要使用…須有迭代器接口
數組方法

構造器上的方法
Array.of()聲明數組
- 替代
new Array()的方式聲明數組 new Array()不傳參數返回空數組,只傳1個參數時,代表數組長度,內容用empty填充,傳多個參數,則代表數組內容,容易有歧義
console.log(new Array()) // []
console.log(new Array(1)) // [empty]
console.log(new Array(1, 2, 3)) // [1, 2, 3]
console.log(Array()) // 不寫new 效果相同 []
console.log(Array(1)) // [empty]
console.log(Array.of()) // []
console.log(Array.of(1)) // [1]
console.log(Array.of(1, 2, 3)) // [1, 2, 3]
Array.from() 轉換為真正的數組
-
Array.from() 方法從一個類似數組或可迭代對象創建一個新的,淺拷貝的數組實例
-
語法
Array.from(arrayLike[, mapFn[, thisArg]])
mapFn可選:如果指定了該參數,新數組中的每個元素會執行該回調函數。
thisArg可選:可選參數,執行回調函數 mapFn 時 this 對象。 -
類數組,打印出來和數組沒什么區別,但不是數組

let obj = {start: [1, 3, 2, 4],end: [5, 7, 6],[Symbol.iterator]() {let index = 0,arr = [...this.start, ...this.end],len = arr.length;return {next() {if (index < len) {return {value: arr[index++],done: false}} else {return {value: undefined,done: true}}}}}
}
console.log(Array.from(obj)) // [1, 3, 2, 4, 5, 7, 6]
console.log(Array.from(obj,function (val,idx) {return `第${idx}個:${val}`
}))
// ["第0個:1", "第1個:3", "第2個:2", "第3個:4", "第4個:5", "第5個:7", "第6個:6"]
原型上的方法
ES6新增有:
[].fill()copyWithin()keys() / values() / entries()includes()find() / findIndex()
arr.fill() 左閉右開
- fill() 方法用一個固定值填充一個數組中從起始索引到終止索引內的全部元素。不包括終止索引。
[ , ) - 修改原數組
- 如果start和end索引相同/或者是非數,則不操作
- 不寫end/end超出長度,就填充直到結束
[1, 2, 3].fill(4); // [4, 4, 4]
[1, 2, 3].fill(4, 1); // [1, 4, 4]
[1, 2, 3].fill(4, 1, 2); // [1, 4, 3]
[1, 2, 3].fill(4, 1, 1); // [1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3].fill(4, 3, 3); // [1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3].fill(4, -3, -2); // [4, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3].fill(4, NaN, NaN); // [1, 2, 3]
[1, 2, 3].fill(4, 3, 5); // [1, 2, 3]
Array(3).fill(4); // [4, 4, 4]
[].fill.call({ length: 3 }, 4); // {0: 4, 1: 4, 2: 4, length: 3}// Objects by reference.
var arr = Array(3).fill({}) // [{}, {}, {}];
// 需要注意如果fill的參數為引用類型,會導致都執行都一個引用類型
// 如 arr[0] === arr[1] 為true
arr[0].hi = "hi"; // [{ hi: "hi" }, { hi: "hi" }, { hi: "hi" }]
keys() / values() / entries()
- 返回值是迭代器對象
- 迭代器對象的原型上有next方法
- 迭代器對象沒有length屬性,不能用for循環遍歷
const arr = [1, 2, 3]
const itKeys = arr.keys()
const itVals = arr.values()
const itEntries = arr.entries()
console.log(itKeys)
console.log(itVals)
console.log(itEntries)
console.log(itKeys.next())
console.log(itKeys.next())
console.log(itKeys.next())
console.log(itKeys.next())
console.log('剩余運算符展開',[...arr.keys()])console.log(itVals.next())
console.log(itVals.next())
console.log(itVals.next())
console.log(itVals.next())
console.log('剩余運算符展開',[...arr.values()])console.log(itEntries.next())
console.log(itEntries.next())
console.log(itEntries.next())
console.log(itEntries.next())
console.log('剩余運算符展開',[...arr.entries()])

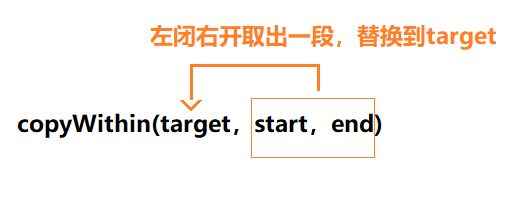
copyWithin
- 淺復制數組的一部分到同一數組中的另一個位置,并返回它,不會改變原數組的長度。
copyWithin(target,start,end)- target從哪里開始被替換
- start原數組從哪開始
- end原數組到哪結束
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4]
console.log(arr.copyWithin(2, 0)) // [1,2,1,2]
console.log([].copyWithin.call({ length: 5, 3: 1 }, 0, 3))
// 沒有用undefined進行填充,沒有對沒有的index進行填充

console.log([].copyWithin.call({ length: 5, 3: 1, 4: 1}, 0, 3))

ES6解決了NaN本身不相等而影響判斷結果的問題
find/findIndex
- find返回數組中滿足提供的測試函數的第一個元素的值。否則返回 undefined。
- findIndex返回數組中滿足提供的測試函數的第一個元素的索引。若沒有找到對應元素則返回-1。
- 接收參數:
callback(val,idx,arr),[thisArg]
const arr = [NaN]
console.log(arr.indexOf(NaN)) // -1 找不到,NaN與自身也不相等
console.log(arr.findIndex((val) => Object.is(val, NaN))) // 0 找到
console.log(arr.findIndex((val) => isNaN(val))) // 0 找到
includes
- 判斷一個數組是否包含一個指定的值,根據情況,如果包含則返回 true,否則返回false。
const arr = [NaN]
console.log(arr.includes(NaN)) // true
數值拓展
- 二進制
binary - 八進制
Octal - 十六進制
hex - 新增二進制/八進制表示方法
- 二進制
0b開頭,八進制0O開頭
// 十進制16轉為二進制
console.log((16).toString(2)) // 10000
// 直接表示這個二進制數
console.log(0b10000) // 16 打印結果是十進制的
// 十進制16轉為八進制
console.log((16).toString(8)) // 20
// 直接表示這個八進制數
console.log(0O20) // 16 打印結果是十進制的
- ES5就有的十六進制是
0x開頭的 - 都不區分大小寫
- parseInt、isNaN等方法在ES5中是定義在全局的,ES6中在Number的構造器上可看到這些方法的定義,也解決了全局方法的一些問題

isNaN 隱式轉換
console.log(isNaN('NaN')) // true,隱式轉換,得到了不符合預期的結果
console.log(Number.isNaN('NaN')) // false
isFinite是有限的
console.log(isFinite(NaN)) // false
console.log(isFinite(Infinity)) // false
console.log(isFinite('42')) // true 隱式轉換
console.log(Number.isFinite('42')) // false
isInteger是整數
console.log(Number.isInteger(24)) // true
console.log(Number.isInteger(24.0)) // true js認為這是整數
console.log(Number.isInteger(24.1)) // false
isSafeInteger 安全整數
- 安全整數的范圍
console.log(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER === Math.pow(2, 53) - 1) // 2的53次方 true
console.log(Number.MIN_SAFE_INTEGER === -Math.pow(2, 53) + 1) // true
Math對象
- 內置對象Math沒有prototype














))唉))





