本內容來自《跟著迪哥學Python數據分析與機器學習實戰》,該篇博客將其內容進行了整理,加上了自己的理解,所做小筆記。若有侵權,聯系立刪。
迪哥說以下的許多函數方法都不用死記硬背,多查API多看文檔,確實,跟著迪哥混就完事了~~~
Numpy官網API
以下代碼段均在Jupyter Notebook下進行運行操作
每天過一遍,騰訊阿里明天見~
一、 基本操作
Ⅰ,array數組
導包
import numpy as np#導包,起個別名np
常規方法對列表中的每一個元素都+1,在python中是不可行的
array = [1,2,2,3]
array + 1
"""
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
TypeError Traceback (most recent call last)
<ipython-input-3-53772fbb9675> in <module>1 array = [7,8,7,0,8,4,9,3,4]
----> 2 array + 1TypeError: can only concatenate list (not "int") to list
"""
#輸出結果顯示此處創建的是一個list結構,無法執行上述操作。
在Numpy中可以使用array()函數創建數組,從而實現對每個元素都+1操作
array = np.array([1,2,2,3])
array + 1
"""
array([2, 3, 3, 4])
"""
print(type(array))
"""
<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
"""
#輸出結果顯示數據類型是ndarray,也就是Numpy中的底層數據類型,后續要進行各種矩陣操作的基本對象就是它。
在Numpy中 如果對數組執行一個四則運算,就相當于要對其中每一元素做相同的操作。
#arrar---[1,2,2,3]
arr = array + 1
arr
"""
array([2, 3, 3, 4])
"""
#arrar---[1,2,2,3]
#arr---[2,3,3,4]
arr + array
"""
array([3, 5, 5, 7])
"""
#arrar---[1,2,2,3]
#arr---[2,3,3,4]
arr * array
"""
array([ 2, 6, 6, 12])
"""
Ⅱ,數組特性
array
"""
array([1, 2, 2, 3])
"""
array.shape
"""
(4,)
"""
#表示當前為一維,其中有4個元素
two_arr = np.array([[1,2,3],[2,3,4]])
two_arr
"""
array([[1, 2, 3],[2, 3, 4]])
"""
two_arr.shape
"""
(2, 3)
"""
#表示當前為2行3列
在使用ndarray數組時,數組中的所有元素必須是同一類型的,若不是同一類型,數組元素會自動地向下進行轉換。
int→float→str
yy = np.array([1,3,4,5])
yy
"""
array([1, 3, 4, 5])
"""
str>int
yy = np.array([1,3,4,'5'])
yy
"""
array(['1', '3', '4', '5'], dtype='<U11')
"""
float>int
yy = np.array([1,3,4,5.0])
yy
"""
array([1., 3., 4., 5.])
"""
str>float
yy = np.array(['1',3.0,4.0,5.0])
yy
"""
array(['1', '3.0', '4.0', '5.0'], dtype='<U32')
"""
Ⅲ,數組屬性操作
two_arr
"""
array([[1, 2, 3],[2, 3, 4]])
"""
當前數據格式
type(two_arr)
"""
numpy.ndarray
"""
當前數據類型
two_arr.dtype
"""
dtype('int32')
"""
當前數組中的元素個數
two_arr.size
"""
6
"""
當前數據維度
two_arr.ndim
"""
2
"""
二、索引與切片
Ⅰ,數值索引
array
"""
array([1, 2, 2, 3])
"""
下標從0開始,左閉右開[1,3)
array[1:3]
"""
array([2, 2])
"""
負數表示從倒數開始取數據,如[–2:]表示從數組中倒數第二個數據開始取到最后。
array[-2:]
"""
array([2, 3])
"""
索引操作在二維數據中也是同理
two_arr
"""
array([[1, 2, 3],[2, 3, 4]])
"""
下標從0開始,左上角為(0,0),第1行,第2列
two_arr[1,2]
"""
4
"""
可以基于索引位置進行賦值操作,前行后列,通過逗號隔開,[行,列]
two_arr[1,1] = 9
two_arr
"""
array([[1, 2, 3],[2, 9, 4]])
"""
下標從0開始,取第1行數據
two_arr[1]
"""
array([2, 9, 4])
"""
下標從0開始,取最后一列數據
two_arr[:,-1]
"""
array([3, 4])
"""
下標從0開始,取第一列數據
two_arr[:,0]
"""
array([1, 2])
"""
Ⅱ,bool索引
arange(0,100,10)表示從0開始到100,每隔10個數取一個元素
beyond = np.arange(0,100,10)
beyond
"""
array([ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90])
"""
mask = np.array([0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0],dtype=bool)
