💝💝💝歡迎來到我的博客,很高興能夠在這里和您見面!希望您在這里可以感受到一份輕松愉快的氛圍,不僅可以獲得有趣的內容和知識,也可以暢所欲言、分享您的想法和見解。
- 推薦:kuan 的首頁,持續學習,不斷總結,共同進步,活到老學到老
- 導航
- 檀越劍指大廠系列:全面總結 java 核心技術點,如集合,jvm,并發編程 redis,kafka,Spring,微服務,Netty 等
- 常用開發工具系列:羅列常用的開發工具,如 IDEA,Mac,Alfred,electerm,Git,typora,apifox 等
- 數據庫系列:詳細總結了常用數據庫 mysql 技術點,以及工作中遇到的 mysql 問題等
- 懶人運維系列:總結好用的命令,解放雙手不香嗎?能用一個命令完成絕不用兩個操作
- 數據結構與算法系列:總結數據結構和算法,不同類型針對性訓練,提升編程思維,劍指大廠
非常期待和您一起在這個小小的網絡世界里共同探索、學習和成長。💝💝💝 ?? 歡迎訂閱本專欄 ??
博客目錄
- 一.認識鏈表
- 1.鏈表定義與分類
- 2.哨兵節點
- 3.查詢性能
- 4.插入和刪除性能
- 二.單向鏈表
- 1.定義
- 2.頭部添加
- 3.while 遍歷
- 4.for 遍歷
- 5.迭代器遍歷
- 6.遞歸遍歷
- 7.尾部添加
- 8.尾部添加多個
- 9.根據索引獲取
- 10.插入
- 11.刪除
- 三.單向鏈表(帶哨兵)
- 1.帶哨兵單向鏈表
- 2.獲取索引節點
- 3.插入刪除節點
- 四.雙向鏈表(帶哨兵)
- 五.環形鏈表(帶哨兵)
- 六.解題模版
- 1.反轉鏈表再正向遍歷
- 2.遞歸遍歷
- 七.鏈表題目
- 1.兩數相加
- 2.兩數相加 II
- 3.合并兩個有序鏈表
- 4.刪除排序鏈表中的重復元素
- 5.環形鏈表
- 6.相交鏈表
- 7.移除鏈表元素
- 8.反轉鏈表
- 9.回文鏈表
- 10.鏈表的中間結點
一.認識鏈表
1.鏈表定義與分類
在計算機科學中,鏈表是數據元素的線性集合,其每個元素都指向下一個元素,元素存儲上并不連續
可以分類為.
單向鏈表,每個元素只知道其下一個元素是誰
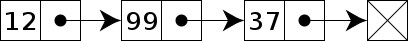
雙向鏈表,每個元素知道其上一個元素和下一個元素

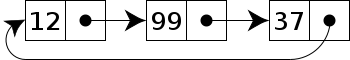
循環鏈表,通常的鏈表尾節點tail指向的都是null,而循環鏈表的tail指向的是頭節點head
2.哨兵節點
鏈表內還有一種特殊的節點稱為哨兵(Sentinel)節點,也叫做啞元( Dummy)節點,它不存儲數據,通常用作頭尾,用來簡化邊界判斷,如下圖所示

3.查詢性能
隨機訪問性能
根據 index 查找,時間復雜度 O(n)
4.插入和刪除性能
插入或刪除性能
- 起始位置:O(1)
- 結束位置:如果已知 tail 尾節點是 O(1),不知道 tail 尾節點是 O(n)
- 中間位置:根據 index 查找時間 + O(1)
二.單向鏈表
1.定義
根據單向鏈表的定義,首先定義一個存儲 value 和 next 指針的類 Node,和一個描述頭部節點的引用
public class SinglyLinkedList {private Node head; // 頭部節點private static class Node { // 節點類int value;Node next;public Node(int value, Node next) {this.value = value;this.next = next;}}
}
- Node 定義為內部類,是為了對外隱藏實現細節,沒必要讓類的使用者關心 Node 結構
- 定義為 static 內部類,是因為 Node 不需要與 SinglyLinkedList 實例相關,多個 SinglyLinkedList 實例能共用 Node 類定義
2.頭部添加
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void addFirst(int value) {this.head = new Node(value, this.head);}
}
- 如果 this.head == null,新增節點指向 null,并作為新的 this.head
- 如果 this.head != null,新增節點指向原來的 this.head,并作為新的 this.head
- 注意賦值操作執行順序是從右到左
3.while 遍歷
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void loop() {Node curr = this.head;while (curr != null) {// 做一些事curr = curr.next;}}
}
4.for 遍歷
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void loop() {for (Node curr = this.head; curr != null; curr = curr.next) {// 做一些事}}
}
- 以上兩種遍歷都可以把要做的事以 Consumer 函數的方式傳遞進來
- Consumer 的規則是一個參數,無返回值,因此像 System.out::println 方法等都是 Consumer
- 調用 Consumer 時,將當前節點 curr.value 作為參數傳遞給它
//使用Consumer傳參
public void loop4(Consumer<Integer> consumer) {Node p = head;while (p != null) {consumer.accept(p.value);p = p.next;}
}
//測試
@Test
@DisplayName("測試 consumer while遍歷 loop4")
public void test5() {SinglyLinkedList list = new SinglyLinkedList();list.addFirst(1);list.addFirst(2);list.addFirst(3);list.addFirst(4);Consumer<Integer> consumer = integer -> System.out.println(integer);list.loop4(consumer);
