*本文是博主對Java各種實驗的再整理與詳解,除了代碼部分和解析部分,一些題目還增加了拓展部分(?)。拓展部分不是實驗報告中原有的內容,而是博主本人自己的補充,以方便大家額外學習、參考。
(解析部分還沒加,過陣子補)
目錄
一、實驗目的
二、實驗內容
1、將下列數據:“hello”、123、6.9、“hello”、“”、“Hello”、StringBuffer s=new StringBuffer(“hello”)中的s,添加到一個ArrayList對象中。
2、使用ArrayList集合,向集合中添加10個整數,并使用Iterator遍歷該集合,并查找鍵盤輸入的元素。
3、分別利用Arraylist和Set隨機生成十個不重復的隨機整數,隨機整數范圍為350到450。
4、集合中不容許有重復的對象,對于多個重復對象只能添加一次。例如在HashSet集合中添加三個Person對象,把姓名相同的人當做同一個人,雖然可以添加多次但集合里只保留一個,但是這對類的設計是有要求的,假設Person類中只包含name和age屬性,則需要重寫hashCode()方法和equals()方法,如果兩個對象的name相同,則hashCode()方法的返回值相同,equals()方法返回true。
5、編寫程序將一組學生對象的姓名和成績存入到一個樹集(TreeSet)中。
6、編寫一個程序,讀取個數不定的整數,然后查找其中出現頻率最高的數字。要求通過鍵盤輸入數據,當輸入為0時,表示結束輸入。如: 如果輸入的數據是2 ??3 ??40 ??3 ??54 ??-3 ??3 ??3 ??2 ??0,那么數字3的出現頻率是最高的。如果出現頻率最高的數字不是一個而是多個,則應該將它們全部輸出。例如當數據是9 ?30 ?3 ?9 ?3 ?2 ?4時,3和9都出現了兩次,3和9都應該輸出。
7、選擇合適的Map集合保存5個用戶的用戶名和密碼,然后將這些鍵值對打印出來。
8、(選做)統計字符串中每個單詞出現的次數,使用HashMap來實現。例如:“Today, We have a class of java, as we kown, java is an object oriented ?programming language, and java is fun! wish you enjoy it!”.
9、(選做)500個人圍成一個圈,從1開始報數,數到3的倍數的人離開圈子,循環往復,直到最后圈子只剩下一人為止,求剩下的人原來在圈子的位置。
三、實驗總結
一、實驗目的
1、掌握容器類的層次結構;
2、掌握Collection接口和List接口的常用方法;
3、掌握Iterator接口的使用方式;
4、掌握Set接口和hashCode的使用方式;
5、掌握Map接口的使用方式。
二、實驗內容
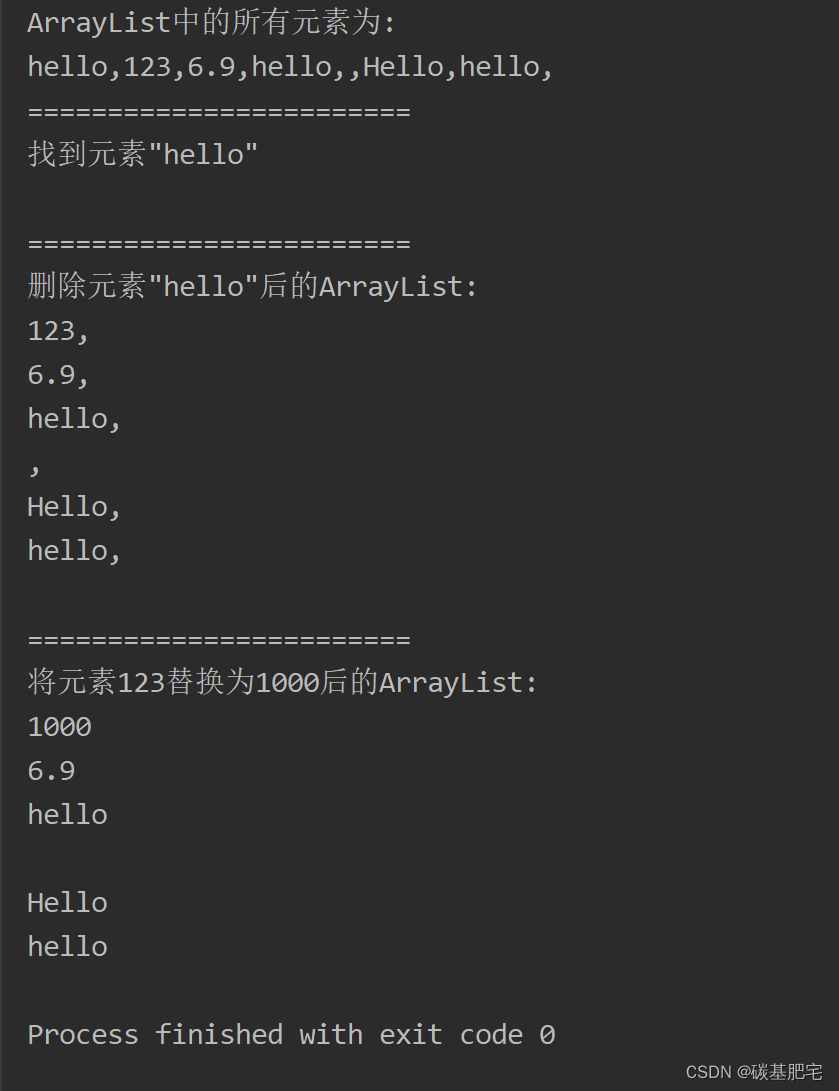
1、將下列數據:“hello”、123、6.9、“hello”、“”、“Hello”、StringBuffer s=new StringBuffer(“hello”)中的s,添加到一個ArrayList對象中。
? 將ArrayList中的所有元素打印輸出。
? 查找元素“hello”。
? 刪除指定的元素“hello”。
? 將元素123替換為1000。
源代碼:
import java.util.ArrayList;public class S6_1 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建ArrayList對象ArrayList<Object> list = new ArrayList<>();// 添加數據到ArrayListlist.add("hello");list.add(123);list.add(6.9);list.add("hello");list.add("");list.add("Hello");StringBuffer s = new StringBuffer("hello");list.add(s);// 打印輸出所有元素System.out.println("ArrayList中的所有元素為:");for (Object element : list) {System.out.print(element + ",");}System.out.println("\n========================");// 查找元素“hello”boolean found = list.contains("hello");if (found) {System.out.println("找到元素\"hello\"");} else {System.out.println("未找到元素\"hello\"");}System.out.println("\n========================");// 刪除指定的元素“hello”list.remove("hello");System.out.println("刪除元素\"hello\"后的ArrayList:");for (Object element : list) {System.out.println(element + ",");}System.out.println("\n========================");// 將元素123替換為1000int index123 = list.indexOf(123);if (index123 != -1) {list.set(index123, 1000);System.out.println("將元素123替換為1000后的ArrayList:");for (Object element : list) {System.out.println(element);}} else {System.out.println("未找到元素123");}}
}
列出測試數據和實驗結果截圖:?
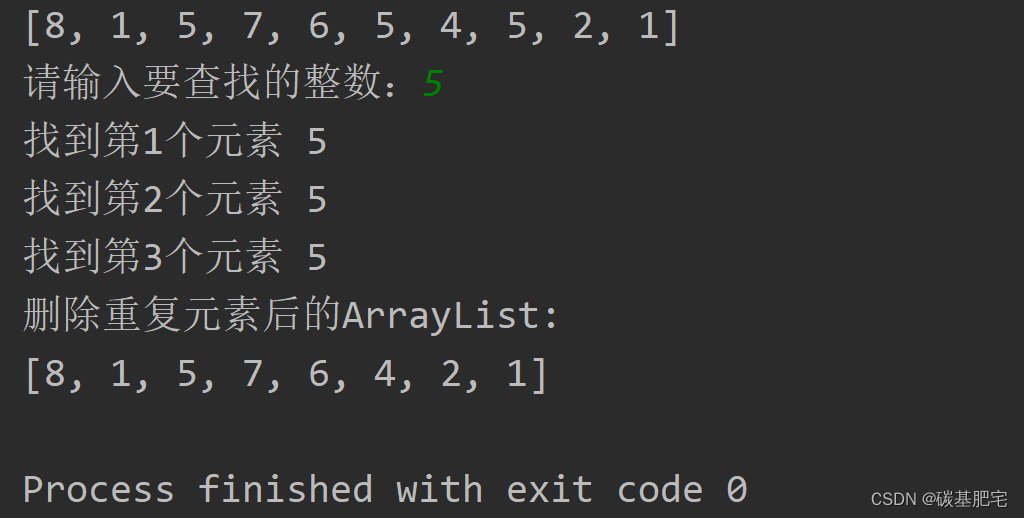
2、使用ArrayList集合,向集合中添加10個整數,并使用Iterator遍歷該集合,并查找鍵盤輸入的元素。
提示:
? 使用add()方法將元素添加到ArrayList集合中。
? 調用集合的iterator()方法獲得Iterator對象,并調用Iterator的hasNext()和next()方法,迭代出集合中的所有元素,完成查找功能,并將重復的元素刪除。
源代碼:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Scanner;public class S6_2 {public static void main(String[] args) {ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();// 1-向集合中添加10個隨機整數for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {list.add(new Random().nextInt(10));}System.out.println(list);// 2-使用Iterator遍歷集合并查找鍵盤輸入的元素Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("請輸入要查找的整數:");int input = reader.nextInt();// 3-去重int count = 0;while (iterator.hasNext()) {int current = iterator.next();if (current == input) {count++;System.out.println("找到第" + count + "個元素 " + input);if(count > 1)iterator.remove(); // 刪除重復的元素}}// 打印刪除重復元素后的集合System.out.println("刪除重復元素后的ArrayList:");System.out.println(list);}
}
列出測試數據和實驗結果截圖:
3、分別利用Arraylist和Set隨機生成十個不重復的隨機整數,隨機整數范圍為350到450。
