vector 的介紹:
1、vector是表示可變大小數組的序列容器。
2、vector就像數組一樣,也采用的連續空間來存儲元素,這也意味著可以采用下標對vector的元素進行訪問。
3、vector與普通數組不同的是,vector的大小是可以動態改變的。
4、當vector需要重新分配大小時,其做法是,分配一個新的數組,然后將全部元素移到這個數組當中,并釋放原來的數組空間。
5、vector分配空間策略:vector會分配一些額外的空間以適應可能的增長,因此存儲空間比實際需要的存儲空間一般更大。不同的庫采用不同的策略權衡空間的使用和重新分配,以至于在末尾插入一個元素的時候是在常數的時間復雜度完成的。
6、由于vector采用連續的空間來存儲元素,與其他動態序列容器相比,vector在訪問元素的時候更加高效,在其末尾添加和刪除元素相對高效,而對于不在其末尾進行的刪除和插入操作效率則相對較低。
?
?
vector 的使用
1.定義方式
法一:構造一個某類型的空容器。
vector<int> v1; //構造int類型的空容器
法二:構造一個含有n個val的某類型容器。
vector<int> v2(10, 2); //構造含有10個2的int類型容器
法三:拷貝構造某類型容器的復制品
vector<int> v3(v2); //拷貝構造int類型的v2容器的復制品
法四:使用迭代器拷貝構造某一段內容。
vector<int> v4(v2.begin(), v2.end()); //使用迭代器拷貝構造v2容器的某一段內容
注意:該方式也可用于拷貝其他容器的某一段內容。
string s("hello world");
vector<char> v5(s.begin(), s.end()); //拷貝構造string對象的某一段內容
vector的空間增長問題
size和capacity
通過size函數獲取當前容器中的有效元素個數,通過capacity函數獲取當前容器的最大容量。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v(10, 2);cout << v.size() << endl; //獲取當前容器中的有效元素個數cout << v.capacity() << endl; //獲取當前容器的最大容量return 0;
}
reserve和resize
通過reserse函數改變容器的最大容量,resize函數改變容器中的有效元素個數。
reserve規則:
?1、當所給值大于容器當前的capacity時,將capacity擴大到該值。
?2、當所給值小于容器當前的capacity時,什么也不做。
resize規則:
?1、當所給值大于容器當前的size時,將size擴大到該值,擴大的元素為第二個所給值,若未給出,則默認為0。
