前言
在進行分析之前,建議快速瀏覽之前寫的理解MyBatis原理、思想,這樣更容易閱讀、理解本篇內容。
驗證一級緩存
MyBatis的緩存有兩級,一級緩存默認開啟,二級緩存需要手動開啟。
重復讀取跑緩存
可以看到,第二次請求的時候,沒有打印SQL,而是使用了緩存。
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);SysRoleMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(SysRoleMapper.class);SysRole role = mapper1.getById(2);SysRole role2 = mapper1.getById(2);System.out.println(role);System.out.println(role2);
}//------------------------------打印SQL--------------------------------------==> Preparing: select * from sys_role where role_id = ?
==> Parameters: 2(Integer)
<== Columns: role_id, role_name, role_key, role_sort, data_scope, status, del_flag, create_by, create_time, update_by, update_time, remark
<== Row: 2, 測試2, common, 2, 2, 0, 0, admin, 2022-08-29 15:58:05, , null, 普通角色
<== Total: 1
SysRole{role_id=2, role_name='測試2'}SysRole{role_id=2, role_name='測試2'}
同一會話的更新操作刷新緩存
通過測試結果可以看到,因為更新操作的原因,兩次查詢都查了數據庫。
@Test
public void test2() throws IOException {String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);SysRoleMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(SysRoleMapper.class);SysRole role = mapper1.getById(2);mapper1.updateRoleNameById("測", 2);SysRole role2 = mapper1.getById(2);System.out.println(role);System.out.println(role2);
}//------------------------------打印SQL--------------------------------------==> Preparing: select * from sys_role where role_id = ?
==> Parameters: 2(Integer)
<== Columns: role_id, role_name, role_key, role_sort, data_scope, status, del_flag, create_by, create_time, update_by, update_time, remark
<== Row: 2, 測試2, common, 2, 2, 0, 0, admin, 2022-08-29 15:58:05, , null, 普通角色
<== Total: 1==> Preparing: update sys_role set role_name = ? where role_id = ?
==> Parameters: 測(String), 2(Integer)
<== Updates: 1==> Preparing: select * from sys_role where role_id = ?
==> Parameters: 2(Integer)
<== Columns: role_id, role_name, role_key, role_sort, data_scope, status, del_flag, create_by, create_time, update_by, update_time, remark
<== Row: 2, 測, common, 2, 2, 0, 0, admin, 2022-08-29 15:58:05, , null, 普通角色
<== Total: 1SysRole{role_id=2, role_name='測試2'}
SysRole{role_id=2, role_name='測'}
跨會話更新數據沒有刷新緩存
@Test