}
5.迭代器遍歷
public class SinglyLinkedList implements Iterable<Integer> {// ...private class NodeIterator implements Iterator<Integer> {Node curr = head;public boolean hasNext() {return curr != null;}public Integer next() {int value = curr.value;curr = curr.next;return value;}}public Iterator<Integer> iterator() {return new NodeIterator();}
}
- hasNext 用來判斷是否還有必要調用 next
- next 做兩件事
- 返回當前節點的 value
- 指向下一個節點
- NodeIterator 要定義為非 static 內部類,是因為它與 SinglyLinkedList 實例相關,是對某個 SinglyLinkedList 實例的迭代
6.遞歸遍歷
public class SinglyLinkedList implements Iterable<Integer> {// ...public void loop() {recursion(this.head);}private void recursion(Node curr) {if (curr == null) {return;}//前面做些事recursion(curr.next);//后面做些事}
}
7.尾部添加
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...private Node findLast() {if (this.head == null) {return null;}Node curr;for (curr = this.head; curr.next != null; ) {curr = curr.next;}return curr;}public void addLast(int value) {Node last = findLast();if (last == null) {addFirst(value);return;}last.next = new Node(value, null);}
}
- 注意,找最后一個節點,終止條件是 curr.next == null
- 分成兩個方法是為了代碼清晰,而且 findLast() 之后還能復用
8.尾部添加多個
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void addLast(int first, int... rest) {Node sublist = new Node(first, null);Node curr = sublist;for (int value : rest) {curr.next = new Node(value, null);curr = curr.next;}Node last = findLast();if (last == null) {this.head = sublist;return;}last.next = sublist;}
}
- 先串成一串 sublist
- 再作為一個整體添加
9.根據索引獲取
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...private Node findNode(int index) {int i = 0;for (Node curr = this.head; curr != null; curr = curr.next, i++) {if (index == i) {return curr;}}return null;}private IllegalArgumentException illegalIndex(int index) {return new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("index [%d] 不合法%n", index));}public int get(int index) {Node node = findNode(index);if (node != null) {return node.value;}throw illegalIndex(index);}
}
- 同樣,分方法可以實現復用
10.插入
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void insert(int index, int value) {if (index == 0) {addFirst(value);return;}Node prev = findNode(index - 1); // 找到上一個節點if (prev == null) { // 找不到throw illegalIndex(index);}prev.next = new Node(value, prev.next);}
}
- 插入包括下面的刪除,都必須找到上一個節點
11.刪除
public class SinglyLinkedList {// ...public void remove(int index) {if (index == 0) {if (this.head != null) {this.head = this.head.next;return;} else {throw illegalIndex(index);}}Node prev = findNode(index - 1);Node curr;if (prev != null && (curr = prev.next) != null) {prev.next = curr.next;} else {throw illegalIndex(index);}}
}
- 第一個 if 塊對應著 removeFirst 情況
- 最后一個 if 塊對應著至少得兩個節點的情況
- 不僅僅判斷上一個節點非空,還要保證當前節點非空
三.單向鏈表(帶哨兵)
1.帶哨兵單向鏈表
觀察之前單向鏈表的實現,發現每個方法內幾乎都有判斷是不是 head 這樣的代碼,能不能簡化呢?
