一、背景知識
在【Spring實戰】Spring容器初始化完成后執行初始化數據方法一文中說要分析其實現原理,于是就從源碼中尋找答案,看源碼容易跑偏,因此應當有個主線,或者帶著問題、目標去看,這樣才能最大限度的提升自身代碼水平。由于上文中大部分都基于注解進行設置的(Spring實戰系列篇demo大部分也都是基于注解實現的),因此就想弄明白Spring中注解是怎么工作的,這個也是分析上文中實現原理的一個基礎。于是索性解析下Spring中注解的工作原理。
二、從context:component-scan標簽或@ComponentScan注解說起 如果想要使用Spring注解,那么首先要在配置文件中配置
context:component-scan標簽或者在配置類中添加@ComponentScan注解。題外話:現在Spring已經完全可以實現無xml(當然有些還是需要xml配置來實現的)的配置,甚至都不需要web.xml,當然這需要Servlet3.0服務器的支持(如Tomcat7或者更高版本)。Spirng In Action Fourth是針對三種bean的裝配機制(xml進行顯示配置、java中進行顯示配置、隱式的bean發現機制和自動裝配)的使用是這樣建議的:

如果要使用自動配置機制,就要在配置文件中配置context:component-scan標簽或者在配置類中添加@ComponentScan注解。基于【Spring實戰】----Spring配置文件的解析
篇文章,本文還是基于xml中的自定義標簽進行解析,當然也可以直接看@ComponentScan注解的解析(ComponentScanAnnotationParser.java,這其中還牽扯到@Configuration以及另外的知識點)。
三、context:component-scan標簽解析
以實戰篇系列demo為例進行分析
<context:component-scan base-package="com.mango.jtt"></context:component-scan>
從【Spring實戰】----Spring配置文件的解析中可知,標簽的處理器為spring.handlers
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/context=org.springframework.context.config.ContextNamespaceHandler
registerBeanDefinitionParser("component-scan", new ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser());
在ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser.java中進行處理
@Override public BeanDefinition parse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) { String basePackage = element.getAttribute(BASE_PACKAGE_ATTRIBUTE); basePackage = parserContext.getReaderContext().getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(basePackage); String[] basePackages = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(basePackage, ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS); // Actually scan for bean definitions and register them. ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = configureScanner(parserContext, element); //得到掃描器 Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = scanner.doScan(basePackages); //掃描文件,并轉化為spring bean,并注冊 registerComponents(parserContext.getReaderContext(), beanDefinitions, element); //注冊其他相關組件 return null; }
從上述代碼中可知,其作用就是掃描basePackages下的文件,轉化為spring中的bean結構,并將其注冊到容器中;最后是注冊相關組件(主要是注解處理器)。注解需要注解處理器來處理。
要知道ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser掃描文件并轉化成spring bean的原則的,就需要看下其定義的屬性值:
private static final String BASE_PACKAGE_ATTRIBUTE = "base-package"; private static final String RESOURCE_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE = "resource-pattern"; private static final String USE_DEFAULT_FILTERS_ATTRIBUTE = "use-default-filters"; private static final String ANNOTATION_CONFIG_ATTRIBUTE = "annotation-config"; private static final String NAME_GENERATOR_ATTRIBUTE = "name-generator"; private static final String SCOPE_RESOLVER_ATTRIBUTE = "scope-resolver"; private static final String SCOPED_PROXY_ATTRIBUTE = "scoped-proxy"; private static final String EXCLUDE_FILTER_ELEMENT = "exclude-filter"; private static final String INCLUDE_FILTER_ELEMENT = "include-filter"; private static final String FILTER_TYPE_ATTRIBUTE = "type"; private static final String FILTER_EXPRESSION_ATTRIBUTE = "expression"; 先簡單解析下上述屬性的作用
base-package:為必須配置屬性,指定了spring需要掃描的跟目錄名稱,可以使用”,” “;” “\t\n(回車符)”來分割多個包名
resource-pattern:配置掃描資源格式.默認”**/*.class”
use-default-filters:是否使用默認掃描策略,默認為”true”,會自動掃描指定包下的添加了如下注解的類,@Component, @Repository, @Service,or @Controller

annotation-config:是否啟用默認配置,默認為”true”,該配置會在BeanDefinition注冊到容器后自動注冊一些BeanPostProcessors對象到容器中.這些處理器用來處理類中Spring’s @Required and
@Autowired, JSR 250’s @PostConstruct, @PreDestroy and @Resource (如果可用),
JAX-WS’s @WebServiceRef (如果可用), EJB 3’s @EJB (如果可用), and JPA’s
@PersistenceContext and @PersistenceUnit (如果可用),但是該屬性不會處理Spring’s @Transactional 和 EJB 3中的@TransactionAttribute注解對象,這兩個注解是通過tx:annotation-driven元素處理過程中對應的BeanPostProcessor來處理的.