public void test() throws IOException {String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);// 會話一System.out.println("會話一");SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);SysRoleMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(SysRoleMapper.class);SysRole role = mapper1.getById(2);System.out.println(role);// 會話二System.out.println("會話二");SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);SysRoleMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(SysRoleMapper.class);mapper2.updateRoleNameById("測試2", 2);System.out.println(mapper2.getById(2));// 會話一重新查詢System.out.println("會話一重新查詢");role = mapper1.getById(2);System.out.println(role);}//------------------------------打印結果--------------------------------------會話一
SysRole{role_id=2, role_name='測試'}
會話二
SysRole{role_id=2, role_name='測試2'}
會話一重新查詢
SysRole{role_id=2, role_name='測試'}
源碼分析的入口點
我們要閱讀、分析源碼,就需要先找準一個切入點,我們以下面代碼為例子,SysRoleMapper#getById()方法作為調試入口:
@Test
public void test1() throws IOException {String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);SysRoleMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(SysRoleMapper.class);// 調試入口SysRole role = mapper1.getById(2);SysRole role2 = mapper1.getById(2);System.out.println(role);System.out.println(role2);
}在分析之前,我們就先約定一下:👉符號表示你的視角要焦距在哪幾行代碼。
一級緩存流程分析
好,現在我們開始分析一級緩存的流程,了解其設計思想,看看能學到什么。
MapperProxy
- 首先,我們可以看到,通過
getMapper方法拿到的對象mapper1,其實是一個代理對象MapperProxy的實例。
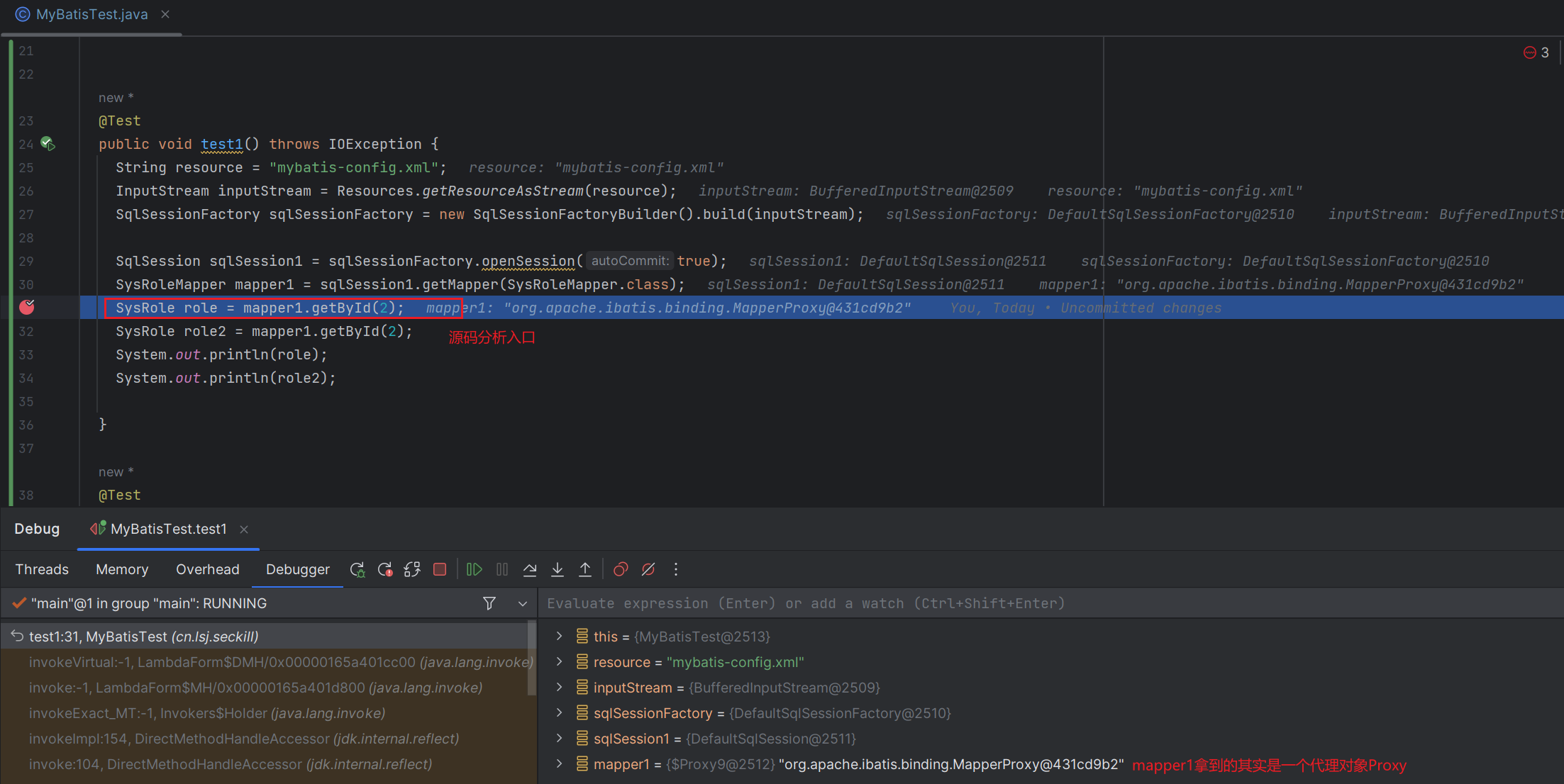
MapperProxy實現了InvocationHandler接口,所以SysRoleMapper調用的 方法 都會進入代理對象MapperProxy的invoke方法。
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler, Serializable {// 略@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {// 先拿到聲明method方法的類(在這里具體指定是SysRoleMapper)。// 如果是 Object 類,則表明調用的是一些通用方法,比如 toString()、hashCode() 等,就直接調用即可。👉👉👉if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);} else {return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}}// 略}
小結:從上面可以知道,我們調用SysRoleMapper接口中的 方法,其實都會進入MapperProxy#invoke方法中。
現在,我們進一步看,由于getById方法不是Object默認的方法,所以會跑else分支,詳情分析請看代碼:
@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {try {if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);} else {// 跑else分支// 整體了解此行代碼的流程:// 1.首先Method會被包裝成MapperMethod;1??// 2.MapperMethod被封裝到PlainMethodInvoker類內;2??// 3.此類(PlainMethodInvoke)提供一個普通的方法invoke,此方法會實際調用MapperMethod的execute方法3??