用一個不參與數據存儲的特殊 Node 作為哨兵,它一般被稱為哨兵或啞元,擁有哨兵節點的鏈表稱為帶頭鏈表
public class SinglyLinkedListSentinel {// ...private Node head = new Node(Integer.MIN_VALUE, null);
}
- 具體存什么值無所謂,因為不會用到它的值
2.獲取索引節點
加入哨兵節點后,代碼會變得比較簡單,先看幾個工具方法
public class SinglyLinkedListSentinel {// ...// 根據索引獲取節點private Node findNode(int index) {int i = -1;for (Node curr = this.head; curr != null; curr = curr.next, i++) {if (i == index) {return curr;}}return null;}// 獲取最后一個節點private Node findLast() {Node curr;for (curr = this.head; curr.next != null; ) {curr = curr.next;}return curr;}
}
- findNode 與之前類似,只是 i 初始值設置為 -1 對應哨兵,實際傳入的 index 也是 [-1, \infty)
- findLast 絕不會返回 null 了,就算沒有其它節點,也會返回哨兵作為最后一個節點
3.插入刪除節點
這樣,代碼簡化為
public class SinglyLinkedListSentinel {// ...public void addLast(int value) {Node last = findLast();/*改動前if (last == null) {this.head = new Node(value, null);return;}*/last.next = new Node(value, null);}public void insert(int index, int value) {/*改動前if (index == 0) {this.head = new Node(value, this.head);return;}*/// index 傳入 0 時,返回的是哨兵Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev != null) {prev.next = new Node(value, prev.next);} else {throw illegalIndex(index);}}public void remove(int index) {/*改動前if (index == 0) {if (this.head != null) {this.head = this.head.next;return;} else {throw illegalIndex(index);}}*/// index 傳入 0 時,返回的是哨兵Node prev = findNode(index - 1);Node curr;if (prev != null && (curr = prev.next) != null) {prev.next = curr.next;} else {throw illegalIndex(index);}}public void addFirst(int value) {/*改動前this.head = new Node(value, this.head);*/this.head.next = new Node(value, this.head.next);// 也可以視為 insert 的特例, 即 insert(0, value);}
}
- 對于刪除,前面說了【最后一個 if 塊對應著至少得兩個節點的情況】,現在有了哨兵,就湊足了兩個節點
四.雙向鏈表(帶哨兵)
public class DoublyLinkedListSentinel implements Iterable<Integer> {private final Node head;private final Node tail;public DoublyLinkedListSentinel() {head = new Node(null, 666, null);tail = new Node(null, 888, null);head.next = tail;tail.prev = head;}private Node findNode(int index) {int i = -1;for (Node p = head; p != tail; p = p.next, i++) {if (i == index) {return p;}}return null;}public void addFirst(int value) {insert(0, value);}public void removeFirst() {remove(0);}public void addLast(int value) {Node prev = tail.prev;Node added = new Node(prev, value, tail);prev.next = added;tail.prev = added;}public void