include-filter:如果有自定義元素可以在該處配置
exclude-filter:配置哪些類型的類不需要掃描
注意:</context:component-scan>元素中默認配置了annotation-config,所以不需要再單獨配置元素.
這些屬性作用配置都是在configureScanner()函數中進行的。
protected ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner configureScanner(ParserContext parserContext, Element element) { boolean useDefaultFilters = true; if (element.hasAttribute(USE_DEFAULT_FILTERS_ATTRIBUTE)) { useDefaultFilters = Boolean.valueOf(element.getAttribute(USE_DEFAULT_FILTERS_ATTRIBUTE)); } // Delegate bean definition registration to scanner class. ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = createScanner(parserContext.getReaderContext(), useDefaultFilters); //包含了掃描策略配置 scanner.setResourceLoader(parserContext.getReaderContext().getResourceLoader()); scanner.setEnvironment(parserContext.getReaderContext().getEnvironment()); scanner.setBeanDefinitionDefaults(parserContext.getDelegate().getBeanDefinitionDefaults()); scanner.setAutowireCandidatePatterns(parserContext.getDelegate().getAutowireCandidatePatterns()); if (element.hasAttribute(RESOURCE_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE)) { scanner.setResourcePattern(element.getAttribute(RESOURCE_PATTERN_ATTRIBUTE)); //配置掃描資源格式 } try { parseBeanNameGenerator(element, scanner); //配置名稱生成器 } catch (Exception ex) { parserContext.getReaderContext().error(ex.getMessage(), parserContext.extractSource(element), ex.getCause()); } try { parseScope(element, scanner); //配置元數據解析器 } catch (Exception ex) { parserContext.getReaderContext().error(ex.getMessage(), parserContext.extractSource(element), ex.getCause()); } parseTypeFilters(element, scanner, parserContext); //配置包含和不包含過濾 return scanner; }
看一下默認掃描策略的配置
/** * Register the default filter for {@link Component @Component}. * <p>This will implicitly register all annotations that have the * {@link Component @Component} meta-annotation including the * {@link Repository @Repository}, {@link Service @Service}, and * {@link Controller @Controller} stereotype annotations. * <p>Also supports Java EE 6's {@link javax.annotation.ManagedBean} and * JSR-330's {@link javax.inject.Named} annotations, if available. * */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected void registerDefaultFilters() { this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter(Component.class)); ClassLoader cl = ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider.class.getClassLoader(); try { this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter( ((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.annotation.ManagedBean", cl)), false)); logger.debug("JSR-250 'javax.annotation.ManagedBean' found and supported for component scanning"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { // JSR-250 1.1 API (as included in Java EE 6) not available - simply skip. } try { this.includeFilters.add(new AnnotationTypeFilter( ((Class<? extends Annotation>) ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Named", cl)), false)); logger.debug("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Named' annotation found and supported for component scanning"); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { // JSR-330 API not available - simply skip. } }
從注釋中看出除了,@Component、和包含元注解@Component的@Controller、@Service、@Repository,還支持Java EE 6的@link javax.annotation.ManagedBean和jsr - 330的 @link javax.inject.Named,如果可用。
- 默認過濾器主要掃描@Component @Repository @Service @Controller注解的類,同樣可以通過配置類掃描過濾器來掃描自定義注解的類。
- 當類路徑下有javax.annotation.ManagedBean和javax.inject.Named類庫時支持這2個注解掃描。
其掃描過程如下:
- 首先構造一個ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner對象,需要傳遞一個BeanDefinitionRegistry對象。
- 根據配置文件配置屬性設置scanner的掃描屬性,比如”resource-pattern”, “name-generator”, “scope-resolver”等。
- 調用scanner.doScan(String… basePackages)方法完成候選類的自動掃描。
下面看一下doScan
/** * Perform a scan within the specified base packages, * returning the registered bean definitions. * <p>This method does <i>not</i> register an annotation config processor * but rather leaves this up to the caller. * @param basePackages the packages to check for annotated classes * @return set of beans registered if any for tooling registration purposes (never {@code null}) */ protected Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) { Assert.notEmpty(basePackages, "At least one base package must be specified"); Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>(); for (String basePackage : basePackages) { Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage); for (BeanDefinition candidate : candidates) { ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = this.scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(candidate); candidate.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName()); String beanName = this.beanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(candidate, this.registry); if (candidate instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) { postProcessBeanDefinition((AbstractBeanDefinition) candidate, beanName); //配置bena屬性 } if (candidate instanceof AnnotatedBeanDefinition) { AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations((AnnotatedBeanDefinition) candidate); //配置通過注解設置的便屬性 } if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) { BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName); definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry); beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder); registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry); } } } return beanDefinitions; }
