋放不是new分配的內存
- 不要使用delete釋放同一個內存塊兩次
- 如果使用new[]為數組分配內存,則應使用delete[]來釋放
- 如果使用new為一個實體分配內存,則應使用delete(沒有方括號)來釋放
- 對空指針應用delete是安全的
// arraynew.cpp -- using the new operator for arrays
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;double *p3 = new double [3]; // space for 3 doublesp3[0] = 0.2; // treat p3 like an array namep3[1] = 0.5;p3[2] = 0.8;cout << "p3[1] is " << p3[1] << ".\n";p3 = p3 + 1; // increment the pointercout << "Now p3[0] is " << p3[0] << " and ";cout << "p3[1] is " << p3[1] << ".\n";p3 = p3 - 1; // point back to beginningdelete [] p3; // free the memory// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
p3[1] is 0.5.
Now p3[0] is 0.5 and p3[1] is 0.8.
*/
不能修改數組名的值,但指針時變量,可以修改它的值。
4.8、指針、數組和指針算術
指針和數組等價的原因在于指針算術和C++內部處理數組的方式。
C++將數組名解釋為地址。
// addpntrs.cpp -- pointer addition
#include <iostream>int main() {using namespace std;double wages[3] = {10000.0, 20000.0, 30000.0};short stacks[3] = {3, 2, 1};// Here are two ways to get the address of an arraydouble *pw = wages; // name of an array = addressshort *ps = &stacks[0]; // or use address operator =stacks
// with array elementcout << "pw = " << pw << ", *pw = " << *pw << endl;pw = pw + 1;cout << "add 1 to the pw pointer:\n";cout << "pw = " << pw << ", *pw = " << *pw << "\n\n";cout << "ps = " << ps << ", *ps = " << *ps << endl;ps = ps + 1;cout << "add 1 to the ps pointer:\n";cout << "ps = " << ps << ", *ps = " << *ps << "\n\n";cout << "access two elements with array notation\n";cout << "stacks[0] = " << stacks[0]<< ", stacks[1] = " << stacks[1] << endl;cout << "access two elements with pointer notation\n";cout << "*stacks = " << *stacks<< ", *(stacks + 1) = " << *(stacks + 1) << endl;cout << sizeof(wages) << " = size of wages array\n";cout << sizeof(pw) << " = size of pw pointer\n";// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
pw = 0x62fdf0, *pw = 10000
add 1 to the pw pointer:
pw = 0x62fdf8, *pw = 20000ps = 0x62fdea, *ps = 3
add 1 to the ps pointer:
ps = 0x62fdec, *ps = 2access two elements with array notation
stacks[0] = 3, stacks[1] = 2
access two elements with pointer notation
*stacks = 3, *(stacks + 1) = 2
24 = size of wages array
8 = size of pw pointer
*/
對于指針的加法
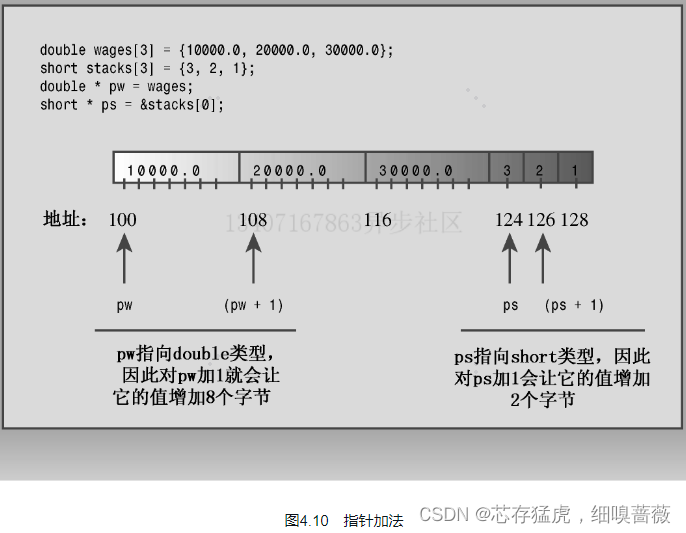
注意:
將指針變量加1后,其增加的值等于指向的類型占用的字節數。
通常,使用數組表示法時,C++都執行下面的轉換
arrayname[i] becomes *(arrayname+i)
如果使用的指針,而不是數組名,則C++也將執行同樣的轉換
pointername[i] becomes *(pointername+i)
因此,在很多情況下,可以相同的方式使用指針名和數組名。對于它們,可以使用數組方括號表示法,也可以使用解除引用運算符(*)。在多數表達式中,它們都表示地址。區別之一是,可以修改指針的值,而數組名是常量:
pointername=pointername+1; //valid
arrayname=arrayname+1; //not allow