mask#0為False,1為True
"""
array([False, False, True, True, False, False, True, True, True,False])
"""
beyond[mask]#通過mask作為索引(True)來找beyond中的數據
"""
array([20, 30, 60, 70, 80])
"""
rand(10)表示在[0,1)區間上隨機選擇10個數
random_arr = np.random.rand(10)
random_arr
"""
array([0.22612583, 0.69781025, 0.1703525 , 0.07685978, 0.38899791,0.75130758, 0.3418809 , 0.68655566, 0.43836518, 0.14533855])
"""
#判斷其中每一個元素是否滿足要求,返回布爾類型。
mask = random_arr > 0.5
mask
"""
array([False, True, False, False, False, True, False, True, False,False])
"""
#找到符合要求的索引位置
yy_array = np.array([10,20,30,20,40,60])
np.where(yy_array > 20)
"""
(array([2, 4, 5], dtype=int64),)
"""
#按照滿足要求的索引來選擇元素
yy_array[np.where(yy_array > 20)]
"""
array([30, 40, 60])
"""
#可以對不同的數組進行對比
x = np.array([1,4,7,8,5,2])
y = np.array([1,4,7,2,5,8])
x == y
"""
array([ True, True, True, False, True, False])
"""
#邏輯與
np.logical_and(x,y)
"""
array([ True, True, True, True, True, True])
"""
#邏輯或
np.logical_or(x,y)
"""
array([ True, True, True, True, True, True])
"""
三、數據類型與數值計算
Ⅰ,數據類型
yy_arr = np.array([1,2,3,4],dtype=np.float32)
yy_arr
"""
array([1., 2., 3., 4.], dtype=float32)
"""
yy_arr.dtype
"""
dtype('float32')
"""
在Numpy中字符串的名字叫object
yy_arr = np.array(['1','1.1','beyond'],dtype=np.object)
yy_arr
"""
array(['1', '1.1', 'beyond'], dtype=object)
"""
對創建好的數組進行類型轉換
yy_arr = np.array([1,2,3,4])
yy_arr1 = np.asarray(yy_arr,dtype=np.float32)
yy_arr1
"""
array([1., 2., 3., 4.], dtype=float32)
"""
Ⅱ,復制與賦值
若用=來對兩個數組賦值的話,如果對其中一個變量進行操作,另一變量的結果也跟著發生變化,說明它們根本就是一樣的,只不過用兩個不同的名字表示罷了。
array_o = np.array([[1,3,1],[2,3,1],[2,1,3]])
array_o
"""
array([[1, 3, 1],[2, 3, 1],[2, 1, 3]])
"""
array_n = array_o
array_n
"""
array([[1, 3, 1],[2, 3, 1],[2, 1, 3]])
"""
array_n[1,1] = 666
array_n
"""
array([[ 1, 3, 1],[ 2, 666, 1],[ 2, 1, 3]])
"""
array_o
"""
array([[ 1, 3, 1],[ 2, 666, 1],[ 2, 1, 3]])
"""
如果想讓賦值后的變量與之前的變量無關,需要通過復制操作。
此時改變其中一個數組的某個變量,另一個數組依舊保持不變,說明它們不僅名字不一樣,而且也根本不是同一件事。
array_y = array_o.copy()
array_o
"""
array([[ 1, 3, 1],[ 2, 666, 1],[ 2, 1, 3]])
"""
array_y
"""
array([[ 1, 3, 1],[ 2, 666, 1],[ 2, 1, 3]])
"""
array_y[0,0] = 1014
array_y
"""
array([[1014, 3, 1],[ 2, 666, 1],[ 2, 1, 3]])
"""
array_o
"""
array([[ 1, 3, 1],[ 2, 666, 1],[ 2, 1, 3]])
"""
Ⅲ,數值運算
對數組中所有元素進行求和
yy_arr = np.array([[1,2,1],[2,1,1,],[3,2,2],[1,1,1]])
np.sum(yy_arr)
"""
18
"""
對一個二維數組來說,既可以對列求和,也可以按行求和
指定axis參數表示可以按照第幾個維度來進行計算
0為列維度、1為行維度
np.sum(yy_arr,axis=0)
"""
array([7, 6, 5])
"""
np.sum(yy_arr,axis=1)
"""
array([4, 4, 7, 3])
"""
yy_arr
"""
array([[1, 2, 1],[2, 1, 1],[3, 2, 2],[1, 1, 1]])
"""
數組中所有元素進行累乘
yy_arr.prod()
"""
48
"""
數組中各列元素進行累乘
yy_arr.prod(axis=0)
"""
array([6, 4, 2])