removeLast() {Node removed = tail.prev;if (removed == head) {throw illegalIndex(0);}Node prev = removed.prev;prev.next = tail;tail.prev = prev;}public void insert(int index, int value) {Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev == null) {throw illegalIndex(index);}Node next = prev.next;Node inserted = new Node(prev, value, next);prev.next = inserted;next.prev = inserted;}public void remove(int index) {Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev == null) {throw illegalIndex(index);}Node removed = prev.next;if (removed == tail) {throw illegalIndex(index);}Node next = removed.next;prev.next = next;next.prev = prev;}private IllegalArgumentException illegalIndex(int index) {return new IllegalArgumentException(String.format("index [%d] 不合法%n", index));}@Overridepublic Iterator<Integer> iterator() {return new Iterator<Integer>() {Node p = head.next;@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return p != tail;}@Overridepublic Integer next() {int value = p.value;p = p.next;return value;}};}static class Node {Node prev;int value;Node next;public Node(Node prev, int value, Node next) {this.prev = prev;this.value = value;this.next = next;}}
}
五.環形鏈表(帶哨兵)
雙向環形鏈表帶哨兵,這時哨兵既作為頭,也作為尾

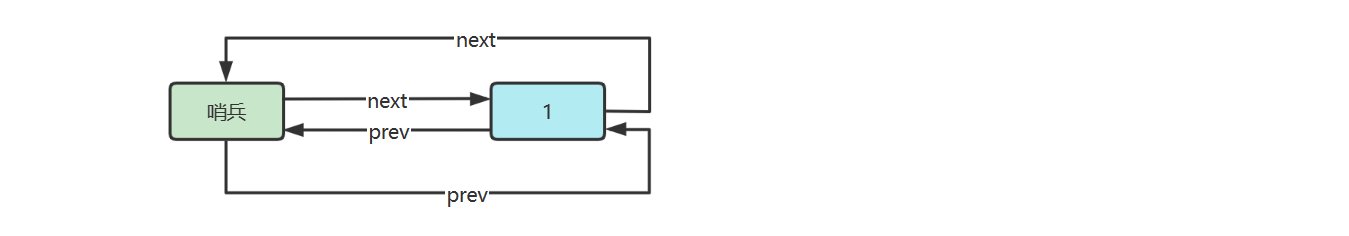
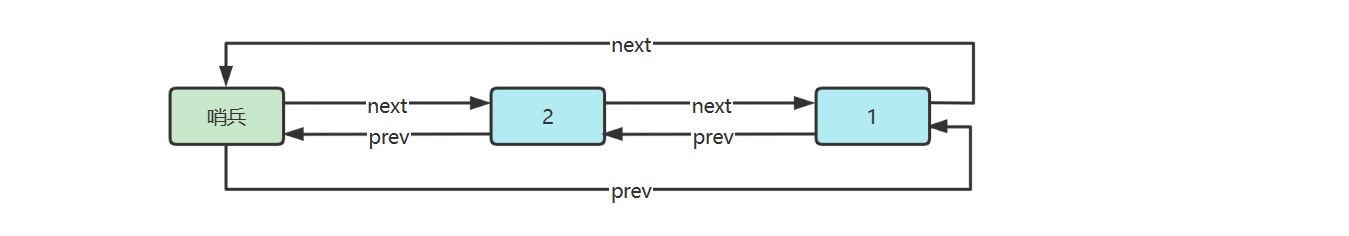
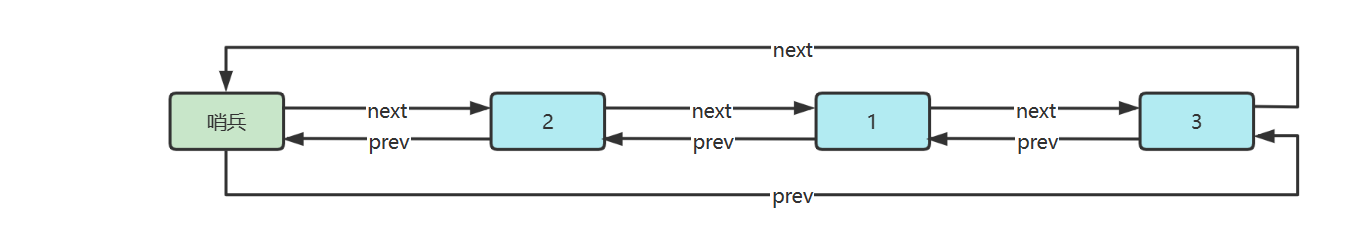
參考實現
public class DoublyLinkedListSentinel implements Iterable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Iterator<Integer> iterator() {return new Iterator<>() {Node p = sentinel.next;@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return p != sentinel;}@Overridepublic Integer next() {int value = p.value;p = p.next;return value;}};}static class Node {Node prev;int value;Node next;public Node(Node prev, int value, Node next) {this.prev = prev;this.value = value;this.next = next;}}private final Node sentinel = new Node(null, -1, null); // 哨兵public DoublyLinkedListSentinel() {sentinel.next = sentinel;sentinel.prev = sentinel;}/*** 添加到第一個* @param value 待添加值*/public void addFirst(int value) {Node next = sentinel.next;Node prev = sentinel;Node added = new Node(prev, value, next);prev.next = added;next.prev = added;}/*** 添加到最后一個* @param value 待添加值*/public void addLast(int value) {Node prev = sentinel.prev;Node next = sentinel;Node added = new Node(prev, value, next);prev.next = added;next.prev = added;}/*** 刪除第一個*/public void removeFirst() {Node removed = sentinel.next;if (removed == sentinel) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("非法");}Node a = sentinel;Node b = removed.next;a.next = b;b.prev = a;}/*** 刪除最后一個*/public void removeLast() {Node removed = sentinel.prev;if (removed == sentinel) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("非法");}Node a = removed.prev;Node b = sentinel;a.next = b;b.prev = a;}/*** 根據值刪除節點* <p>假定 value 在鏈表中作為 key, 有唯一性</p>* @param value 待刪除值*/public void removeByValue(int value) {Node removed = findNodeByValue(value);if (removed != null) {Node prev = removed.prev;Node next = removed.next;prev.next = next;next.prev = prev;}}private Node findNodeByValue(int value) {Node p = sentinel.next;while (p != sentinel) {if (p.value == value) {return p;}p = p.next;}return null;}}
六.解題模版
1.反轉鏈表再正向遍歷
可以先將鏈表反轉,然后正向遍歷即可實現從后往前遍歷。這種方法的時間復雜度為 O(N),其中 N 為鏈表的長度。
CLASS LISTNODE:DEF __INIT__(SELF, VAL=0, NEXT=NONE):SELF.VAL = VALSELF.NEXT = NEXT
DEF REVERSELIST(HEAD):PREV, CURR = NONE, HEADWHILE CURR:NEXT_NODE = CURR.NEXTCURR.NEXT = PREVPREV = CURRCURR = NEXT_NODERETURN PREVDEF TRAVERSELIST(HEAD):NEW_HEAD = REVERSELIST(HEAD)WHILE NEW_HEAD:PRINT(NEW_HEAD.VAL)NEW_HEAD = NEW_HEAD.NEXT
2.遞歸遍歷
可以使用遞歸的方式遍歷鏈表,每次遍歷到鏈表末尾時再開始輸出節點的值。這種方法的時間復雜度也為 O(N),其中 N 為鏈表的長度。
CLASS LISTNODE:DEF __INIT__(SELF, VAL=0, NEXT=NONE):SELF.VAL = VALSELF.NEXT = NEXTDEF TRAVERSELIST(HEAD):IF NOT HEAD:RETURNTRAVERSELIST(HEAD.NEXT)PRINT(HEAD.VAL)
需要注意的是,遞歸遍歷鏈表時,如果鏈表過長,可能會導致遞歸層數過深,從而出現棧溢出的情況。因此,如果鏈表長度較大,建議使用反轉鏈表再正向遍歷的方法。
七.鏈表題目
1.兩數相加
給你兩個 非空 的鏈表,表示兩個非負的整數。它們每位數字都是按照 逆序 的方式存儲的,并且每個節點只能存儲 一位 數字。
請你將兩個數相加,并以相同形式返回一個表示和的鏈表。
你可以假設除了數字 0 之外,這兩個數都不會以 0 開頭。
示例 1:
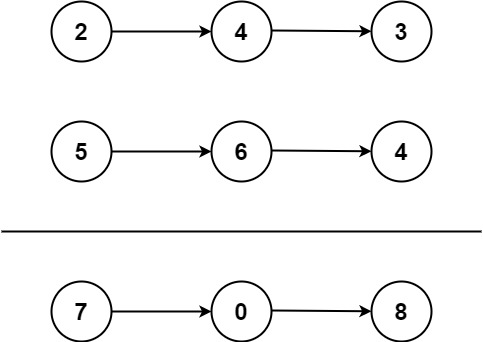
輸入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
輸出:[7,0,8]
解釋:342 + 465 = 807.
示例 2:
輸入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
輸出:[0]
示例 3:
輸入:l1 = [9,9,9,9,9,9,9], l2 = [9,9,9,9]
輸出:[8,9,9,9,0,0,0,1]
題解:
具體實現步驟如下:
- 首先,我們需要創建一個新的鏈表,用來存儲兩個鏈表相加的結果。同時,我們需要定義一個指針,用來遍歷鏈表。
- 接著,我們可以從兩個鏈表的頭節點開始,依次遍歷它們的每一個節點,將它們對應位置的數字相加,并記錄進位。
- 如果其中一個鏈表已經遍歷結束,我們就可以直接將另一個鏈表剩余的部分接到結果鏈表的后面(注意,這里還需要考慮進位)。
- 最后,如果遍歷完成后還有進位,我們就需要在結果鏈表的末尾添加一個新節點,存儲進位。
