一 對象密封
1 Object.preventExtensions 禁止對象拓展,仍可刪除
- 嚴格模式下報錯
const origin = {a: 1
}
const fixed = Object.preventExtensions(origin)
console.log(origin === fixed) // true
console.log(Object.isExtensible(origin)) // false 不可拓展
origin.b = 100
console.log(origin) // 不變
2 Object.defineProperty
const obj = {}
obj.b = 1 // 屬性描述符全是true
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, 'b'))
Object.defineProperty(obj, 'c', {value: 100 // 屬性描述符全是false
})
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, 'c'))
3 Object.seal 對象密封 禁止拓展+不可刪除,仍可修改
- 嚴格模式下報錯
const origin = {a: 1
}
const fixed = Object.seal(origin)
console.log(origin === fixed) // true
console.log(Object.isSealed(origin)) // true 密封的
console.log(Object.isExtensible(origin)) // false 不可拓展
delete origin.a
console.log(origin) // 不變,不可刪除
origin.a = 100
console.log(origin) // 不可刪除, 仍可修改
4. Object.freeze - 凍結的 不可增刪改
const origin = {a: 1
}
const fixed = Object.freeze(origin)
console.log(origin === fixed) // true
console.log(Object.isFrozen(origin)) // true 凍結的
console.log(Object.isSealed(origin)) // true 密封的
console.log(Object.isExtensible(origin)) // false 不可拓展
origin.a = 100
console.log(origin) // 不可修改
二 Object.is
console.log(NaN === NaN) // false
console.log(+0 === -0) // true
console.log(Object.is(NaN, NaN)) // true 和全等不同的
console.log(Object.is(+0, -0)) // false 和全等不同的
console.log(Object.is({}, {})) // false
三 Object.assign(tar, …sources) 合并對象
const tar = {}
const obj = {a: 1}
const copy = Object.assign(tar, obj)
console.log(copy === tar) // true
// 直接使用tar
-
屬性覆蓋:取后寫的
-
當tar是不能轉為對象的原始值null/undefined時,報錯
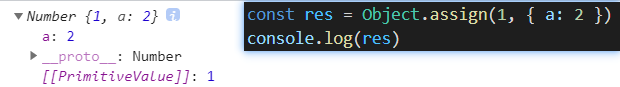

-
source能轉成對象,且屬性的可枚舉性為真,則可以合并得到新的對象
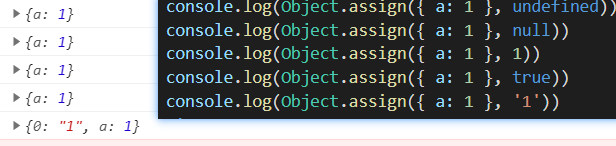
-
source為數組時