實際上掃描文件并包裝成BeanDefinition是由findCandidateComponents來做的
/** * Scan the class path for candidate components. * @param basePackage the package to check for annotated classes * @return a corresponding Set of autodetected bean definitions */ public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) { Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinition>(); try { String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX + resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + "/" + this.resourcePattern; Resource[] resources = this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(packageSearchPath); boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled(); boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled(); for (Resource resource : resources) { if (traceEnabled) { logger.trace("Scanning " + resource); } if (resource.isReadable()) { try { MetadataReader metadataReader = this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource); if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) { ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader); sbd.setResource(resource); sbd.setSource(resource); if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource); } candidates.add(sbd); } else { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource); } } } else { if (traceEnabled) { logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource); } } } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException( "Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex); } } else { if (traceEnabled) { logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource); } } } } catch (IOException ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex); } return candidates; }
大致的流程如下:
(1)先根據context:component-scan 中屬性的base-package="com.mango.jtt"配置轉換為classpath*:com/mango/jtt/**/*.class(默認格式),并掃描對應下的class和jar文件并獲取類對應的路徑,返回Resources
(2)根據指定的不掃描包,指定的掃描包配置進行過濾不包含的包對應下的class和jar。
(3)封裝成BeanDefinition放到隊列里。
實際上,是把所有包下的class文件都掃描了的,并且利用asm技術讀取java字節碼并轉化為MetadataReader中的AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor結構
MetadataReader metadataReader = this.metadataReaderFactory.getMetadataReader(resource);
SimpleMetadataReader(Resource resource, ClassLoader classLoader) throws IOException { InputStream is = new BufferedInputStream(resource.getInputStream()); ClassReader classReader; try { classReader = new ClassReader(is); } catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) { throw new NestedIOException("ASM ClassReader failed to parse class file - " + "probably due to a new Java class file version that isn't supported yet: " + resource, ex); } finally { is.close(); } AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor visitor = new AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor(classLoader); classReader.accept(visitor, ClassReader.SKIP_DEBUG); this.annotationMetadata = visitor; // (since AnnotationMetadataReadingVisitor extends ClassMetadataReadingVisitor) this.classMetadata = visitor; this.resource = resource; } 此處不深究牛X的asm技術,繼續看其兩個if判斷,只有符合這兩個if的才add到candidates,也就是候選者BeanDefinition,函數名字起得名副其實。
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) { ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader); sbd.setResource(resource); sbd.setSource(resource); if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource); } candidates.add(sbd); } else { if (debugEnabled) { logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource); } } }
先看第一個判斷
/** * Determine whether the given class does not match any exclude filter * and does match at least one include filter. * @param metadataReader the ASM ClassReader for the class * @return whether the class qualifies as a candidate component */ protected boolean isCandidateComponent(MetadataReader metadataReader) throws IOException { for (TypeFilter tf : this.excludeFilters) { if (tf.match(metadataReader, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { return false; } } for (TypeFilter tf : this.includeFilters) { if (tf.match(metadataReader, this.metadataReaderFactory)) { return isConditionMatch(metadataReader); } } return false; }
這里的判斷就用到了前面說的屬性設置,在本例中excludeFilters是沒有內容的,includeFilters包含有@Component和@Named兩個的AnnotationTypeFilter。因此只有第二個循環起作用,也就是是有符合@Component且元注解為@Component的注解和@Named兩種注解的才可以。
第二個if就是判斷類是否是實現類,抽象類好接口類都不不可以