👉👉👉return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}}private MapperMethodInvoker cachedInvoker(Method method) throws Throwable {try {return MapUtil.computeIfAbsent(methodCache, method, m -> {// 是否Java語言規范定義的默認方法?否if (m.isDefault()) {// 這里的細節不要深究了try {if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava8(method));} else {return new DefaultMethodInvoker(getMethodHandleJava9(method));}} catch (IllegalAccessException | InstantiationException | InvocationTargetException| NoSuchMethodException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}} else { // 看這里,跑的是else分支// 對于普通的方法(如SysRoleMapper#getById),使用的是PlainMethodInvoker實現類。// >> 其中,MapperMethod表示對原始的Method方法對象進行了一次包裝(細節就先不深究了)// >> mapperInterface 信息在創建MapperProxy對象的時候寫入,信息默認來源于我們定義的mybatis-config.xml文件, 包括sqlSession也是。return new PlainMethodInvoker(new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration())1??);}});} catch (RuntimeException re) {Throwable cause = re.getCause();throw cause == null ? re : cause;}}private static class PlainMethodInvoker implements MapperMethodInvoker {private final MapperMethod mapperMethod;public PlainMethodInvoker(MapperMethod mapperMethod) {super();this.mapperMethod = mapperMethod;2??}@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);3??}}
從上面注釋中,相信你已經了解到MapperProxy#invoke方法下一步會流向哪個類:MapperMethod#execute()

MapperMethod
現在我們看看MapperMethod#execute()做了什么:根據command屬性提供的sql方法類型調用sqlSession接口中合適的的處理方法。
public class MapperMethod {// 方法對應的sql類型:select、update、delete、insert// 在MapperProxy#invoke#cachedInvoker方法中創建MapperMethod類時設置的,感興趣的可以回看private final SqlCommand command; private final MethodSignature method;public MapperMethod(Class<?> mapperInterface, Method method, Configuration config) {this.command = new SqlCommand(config, mapperInterface, method);this.method = new MethodSignature(config, mapperInterface, method);}// 這個方法整體做了什么?根據command提供的sql方法類型調用sqlSession接口中合適的的處理方法。// >> 我們之前封裝MapperMethod的時候,定義了此類的command、method屬性;// >> 其中command這個屬性表示sql方法的類型
👉👉public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object result;// getById方法是查詢語句,所以會進入SELECT分支switch (command.getType()) {case INSERT: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));break;}case UPDATE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));break;}case DELETE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));break;}case SELECT:if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) { // 無返回值,同時有專門的結果處理類executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);result = null;} else if (method.returnsMany()) { // 返回多個結果result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsMap()) { // 返回map類型的結果result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);} else if (method.returnsCursor()) { // 返回結果是數據庫游標類型result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);} else { // 看這里,跑的是else分支:// 獲取參數對象,不用關注細節Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// SysRoleMapper#getById結果類型是單個對象,所以最終跑的是這行代碼👉👉result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);// 下面代碼細節不重要,就不展開了if (method.returnsOptional()&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {result = Optional.ofNullable(result);}}break;case FLUSH:result = sqlSession.flushStatements();break;default:throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());}if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");}return result;}// 略}