class Solution:def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: Optional[ListNode], l2: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:"""鏈表遍歷:param l1::param l2::return:"""res = ListNode(0)cur = rescarry = 0while l1 or l2:x = l1.val if l1 else 0y = l2.val if l2 else 0s = x + y + carrycarry = s // 10cur.next = ListNode(s % 10)cur = cur.nextif l1:l1 = l1.nextif l2:l2 = l2.nextif carry:cur.next = ListNode(carry)return res.next
時間復雜度:O(max(m, n)),其中 m 和 n 分別是 l1 和 l2 的長度。
空間復雜度:O(max(m, n)),我們需要使用一個鏈表來存儲結果。
2.兩數相加 II
給你兩個 非空 鏈表來代表兩個非負整數。數字最高位位于鏈表開始位置。它們的每個節點只存儲一位數字。將這兩數相加會返回一個新的鏈表。
你可以假設除了數字 0 之外,這兩個數字都不會以零開頭。
示例 1:
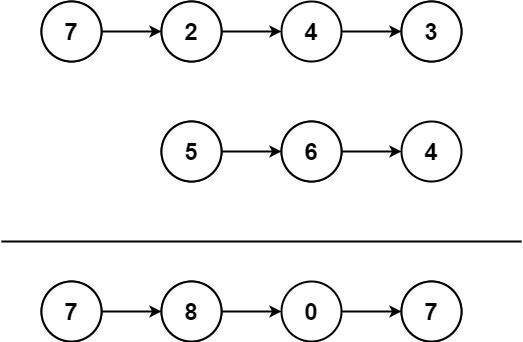
輸入:l1 = [7,2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
輸出:[7,8,0,7]
示例 2:
輸入:l1 = [2,4,3], l2 = [5,6,4]
輸出:[8,0,7]
示例 3:
輸入:l1 = [0], l2 = [0]
輸出:[0]
題解:
解題思路:
- 先把兩個鏈表逆序,使得最低位在鏈表頭部,這樣就可以從頭部開始相加了。
- 定義一個 carry 變量,表示進位,初始值為 0。
- 定義一個新的鏈表 dummyHead,表示相加的結果。
- 從鏈表 1 和鏈表 2 的頭部開始遍歷,對于每一位進行相加,同時加上進位 carry。
- 如果當前的和大于等于 10,就需要進位,將 carry 變為 1,同時將和減去 10。
- 將當前的和插入到新的鏈表 dummyHead 的末尾。
- 遍歷完鏈表 1 和鏈表 2 后,如果進位 carry 為 1,還需要將 carry 插入到 dummyHead 的末尾。
- 最后將 dummyHead 逆序,得到正常的結果鏈表。
class ListNode:def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):self.val = valself.next = next# 翻轉鏈表
def reverseList(head: ListNode) -> ListNode:pre = Nonecurr = headwhile curr:next = curr.nextcurr.next = prepre = currcurr = nextreturn preclass Solution:def addTwoNumbers(self, l11: Optional[ListNode], l22: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:l1 = reverseList(l11)l2 = reverseList(l22)res = ListNode(0)cur = rescarry = 0while l1 or l2:x = l1.val if l1 else 0y = l2.val if l2 else 0s = x + y + carrycarry = s // 10cur.next = ListNode(s % 10)cur = cur.nextif l1:l1 = l1.nextif l2:l2 = l2.nextif carry:cur.next = ListNode(carry)return reverseList(res.next)
3.合并兩個有序鏈表
將兩個升序鏈表合并為一個新的 升序 鏈表并返回。新鏈表是通過拼接給定的兩個鏈表的所有節點組成的。
輸入:l1 = [1,2,4], l2 = [1,3,4]
輸出:[1,1,2,3,4,4]
示例 2:
輸入:l1 = [], l2 = []
輸出:[]
示例 3:
輸入:l1 = [], l2 = [0]
輸出:[0]
題解:
要合并兩個有序鏈表,可以使用遞歸或迭代的方法。下面是使用迭代的方法實現合并兩個有序鏈表的 Python 代碼示例:
pythonCopy code
class ListNode:def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):self.val = valself.next = nextdef mergeTwoLists(l1, l2):# 創建一個啞節點(dummy node)作為合并后鏈表的頭節點dummy = ListNode(0)# 創建一個指針指向合并后鏈表的當前節點current = dummy# 循環比較l1和l2的節點值,并將較小的節點添加到合并后鏈表中while l1 and l2:if l1.val < l2.val:current.next = l1l1 = l1.nextelse:current.next = l2l2 = l2.nextcurrent = current.next# 處理剩余的節點current.next = l1 if l1 else l2# 返回合并后鏈表的頭節點的下一個節點,即去除啞節點return dummy.next