/** * Determine whether the given bean definition qualifies as candidate. * <p>The default implementation checks whether the class is concrete * (i.e. not abstract and not an interface). Can be overridden in subclasses. * @param beanDefinition the bean definition to check * @return whether the bean definition qualifies as a candidate component */ protected boolean isCandidateComponent(AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition) { return (beanDefinition.getMetadata().isConcrete() && beanDefinition.getMetadata().isIndependent()); }
總結:掃描器采用asm技術掃描java字節碼文件,即.class文件。掃描時是掃描指定包下的全部class文件,轉換成指定的MetadataReader結構后,再去判斷是否符合掃描規則,符合的才加入候選bean中,并注冊到容器中。
至此,注解掃描分析完了,看一下bean注冊,回到doScan中
if (checkCandidate(beanName, candidate)) { BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(candidate, beanName); definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry); beanDefinitions.add(definitionHolder); registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder, this.registry); }
也是只有符合條件的才注冊,主要是容器中沒有的,或者不和容器中有的沖突的。
再看下其他組件注冊,回到最初的parse
registerComponents(parserContext.getReaderContext(), beanDefinitions, element);
protected void registerComponents( XmlReaderContext readerContext, Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions, Element element) { Object source = readerContext.extractSource(element); CompositeComponentDefinition compositeDef = new CompositeComponentDefinition(element.getTagName(), source); for (BeanDefinitionHolder beanDefHolder : beanDefinitions) { compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(beanDefHolder)); } // Register annotation config processors, if necessary. boolean annotationConfig = true; if (element.hasAttribute(ANNOTATION_CONFIG_ATTRIBUTE)) { //本例中沒有配置annotation-config,默認為true annotationConfig = Boolean.valueOf(element.getAttribute(ANNOTATION_CONFIG_ATTRIBUTE)); } if (annotationConfig) { Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> processorDefinitions = AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(readerContext.getRegistry(), source); //注冊注解處理器 for (BeanDefinitionHolder processorDefinition : processorDefinitions) { compositeDef.addNestedComponent(new BeanComponentDefinition(processorDefinition)); } } readerContext.fireComponentRegistered(compositeDef); //目前沒啥卵用,EmptyReaderEventListener.java中都是空操作,擴展用 } 上述代碼的作用主要是注冊注解處理器,本例中沒有配置annotation-config,默認值為true,這里也就說明了為什么配置了context:component-scan標簽就不需要再配置context:annotation-config標簽的原因。看下注冊注解處理器:
org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigUtils.java
/** * Register all relevant annotation post processors in the given registry. * @param registry the registry to operate on * @param source the configuration source element (already extracted) * that this registration was triggered from. May be {@code null}. * @return a Set of BeanDefinitionHolders, containing all bean definitions * that have actually been registered by this call */ public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors( BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) { DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry); if (beanFactory != null) { if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) { beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE); //設置注解比較器,為Spring中的Order提供支持 } if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) { beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver()); //設置AutowireCandidateResolver,為qualifier注解和lazy注解提供支持 } } Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinitionHolder>(4); if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)); //注冊@Configuration處理器 } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));//注冊@Autowired、@Value、@Inject處理器 } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, REQUIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));//注冊@Required處理器<span style="white-space:pre"> </span> } // Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor. if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));//在支持JSR-250條件下注冊javax.annotation包下注解處理器,包括@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、@Resource注解等 } // Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor. if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(); try { def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader())); } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex); } def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));//支持jpa的條件下,注冊org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor處理器,處理jpa相關注解 } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));//注冊@EventListener處理器 } if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) { RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class); def.setSource(source); beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));//注冊支持@EventListener注解的處理器 } return beanDefs; }
真正的注冊是如下函數:
private static BeanDefinitionHolder registerPostProcessor( BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, RootBeanDefinition definition, String beanName) { definition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE); //角色屬于后臺角色,框架內部使用,和最終用戶無關 registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definition); //也是注冊到beanFactory中的beanDefinitionMap中,其實和注冊bean一樣,并且beanName是定義好了的 return new BeanDefinitionHolder(definition, beanName); }
