前言
本系列的主要目的是告訴大家在遇到性能問題時,有哪些方案可以去優化;并不是要求大家一開始就使用這些方案來提升性能。
在之前幾篇文章中,有很多網友就有一些非此即彼的觀念,在實際中,處處都是開發效率和性能之間取舍的藝術。《計算機編程藝術》一書中提到過早優化是萬惡之源,在進行性能優化時,你必須要問自己幾個問題,看需不要進行性能優化。
優化的成本高么?
如果立刻開始優化會帶來什么影響?
因為對任務目標的影響或是興趣等其他原因而關注這個問題?
任務目標影響有多大?
隨著硬件性能提升或者框架版本升級,優化的結果會不會過時?
如果不進行優化或延遲優化的進行會帶來什么負面的影響?
如果不進行優化或延遲優化,相應的時間或成本可以完成什么事情,是否更有價值?
如果評估下來,還是優化的利大于弊,而且在合理的時間范圍內,那么就去做;如果覺得當前應用的QPS不高、用戶體驗也還好、內存和CPU都有空余,那么就放一放,主要放在二八法則中能為你創建80%價值的事情上。但是大家要記住過早優化是萬惡之源不是寫垃圾代碼的借口。
回到正題,在上篇文章《使用結構體替代類》中有寫在緩存和大數據量計算時使用結構體有諸多的好處,最后關于計算性能的例子中,我使用的是簡單的for循環語句,但是在C#中我們使用LINQ多于使用for循環。有小伙伴就問了兩個問題:
平時使用的
LINQ對于結構體是值傳遞還是引用傳遞?如果是值傳遞,那么有沒有辦法改為引用傳遞?達到更好性能?
針對這兩個問題特意寫一篇回答一下,字數不多,幾分鐘就能閱讀完。
Linq是值傳遞
在.NET平臺上,默認對于值類型的方法傳參都是值傳遞,除非在方法參數上指定ref,才能變為引用傳遞。
同樣,在LINQ實現的Where、Select、Take眾多方法中,也沒有加入ref關鍵字,所以在LINQ中全部都是值傳遞,如果結構體Size大于8byte(當前平臺的指針大小),那么在調用方法時,結構體的速度要慢于引用傳遞的類。
比如我們編寫如下代碼,使用常見的Linq API進行數據的結構化查詢,分別使用結構體和類,看看效果,數組數據量為1w。
public class SomeClass
{ public int Value1; public int Value2; public float Value3; public double Value4; public string? Value5; public decimal Value6; public DateTime Value7; public TimeOnly Value8; public DateOnly Value9;
} public struct SomeStruct
{ public int Value1; public int Value2; public float Value3; public double Value4; public string? Value5; public decimal Value6; public DateTime Value7; public TimeOnly Value8; public DateOnly Value9;
}[MemoryDiagnoser]
[Orderer(SummaryOrderPolicy.FastestToSlowest)]
public class Benchmark
{ private static readonly SomeClass[] ClassArray; private static readonly SomeStruct[] StructArray; static Benchmark() { var baseTime = DateTime.Now; ClassArray = new SomeClass[10000]; StructArray = new SomeStruct[10000]; for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) { var item = new SomeStruct { Value1 = i, Value2 = i, Value3 = i, Value4 = i, Value5 = i.ToString(), Value6 = i, Value7 = baseTime.AddHours(i), Value8 = TimeOnly.MinValue, Value9 = DateOnly.MaxValue }; StructArray[i] = item; ClassArray[i] = new SomeClass { Value1 = i, Value2 = i, Value3 = i, Value4 = i, Value5 = i.ToString(), Value6 = i, Value7 = baseTime.AddHours(i), Value8 = TimeOnly.MinValue, Value9 = DateOnly.MaxValue }; } } [Benchmark(Baseline = true)] public decimal Class() { return ClassArray.Where(x => x.Value1 > 5000) .Where(x => x.Value3 > 5000) .Where(x => x.Value7 > DateTime.MinValue) .Where(x => x.Value5 != string.Empty) .Where(x => x.Value6 > 1) .Where(x => x.Value8 > TimeOnly.MinValue) .Where(x => x.Value9 > DateOnly.MinValue) .Skip(100) .Take(10000) .Select(x => x.Value6) .Sum(); } [Benchmark] public decimal Struct() { return StructArray.Where(x => x.Value1 > 5000) .Where(x => x.Value3 > 5000) .Where(x => x.Value7 > DateTime.MinValue) .Where(x => x.Value5 != string.Empty) .Where(x => x.Value6 > 1) .Where(x => x.Value8 > TimeOnly.MinValue) .Where(x => x.Value9 > DateOnly.MinValue) .Skip(100) .Take(10000) .Select(x => x.Value6) .Sum(); }
}Benchmakr的結果如下,大家看到在速度上有5倍的差距,結構體由于頻繁裝箱內存分配的也更多。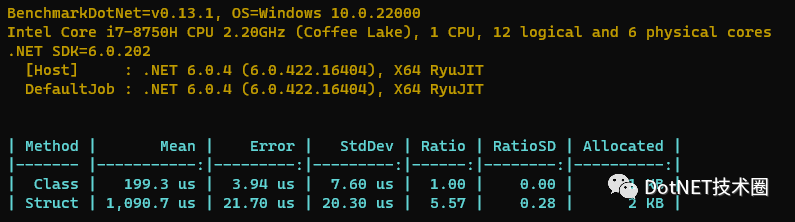
那么注定沒辦開開心心的在結構體上用LINQ了嗎?那當然不是,引入我們今天要給大家介紹的項目。