"""
數組中各行元素進行累乘
yy_arr.prod(axis=1)
"""
array([ 2, 2, 12, 1])
"""
找數組中所有元素的最小值
yy_arr.min()
"""
1
"""
找數組中所有元素的最小值的索引
yy_arr.argmin()
"""
0
"""
找數組中每一列中元素的最小值
yy_arr.min(axis=0)
"""
array([1, 1, 1])
"""
找數組中每一列中元素的最小值的索引
yy_arr.argmin(axis=0)
"""
array([0, 1, 0], dtype=int64)
"""
找數組中每一行中元素的最小值
yy_arr.min(axis=1)
"""
array([1, 1, 2, 1])
"""
找數組中每一行中元素的最小值的索引
yy_arr.argmin(axis=1)
"""
array([0, 1, 1, 0], dtype=int64)
"""
求所有元素的均值
yy_arr.mean()
"""
1.5
"""
求每列元素的各自均值
yy_arr.mean(axis=0)
"""
array([1.75, 1.5 , 1.25])
"""
求每行元素的各自均值
yy_arr.mean(axis=1)
"""
array([1.33333333, 1.33333333, 2.33333333, 1. ])
"""
求所有元素的標準差
yy_arr.std()
"""
0.6454972243679028
"""
求每列元素的標準差
yy_arr.std(axis=0)
"""
array([0.8291562, 0.5 , 0.4330127])
"""
求每行元素的標準差
yy_arr.std(axis=1)
"""
array([0.47140452, 0.47140452, 0.47140452, 0. ])
"""
求所有元素的方差
yy_arr.var()
"""
0.4166666666666667
"""
求每列元素的方差
yy_arr.var(axis=0)
"""
array([0.6875, 0.25 , 0.1875])
"""
求每行元素的方差
yy_arr.var(axis=1)
"""
array([0.22222222, 0.22222222, 0.22222222, 0. ])
"""
比1小的全部賦值為1,比2大的全部賦值為2
yy_arr.clip(1,2)
"""
array([[1, 2, 1],[2, 1, 1],[2, 2, 2],[1, 1, 1]])
"""
對數組中的元素四舍五入
yy_arr = np.array([1.26,3.45,4.52])
yy_arr.round()
"""
array([1., 3., 5.])
"""
指定一個精度(2位小數)四舍五入
yy_arr.round(decimals=2)
"""
array([1.26, 3.45, 4.52])
"""
Ⅳ,矩陣乘法
x = np.array([2,2])
y = np.array([3,3])
對應位置元素進行相乘
np.multiply(x,y)
"""
array([6, 6])
"""
在數組中進行矩陣乘法
np.dot(x,y)
"""
12
"""
np.dot(y,x)
"""
12
"""
很顯然,若是一維數組的話,multiply就是各元素對應相乘,最后的結果還是一維數組;dot就是各元素對應相乘再相加是一個數
接下來看下二維數組的情況,基本常識,行列數需要滿足前行乘后列原則
x.shape = 2,1
x
"""
array([[2],[2]])
"""
y.shape = 1,2
y
"""
array([[3, 3]])
"""
np.dot(x,y)
"""
array([[6, 6],[6, 6]])
"""
np.dot(y,x)
"""
array([[12]])
"""
四、常用功能模塊
Ⅰ,排序操作
beyond_arr = np.array([[1.2,2.3,0.5],[1.5,1.9,2.2],[4.2,1.9,6.6],[9.5,10.0,14.1]])
beyond_arr
"""
array([[ 1.2, 2.3, 0.5],[ 1.5, 1.9, 2.2],[ 4.2, 1.9, 6.6],[ 9.5, 10. , 14.1]])
"""
默認按行進行排序,以元素值進行顯示
np.sort(beyond_arr)
"""
array([[ 0.5, 1.2, 2.3],[ 1.5, 1.9, 2.2],[ 1.9, 4.2, 6.6],[ 9.5, 10. , 14.1]])
"""
默認按行進行排序,以元素值所對應的索引進行顯示
np.argsort(beyond_arr)
"""
array([[2, 0, 1],[0, 1, 2],[1, 0, 2],[0, 1, 2]], dtype=int64)
"""
指定按列進行排序,以元素值進行顯示
np.sort(beyond_arr,axis=0)
"""
array([[ 1.2, 1.9, 0.5],[ 1.5, 1.9, 2.2],[ 4.2, 2.3, 6.6],[ 9.5, 10. , 14.1]])
"""
指定按列進行排序,以元素值所對應的索引進行顯示
np.argsort(beyond_arr,axis=0)
"""
array([[0, 1, 0],[1, 2, 1],[2, 0, 2],[3, 3, 3]], dtype=int64)
"""
linspace(0,10,10)函數表示在0~10之間產生等間隔的10個數
yy_arr = np.linspace(0,10,10)
yy_arr
"""
array([ 0. , 1.11111111, 2.22222222, 3.33333333, 4.44444444,5.55555556, 6.66666667, 7.77777778, 8.88888889, 10. ])
"""
此時又新增一組數據,想要按照大小順序把它們插入剛創建的數組中,應當放到什么位置?