這段代碼中,我們創建了一個啞節點(dummy node)作為合并后鏈表的頭節點。然后使用一個指針current指向合并后鏈表的當前節點。在循環中,我們比較l1和l2的節點值,并將較小的節點添加到合并后鏈表中,同時移動相應的指針。最后,我們處理剩余的節點,將其添加到合并后鏈表的尾部。最后返回合并后鏈表的頭節點的下一個節點,即去除啞節點。
你可以調用mergeTwoLists函數,傳入兩個有序鏈表的頭節點,然后它將返回合并后的有序鏈表的頭節點。
4.刪除排序鏈表中的重復元素
給定一個已排序的鏈表的頭
head, 刪除所有重復的元素,使每個元素只出現一次 。返回 已排序的鏈表 。
示例 1:
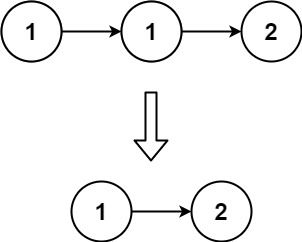
輸入:head = [1,1,2]
輸出:[1,2]
示例 2:
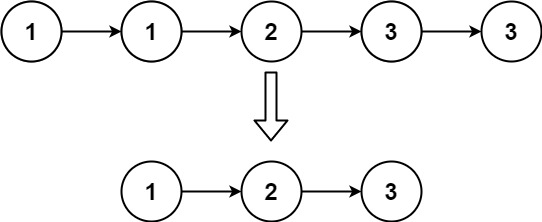
輸入:head = [1,1,2,3,3]
輸出:[1,2,3]
題解:
class Solution:def deleteDuplicates(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:dummy = headwhile dummy and dummy.next:# 如果當前節點和下一個節點的值相同,刪除下一個節點if dummy.val == dummy.next.val:dummy.next = dummy.next.nextelse:dummy = dummy.nextreturn head
5.環形鏈表
給你一個鏈表的頭節點
head,判斷鏈表中是否有環。如果鏈表中有某個節點,可以通過連續跟蹤
next指針再次到達,則鏈表中存在環。 為了表示給定鏈表中的環,評測系統內部使用整數pos來表示鏈表尾連接到鏈表中的位置(索引從 0 開始)。注意:pos不作為參數進行傳遞 。僅僅是為了標識鏈表的實際情況。如果鏈表中存在環 ,則返回
true。 否則,返回false。
輸入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
輸出:true
解釋:鏈表中有一個環,其尾部連接到第二個節點。
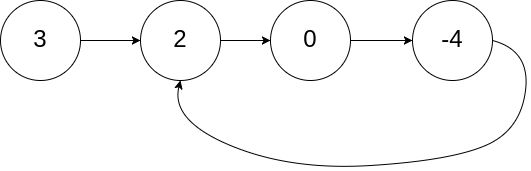
題解:
class Solution:def hasCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:"""雙指針,一個快指針,一個慢指針,如果有環 一定會相聚:param head::return:"""if head is None or head.next is None:return Falseslow = headfast = head.nextwhile slow != fast:if fast is None or fast.next is None:return Falseslow = slow.nextfast = fast.next.nextreturn True
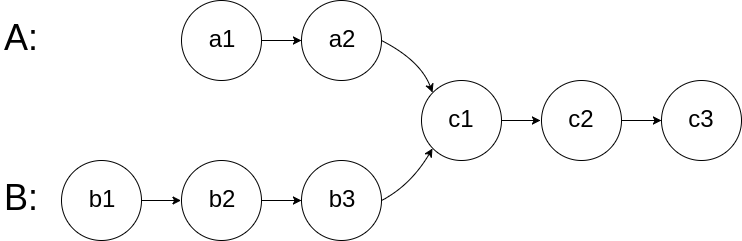
6.相交鏈表
給你兩個單鏈表的頭節點
headA和headB,請你找出并返回兩個單鏈表相交的起始節點。如果兩個鏈表不存在相交節點,返回null。圖示兩個鏈表在節點
c1開始相交**:**
題目數據 保證 整個鏈式結構中不存在環。
注意,函數返回結果后,鏈表必須 保持其原始結構 。
自定義評測:
評測系統 的輸入如下(你設計的程序 不適用 此輸入):
intersectVal- 相交的起始節點的值。如果不存在相交節點,這一值為0listA- 第一個鏈表listB- 第二個鏈表skipA- 在listA中(從頭節點開始)跳到交叉節點的節點數skipB- 在listB中(從頭節點開始)跳到交叉節點的節點數評測系統將根據這些輸入創建鏈式數據結構,并將兩個頭節點
headA和headB傳遞給你的程序。如果程序能夠正確返回相交節點,那么你的解決方案將被 視作正確答案 。
示例 1:
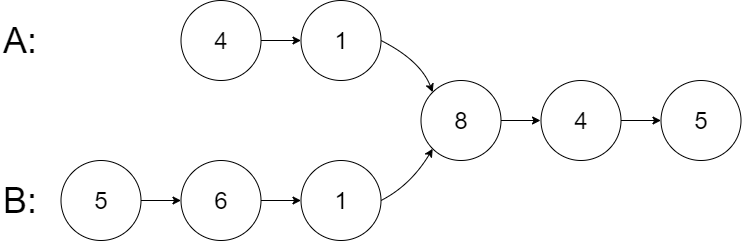
輸入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
輸出:Intersected at '8'
解釋:相交節點的值為 8 (注意,如果兩個鏈表相交則不能為 0)。
從各自的表頭開始算起,鏈表 A 為 [4,1,8,4,5],鏈表 B 為 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交節點前有 2 個節點;在 B 中,相交節點前有 3 個節點。
— 請注意相交節點的值不為 1,因為在鏈表 A 和鏈表 B 之中值為 1 的節點 (A 中第二個節點和 B 中第三個節點) 是不同的節點。換句話說,它們在內存中指向兩個不同的位置,而鏈表 A 和鏈表 B 中值為 8 的節點 (A 中第三個節點,B 中第四個節點) 在內存中指向相同的位置。
題解:
class Solution:def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> Optional[ListNode]:"""思路:如果存在交點,則肯定在兩個鏈表分別遍歷對方時相交:param headA::param headB::return:"""if not headA or not headB:return NonenodeA, nodeB = headA, headBwhile nodeA != nodeB:nodeA = nodeA.next if nodeA else headBnodeB = nodeB.next if nodeB else headAreturn nodeA
7.移除鏈表元素
給你一個鏈表的頭節點
head和一個整數val,請你刪除鏈表中所有滿足Node.val == val的節點,并返回 新的頭節點 。
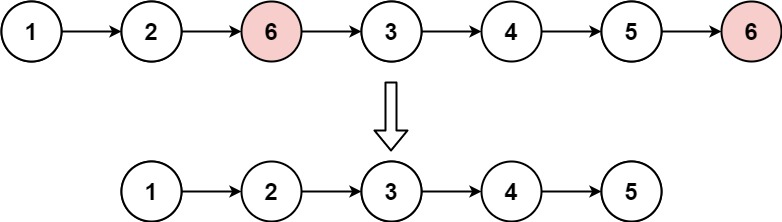
示例 1:
輸入:head = [1,2,6,3,4,5,6], val = 6
輸出:[1,2,3,4,5]
示例 2:
輸入:head = [], val = 1
輸出:[]
示例 3:
輸入:head = [7,7,7,7], val = 7
輸出:[]
題解:
class Solution:def removeElements(self, head: Optional[ListNode], val: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:"""鏈表的合適是操作2個節點,前驅和后繼:param head::param val::return:"""# 處理頭部節點while head and head.val == val:head = head.next# 處理非頭部cur = headwhile cur and cur.next:if cur.next.val == val:cur.next = cur.next.nextelse:cur = cur.nextreturn head
8.反轉鏈表
給你單鏈表的頭節點
head,請你反轉鏈表,并返回反轉后的鏈表。
示例 1:
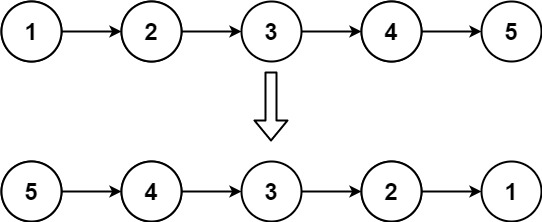
輸入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
輸出:[5,4,3,2,1]
示例 2:
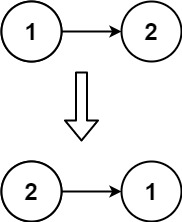
輸入:head = [1,2]
輸出:[2,1]
示例 3:
輸入:head = []
輸出:[]
題解:
class Solution:def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:"""反轉鏈表:定義前節點和當前節點:param head::return:"""pre, curr = None, headwhile curr is not None:next = curr.nextcurr.next = prepre = currcurr = nextreturn pre
9.回文鏈表
給你一個單鏈表的頭節點
head,請你判斷該鏈表是否為回文鏈表。如果是,返回true;否則,返回false。
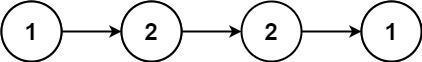
輸入:head = [1,2,2,1]
輸出:true
題解:
class Solution:def isPalindrome(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> bool:"""回文鏈表:param head::return:"""contain = []curr = headwhile curr is not None:contain.append(curr.val)curr = curr.nextcurr2 = headwhile curr2 is not None:if contain.pop() != curr2.val:return Falsecurr2 = curr2.nextreturn True
10.鏈表的中間結點
給你單鏈表的頭結點
head,請你找出并返回鏈表的中間結點。如果有兩個中間結點,則返回第二個中間結點。
輸入:head = [1,2,3,4,5]
輸出:[3,4,5]
解釋:鏈表只有一個中間結點,值為 3 。
題解:
class Solution:def middleNode(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:"""鏈表的中間結點,如果有2個 返回第二個 快慢指針:param head::return:"""fast, slow = head, headwhile fast is not None and fast.next is not None:slow = slow.nextfast = fast.next.nextreturn slow
覺得有用的話點個贊
👍🏻唄。
??????本人水平有限,如有紕漏,歡迎各位大佬評論批評指正!😄😄😄💘💘💘如果覺得這篇文對你有幫助的話,也請給個點贊、收藏下吧,非常感謝!👍 👍 👍
🔥🔥🔥Stay Hungry Stay Foolish 道阻且長,行則將至,讓我們一起加油吧!🌙🌙🌙





)




)
)



)