源代碼:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.Set;public class S6_3 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 使用 ArrayList 生成不重復的隨機整數ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = generateRandomNumbersArrayList();System.out.println("ArrayList中的隨機數:");System.out.println(arrayList);// 使用 Set 生成不重復的隨機整數Set<Integer> set = generateRandomNumbersSet();System.out.println("Set中的隨機數:");System.out.println(set);}// 生成 ArrayList 中的隨機整數private static ArrayList<Integer> generateRandomNumbersArrayList() {ArrayList<Integer> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();Random random = new Random();while (arrayList.size() < 10) {int randomNumber = random.nextInt(101) + 350; // 生成350到450的隨機數if (!arrayList.contains(randomNumber)) {arrayList.add(randomNumber);}}return arrayList;}// 生成 Set 中的隨機整數private static Set<Integer> generateRandomNumbersSet() {Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();Random random = new Random();while (set.size() < 10) {int randomNumber = random.nextInt(101) + 350; // 生成350到450的隨機數set.add(randomNumber); //因為Set內置去重功能,故添加后無需判斷}return set;}
}
列出測試數據和實驗結果截圖:

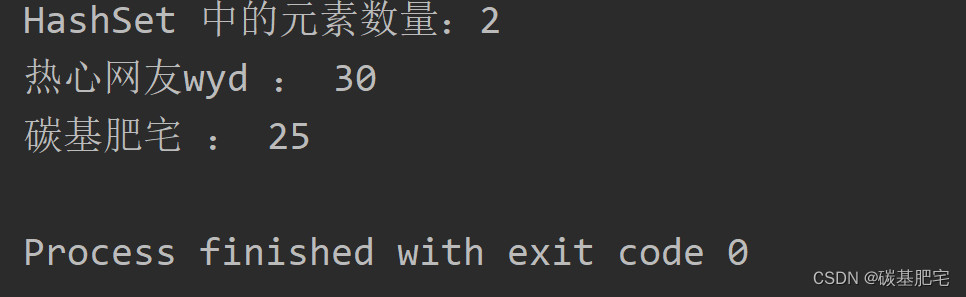
4、集合中不容許有重復的對象,對于多個重復對象只能添加一次。例如在HashSet集合中添加三個Person對象,把姓名相同的人當做同一個人,雖然可以添加多次但集合里只保留一個,但是這對類的設計是有要求的,假設Person類中只包含name和age屬性,則需要重寫hashCode()方法和equals()方法,如果兩個對象的name相同,則hashCode()方法的返回值相同,equals()方法返回true。
源代碼:
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Objects;class Person {private String name;private int age;public Person(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}// Getters and setterspublic String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}public int getAge() {return age;}public void setAge(int age) {this.age = age;}// 重寫 hashCode 方法@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(name);}// 重寫 equals 方法@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {if (this == obj) {return true;}if (obj == null || getClass() != obj.getClass()) {return false;}Person person = (Person) obj;return Objects.equals(name, person.name);}