好了,看完上面代碼,相信你已經知道下一步代碼會跑到那里了:SqlSession#selectOne()
SqlSession是一個接口,定義了一些列通用的SQL操作,如selectList、insert、update、commit 和 rollback等操作。
小結:通過上面的分析,我們已經知道,我們調用SysRoleMapper#getById方法本質上其實還是調用SqlSession接口提供的通用SQL操作方法。只不過利用 代理 Mapper接口 的方式,實現方法調用 自動路由到SqlSession接口對應的方法。

SqlSession
通過上面分析,想必你已經知道下一步要走哪了,SqlSession接口默認的實現類是DefaultSqlSession,所以selectOne方法跑的是這個實現類:
public class DefaultSqlSession implements SqlSession {// 略@Overridepublic <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.(譯:大眾投票是在 0 個結果上返回 null,并在太多結果上拋出異常。)// 很明顯,selectOne最終跑的是selectList方法List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);// 下面代碼不用關注if (list.size() == 1) {return list.get(0);} else if (list.size() > 1) {throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());} else {return null;}}// 略/*** 封裝MappedStatement對象,通過executor發起查詢。* @param statement 映射信息,方法的全路徑:cn.lsj.seckill.SysRoleMapper.getById* @param parameter SQL參數* @param rowBounds 輔助分頁,默認不分頁。RowBounds(int offset, int limit)* @param handler 處理結果回調。查詢完成之后調用回調* @return* @param <E>*/private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {try {// 這個類主要封裝了SysRoleMapper相關信息,包括:方法全路徑(id)、原始xml文件(resource)、// sql語句相關信息(sqlSource)、結果類型映射信息、與映射語句關聯的緩存配置信息(cache)等MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);// wrapCollection是懶加載機制的一部分,不用關注細節👉👉👉return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);} catch (Exception e) {throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);} finally {ErrorContext.instance().reset();}}}
通過上述代碼可以知道,selectOne方法內部最終還是依靠Executor接口的query方法去執行具體的sql,只不過在此之前會從Configuration配置類里面通過 映射信息 statement 拿到MappedStatement封裝對象,然后傳遞給query方法。

Executor
在上面,我們了解到下一步走的是Executor接口的query方法,CachingExecutor是Executor接口的實現類,基于裝飾者模式對Executor功能進行了增強:增加了緩存機制。
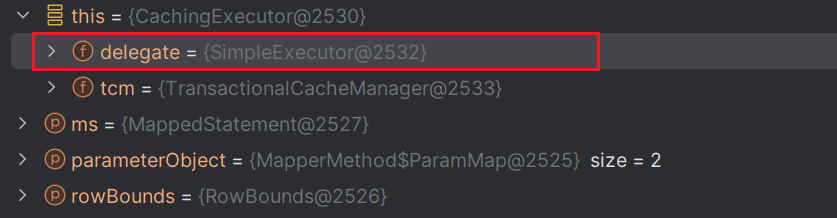
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {private final Executor delegate; // 默認被裝飾的實現類 SimpleExecutorprivate final TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {this.delegate = delegate;delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this);}// 略@Overridepublic <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {// 表示一條 SQL 語句以及相關參數(不用關注細節)BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);// 構造緩存的KEY(不用關注細節)CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);}@Overridepublic <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)throws SQLException {// 讀取二級緩存的緩存對象Cache cache = ms.getCache();// 開啟二級緩存時跑這個分支,先不關注if (cache != null) {flushCacheIfRequired(ms);if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);if (list == null) {list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116}return list;}}// 通過斷點可以看到:默認被裝飾的Executor接口實現類是SimpleExecutor (圖1??)// 由于SimpleExecutor繼承了抽象類BaseExecutor 但沒有實現query方法,所以,最終指向的還是BaseExecutor#query() (圖2??)
👉👉👉return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);}// 略}- 圖1??
- 圖2??
