Here are several convenient ways to tell whether a .NET assembly is strongly named.? (English language note: I assume the form “strongly named” is preferred over “strong named” since that’s the form used in the output of the sn.exe tool shown immediately below.)
Towards the end, this post discusses use of Strong Names with Silverlight.
Then in the final section of this post the often confusing – though very important – differences between Strongly Named assemblies and Digitally Signed assemblies are clarified.
But first, here are three approaches for telling whether a .NET Assembly is Strongly Named...
Approach #1: Testing for Strong Name on Command Line or in a Script
You tell whether an Assembly/DLL has been successfully strong-named using the Strong Name Tool (sn.exe) (which can be found somewhere like here: C:\Program Files\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v7.0A\bin\sn.exe) by running the following at the command line:
sn -vf System.Data.dll
Here are the results when running against a strongly named assembly, then one that is not strongly named.
C:\> sn -v C:\WINDOWS\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\System.Data.dll
Microsoft (R) .NET Framework Strong Name Utility? Version 4.0.30128.1
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.? All rights reserved.
Assembly 'C:\...\System.Data.dll' is valid
C:\> sn -v C:\WINDOWS\ismif32.dll
Microsoft (R) .NET Framework Strong Name Utility? Version 4.0.30128.1
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.? All rights reserved.
C:\WINDOWS\ismif32.dll does not represent a strongly named assembly
Since the return value from sn.exe is 0 (zero) when the strong name is in place, and 1 (one) if not correctly strong named, you can test for this in a script by examining ERRORLEVEL, as in the following (put it into a text file called “sn-test.bat” for example and run as “sn-test foo.dll”):
@ echo off
if "%1"=="" goto END sn -q?-vf %1 > NUL if ERRORLEVEL 1 goto NOT_STRONG
:STRONG
echo Has strong name: %1
goto END
:NOT_STRONG
echo Not strong named: %1
goto END
:END
Note that this will tell you whether it has SOME strong name, but does not tell you which one. So this technique is not appropriate for all uses, but might help in, say, an automated script that checks your about-to-be-released assemblies to make sure you remembered to add the strong names to them. (See note below – “Strong Names not for Security”.)
If you need finer-grain control and wish to write low-level code to ascertain the strong-naming status of an assembly, you can do that too.
Approach #2: Viewing Strong Name Details with IL DASM
Visual Studio ships with a handy utility – the Microsoft Intermediate Language Disassembler (ILDASM.EXE (tutorial)) – which can be used for disassembling .NET binaries?to peruse the contents, perhaps for viewing the?method signatures or viewing the .NET Assembly Manifest.?It is helpful to load an assembly using IL DASM?and examine the manifest to see whether there is a strong name key available. Your first step is to load the desired Assembly using the ildasm.exe utility. On my Windows 7 machine, IL DASM is found at
C:\Program Files\Microsoft SDKs\Windows\v7.0A\bin\ildasm.exe
and you can load up the System.Drawing.dll .NET Assembly as in the following example:
C:\> ildasm C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\System.Drawing.dll
Once loaded, you will see a screen like the one below.
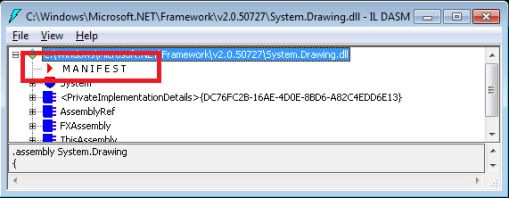
Note the MANIFEST section highlighted. Double-click on MANIFEST which load the following screen of manifest-specific data:
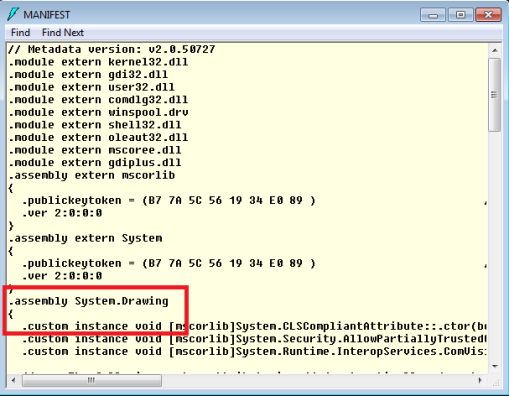
Find the section for the Assembly you’ve loaded – in this case, System.Drawing and following the section (which is marked with the “.assembly System.Drawing” directive highlighted above, and the content begins with the opening brace (“{“) shown above, and ends with its matching brace?later in the manifest, and shown below.