另一個區別是,對數組應用sizeof運算符得到的是數組的長度,而對指針應用sizeof得到的是指針的長度,即使指針指向的是一個數組。
數組的指針
short tell[10];
cout<<tell; //displays &tell[0]
cout<<&tell; //displays address of whole array
? 從數字上說,兩個地址是相同的;但從概念上說,&tell[0](即tell)是一個2字節內存塊的地址,而&tell是一個20字節內存塊的地址。換句話說,tell是一個short指針(short*),而&tell是一個這樣的指針,即指向包含10個元素的short數組(short( * )[10])。
short(*pas)[10]=&tell;
指針小結
- 聲明指針
typeName* pointerName;
double* pn;
char* pc;
- 給指針賦值
應將內存地址賦給指針。可以對變量名應用 &運算符,來獲得被命名的內存的地址,new運算符返回未命名的內存的地址。
double* pn;
double* pa;
char *pc;
double bubble=3.2;pn=&bubble;
pc=new char;
pa=new double[30];
- 對指針解除引用
cout<< *pn; //3.2
*pc='s';
另一種對指針解除引用的方法是使用數組表示法,例如,pn[0]與*pn是一樣的。決不要對未被初始化為適當地址的指針解除引用。
- 區分指針和指針所指向的值
int* pt=new int; //assigns an address to the pointer pt
*pt=5; //stores the value 5 at that address
- 數組名
在多數情況下,C++將數組名視為數組的第1個元素的地址
int tacos[10];
- 指針算術
C++允許將指針和整數相加。加1的結果等于原來的地址值加上指向的對象占用的總字節數。還可以將一個指針減去另一個指針,獲得兩個指針的差。
僅當兩個指針指向同一個數組(也可以指向超出結尾的一個位置)時,這種運算才有意義。
int tacos[10]={5,2,8,2,3,4,5,5,6,7};
int* pt=tacos;
pt=pt+1;
int* pe=&tacos[9];
pe=pe-1;
int diff=pe-pt;
- 數組的動態聯編和靜態聯編
//static
int tacos[10];//dynamic
int size;
cin>>size;
int *pz=new int[size];
...
delete[]pz;
- 數組表示法和指針表示法
使用方括號數組表示法等同于對指針解除引用
tacos[0]
tacos[3]
數組名和指針變量都是如此。因此對于指針和數組名,即可以使用指針表示法,也可以使用數組表示法
int *pt=new int[10];
*pt=5;
pt[0]=6;
pt[9]=44;int coats[10];
*(coats+4)=12;
指針和字符串
注意:
在cout和多數C++表達式中,char數組名、char指針以及用括號擴起來的字符串常量都被解釋為字符串第一個字符的地址。
// ptrstr.cpp -- using pointers to strings
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // declare strlen(), strcpy()int main() {using namespace std;char animal[20] = "bear"; // animal holds bearconst char *bird = "wren"; // bird holds address of stringchar *ps; // uninitializedcout << animal << " and "; // display bearcout << bird << "\n"; // display wren// cout << ps << "\n"; //may display garbage, may cause a crashcout << "Enter a kind of animal: ";cin >> animal; // ok if input < 20 chars// cin >> ps; Too horrible a blunder to try; ps doesn't// point to allocated spaceps = animal; // set ps to point to stringcout << ps << "!\n"; // ok, same as using animalcout << "Before using strcpy():\n";cout << animal << " at " << (int *) animal << endl;cout << ps << " at " << (int *) ps << endl;ps = new char[strlen(animal) + 1]; // get new storagestrcpy(ps, animal); // copy string to new storagecout << "After using strcpy():\n";cout << animal << " at " << (int *) animal << endl;cout << ps << " at " << (int *) ps << endl;delete [] ps;// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
bear and wren
Enter a kind of animal: fox
fox!