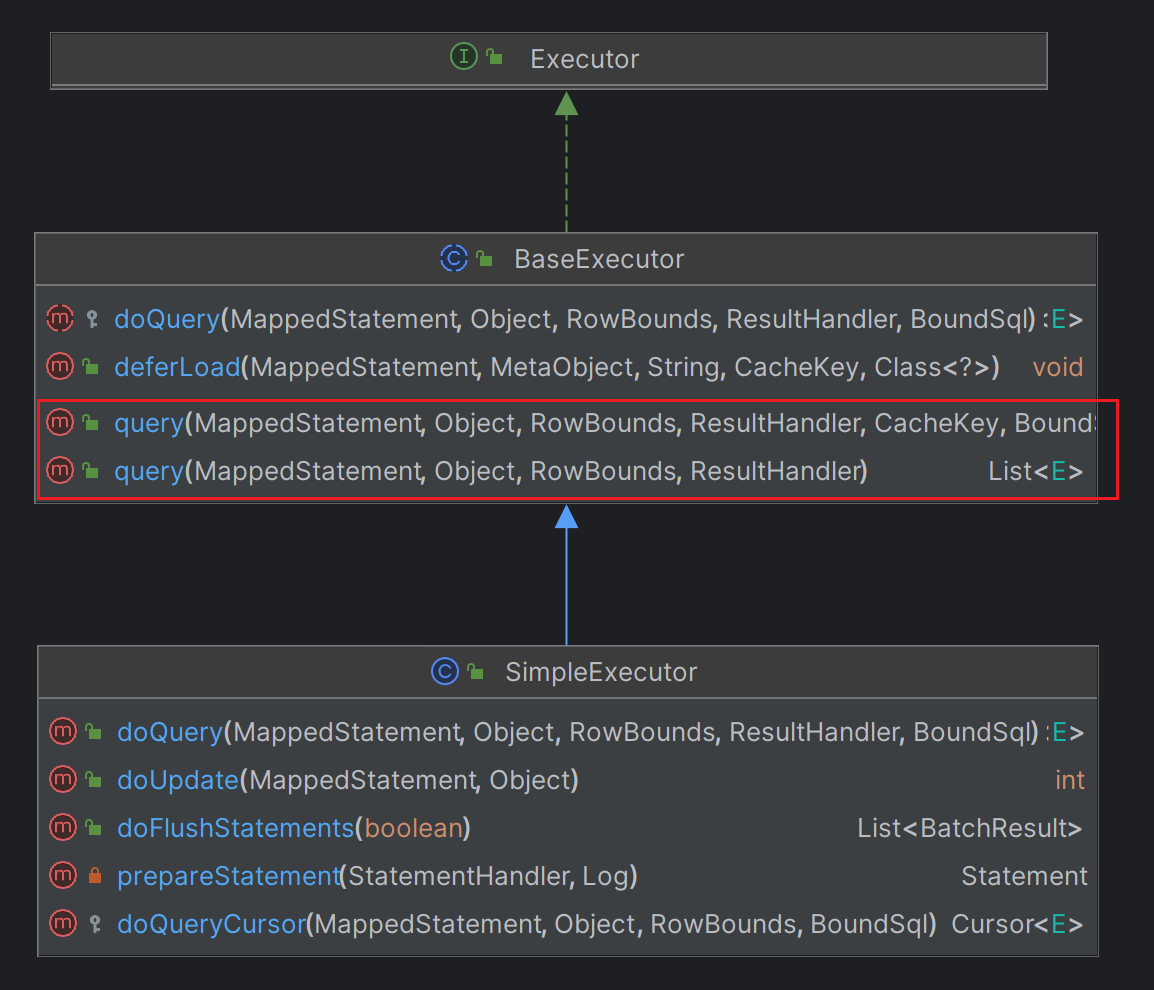
通過上面代碼注釋,我們最終了解到CachingExecutor#query方法跑向的是BaseExecutor#query。

現在,我們看一下BaseExecutor類的query方法:
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {// 略protected PerpetualCache localCache; // 緩存Cache(一級緩存)具體的一個實現類// 略@Overridepublic <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());if (closed) {throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");}if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {clearLocalCache();}// 很明顯,這個是存儲查詢結果的,我們圍繞這個對象來看代碼List<E> list;try {queryStack++;// 從緩存中讀取結果(第一次查詢沒有緩存)list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;if (list != null) {handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);} else { // 跑else分支// 從數據庫中讀取👉👉👉list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);}} finally {queryStack--;}if (queryStack == 0) {for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {deferredLoad.load();}// issue #601deferredLoads.clear();if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {// issue #482clearLocalCache();}}return list;}// 略private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {List<E> list;// 給key對應的緩存值設置一個占位值(只是用于占位)localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);try {// 真正處理查詢的方法// 抽象類沒有實現doQuery方法,所以方法的調用是其實現類 SimpleExecutor#doQuery👉👉👉list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);} finally {localCache.removeObject(key);}localCache.putObject(key, list);if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);}return list;}
}

StatementHandler
RoutingStatementHandler
現在,我們在看看SimpleExecutor#doQuery方法,沒有太多復雜邏輯,直接是交由StatementHandler接口處理了,接口的實現類是RoutingStatementHandler。
在劃分上,
StatementHandler屬于Executor的一部分,參與SQL處理:
RoutingStatementHandler:根據執行的 SQL 語句的類型(SELECT、UPDATE、DELETE 等)選擇不同的 StatementHandler 實現進行處理。PreparedStatementHandler:處理預編譯 SQL 語句的實現類。預編譯 SQL 語句是指在數據庫預先編譯 SQL 語句并生成執行計劃,然后在后續的執行中,只需要傳遞參數并執行編譯好的執行計劃,可以提高 SQL 的執行效率。
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {Statement stmt = null;try {Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();// 此接口用于處理數據庫的 Statement 對象的創建和執行StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
👉👉👉return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler); // 打斷點可以看到handler實現類:RoutingStatementHandler,它作用就是選擇合適的StatementHandler實現類執行SQL} finally {closeStatement(stmt);}