values = np.array([2.5,6.5,9.5])
np.searchsorted(yy_arr,values)#算出合適的插入位置
"""
array([3, 6, 9], dtype=int64)
"""
將數據按照第一列的升序或者降序對整體數據進行排序:
按照第一列進行降序
yy_arr = np.array([[9,6,3],[2,8,5],[7,4,1],[10,55,42]])
yy_arr
"""
array([[ 9, 6, 3],[ 2, 8, 5],[ 7, 4, 1],[10, 55, 42]])
"""
index = np.lexsort([-1*yy_arr[:,0]])
index
"""
array([3, 0, 2, 1], dtype=int64)
"""
#得到按照第一列進行降序后的索引
#將索引傳入原數組中
yy_arr[index]
"""
array([[10, 55, 42],[ 9, 6, 3],[ 7, 4, 1],[ 2, 8, 5]])
"""
按照第一列進行升序
yy_arr
"""
array([[ 9, 6, 3],[ 2, 8, 5],[ 7, 4, 1],[10, 55, 42]])
"""
index = np.lexsort([yy_arr[:,0]])
index
"""
array([1, 2, 0, 3], dtype=int64)
"""
#得到按照第一列進行升序后的索引
#將索引傳入原數組中
yy_arr[index]
"""
array([[ 2, 8, 5],[ 7, 4, 1],[ 9, 6, 3],[10, 55, 42]])
"""
Ⅱ,數組形狀操作
beyond_arr = np.arange(10)
beyond_arr
"""
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
"""
beyond_arr.shape
"""
(10,)
"""
#一維
可以通過shape屬性來改變數組形狀,前提是變換前后元素個數必須保持一致。
beyond_arr.shape = 2,5
beyond_arr
"""
array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],[5, 6, 7, 8, 9]])
"""
#二維 2行5列
當創建一個數組之后,還可以給它增加一個維度
yy = np.arange(10)
yy
"""
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
"""
yy.shape
"""
(10,)
"""
#一維
yy = yy[np.newaxis,:]
yy
"""
array([[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]])
"""
yy.shape
"""
(1, 10)
"""
#二維 1行10列
也可以對數組進行壓縮操作,把多余的維度去掉
yy = yy.squeeze()
yy
"""
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
"""
yy.shape
"""
(10,)
"""
#一維
還可以對數組進行轉置操作
beyond = np.array([[1,2,4,5],[9,6,3,2],[7,5,6,3]])
beyond
"""
array([[1, 2, 4, 5],[9, 6, 3, 2],[7, 5, 6, 3]])
"""
方法一:
beyond.transpose()
"""
array([[1, 9, 7],[2, 6, 5],[4, 3, 6],[5, 2, 3]])
"""
方法二:
beyond.T
"""
array([[1, 9, 7],[2, 6, 5],[4, 3, 6],[5, 2, 3]])
"""
Ⅲ,數組的拼接
可以通過拼接將兩份數據組合到一起
concatenate函數用于把數據拼接在一起,注意:原來a、b都是二維的,拼接后的結果也是二維的,相當于在原來的維度上進行拼接,默認axis=0,也可以指定拼接維度。
a = np.array([[2,4,1],[4,5,3]])
b = np.array([[7,4,1],[4,5,6]])
np.concatenate((a,b))
"""
array([[2, 4, 1],[4, 5, 3],[7, 4, 1],[4, 5, 6]])
"""
np.concatenate((a,b),axis=1)
"""
array([[2, 4, 1, 7, 4, 1],[4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 6]])