注冊注解處理器的過程也是講處理包裝成RootBeanDefinition,放到beanFactory(這里是DefaultListableBeanFactory)中的beanDefinitionMap中。
至此,標簽context:component-scan的解析已經分析完了,總結如下:
1)根據配置利用asm技術掃描.class文件,并將包含@Component及元注解為@Component的注解@Controller、@Service、@Repository或者還支持Java EE 6的@link javax.annotation.ManagedBean和jsr - 330的 @link javax.inject.Named,如果可用。的bean注冊到beanFactory中
2)注冊注解后置處理器,主要是處理屬性或方法中的注解,包含:
注冊@Configuration處理器ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,
注冊@Autowired、@Value、@Inject處理器AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,
注冊@Required處理器RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor、
在支持JSR-250條件下注冊javax.annotation包下注解處理器CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,包括@PostConstruct、@PreDestroy、@Resource注解等、
支持jpa的條件下,注冊org.springframework.orm.jpa.support.PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor處理器,處理jpa相關注解
注冊@EventListener處理器EventListenerMethodProcessor
使用注解的.class文件也掃描完了,注解處理器也注冊完了,那么注解是什么時候處理的呢?下一節會繼續分析。
四、注解處理器實例化
要想使用注解處理器,必須要實例化注解處理器,那么其實例化是在哪里進行的呢,這里還需要回到org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.java中的refresh()函數
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); //初始化前的準備,例如對系統屬性或者環境變量進行準備及驗證 // Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory. ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); //初始化BeanFactory,解析xml配置文件,其中標簽<context:component-scan>就是在這里解析的 // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); //配置工廠的標準上下文特征,例如上下文的類加載器和后處理器。 try { // Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses. postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); //子類覆蓋方法,做特殊處理,主要是后處理器相關 // Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); //激活各種beanFactory處理器,實例化并調用所有注冊的BeanFactoryPostProcessor bean,
如果給定的話,尊重顯式的順序。注意這里和掃描時的bean處理器的區別。 // Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); //<span style="color: rgb(46, 48, 51); font-family: Arial, "Microsoft YaHei", 微軟雅黑, 宋體, "Malgun Gothic", Meiryo, sans-serif; line-height: 18px;">實例化并調用所有已注冊的BeanPostProcessor bean,</span><span style="color: rgb(46, 48, 51); font-family: Arial, "Microsoft YaHei", 微軟雅黑, 宋體, "Malgun Gothic", Meiryo, sans-serif; line-height: 18px;">如果給定的話,尊重顯式的順序。</span><br style="box-sizing: border-box; color: rgb(46, 48, 51); font-family: Arial, "Microsoft YaHei", 微軟雅黑, 宋體, "Malgun Gothic", Meiryo, sans-serif; line-height: 18px;"><div class="br-height" style="box-sizing: border-box; margin: 0px; padding: 0px; height: 22px; display: inline-block; color: rgb(46, 48, 51); font-family: Arial, "Microsoft YaHei", 微軟雅黑, 宋體, "Malgun Gothic", Meiryo, sans-serif; line-height: 18px;"></div><span style="color: rgb(46, 48, 51); font-family: Arial, "Microsoft YaHei", 微軟雅黑, 宋體, "Malgun Gothic", Meiryo, sans-serif; line-height: 18px;">必須在應用程序bean的任何實例化之前調用它。這是本節的分析重點。這里就是實例化上面注冊的bean處理器</span> // Initialize message source for this context. initMessageSource(); //初始化消息資源,國際化等用 // Initialize event multicaster for this context. initApplicationEventMulticaster(); //初始化應用事件廣播 // Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses. onRefresh(); //子類擴展 // Check for listener beans and register them. registerListeners(); //注冊監聽器 // Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons. finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); //實例化非延遲加載單例,包括所有注冊非延遲加載bean的實例化 // Last step: publish corresponding event. finishRefresh(); //完成刷新過程,通知生命周期處理器lifecycleProcessor刷新過程,同時發出ContextRefreshEvent通知別人 } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } } 從上述代碼看,注解處理器也是在registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);中進行實例化的:
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) { //獲取所有beanFactory注冊的BeanPostProcessor類型的bean處理器,三中注冊的bean處理器在這里都會獲取到 String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when // a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when // a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors. int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length; beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount)); //以下是實例化bean處理器,并按照次序或無序添加到BeanFactory的beanPostProcessors列表中 // Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors); // Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered. List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); orderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors); // Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors. List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class); nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp); if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) { internalPostProcessors.add(pp); } } registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors); // Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors. sortPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors); beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext)); }