使用StructLinq
首先來介紹一下StructLinq,在C#中用結構體實現LINQ,以大幅減少內存分配并提高性能。引入IRefStructEnumerable,以提高元素為胖結構體(胖結構體是指結構體大小大于16Byte)時的性能。
引入StructLinq
這個庫已經分發在?NuGet上。可以直接通過下面的命令安裝?StructLinq?:
PM> Install-Package StructLinq簡單使用
下方就是一個簡單的使用,用來求元素和。唯一不同的地方就是需要調用ToStructEnumerable方法。
using StructLinq;int[] array = new [] {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};int result = array.ToStructEnumerable().Where(x => (x & 1) == 0, x=>x).Select(x => x *2, x => x).Sum();x=>x用于避免裝箱(和分配內存),并幫助泛型參數推斷。你也可以通過對Where和Select函數使用結構來提高性能。
性能
所有的跑分結果你可以在這里找到. 舉一個例子,下方代碼的Linq查詢:
list.Where(x => (x & 1) == 0).Select(x => x * 2).Sum();可以被替換為下面的代碼:
list.ToStructEnumerable().Where(x => (x & 1) == 0).Select(x => x * 2).Sum();或者你想零分配內存,可以像下面一樣寫(類型推斷出來,沒有裝箱):
list.ToStructEnumerable().Where(x => (x & 1) == 0, x=>x).Select(x => x * 2, x=>x).Sum(x=>x);如果想要零分配和更好的性能,可以像下面一樣寫:
var where = new WherePredicate();var select = new SelectFunction();list.ToStructEnumerable().Where(ref @where, x => x).Select(ref @select, x => x, x => x).Sum(x => x);上方各個代碼的Benchmark結果如下所示:
BenchmarkDotNet=v0.12.1, OS=Windows 10.0.19042
Intel Core i7-8750H CPU 2.20GHz (Coffee Lake), 1 CPU, 12 logical and 6 physical cores
.NET Core SDK=5.0.101[Host] : .NET Core 5.0.1 (CoreCLR 5.0.120.57516, CoreFX 5.0.120.57516), X64 RyuJITDefaultJob : .NET Core 5.0.1 (CoreCLR 5.0.120.57516, CoreFX 5.0.120.57516), X64 RyuJIT| Method | Mean | Error | StdDev | Ratio | Gen 0 | Gen 1 | Gen 2 | Allocated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LINQ | 65.116 μs | 0.6153 μs | 0.5756 μs | 1.00 | - | - | - | 152 B |
| StructLinqWithDelegate | 26.146 μs | 0.2402 μs | 0.2247 μs | 0.40 | - | - | - | 96 B |
| StructLinqWithDelegateZeroAlloc | 27.854 μs | 0.0938 μs | 0.0783 μs | 0.43 | - | - | - | - |
| StructLinqZeroAlloc | 6.872 μs | 0.0155 μs | 0.0137 μs | 0.11 | - | - | - | - |
StructLinq在這些場景里比默認的LINQ實現快很多。
在上文場景中使用
我們也把上面的示例代碼使用StructLinq改寫一下。
// 引用類型使用StructLinq
[Benchmark]
public double ClassStructLinq()
{ return ClassArray .ToStructEnumerable() .Where(x => x.Value1 > 5000) .Where(x => x.Value3 > 5000) .Where(x => x.Value7 > DateTime.MinValue) .Where(x => x.Value5 != string.Empty) .Where(x => x.Value6 > 1) .Where(x => x.Value8 > TimeOnly.MinValue) .Where(x => x.Value9 > DateOnly.MinValue) .Skip(100) .Take(10000) .Select(x => x.Value4) .Sum(x => x);
} // 結構體類型使用StructLinq
[Benchmark]
public double StructLinq()
{ return StructArray .ToStructEnumerable() .Where(x => x.Value1 > 5000) .Where(x => x.Value3 > 5000) .Where(x => x.Value7 > DateTime.MinValue) .Where(x => x.Value5 != string.Empty) .Where(x => x.Value6 > 1) .Where(x => x.Value8 > TimeOnly.MinValue) .Where(x => x.Value9 > DateOnly.MinValue) .Skip(100) .Take(10000) .Select(x => x.Value4) .Sum(x => x);
} // 結構體類型 StructLinq 零分配
[Benchmark]
public double StructLinqZeroAlloc()