?2、當所給值小于容器當前的size時,將size縮小到該值。
?
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v(10, 2);cout << v.size() << endl; //10cout << v.capacity() << endl; //10v.reserve(20); //改變容器的capacity為20,size不變cout << v.size() << endl; //10cout << v.capacity() << endl; //20v.resize(15); //改變容器的size為15cout << v.size() << endl; //15cout << v.capacity() << endl; //20return 0;
}
empty
通過empty函數判斷當前容器是否為空。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v(10, 2);cout << v.empty() << endl;return 0;
}
vector的迭代器使用
?
?
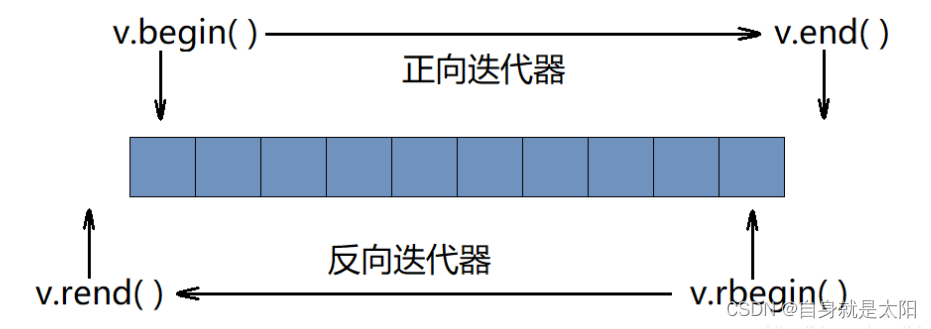
begin和end
通過begin函數可以得到容器中第一個元素的正向迭代器,通過end函數可以得到容器中最后一個元素的后一個位置的正向迭代器。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v(10, 2);//正向迭代器遍歷容器vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin();while (it != v.end()){cout << *it << " ";it++;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
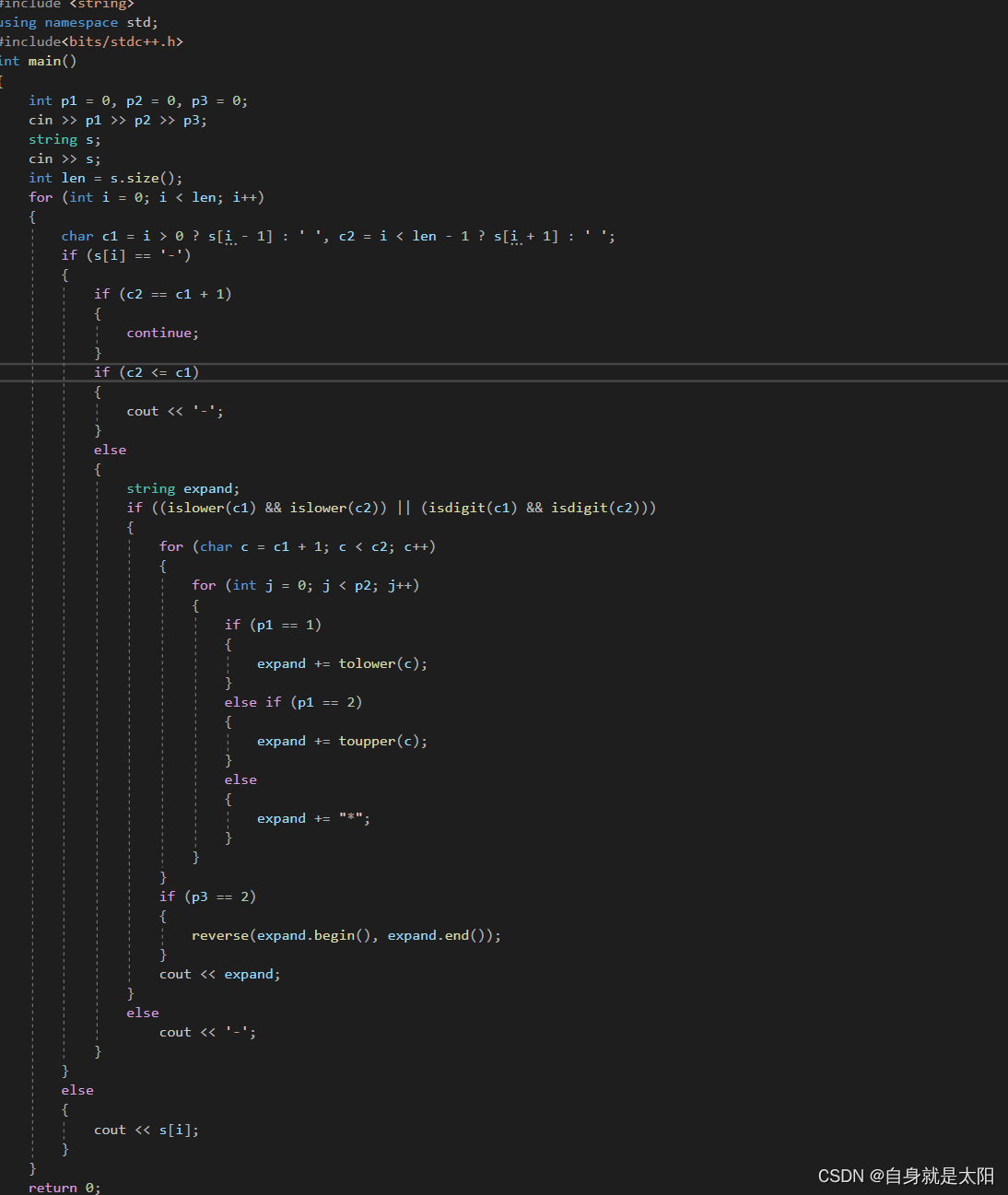
比方說這道題中,在一行中需要,排序,我們這里使用了迭代器

rbegin和rend
通過rbegin函數可以得到容器中最后一個元素的反向迭代器,通過rend函數可以得到容器中第一個元素的前一個位置的反向迭代器。
反向迭代器遍歷容器:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v(10, 2);//反向迭代器遍歷容器vector<int>::reverse_iterator rit = v.rbegin();while (rit != v.rend()){cout << *rit << " ";rit++;}cout << endl;return 0;
}
vector的增刪查改
?