上述代碼實現了bean處理器實例化和排序工作,最終通過registerBeanPostProcessors添加到BeanFactory的beanPostProcessors列表中。
/** * Register the given BeanPostProcessor beans. */ private static void registerBeanPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanPostProcessor> postProcessors) { for (BeanPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) { beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(postProcessor); } }
AbstractBeanFactory.java
@Override public void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor) { Assert.notNull(beanPostProcessor, "BeanPostProcessor must not be null"); this.beanPostProcessors.remove(beanPostProcessor); this.beanPostProcessors.add(beanPostProcessor); if (beanPostProcessor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) { this.hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors = true; } if (beanPostProcessor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) { this.hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors = true; } }
這里的beanPostProcessors在應用bean實例化的時候會進行調用。bean處理器的實例化這里不細說,也是通過beanFactory.getBean()實現的。
五、注解處理器的調用
以【Spring實戰】Spring容器初始化完成后執行初始化數據方法中的注解@PostConstruct為例分析其注解處理器的調用。四種分析了處理器的實例化,看一下@postConstruct處理器CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java,其構造函數如下:
/** * Create a new CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor, * with the init and destroy annotation types set to * {@link javax.annotation.PostConstruct} and {@link javax.annotation.PreDestroy}, * respectively. */ public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() { setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 3); setInitAnnotationType(PostConstruct.class); setDestroyAnnotationType(PreDestroy.class); ignoreResourceType("javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext"); }
其中設置了初始化注解類型PostConstruct。下面看下這個注解處理器是在哪調用的,那就是創建bean,初始化bean時。創建bean的大概包括以下幾步(在這里不做代碼分析):
1)創建bean實例,也就是bean的實例化,其實例化策略并不是簡單的使用反射方法直接反射來構造實例對象的,而是反射方法和動態代理(主要針對aop)相結合的方式。
2)記錄創建bean的objectFactory
3)屬性注入
4)初始化bean
5)注冊disposablebean
附上spring bean的生命周期
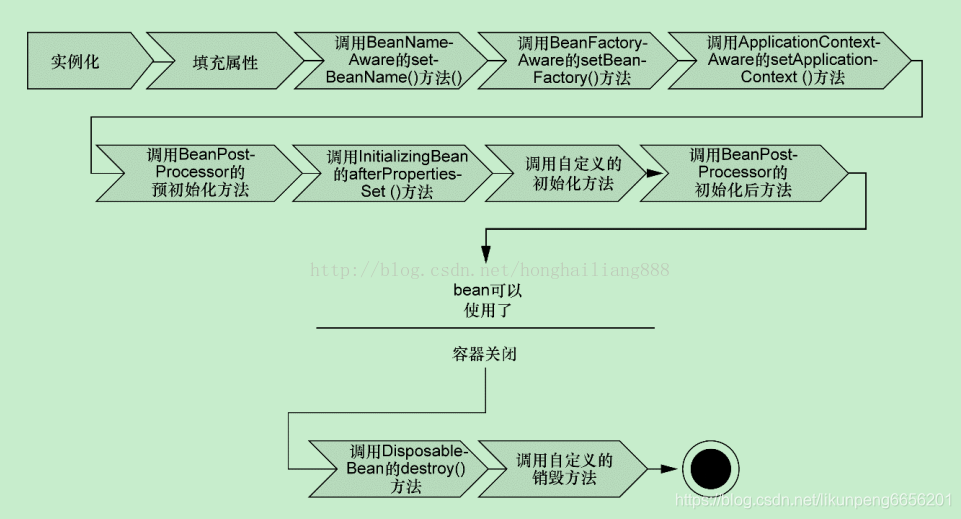
其中@PostConstruct處理器的調用就是在初始化bean時調用的,而屬性的注解,如@Autowired處理器是在屬性注入的時候調用的。先看下調用棧
@PostConstuct的
at com.mango.jtt.init.InitMango.init(InitMango.java:29) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:-1) at sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62) at sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43) at java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498) at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$LifecycleElement.invoke(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:365) at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor$LifecycleMetadata.invokeInitMethods(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:310) at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:133) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:408) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.initializeBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1570) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:545) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:482) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory$1.getObject(AbstractBeanFactory.java:306) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:230) - locked <0xe68> (a java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:302) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:197) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:776) at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(AbstractApplicationContext.java:861) at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:541) - locked <0x19af> (a java.lang.Object) at org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ContextLoader.java:444) at org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(ContextLoader.java:326) at org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener.contextInitialized(ContextLoaderListener.java:107) @Autowired處理器的調用棧
at org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.postProcessPropertyValues(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java:347) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.populateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:1214) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.doCreateBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:543) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.createBean(AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java:482) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory$1.getObject(AbstractBeanFactory.java:306) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.getSingleton(DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry.java:230) - locked <0xe4f> (a java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:302) at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:202) at org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.java:228) at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.registerBeanPostProcessors(AbstractApplicationContext.java:697) at org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(AbstractApplicationContext.java:526) - locked <0xe50> (a java.lang.Object) at org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ContextLoader.java:444) at org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(ContextLoader.java:326) at org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener.contextInitialized(ContextLoaderListener.java:107)