"""
還有另一種拼接方法
原始數據都是一維的,但是拼接后是二維的,相當于新創建一個維度。
a1 = np.array([7,8,9])
b1 = np.array([9,6,3])
a1.shape
"""
(3,)
"""
#一維
b1.shape
"""
(3,)
"""
#一維
np.stack((a1,b1))
"""
array([[7, 8, 9],[9, 6, 3]])
"""
#拼接之后就變成了二維了
類似還有hstack和vstack操作,分別表示水平和豎直的拼接方式。
np.hstack((a1,b1))
"""
array([7, 8, 9, 9, 6, 3])
"""
np.vstack((a1,b1))
"""
array([[7, 8, 9],[9, 6, 3]])
"""
在數據維度等于1時,它們的作用相當于stack,用于創建新軸。
在維度大于或等于2時,它們的作用相當于cancatenate,用于在已有軸上進行操作。
np.hstack((a,b))
"""
array([[2, 4, 1, 7, 4, 1],[4, 5, 3, 4, 5, 6]])
"""
np.vstack((a,b))
"""
array([[2, 4, 1],[4, 5, 3],[7, 4, 1],[4, 5, 6]])
"""
對于多維數組,還可以將其拉平
a
"""
array([[2, 4, 1],[4, 5, 3]])
"""
a.flatten()
"""
array([2, 4, 1, 4, 5, 3])
"""
Ⅳ,創建數組函數
np.arange()可以自己定義數組的取值區間以及取值間隔,這里表示在[2,20)區間上每隔2個數值取一個元素
np.arange(2,20,2)
"""
array([ 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18])
"""
對數函數默認以10為底,[0,1)平均取5個數,取對數
np.logspace(0,1,5)
"""
array([ 1. , 1.77827941, 3.16227766, 5.62341325, 10. ])
"""
快速創建行向量
np.r_[0:5:1]
"""
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
"""
快速創建列向量
np.c_[0:5:1]
"""
array([[0],[1],[2],[3],[4]])
"""
創建零矩陣,里面包括3個元素
np.zeros(3)
"""
array([0., 0., 0.])
"""
創建3×3的零矩陣
np.zeros((3,3))
"""
array([[0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0.]])
"""
創建3×3的單位矩陣
np.ones((3,3))
"""
array([[1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1.],[1., 1., 1.]])
"""
想生成任意數值的數組,可以根據需求來進行變換
np.ones((3,3))*8
"""
array([[8., 8., 8.],[8., 8., 8.],[8., 8., 8.]])
"""
指定一個空的,指定好其大小,之后再往里面進行填充
a = np.empty(6)
a
"""
array([0., 0., 0., 0., 0., 0.])
"""
全部填充為1
a.fill(1)
a
"""
array([1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.])
"""
創建一個數組,初始化一個零矩陣,讓它和某個數組的維度一致
yy = np.array([5,22,10,14])
np.zeros_like(yy)
"""
array([0, 0, 0, 0])
"""
只有對角線有數值,并且為1,也就是創建指定維度的單位矩陣
np.identity(5)
"""
array([[1., 0., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 1., 0., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 1., 0., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 1., 0.],[0., 0., 0., 0., 1.]])