-
Object.assign拷貝的是可枚舉屬性,繼承屬性和不可枚舉屬性不可拷貝
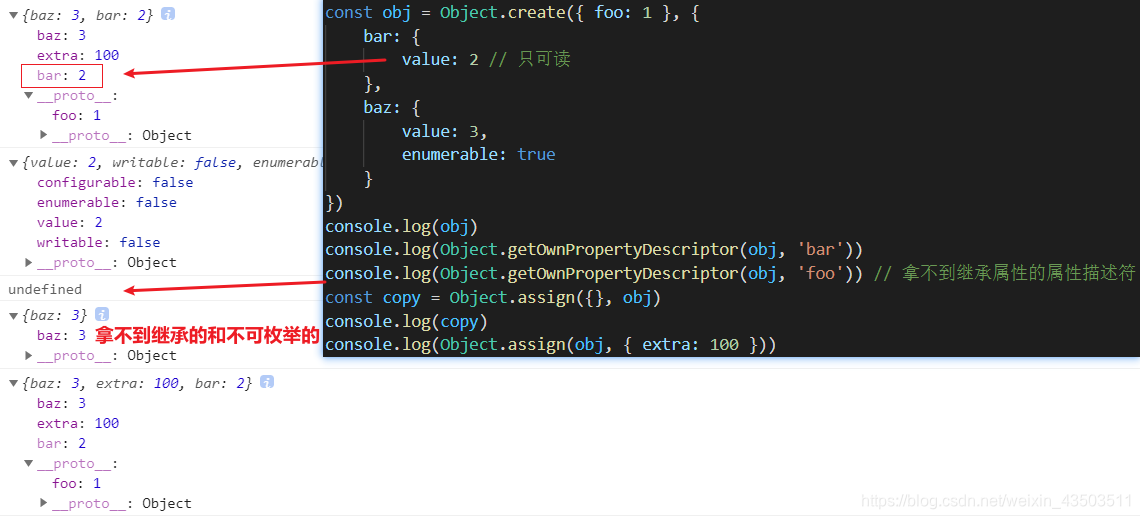
const obj = Object.create({ foo: 1 }, {bar: {value: 2 // 只可讀},baz: {value: 3,enumerable: true}
})
console.log(obj)
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, 'bar'))
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj, 'foo')) // 拿不到繼承屬性的屬性描述符
const copy = Object.assign({}, obj)
console.log(copy)
console.log(Object.assign(obj, { extra: 100 }))
Object.assign是淺拷貝
- 在嵌套的對象里要尤其注意
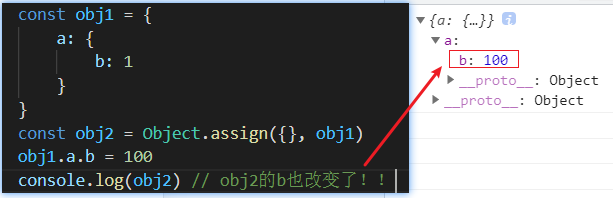
嵌套對象,同名屬性會被后者替換
console.log(Object.assign([1,2,3],[4,5]))
// {0: 4, 1: 5, 2: 3}
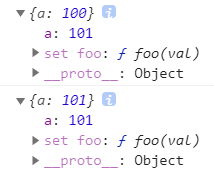
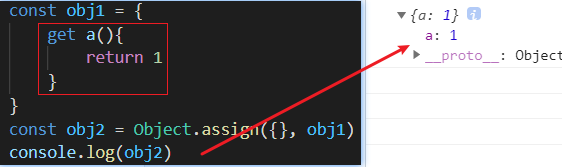
含getter

含setter
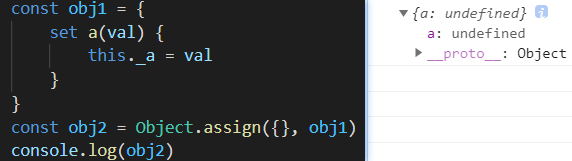
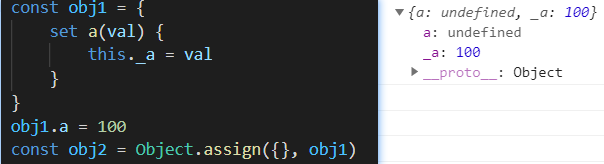
const obj1 = {set a(val) {this._a = val}
}
obj1.a = 100
const obj2 = Object.assign({}, obj1)
console.log(obj2)
擴充原型上的方法、屬性
function Person() { }
Object.assign(Person.prototype, {name: 'hh',eat() { }
})
console.log(Person.prototype)
設置默認項
const DEFAULT = {url: {host: 'www.baidu.com',port: 80}
}
function test(opt) {opt = Object.assign({}, DEFAULT, opt)console.log(opt)
}
test({url: { port: 8080 }
})
test()

四 Symbol 原始類型
- 可以看成永遠不會重復的字符串
const a = Symbol('1')
const b = Symbol('1')
console.log(a) // Symbol(1)
console.log(b) // Symbol(1)
console.log(a === b) // false
console.log(a == b) // false
五Object.defineProperties/getOwnPropertyDescriptors
- 獲取多個描述/定義多個屬性
const obj1 = {}
Object.defineProperty(obj1, 'a', {value: 'a'
})Object.defineProperties(obj1, {b: {value: 'b'},c: {value: 'c'},
})
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj1, 'a'))
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj1, 'b'))
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptor(obj1, 'c'))
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj1))

- 解決Object.assign不能拷貝setter/getter的問題
const source = {set foo(val) {this.a = val}
}
console.log(source)
const tar = {}
Object.defineProperties(tar, Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(source))
console.log(tar)
console.log(Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(tar))
tar.foo = 100
console.log(tar)

- 拷貝
const source = {a: 100,set foo(val) {this.a = val}
}
const clone = Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(source), Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(source))
console.log(clone)
clone.foo = 101
console.log(clone)