Before using strcpy():
fox at 0x62fdf0
fox at 0x62fdf0
After using strcpy():
fox at 0x62fdf0
fox at 0x2576cd0
*/
通過使用strcpy()和new,將獲得"fox"的兩個獨立副本
經常需要將字符串放到數組中。初始化數組時,請使用=運算符;否則應使用strcpy()或strncpy()。
char food[20]="carrots"; //initalization
strcpy(food,"flan"); //otherwise
對于strncpy()
strncpy(food,"a picnic basket filled with many goodies",19);
food[19]='\0';
這樣最多將19個字符復制到數組中,然后將最后一個元素設置成空字符。如果該字符串少于19個字符,則strncpy()將在復制完該字符串之后加上空字符,以 標記該字符串的結尾。
使用new創建動態結構
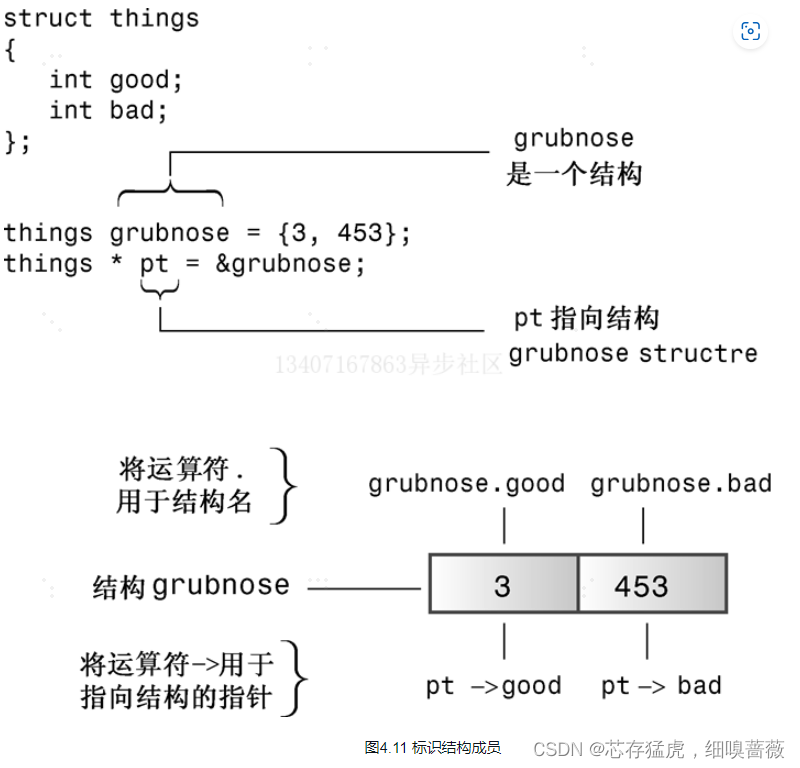
提示
如果結構標識符時結構名,則使用句點運算符;如果標識符是指向結構的指針,則使用箭頭運算符。
另一種訪問結構成員的方法是,如果ps是指向結構的指針,則*ps就是被指向的值——結構本身。由于*ps是一個結構,因此(*ps).price是該結構的price成員。
// newstrct.cpp -- using new with a structure
#include <iostream>struct inflatable { // structure definitionchar name[20];float volume;double price;
};int main() {using namespace std;inflatable *ps = new inflatable; // allot memory for structurecout << "Enter name of inflatable item: ";cin.get(ps->name, 20); // method 1 for member accesscout << "Enter volume in cubic feet: ";cin >> (*ps).volume; // method 2 for member accesscout << "Enter price: $";cin >> ps->price;cout << "Name: " << (*ps).name << endl; // method 2cout << "Volume: " << ps->volume << " cubic feet\n"; // method 1cout << "Price: $" << ps->price << endl; // method 1delete ps; // free memory used by structure// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
Enter name of inflatable item: Fab
Enter volume in cubic feet: 1.4
Enter price: $27.99
Name: Fab
Volume: 1.4 cubic feet
Price: $27.99
*/
- 使用new和delete
// delete.cpp -- using the delete operator
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // or string.h
using namespace std;
char *getname(void); // function prototypeint main() {char *name; // create pointer but no storagename = getname(); // assign address of string to namecout << name << " at " << (int *) name << "\n";delete [] name; // memory freedname = getname(); // reuse freed memorycout << name << " at " << (int *) name << "\n";delete [] name; // memory freed again// cin.get();// cin.get();return 0;