"""
Ⅴ,隨機模塊
隨機生成3行2列的數組
np.random.rand(3,2)
"""
array([[0.0321769 , 0.58387082],[0.49930902, 0.77043111],[0.52521361, 0.54218806]])
"""
返回區間[0,10)之間的隨機整數
np.random.randint(10,size=(5,4))
"""
array([[1, 8, 6, 7],[1, 8, 4, 5],[9, 3, 1, 4],[2, 2, 4, 7],[1, 7, 5, 2]])
"""
只返回一個隨機值
np.random.rand()
"""
0.9361433744193344
"""
指定區間并選擇隨機數的個數
np.random.randint(0,10,3)
"""
array([3, 9, 7])
"""
指定分布類型,以及所需參數來隨機生成隨機數初始化
例如高斯分布,均值為0,標準差為0.1
np.random.normal(0,0.1,10)
"""
array([-1.97e-01, -8.71e-02, -1.11e-01, 2.75e-02, -3.64e-02, -1.17e-01,-1.34e-01, 1.45e-01, 1.17e-04, -1.19e-03])
"""
返回的結果中小數點后面的位數實在太多了,指定返回結果的小數位數
np.set_printoptions(precision=2)
np.random.normal(0,0.1,10)
"""
array([ 0.07, -0.12, -0.06, -0.06, -0.13, -0.06, 0.02, -0.1 , 0.03,-0.15])
"""
數據一般都是按照采集順序排列的,但是在機器學習中很多算法都要求數據之間相互獨立,所以需要先對數據集進行洗牌操作:
sq = np.arange(10)
sq
"""
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
"""
np.random.shuffle(sq)
sq
"""
array([4, 1, 0, 7, 2, 6, 3, 9, 8, 5])
"""
很容易發現當數據集變化時,參數也發生變化
有些時候希望進行隨機操作,但卻要求每次的隨機結果都相同
此時就需要指定隨機種子
這里每次都把種子設置成10,說明隨機策略相同,無論執行多少次隨機操作,其結果都是相同的
我的理解就是,隨機種子的不同表示隨機表的不同,有很多隨機表,看你用哪一個,不同的隨機種子對應不同的隨機表
np.random.seed(10)
np.random.normal(0,0.1,10)
"""
array([ 0.13, 0.07, -0.15, -0. , 0.06, -0.07, 0.03, 0.01, 0. ,-0.02])
"""
Ⅵ,文件讀寫
Notebook的魔法指令,相當于寫了一個beyond.txt文件
%%writefile beyond.txt
1 2 3 7 8 9
5 6 9 1 4 7
"""
Writing beyond.txt
"""

data = np.loadtxt('beyond.txt')
data
"""
array([[1., 2., 3., 7., 8., 9.],[5., 6., 9., 1., 4., 7.]])
"""
數據中帶有分隔符
%%writefile beyond1.txt
1,2,3,7,8,9
5,6,9,1,4,7
"""
Writing beyond1.txt
"""

#讀取數據的時候也需要提前指定好分隔符
data = np.loadtxt('beyond1.txt',delimiter=',')
data
"""
array([[1., 2., 3., 7., 8., 9.],[5., 6., 9., 1., 4., 7.]])
"""
多加入一列描述,可以把它當作無關項
%%writefile beyond2.txt
q,w,e,r,t,y
1,2,3,7,8,9
5,6,9,1,4,7
"""
Writing beyond2.txt
"""
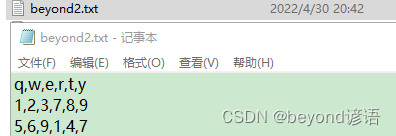
#讀取數據的時候可以去掉前幾行,直接從第1行開始讀取
data = np.loadtxt('beyond2.txt',delimiter=',',skiprows=1)
data
"""
array([[1., 2., 3., 7., 8., 9.],[5., 6., 9., 1., 4., 7.]])
"""
可以通過help來查看幫助文檔
print(help(np.loadtxt))
"""
Help on function loadtxt in module numpy:loadtxt(fname, dtype=<class 'float'>, comments='#', delimiter=None, converters=None, skiprows=0, usecols=None, unpack=False, ndmin=0, encoding='bytes', max_rows=None, *, like=None)Load data from a text file.Each row in the text file must have the same number of values.Parameters----------fname : file, str, pathlib.Path, list of str, generatorFile, filename, list, or generator to read. If the filenameextension is ``.gz`` or ``.bz2``, the file is first decompressed. Notethat generators must return bytes or strings. The stringsin a list or produced by a generator are treated as lines.dtype : data-type, optionalData-type of the resulting array; default: float. If this is astructured data-type, the resulting array will be 1-dimensional, andeach row will be interpreted as an element of the array. In thiscase, the number of columns used must match the number of fields inthe data-type.comments : str or sequence of str, optionalThe characters or list of characters used to indicate the start of acomment. None implies no comments. For backwards compatibility, bytestrings will be decoded as 'latin1'. The default is '#'.delimiter : str, optionalThe string used to separate values. For backwards compatibility, bytestrings will be decoded as 'latin1'. The default is whitespace.converters : dict, optionalA dictionary mapping column number to a function that will parse thecolumn string into the desired value. E.g., if column 0 is a datestring: ``converters = {0: datestr2num}``. Converters can also beused to provide a default value for missing data (but see also`genfromtxt`): ``converters = {3: lambda s: float(s.strip() or 0)}``.Default: None.skiprows : int, optionalSkip the first `skiprows` lines, including comments; default: 0.usecols : int or sequence, optionalWhich columns to read, with 0 being the first. For example,``usecols = (1,4,5)`` will extract the 2nd, 5th and 6th columns.The default, None, results in all columns being read... versionchanged:: 1.11.0When a single column has to be read it is possible to usean integer instead of a tuple. E.g ``usecols = 3`` reads thefourth column the same way as ``usecols = (3,)`` would.unpack : bool, optionalIf True, the returned array is transposed, so that arguments may beunpacked using ``x, y, z = loadtxt(...)``. When used with astructured data-type, arrays are returned for each field.Default is False.ndmin : int, optionalThe returned array will have at least `ndmin` dimensions.Otherwise mono-dimensional axes will be squeezed.Legal values: 0 (default), 1 or 2... versionadded:: 1.6.0encoding : str, optionalEncoding used to decode the inputfile. Does not apply to input streams.The special value 'bytes' enables backward compatibility workaroundsthat ensures you receive byte arrays as results if possible and passes'latin1' encoded strings to converters. Override this value to receiveunicode arrays and pass strings as input to converters. If set to Nonethe system default is used. The default value is 'bytes'... versionadded:: 1.14.0max_rows : int, optionalRead `max_rows` lines of content after `skiprows` lines. The defaultis to read all the lines... versionadded:: 1.16.0like : array_likeReference object to allow the creation of arrays which are notNumPy arrays. If an array-like passed in as ``like`` supportsthe ``__array_function__`` protocol, the result will be definedby it. In this case, it ensures the creation of an array objectcompatible with that passed in via this argument... versionadded:: 1.20.0Returns-------out : ndarrayData read from the text file.See Also--------load, fromstring, fromregexgenfromtxt : Load data with missing values handled as specified.scipy.io.loadmat : reads MATLAB data filesNotes-----This function aims to be a fast reader for simply formatted files. The`genfromtxt` function provides more sophisticated handling of, e.g.,lines with missing values... versionadded:: 1.10.0The strings produced by the Python float.hex method can be used asinput for floats.Examples-------->>> from io import StringIO # StringIO behaves like a file object>>> c = StringIO("0 1\n2 3")>>> np.loadtxt(c)array([[0., 1.],[2., 3.]])>>> d = StringIO("M 21 72\nF 35 58")>>> np.loadtxt(d, dtype={'names': ('gender', 'age', 'weight'),... 'formats': ('S1', 'i4', 'f4')})array([(b'M', 21, 72.), (b'F', 35, 58.)],dtype=[('gender', 'S1'), ('age', '<i4'), ('weight', '<f4')])>>> c = StringIO("1,0,2\n3,0,4")>>> x, y = np.loadtxt(c, delimiter=',', usecols=(0, 2), unpack=True)>>> xarray([1., 3.])>>> yarray([2., 4.])This example shows how `converters` can be used to convert a fieldwith a trailing minus sign into a negative number.>>> s = StringIO('10.01 31.25-\n19.22 64.31\n17.57- 63.94')>>> def conv(fld):... return -float(fld[:-1]) if fld.endswith(b'-') else float(fld)...>>> np.loadtxt(s, converters={0: conv, 1: conv})array([[ 10.01, -31.25],[ 19.22, 64.31],[-17.57, 63.94]])None
"""
Numpy工具包不僅可以讀取數據,而且可以將數據寫入文件中
#把結果保存為npy格式
beyond = np.array([[1,4,7,8],[5,2,3,6]])
np.save('yy.npy',beyond,)

#讀取之前保存的結果,依舊是Numpy數組格式
np.load('yy.npy')
"""
array([[1, 4, 7, 8],[5, 2, 3, 6]])
"""
俺迪哥說了,在數據處理過程中,中間的結果都保存在內存中,如果關閉Notebook或者重啟IDE,再次使用的時候就要從頭再來,十分耗時。如果能將中間結果保存下來,下次直接讀取處理后的結果就非常高效,保存成“.npy”格式的方法非常實用。





---小練習)



方法與示例)

---講解)


函數與示例)



方法與示例)
---講解)