}

我們再看看RoutingStatementHandler#query方法,使用了裝飾者模式,被裝飾類是PreparedStatementHandler。
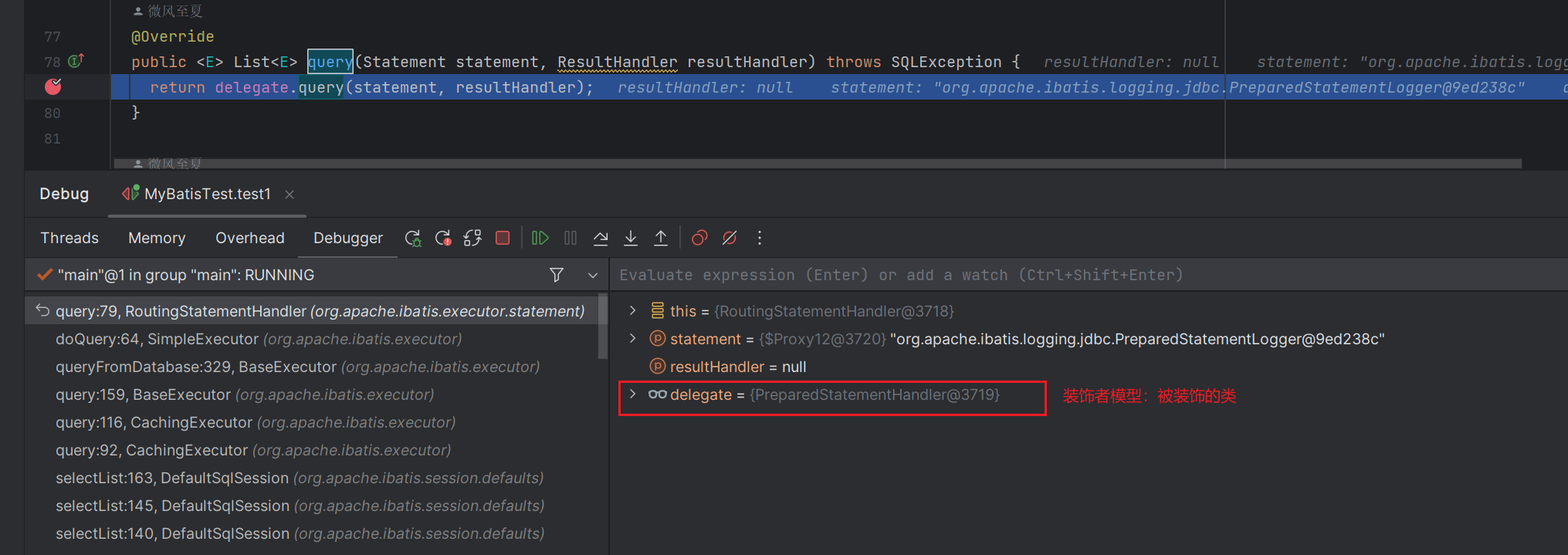
PreparedStatementHandler
RoutingStatementHandler選擇了合適的處理類來執行SQL:PreparedStatementHandler。
現在打開看看PreparedStatementHandler#query方法:
@Overridepublic <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {// Java JDBC 中的一個接口,用于執行預編譯的 SQL 語句。使用過JDBC編程的應該見過,可以看文末的JDBC編程Demo回憶回憶。PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;// 執行 SQL 語句。ps.execute();// “結果處理器”會處理并返回查詢結果(在這里就不深究了)return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);}
現在,讓我們往回看BaseExecutor#queryFromDatabase方法:
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {List<E> list;// 給key對應的緩存值設置一個占位值(只是用于占位)localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);try {// 此時,我們已經拿到結果了👉👉list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);} finally {localCache.removeObject(key);}// 將結果寫入到緩存中 localCache.putObject(key, list);if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);}return list;}
到這里,我們經歷了一次(第一次)查詢的過程,并在BaseExecutor#queryFromDatabase方法中,將查詢結果寫入到localCache屬性中。
我們再查一次,就會發現,在BaseExecutor#query中,這次直接拿到了緩存的數據:
@Overridepublic <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {// 略List<E> list;try {queryStack++;// 從本地緩存拿到了上次的查詢結果👉👉👉list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;if (list != null) {handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);} else {list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);}} finally {queryStack--;}// 略return list;}
小結
整個流程下來,發現最關鍵的地方就是BaseExecutor抽象類的query、queryFromDatabase這兩個方法,它們在一級緩存方面,圍繞localCache屬性做緩存操作。
- 第一次查詢,跑
queryFromDatabase方法,并將查詢結果寫入localCache屬性; - 第二次相同的查詢,直接從
localCache屬性中讀取緩存的查詢結果。
二級緩存流程分析
開啟二級緩存
添加配置到mybatis-config.xml文件:
<settings><!-- 二級緩存--><setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
修改SysRoleMapper.xml文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="cn.lsj.seckill.SysRoleMapper"><!-- 表示此namespace開啟二級緩存 --><cache/><select id="getById" resultType="cn.lsj.seckill.SysRole" >select * from sys_role where role_id = #{id}</select></mapper>
流程分析
當我們開啟二級緩存之后,查詢過程就變成:二級緩存->一級緩存->數據庫
二級緩存的驗證代碼:
@Testpublic void test1() throws IOException {String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);SqlSession sqlSession1 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);SysRoleMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(SysRoleMapper.class);SysRole role = mapper1.getById(2);System.out.println(role);// 提交事務二級緩存數據才生效sqlSession1.commit();SqlSession sqlSession2 = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);SysRoleMapper mapper2 = sqlSession2.getMapper(SysRoleMapper.class);SysRole role2 = mapper2.getById(2);System.out.println(role2);System.out.println(mapper1.getById(2));}
在前面的CachingExecutor#query方法中,我們看到了二級緩存的代碼:
@Overridepublic <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)throws SQLException {Cache cache = ms.getCache();// 假如我們開啟了二級緩存,那么我們的查詢會先跑此分支if (cache != null) {flushCacheIfRequired(ms);if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")// 從緩存中讀取數據👉👉👉 List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);// 二級緩存中沒有數據時再查數據庫if (list == null) {list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);// 將查詢結果寫入到二級緩存中tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116}return list;}}return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);}
總結
看到這里,我們回顧一下,在之前的分析中,我們看到裝飾者模式出現得比較頻繁;此外還是用到動態代理技術。
整個分析下來,相信你收獲的不止這些,源碼閱讀能力應該能得到一些提升,對設計模式、動態代理的理解也會有一些加深。
好了,如果你感興趣的話,可以進一步深入分析緩存如何刷新、生效,如何做到緩存會話級別、Mapper級別的隔離的。
最后,留下一些思考問題:
- 開啟二級緩存之后,為什么
sqlSession1.commit();之后二級緩存才生效?
附:JDBC編程Demo
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;public class JDBCDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// MySQL服務器的JDBC URL、用戶名和密碼String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/你的數據庫名";String user = "你的用戶名";String password = "你的密碼";try {// 加載JDBC驅動程序Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");// 建立數據庫連接Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);// 創建SQL語句String sql = "SELECT * FROM 你的表名";PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);// 執行查詢ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();// 處理結果集while (resultSet.next()) {int id = resultSet.getInt("id");String name = resultSet.getString("name");String email = resultSet.getString("email");System.out.println("ID: " + id + ", Name: " + name + ", Email: " + email);}// 關閉資源resultSet.close();preparedStatement.close();connection.close();} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
}


)