The highlighted part of the manifest is the public key for this assembly. This public key can also be seen using the sn.exe tool, as follows:
C:\> sn -Tp C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v2.0.50727\System.Drawing.dll echo Not strong named: %1
Microsoft (R) .NET Framework Strong Name Utility? Version 3.5.30729.1
Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.? All rights reserved.
Public key is 002400000480000094000000060200000024000052534131000400000100010007d1fa57c4aed9?f0a32e84aa0faefd0de9e8fd6aec8f87fb03766c834c99921eb23be79ad9d5dcc1dd9ad2361321?02900b723cf980957fc4e177108fc607774f29e8320e92ea05ece4e821c0a5efe8f1645c4c0c93?c1ab99285d622caa652c1dfad63d745d6f2de5f17e5eaf0fc4963d261c8a12436518206dc09334?4d5ad293
Public key token is b03f5f7f11d50a3a
Note that the Public key in the output from sn.exe matches the highlighted public key in the image immediately above it (of course you should ignore the spaces between pairs of digits in the screen shot).
If an assembly is not strongly named, the Public key will be missing from the manifest and will not be displayed by sn -Tp command.
Since IL DASM comes with both Visual Studio and with the .NET SDK, it is already on the desktop for most .NET Developers, and is therefore sometimes the handiest tool. The third option, .NET Reflector, is a third-party tool, though one adopted by many .NET Developers due to its awesomeness. Reflector conveniently shows more details about the strong name.
Approach #3: Viewing Strong Name Details with Reflector
You can load an assembly in the free version?RedGate’s .NET Reflector and quickly see the strong name details – or lack thereof for non-strong named assemblies. In the image below, see at the bottom where the strong name string is highlighted. Note that the strong name has five parts (though the Culture is optional):
- Simple Name or Assembly name without the “.dll” extension (“System.Data” in case of assembly “System.Data.dll”)
- Assembly version (“2.0.0.0″ in case of “System.Data.dll”)
- Culture (“neutral” in case of “System.Data.dll”, but might be “en-us” for US English, or one of many others)
- Public Key or PublicKeyToken?(public part of the cryptographic public/private key pair used to sign the assembly, “b77a5c561934e089″ in case of “System.Data.dll”)
- Processor Architecture – Defines the assembly’s format, such as MSIL (intermediate language) or x86 (binary for Intel x86 processors)

In the next image, see at the bottom where the LACK OF complete name string is highlighted; this assembly does not have a strong name to display, so “Name” field includes a null value for PublicKeyToken. (Note that in the real world, Spring.Core.dll is in fact released as strongly named by the good folks on the Spring.NET project; the screen shot below was done on a non-production version of that DLL.)

While you are at it… make Reflector the default program for “launching”?assemblies (actually would need to be for all files ending in the .DLL extension, but Reflector is smart enough to not choke on non-.NET assemblies).
Approach #4: (Bonus!) Viewing Strong Name with Windows Explorer
This post promised three ways to tell if a .NET?Assembly has a strong name?- but here is a bonus?4th way. Windows Explorer will not show you the strong name characteristics of an assembly, with one exception – for assemblies in the Global Assembly Cache (GAC), strong name data is included in the Properties dialog. If ?you are examining the GAC, this can be handy.
Of course, if an assembly is in the GAC at all, it is strongly named by definition; assemblies are required by .NET to be strongly named to be allowed in the GAC.
Strong Naming for Silverlight
Silverlight also has support for strongly named assemblies, which is needed for the Cached Assembly Feature introduced in Silverlight 3.0.
(Silverlight 4 also introduces supports for digital signatures on XAP files, created by signtool.exe, which are validated by the Silverlight runtime for out-of-browser (OOB) applications running with elevated trust.)
Strongly Name Assembly != Digitally Signed Assembly
Strong Names and Digital Signatures are Orthogonal Concerns?- Almost
Strongly Naming and Digitally Signing are largely orthogonal concerns. They have different purposes, different tools, and the digital certificates may come from different sources (for publicly distributed binaries, the certs for Digital Signing usually will come from a PKI source, though that is not essential for the Strong Naming certs).
The only dependency among them is that if the Assembly is to be Strongly Named, then the?Strong Naming step has to happen before the Digital Signing step.3
How do I check whether an assembly is Digitally Signed? You can run the following command to determine whether assembly “foo.dll” is digitally signed:
signtool verify /pa foo.dll
If you want to see the hash – for example, to compare with another assembly’s hash – then you can view it using the following command sequence:
signtool verify /v /pa /ph foo.dll | find "Hash"
Of course, you can use sn.exe and signtool.exe together (one after another) to examine an assembly to ascertain both whether it is strongly named and whether it has been digitally signed.
Strong Names are NOT for Security!
Finally, a word of caution… Strong names are about versioning, not about security. Strong names are more about avoiding DLL Hell (which is largely an accidental concern) than about avoiding hackers (which is deliberate).?While a strong name may help alert you to tampering, realize that strong names can be hacked, and Microsoft emphasizes that??strong-named assemblies do not give the same level of trust as digitally signing:
Strong names provide a strong integrity check. Passing the .NET Framework security checks guarantees that the contents of the assembly have not been changed since it was built. Note, however, that strong names in and of themselves do not imply a level of trust like that provided, for example, by a digital signature and supporting certificate.
Consider?digitally signing your .NET assemblies if it is important to you or your customers that the origin of the assemblies be traceable and verifiable. One source of digital certificates that can be used for Digitally Signing assemblies is Verisign which has Authenticode Certificates.








方法與示例)




移動語義底層分析)
的矩陣| 使用Python的線性代數)

![Xpath[轉]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/Xpath[轉])

的底層分析)