}public class S6_4 {public static void main(String[] args) {HashSet<Person> personSet = new HashSet<>();// 添加三個 Person 對象,其中兩個 name 相同Person person1 = new Person("碳基肥宅", 25);Person person2 = new Person("熱心網友wyd", 30);Person person3 = new Person("碳基肥宅", 28);personSet.add(person1);personSet.add(person2);personSet.add(person3);// 打印 HashSet 中的元素數量System.out.println("HashSet 中的元素數量:" + personSet.size());for (Person person : personSet) {System.out.println(person.getName() + " : " + person.getAge());}}
}
列出測試數據和實驗結果截圖:
5、編寫程序將一組學生對象的姓名和成績存入到一個樹集(TreeSet)中。
完成以下要求:
? 使得按照成績自動降序排列,并輸出排序的結果。
源代碼:
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.TreeSet;// 學生類
class Student {private String name;private int score;public Student(String name, int score) {this.name = name;this.score = score;}// Getterspublic String getName() {return name;}public int getScore() {return score;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return name + " : " + score;}
}public class S6_5 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建 TreeSet 并指定降序排序的比較器TreeSet<Student> studentSet = new TreeSet<>(Comparator.comparingInt(Student::getScore).reversed());// 向 TreeSet 中添加學生對象studentSet.add(new Student("碳基肥宅", 85));studentSet.add(new Student("熱心網友wyd", 75));studentSet.add(new Student("叮當同學", 92));studentSet.add(new Student("朵拉", 68));// 輸出排序結果(按照成績降序)System.out.println("按照成績降序排列的學生信息:");for (Student student : studentSet) {System.out.println(student);}}
}
列出測試數據和實驗結果截圖:

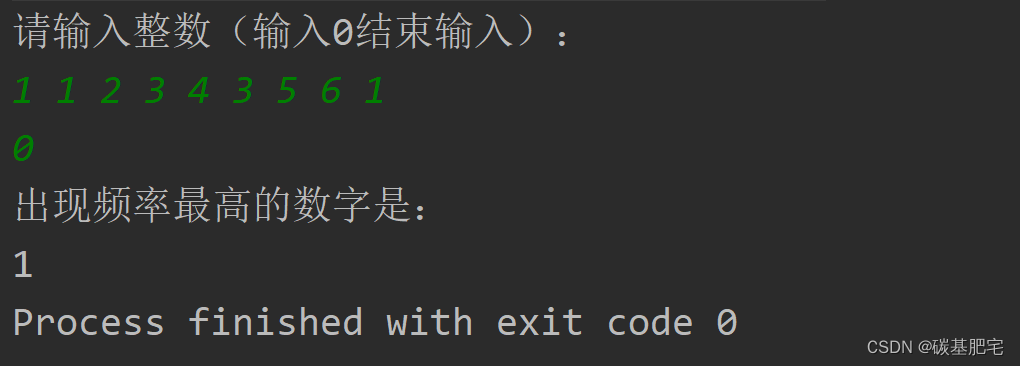
6、編寫一個程序,讀取個數不定的整數,然后查找其中出現頻率最高的數字。要求通過鍵盤輸入數據,當輸入為0時,表示結束輸入。如: 如果輸入的數據是2 ??3 ??40 ??3 ??54 ??-3 ??3 ??3 ??2 ??0,那么數字3的出現頻率是最高的。如果出現頻率最高的數字不是一個而是多個,則應該將它們全部輸出。例如當數據是9 ?30 ?3 ?9 ?3 ?2 ?4時,3和9都出現了兩次,3和9都應該輸出。