push_back和pop_back
通過push_back函數對容器進行尾插,pop_back函數對容器進行尾刪。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1); //尾插元素1v.push_back(2); //尾插元素2v.push_back(3); //尾插元素3v.push_back(4); //尾插元素4v.pop_back(); //尾刪元素v.pop_back(); //尾刪元素v.pop_back(); //尾刪元素v.pop_back(); //尾刪元素return 0;
}
這里的應用非常廣,尤其在字符串那一塊,這里給大家整一道相關的編程題
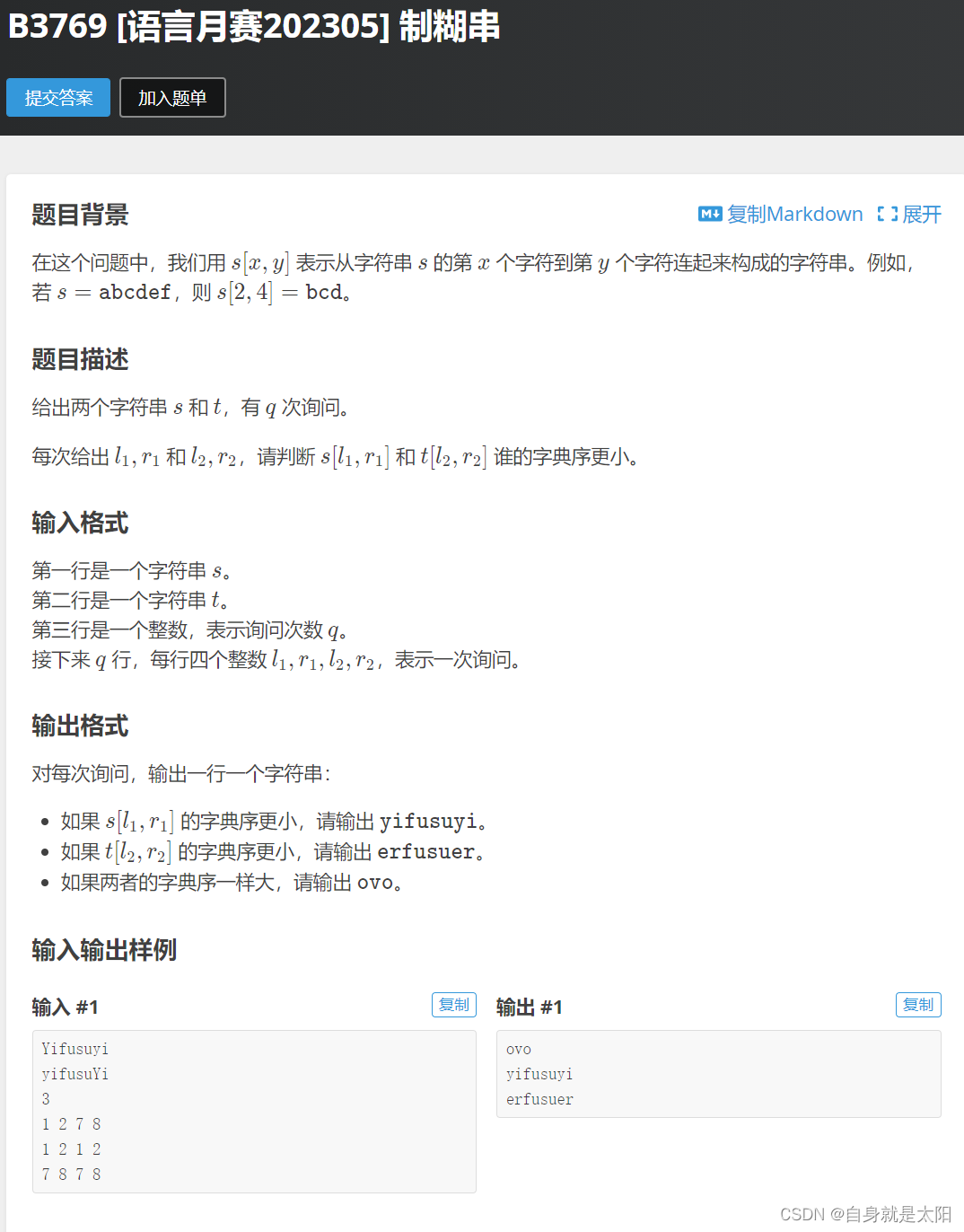
?