具體分析下@PostConstruct的注解處理器調用
/** * Actually create the specified bean. Pre-creation processing has already happened * at this point, e.g. checking {@code postProcessBeforeInstantiation} callbacks. * <p>Differentiates between default bean instantiation, use of a * factory method, and autowiring a constructor. * @param beanName the name of the bean * @param mbd the merged bean definition for the bean * @param args explicit arguments to use for constructor or factory method invocation * @return a new instance of the bean * @throws BeanCreationException if the bean could not be created * @see #instantiateBean * @see #instantiateUsingFactoryMethod * @see #autowireConstructor */ protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) { // Instantiate the bean. BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null; if (mbd.isSingleton()) { instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName); } if (instanceWrapper == null) { instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args); } final Object bean = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance() : null); Class<?> beanType = (instanceWrapper != null ? instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass() : null); // Allow post-processors to modify the merged bean definition. synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) { if (!mbd.postProcessed) { applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName); mbd.postProcessed = true; } } // Eagerly cache singletons to be able to resolve circular references // even when triggered by lifecycle interfaces like BeanFactoryAware. boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)); if (earlySingletonExposure) { if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Eagerly caching bean '" + beanName + "' to allow for resolving potential circular references"); } addSingletonFactory(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() { @Override public Object getObject() throws BeansException { return getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean); } }); } // Initialize the bean instance. Object exposedObject = bean; try { populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper); if (exposedObject != null) { exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd); } } catch (Throwable ex) { if (ex instanceof BeanCreationException && beanName.equals(((BeanCreationException) ex).getBeanName())) { throw (BeanCreationException) ex; } else { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Initialization of bean failed", ex); } } if (earlySingletonExposure) { Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false); if (earlySingletonReference != null) { if (exposedObject == bean) { exposedObject = earlySingletonReference; } else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) { String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName); Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<String>(dependentBeans.length); for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) { if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) { actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean); } } if (!actualDependentBeans.isEmpty()) { throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName, "Bean with name '" + beanName + "' has been injected into other beans [" + StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(actualDependentBeans) + "] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been " + "wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the " + "bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using " + "'getBeanNamesOfType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example."); } } } } // Register bean as disposable. try { registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd); } catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Invalid destruction signature", ex); } return exposedObject; }
上述代碼包含了創建bean的所有步驟,直接看下bean的初始化initializeBean