提示:可以利用集合的元素不能重復這一特性。
源代碼:
import java.util.*;public class S6_6 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner reader = new Scanner(System.in);Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();System.out.println("請輸入整數(輸入0結束輸入):");int input;while ((input = reader.nextInt()) != 0) {map.put(input, map.getOrDefault(input, 0) + 1);}// 找出最大頻率int maxFrequency = Collections.max(map.values());// 輸出出現最大頻率的數字System.out.println("出現頻率最高的數字是:");for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : map.entrySet()) {if (entry.getValue() == maxFrequency) {System.out.print(entry.getKey());}}}
}
列出測試數據和實驗結果截圖:
也可以用PriorityQueue完成,感興趣的朋友可以試試,具體的實現過陣子補在這里。
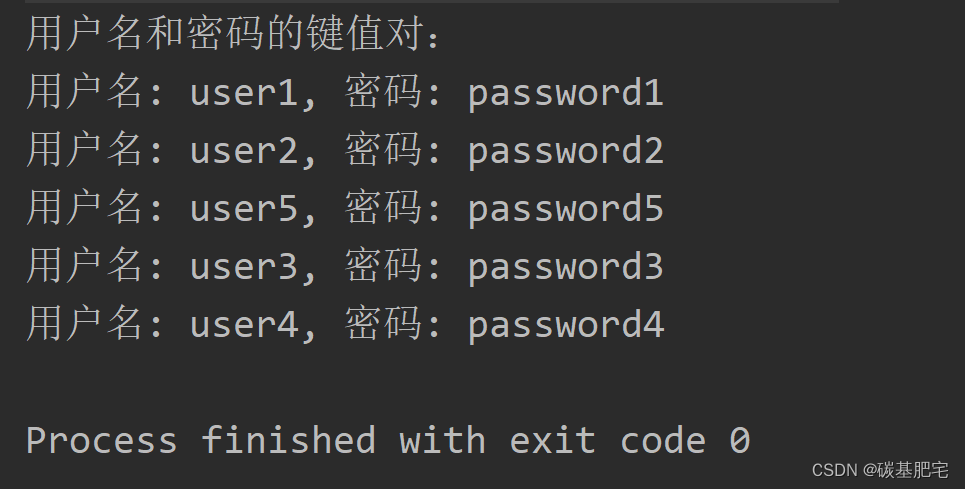
7、選擇合適的Map集合保存5個用戶的用戶名和密碼,然后將這些鍵值對打印出來。
源代碼:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class S6_7 {public static void main(String[] args) {// 創建一個 HashMap 來保存用戶名和密碼Map<String, String> userCredentials = new HashMap<>();// 添加用戶的用戶名和密碼userCredentials.put("user1", "password1");userCredentials.put("user2", "password2");userCredentials.put("user3", "password3");userCredentials.put("user4", "password4");userCredentials.put("user5", "password5");// 打印用戶名和密碼的鍵值對System.out.println("用戶名和密碼的鍵值對:");for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : userCredentials.entrySet()) {System.out.println("用戶名: " + entry.getKey() + ", 密碼: " + entry.getValue());}}
}
列出測試數據和實驗結果截圖:
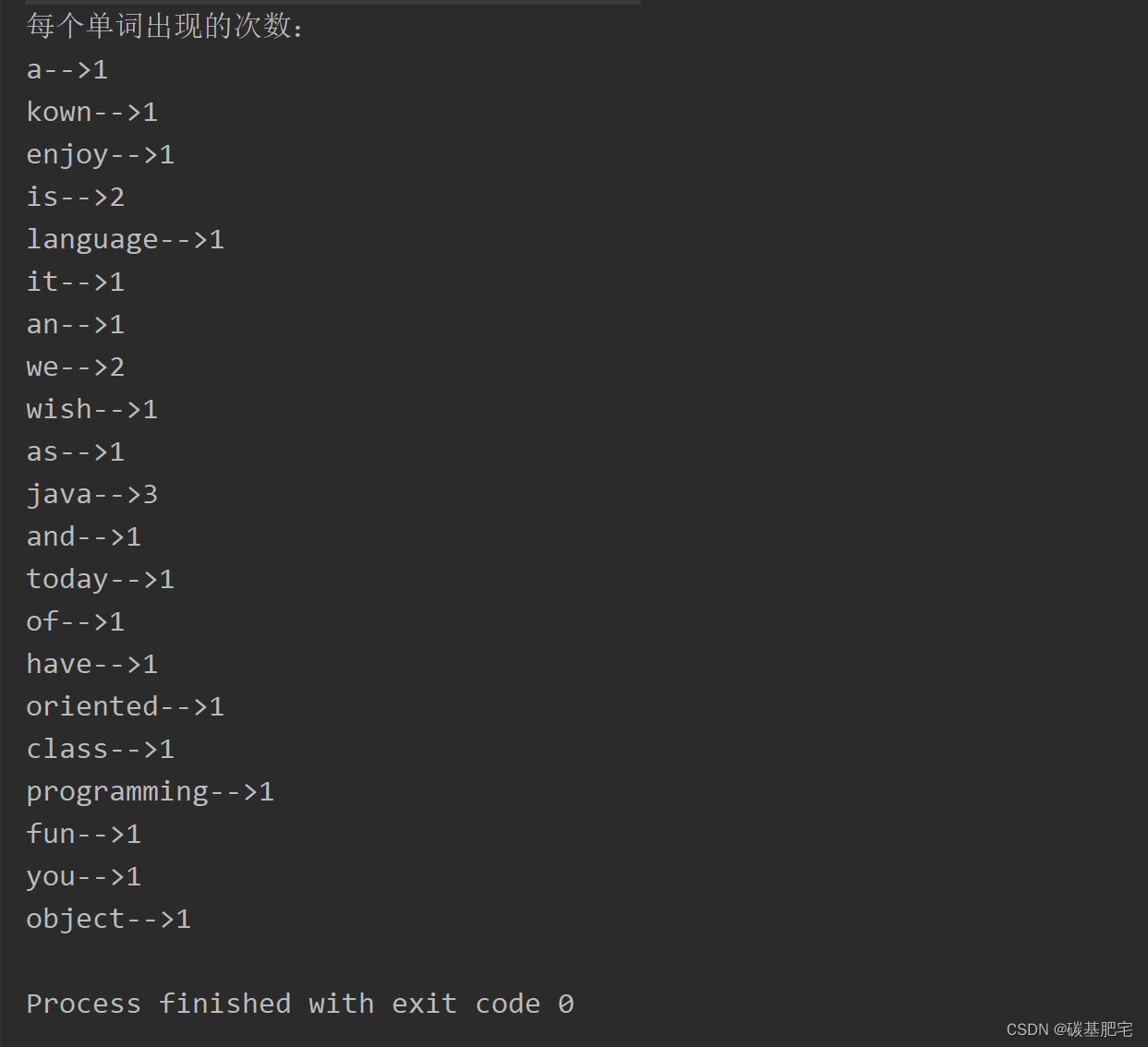
8、(選做)統計字符串中每個單詞出現的次數,使用HashMap來實現。例如:“Today, We have a class of java, as we kown, java is an object oriented ?programming language, and java is fun! wish you enjoy it!”.
統計結果存儲成以下形式:
a-->1
an-->1
and-->1
as-->1……
is-->2
提示:使用String.split(("[ \n\t\r.,;:!?()]")方法進行分詞。
