通過以下思維導圖,學習委托的基本概念,后面著重講解委托的運用,希望通過最簡單的方式收獲更多的知識。
1.委托的各種寫法
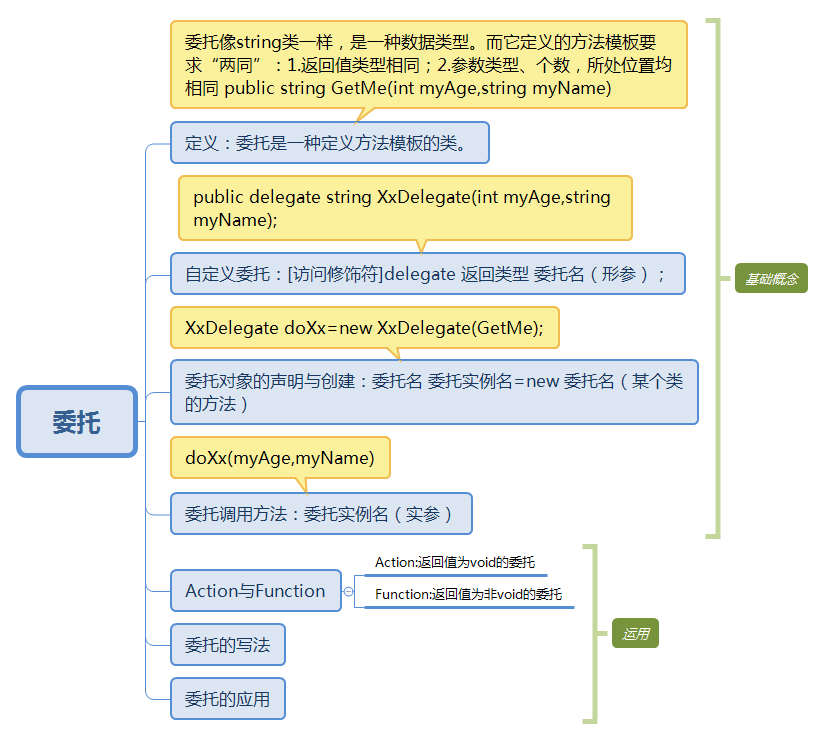
1、委托 委托名=new 委托(會調用的方法名); 委托名(參數);
2、委托 委托名 =會調用的方法名; 委托名(參數);
3、匿名方法:委托 委托名=delegate(參數){會調用的方法體};委托名(參數);
4、拉姆達表達式:委托 委托名=((參數1,。。參數n)=>{會調用的方法體});委托名(參數);
5、用Action<T>和Func<T>
Action<參數1, 參數2,> 委托名= ((參數1,參數2) => {不帶返回值的方法體 });委托名(參數1,參數2);
Func<參數1, 參數2, 返回值> 委托名= ((參數1,參數2) => {帶返回值的方法體 });返回值=委托名(參數1,參數2);
示例:
public delegate int Call(int num1, int num2);
class SimpleMath
{// 乘法方法public static int Multiply(int num1, int num2){return num1 * num2;}// 除法方法public int Divide(int num1, int num2){return num1 / num2;}
}class Test
{static void Main(string[] args){//--------------------第一種寫法------------------------//Call objCall = new Call(SimpleMath.Multiply);Call objCall1 = new Call(new SimpleMath().Divide);//--------------------第二種寫法------------------------//Call objCall = SimpleMath.Multiply;Call objCall1 = new SimpleMath().Divide;//--------------------第三種寫法------------------------//Call objCall = delegate(int a, int b){return a * b;};Call objCall1 = delegate(int a, int b){return a / b;};//--------------------第四種寫法------------------------//Call objCall =((int a,int b)=> { return a*b;});Call objCall1 = ((int a, int b) => { return a / b; });//--------------------第五種寫法------------------------//Func<int, int, int> objCall = ((a, b) => { return a * b; });Func<int, int, int> objCall1 = ((a, b) => { return a / b; });Action<int, int> ob = ((a, b) => { Console.WriteLine(a * b); });ob(5, 3);//----------------------------------------------------//int result = objCall(5, 3);int result1 = objCall1(5, 3);System.Console.WriteLine("結果1為 {0},結果2為{1}", result,result1);Console.ReadKey();}
}2.委托的運用
委托的運用記住兩點:
1.將方法當作參數實例化委托對象;
?2.將方法的參數傳遞給委托對象,以實現實際的方法調用。
委托常用場景:
1.模板方法:
?如以下定義類CalculateFactory,用于定義各種計算方法,然后通過Calculate方法暴露出來給外界使用,而Calculate方法通過傳入委托對象new Calculate(x1.Add)來實現對Add方法的調用。這是委托模板方法使用較簡單的一種形式,它還可以有很多變種。
? 下面這段程序不用委托完全可以實現同樣的邏輯,為什么要“故弄玄虛”呢?因為示例是為了說明委托作為模板方法的用法,故而用了最簡單的一種,實際運用過程中,通常與設計模式相結合,以實現代碼的高復用低耦合。進一步延伸,實際設計模式中也較少用委托,而用接口、抽象類來實現“模板方法”的功能,具體要怎么用是看個人習慣和便捷程度。委托用的最多的場景是下面要介紹的回調方法。
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){CalculateFactory x1 = new CalculateFactory();CalculateFactory x2 = new CalculateFactory();x1.Calculate(10, 9, new Calculate(x1.Add));x2.Calculate(10, 9, new Calculate(x2.Reduce));Console.ReadKey();}}public delegate void Calculate(int a, int b);public class CalculateFactory{public void Calculate(int a, int b, Calculate calculateDelegae){calculateDelegae(a, b);}public void Add(int a, int b){Console.WriteLine(string.Format("This is a+b={0}", a + b));}public void Reduce(int a, int b){Console.WriteLine(string.Format("This is a-b={0}", a - b));}}2.回調方法:
? 回調方法與模板方法并不是并列的兩種類型,其本質都是一樣的,即將方法當成參數傳遞并調用,是通過應用場景來分類的。主調方法(調用回調方法的方法體)在滿足某種條件或完成某種邏輯后去調用的方法,稱為回調方法。將上面示例改造成含有回調方法的程序。
class Program{static void Main(string[] args){ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeToyCar);Logger logger = new Logger();Action<Product> log = new Action<Product>(logger.Log); //Log的委托;Box box1 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func1, log);Box box2 = wrapFactory.WrapProduct(func2, log);Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);}class Product //產品類{public string Name { get; set; }public double Price { get; set; }}class Box //盒子類{public Product Product { get; set; }}class Logger{public void Log(Product product){Console.WriteLine(product.Price);}}class WrapFactory //包裝工廠{public Box WrapProduct(Func<Product> getProduct, Action<Product> logCallback){Box box = new Box();Product product = getProduct.Invoke();//此處使用的是間接的同步調用,如果使用間接異步調用用BeginInvoke();if (product.Price > 50) //如果產品價格大于50,就執行回調方法;{logCallback(product);}box.Product = product;return box;}}class ProductFactory //產品工廠{public Product MakePizza(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "Pizza";product.Price = 30;return product;}public Product MakeToyCar(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "ToyCar";product.Price = 100;return product;}}}?












)