/** * Initialize the given bean instance, applying factory callbacks * as well as init methods and bean post processors. * <p>Called from {@link #createBean} for traditionally defined beans, * and from {@link #initializeBean} for existing bean instances. * @param beanName the bean name in the factory (for debugging purposes) * @param bean the new bean instance we may need to initialize * @param mbd the bean definition that the bean was created with * (can also be {@code null}, if given an existing bean instance) * @return the initialized bean instance (potentially wrapped) * @see BeanNameAware * @see BeanClassLoaderAware * @see BeanFactoryAware * @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization * @see #invokeInitMethods * @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization */ protected Object initializeBean(final String beanName, final Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) { if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) { AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() { @Override public Object run() { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); return null; } }, getAccessControlContext()); } else { invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean); } Object wrappedBean = bean; if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } try { invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException( (mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null), beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex); } if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) { wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName); } return wrappedBean; }
初始化給定的bean實例,應用工廠回調以及init方法和bean post處理器。順便說一句,實現了InitializingBean接口的bean的afterPropertiseSet()方法是在
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);中進行調用的。接著看
@Override public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException { Object result = existingBean; for (BeanPostProcessor beanProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) { result = beanProcessor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName); if (result == null) { return result; } } return result; }
這里就用到了前面注冊的beanPostProcessors列表,于是就調用到了CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor中的postProcessBeforeInitialization()方法(繼承自InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.java)
@Override public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { LifecycleMetadata metadata = findLifecycleMetadata(bean.getClass()); try { metadata.invokeInitMethods(bean, beanName); } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex.getTargetException()); } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Failed to invoke init method", ex); } return bean; } 上述代碼也很簡單,就是獲取用@PostConstruct注解標注的method,然后調用,看下findLifecycleMetadata實現
private LifecycleMetadata buildLifecycleMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) { final boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled(); LinkedList<LifecycleElement> initMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>(); LinkedList<LifecycleElement> destroyMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>(); Class<?> targetClass = clazz; do { final LinkedList<LifecycleElement> currInitMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>(); final LinkedList<LifecycleElement> currDestroyMethods = new LinkedList<LifecycleElement>(); ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalMethods(targetClass, new ReflectionUtils.MethodCallback() { @Override public void doWith(Method method) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException { if (initAnnotationType != null) { if (method.getAnnotation(initAnnotationType) != null) { LifecycleElement element = new LifecycleElement(method); currInitMethods.add(element); if (debug) { logger.debug("Found init method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method); } } } if (destroyAnnotationType != null) { if (method.getAnnotation(destroyAnnotationType) != null) { currDestroyMethods.add(new LifecycleElement(method)); if (debug) { logger.debug("Found destroy method on class [" + clazz.getName() + "]: " + method); } } } } }); initMethods.addAll(0, currInitMethods); destroyMethods.addAll(currDestroyMethods); targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass(); } while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class); return new LifecycleMetadata(clazz, initMethods, destroyMethods); } 是不是有種豁然開朗的感覺。
public void invokeInitMethods(Object target, String beanName) throws Throwable { Collection<LifecycleElement> initMethodsToIterate = (this.checkedInitMethods != null ? this.checkedInitMethods : this.initMethods); if (!initMethodsToIterate.isEmpty()) { boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled(); for (LifecycleElement element : initMethodsToIterate) { if (debug) { logger.debug("Invoking init method on bean '" + beanName + "': " + element.getMethod()); } element.invoke(target); } } } public void invoke(Object target) throws Throwable { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(this.method); this.method.invoke(target, (Object[]) null); }
熟悉的java反射。至此整個Spring注解的工作原理就分析完了,總結如下:
1)利用asm技術掃描class文件,轉化成Spring bean結構,把符合掃描規則的(主要是是否有相關的注解標注,例如@Component)bean注冊到Spring 容器中beanFactory
2)注冊處理器,包括注解處理器
4)實例化處理器(包括注解處理器),并將其注冊到容器的beanPostProcessors列表中
5)創建bean的過程中個,屬性注入或者初始化bean時會調用對應的注解處理器進行處理













)
——遠程倉庫的操作)



簡介)
;)