如果用上述我說的來解決的話
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s, t;cin >> s >> t;int q;cin >> q;while (q--){string s1, t1;int l1, r1, l2, r2;cin >> l1 >> r1 >> l2 >> r2;for (int i = l1-1; i <= r1-1; i++){s1.push_back(s[i]);}for (int i = l2 - 1; i <= r2-1; i++){t1.push_back(t[i]);}if (s1 > t1)cout << "erfusuer"<<endl;else if (s1 < t1){cout << "yifusuyi" << endl;}elsecout << "ove"<<endl;s1 = "";t1 = "";}return 0;
}即可依葫蘆畫瓢解決,詳解在我之前發的字符串的編程題有解釋,若代碼看不懂可以往前看。
insert和erase
通過insert函數可以在所給迭代器位置插入一個或多個元素,通過erase函數可以刪除所給迭代器位置的元素,或刪除所給迭代器區間內的所有元素(左閉右開)。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);v.insert(v.begin(), 0); //在容器開頭插入0v.insert(v.begin(), 5, -1); //在容器開頭插入5個-1v.erase(v.begin()); //刪除容器中的第一個元素v.erase(v.begin(), v.begin() + 5); //刪除在該迭代器區間內的元素(左閉右開)return 0;
}
find函數:
find函數共三個參數,前兩個參數確定一個迭代器區間(左閉右開),第三個參數確定所要尋找的值。
find函數在所給迭代器區間尋找第一個匹配的元素,并返回它的迭代器,若未找到,則返回所給的第二個參數。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v;v.push_back(1);v.push_back(2);v.push_back(3);v.push_back(4);vector<int>::iterator pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 2); //獲取值為2的元素的迭代器v.insert(pos, 10); //在2的位置插入10pos = find(v.begin(), v.end(), 3); //獲取值為3的元素的迭代器v.erase(pos); //刪除3return 0;
}
注意:?find函數是在算法模塊(algorithm)當中實現的,不是vector的成員函數。
在這里再給大家介紹一個典型題
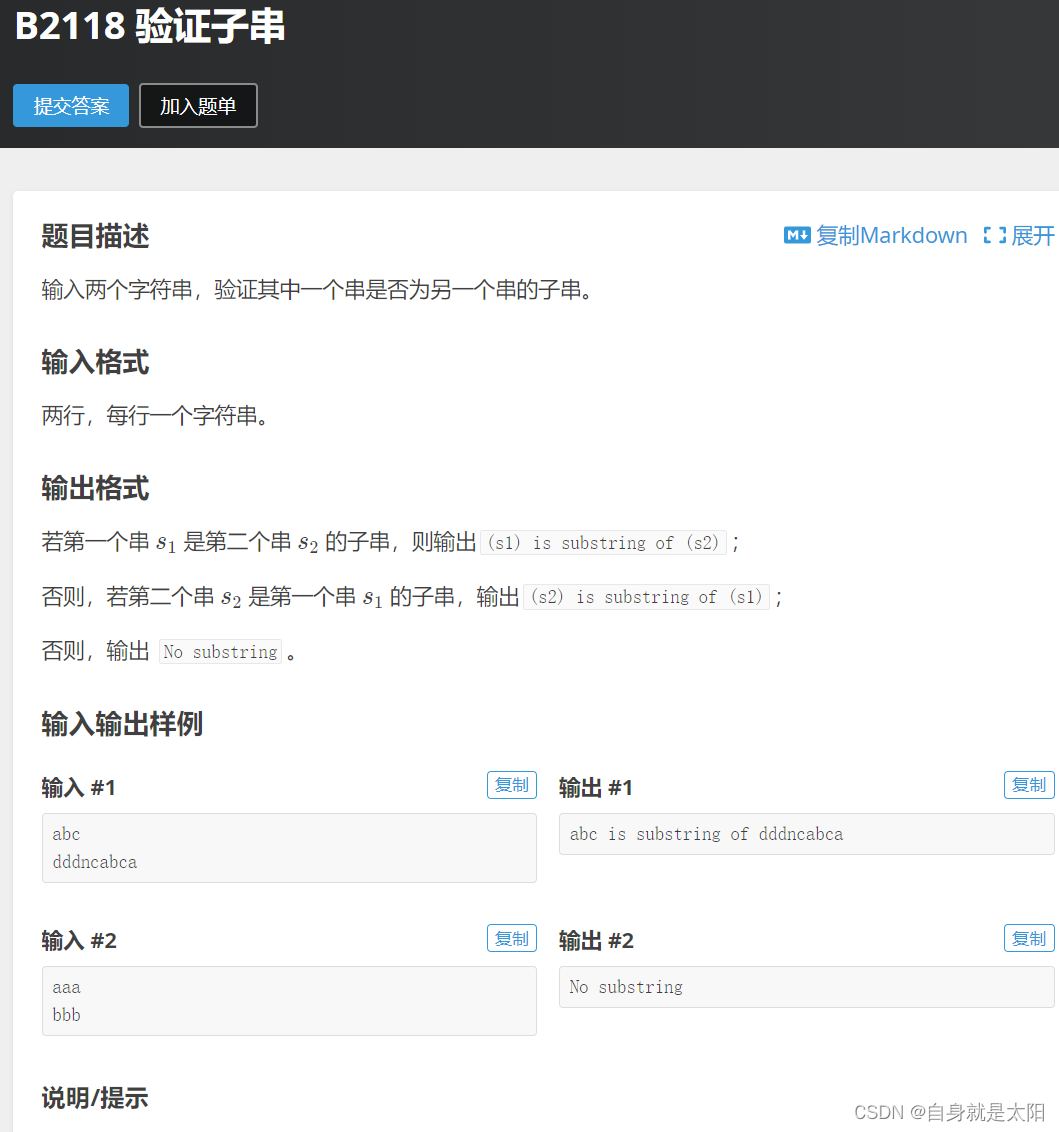
代碼:
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string s1, s2;cin >> s1 >> s2;if (s2.find(s1) != -1)//如果找到返回首位置,未找到返回-1{cout << s1 << " is substring of " << s2 << endl;}else if (s1.find(s2) != -1){cout << s2 << " is substring of " << s1 << endl;}elsecout << "No substring" << endl;return 0;