{ return StructArray .ToStructEnumerable() .Where(x => x.Value1 > 5000, x=> x) .Where(x => x.Value3 > 5000, x => x) .Where(x => x.Value7 > DateTime.MinValue, x => x) .Where(x => x.Value5 != string.Empty, x => x) .Where(x => x.Value6 > 1, x => x) .Where(x => x.Value8 > TimeOnly.MinValue, x => x) .Where(x => x.Value9 > DateOnly.MinValue, x => x) .Skip(100) .Take(10000) .Select(x => x.Value4, x => x) .Sum(x => x);
} // 結構體類型 StructLinq 引用傳遞
[Benchmark]
public double StructLinqRef()
{ return StructArray .ToRefStructEnumerable() // 這里使用的是ToRefStructEnumerable.Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value1 > 5000) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value3 > 5000) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value7 > DateTime.MinValue) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value5 != string.Empty) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value6 > 1) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value8 > TimeOnly.MinValue) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value9 > DateOnly.MinValue) .Skip(100) .Take(10000) .Select((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value4) .Sum(x => x);
} // 結構體類型 StructLinq 引用傳遞 零分配
[Benchmark]
public double StructLinqRefZeroAlloc()
{ return StructArray .ToRefStructEnumerable() .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value1 > 5000, x=> x) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value3 > 5000, x=> x) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value7 > DateTime.MinValue, x=> x) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value5 != string.Empty, x=> x) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value6 > 1, x => x) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value8 > TimeOnly.MinValue, x=> x) .Where((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value9 > DateOnly.MinValue, x=> x) .Skip(100, x => x) .Take(10000, x => x) .Select((in SomeStruct x) => x.Value4, x=> x) .Sum(x => x, x=>x);
} // 結構體 直接for循環
[Benchmark]
public double StructFor()
{ double sum = 0; int skip = 100; int take = 10000; for (int i = 0; i < StructArray.Length; i++) { ref var x = ref StructArray[i]; if(x.Value1 <= 5000) continue; if(x.Value3 <= 5000) continue; if(x.Value7 <= DateTime.MinValue) continue; if(x.Value5 == string.Empty) continue; if(x.Value6 <= 1) continue; if(x.Value8 <= TimeOnly.MinValue) continue; if(x.Value9 <= DateOnly.MinValue) continue; if(i < skip) continue; if(i >= skip + take) break; sum += x.Value4; } return sum;
}最后的Benchmark結果如下所示。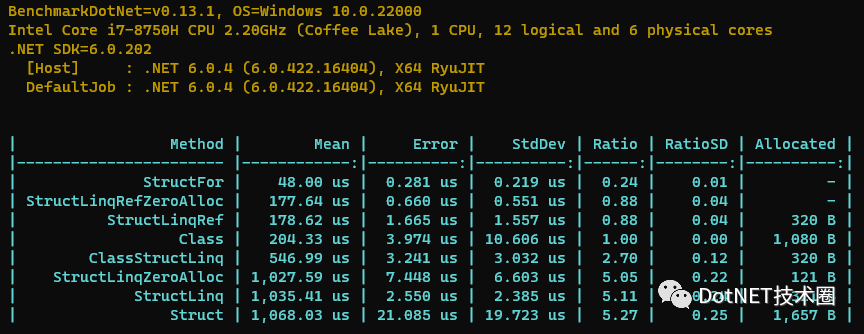
從以上Benchmark結果可以得出以下結論:
類和結構體都可以使用
StructLinq來減少內存分配。類和結構體使用
StructLinq都會導致代碼跑的更慢。結構體類型使用
StructLinq的引用傳遞模式可以獲得5倍的性能提升,比引用類型更快。無論是
LINQ還是StructLinq由于本身的復雜性,性能都沒有For循環來得快。
總結
在已經用上結構體的高性能場景,其實不建議使用LINQ了,因為LINQ本身它性能就存在瓶頸,它主要就是為了提升開發效率。建議直接使用普通循環。
如果一定要使用,那么建議大于8byte的結構體使用StructLinq的引用傳遞模式(ToRefStructEnumerable),這樣可以把普通LINQ結構體的性能提升5倍以上,也能幾乎不分配額外的空間。
作者:InCerry
出處:https://www.cnblogs.com/InCerry/p/Dotnet-Perf-Opt-Use-StructLinq-For-ValueType.html
版權:本作品采用「署名-非商業性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 國際」許可協議進行許可。
聲明:本博客版權歸「InCerry」所有。

我把魔法變成了積木)
:如何在Activity中獲取調用者?)






)
)


)



完整操作圖文教程(Erdas版))