源代碼:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;public class S6_8 {public static void main(String[] args) {String text = "Today, We have a class of java, as we kown, java is an object oriented programming language, and java is fun! wish you enjoy it!";// 去除標點符號并分割字符串為單詞String[] words = text.split("[ \n\t\r.,;:!?()]");// 創建 HashMap 來存儲單詞及其出現的次數Map<String, Integer> wordCount = new HashMap<>();// 統計單詞出現的次數for (String word : words) {word = word.toLowerCase(); // 將單詞轉換為小寫if (!word.isEmpty()) {wordCount.put(word, wordCount.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);}}// 打印每個單詞及其出現的次數System.out.println("每個單詞出現的次數:");for (Map.Entry<String, Integer> entry : wordCount.entrySet()) {System.out.println(entry.getKey() + "-->" + entry.getValue());}}
}
列出測試數據和實驗結果截圖:
9、(選做)500個人圍成一個圈,從1開始報數,數到3的倍數的人離開圈子,循環往復,直到最后圈子只剩下一人為止,求剩下的人原來在圈子的位置。
提示:可以使用集合(ArrayList)或隊列(Deque)實現。
源代碼:
這個問題其實是著名的約瑟夫問題(Josephus problem),可以用遞推的方式求解。
以下是使用隊列(Deque)來模擬這個問題并求解最后剩下的人在原來圈子的位置:
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;public class S6_9 {public static void main(String[] args) {int totalPeople = 500;int count = 3;Deque<Integer> circle = new ArrayDeque<>();// 初始化圈子,編號從1到500for (int i = 1; i <= totalPeople; i++) {circle.addLast(i);}// 開始循環報數,直到圈子中只剩一個人為止while (circle.size() > 1) {for (int i = 0; i < count - 1; i++) {int person = circle.removeFirst();circle.addLast(person);}circle.removeFirst(); // 數到3的倍數的人離開圈子}// 打印最后剩下的人在原來圈子的位置System.out.println("最后剩下的人在原來圈子的位置是:" + circle.peek());}
}
列出測試數據和實驗結果截圖:

三、實驗總結
在這個實驗中我學到了很多關于集合類、循環和算法的知識,這些練習加深了我對集合、字符串處理和算法設計的理解。通過這些題目,我學會了:
- 掌握了ArrayList、HashSet、TreeSet、HashMap 等集合類的基本操作,包括添加、刪除、遍歷和使用鍵值對等。
- 學會了使用 split() 方法分割字符串,以及在字符串中搜索特定的內容。
- 理解了為了在集合中正確比較和存儲自定義對象,需要重寫 hashCode() 和 equals() 方法的重要性。
- 解決了一些經典問題,比如約瑟夫問題,提高了算法思維和編碼能力。


)

覆蓋優化 - 附代碼)






)