}swap
通過swap函數可以交換兩個容器的數據空間,實現兩個容器的交換。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v1(10, 1);vector<int> v2(10, 2);v1.swap(v2); //交換v1,v2的數據空間return 0;
}
在c語言中交換兩個數我們需要設立中間變量,而在c++中可以直接通過swap函數來解決
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v1(10, 1);vector<int> v2(10, 2);v1.swap(v2); //交換v1,v2的數據空間return 0;
}
clear
清除字符串內容
#include"vector.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{//dabai::test1();vector<int> arr;vector<int> s;arr.push_back(11);arr.push_back(11);arr.push_back(11);arr.push_back(11);arr.pop_back();arr.insert(arr.begin()+2, 30);arr.erase(arr.begin() + 2);//arr.resize(2);//arr.reserve(100);s.swap(arr);cout << arr.size()<< endl;cout << s.size() << endl;s.clear();cout << s.size() << endl;return 0;
}
其實也相當于 s="";
元素訪問
vector當中實現了 [ ] 操作符的重載,因此我們也可以通過“下標+[ ]”的方式對容器當中的元素進行訪問。
即你可以把他當作數組一樣使用
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v(10, 1);//使用“下標+[]”的方式遍歷容器for (size_t i = 0; i < v.size(); i++){cout << v[i] << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
我們上面說到vector是支持迭代器的,所以我們還可以用范圍for對vector容器進行遍歷。(支持迭代器就支持范圍for,因為在編譯時編譯器會自動將范圍for替換為迭代器的形式)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;int main()
{vector<int> v(10, 1);//范圍forfor (auto e : v){cout << e << " ";}cout << endl;return 0;
}
?
?
?


覆蓋優化 - 附代碼)






![[Linux] 用LNMP網站框架搭建論壇](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Linux] 用LNMP網站框架搭建論壇)



 的 Menu控件)
)