}char *getname() { // return pointer to new stringchar temp[80]; // temporary storagecout << "Enter last name: ";cin >> temp;char *pn = new char[strlen(temp) + 1];strcpy(pn, temp); // copy string into smaller spacereturn pn; // temp lost when function ends
}/*
Enter last name: Fredlkin
Fredlkin at 0x726cd0
Enter last name: Pook
Pook at 0x726cd0
*/
自動存儲、靜態存儲和動態存儲
- 自動存儲
? 在函數內部定義的常規變量使用自動存儲空間,被稱為自動變量,這以為著它們在所屬的函數被調用時自動產生,在該函數結束時消亡。
? 實際上,自動變量是一個局部變量,其作用域為包含它的代碼塊。
? 自動變量通常存儲在棧中。這意味著執行代碼塊時,其中的變量依次加入到棧中,而離開代碼塊時,將按相反的順序釋放這些變量。這被稱為后進先出(LIFO)。因此,在程序執行的過程中,棧不斷地增大和縮小。
- 靜態存儲
? 靜態存儲是整個程序執行期間都存在的存儲方式。使變量稱為靜態的方式有兩種:一種是在函數外面定義它;另一種是在聲明變量時使用關鍵字static:
static double fee=56.50;
- 動態存儲
? new和delete運算符提供了一種比自動變量和靜態變量更靈活的方法。它們管理了一個內存池,這在C++中被稱為自由存儲空間(free store)或堆(heap)。該內存池同用于靜態變量和自動變量的內存時分開的。
? new和delete讓我們能夠在一個函數中分配內存,在另一個函數中釋放它。因此,數據的生命周期不完全受程序或函數的生存時間控制。
棧、堆和內存泄漏
? 如果使用了new運算符在自由存儲空間(或堆)上創建變量后,沒有調用delete,將會發生什么?
? 如果沒有調用delete,則即使包含指針的內存由于作用域規則和對象生命周期的原因而被釋放,在自由存儲空間上動態分配的變量或結構也將繼續存在。實際上,將會無法訪問自由存儲空間中的結構,因為指向這些內存的指針無效。這將導致內存泄漏。被泄漏的內存將在程序的整個生命周期內都不可使用;這些內存被分配出去,但無法收回。
4.9、類型組合
//結構定義
struct antarctica_year_end
{int year;
};antarctica_year_end s01,s02,s03; //創建變量
s01.year=1998; //使用成員運算符訪問成員antarctica_year_end=&s02; //創建指向這種結構的指針
pa->year=1999; //使用間接成員運算符訪問成員antarctica_year_end trio[3]; //創建結構數組
trio[0].year=2003; //使用成員運算符訪問成員
(trio+1)->year=2004; //使用間接成員運算符const antarctica_year_end* arp[3]={&s01,&s02,&s03}; //創建指針數組
std::cout<<arp[1]->year<<std::endl; //使用間接運算符const antarctica_year_end** ppa=arp; //創建上面數組的指針 ppa=arp
std::cout<<(*ppa)->year<<std::endl; //*ppa為&s01,式子為s01的year成員
std::cout<<(*(ppb+1))->year<<std::endl;
例子
// mixtypes.cpp --some type combinations
#include <iostream>struct antarctica_years_end
{int year;/* some really interesting data, etc. */
};int main()
{antarctica_years_end s01, s02, s03; s01.year = 1998;antarctica_years_end * pa = &s02;pa->year = 1999;antarctica_years_end trio[3]; // array of 3 structurestrio[0].year = 2003;std::cout << trio->year << std::endl;const antarctica_years_end * arp[3] = {&s01, &s02, &s03};std::cout << arp[1]->year << std::endl;const antarctica_years_end ** ppa = arp; auto ppb = arp; // C++0x automatic type deduction
// or else use const antarctica_years_end ** ppb = arp; std::cout << (*ppa)->year << std::endl;std::cout << (*(ppb+1))->year << std::endl;// std::cin.get();return 0;
}
/*
2003
1999
1998
1999
*/
4.10、vector、array
vector
模板類vector類似于string類,也是一種動態數組。可以在運行階段設置vector對象的長度,可以在末尾附加新數據,還可以再中間插入新數據。
聲明創建一個名為vt的vector對象,它可以存儲n_elem個類型為typeName的元素
vector<typeName> vt(n_elem)
//其中參數n_elem可以是整型常量,也可以是整型變量。#include<vector>
using namespace std;
vector<int>vi;
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<double> vd(n);
array
? vector類的功能比數組強大,但代價是效率較低。如果需要長度固定的數組,使用數組是更佳的選擇,但代價是不那么方便和安全。array,也位于名稱空間std中。
? 與數組一樣,array對象的長度也是固定的,也使用棧(靜態內存分配),而不是自由存儲區,因此其效率與數組相同,但更方便、安全。
array<typeName,n_elem> arr;
//聲明創建一個名為arr的array對象,它包含n_elem個類型為typeName的元素。
//n_elem不能是變量#include<array>
....
using namespace std;
array<int,5> ai;
array<double,4>ad={1.2, 2.1, 3.43, 4.3};
對比
// choices.cpp -- array variations
#include <iostream>
#include <vector> // STL C++98
#include <array> // C++0xint main() {using namespace std;
// C, original C++double a1[4] = {1.2, 2.4, 3.6, 4.8};
// C++98 STLvector<double> a2(4); // create vector with 4 elements
// no simple way to initialize in C98a2[0] = 1.0 / 3.0;a2[1] = 1.0 / 5.0;a2[2] = 1.0 / 7.0;a2[3] = 1.0 / 9.0;
// C++0x -- create and initialize array objectarray<double, 4> a3 = {3.14, 2.72, 1.62, 1.41};array<double, 4> a4;a4 = a3; // valid for array objects of same size
// use array notationcout << "a1[2]: " << a1[2] << " at " << &a1[2] << endl;cout << "a2[2]: " << a2[2] << " at " << &a2[2] << endl;cout << "a3[2]: " << a3[2] << " at " << &a3[2] << endl;cout << "a4[2]: " << a4[2] << " at " << &a4[2] << endl;
// misdeeda1[-2] = 20.2;cout << "a1[-2]: " << a1[-2] << " at " << &a1[-2] << endl;cout << "a3[2]: " << a3[2] << " at " << &a3[2] << endl;cout << "a4[2]: " << a4[2] << " at " << &a4[2] << endl;// cin.get();return 0;
}/*
a1[2]: 3.6 at 0x62fdf0
a2[2]: 0.142857 at 0x25b6720
a3[2]: 1.62 at 0x62fdb0
a4[2]: 1.62 at 0x62fd90
a1[-2]: 20.2 at 0x62fdd0
a3[2]: 1.62 at 0x62fdb0
a4[2]: 1.62 at 0x62fd90
*/
首先,無論是數組、vector對象還是array對象,都可以使用標準數組表示法來訪問各個元素。
其次,從地址中可知,array對象和數組存儲在相同的內存區域(即棧)中,而vector對象存儲在另一個區域(自由存儲區或堆)中。
第三,可以將一個array對象賦給另一個array對象;對于數組,必須逐個元素復制數據。
數組越界無法禁止。對于vector和array對象,可以禁止,但仍然不安全。














)




)