🔥博客主頁:?小扳_-CSDN博客
?感謝大家點贊👍收藏?評論????


文章目錄
? ? ? ? 1.0 單鏈表的說明
? ? ? ? 2.0 單鏈表的創建
? ? ? ? 2.1 單鏈表 - 頭插節點
? ? ? ? 2.2 單鏈表 - 遍歷
? ? ? ? 2.2.1?使用簡單的 for/while?循環
? ? ? ? 2.2.2 實現 forEach 方法
? ? ? ? 2.2.3?實現迭代器的方法
? ? ? ? 2.3 單鏈表 - 尾插節點
? ? ? ? 2.4 單鏈表 - 通過索引獲取數據
? ? ? ? 2.5 單鏈表 - 通過索引插入數據
? ? ? ? 2.6 單鏈表 - 頭刪節點
? ? ? ? 2.7 單鏈表 - 根據節點來刪除數據
?????????3.0 實現單鏈表的完整代碼
? ? ? ? 4.0 實現加 "哨兵" 的單鏈表?
? ? ? ? 1.0 單鏈表的說明
????????單鏈表是一種數據結構。數據結構是指數據的組織、管理和存儲的方式,而單鏈表是一種常見的線性數據結構,用于存儲一系列具有相同類型的元素。它由一系列節點組成,每個節點包含一個數據元素和一個指向下一個節點的指針。單鏈表可以通過指針的方式實現元素的插入、刪除和查找等操作。
? ? ? ? 2.0 單鏈表的創建
? ? ? ?把單鏈表封裝成一個類,面向對象編程的思路。類中需要的成員變量為頭節點、節點,又可以把節點封裝成一個類,為更好把節點類封裝起來,將其設置為靜態內部類。
代碼如下:
public class SingleLists{//頭節點private Node hand = null;//節點private static class Node {//數據private int data;//指向下一個節點private Node next;public Node() {}}? ? ? ? 注意的是,這些成員都不會對外訪問的,所以需要把成員變為私有成員。
? ? ? ? 2.1 單鏈表 - 頭插節點
? ? ? ?顧名思義,就是在頭節點處插入新的節點,使其成為新的頭節點。需要考慮兩種情況,第一種情況,頭節點為 null 時,直接就可以將創建出來的對象被 hand 引用了。第二種情況,頭節點不為 null 時,需要將創建的對象的 next 引用指向 hand 的引用,而當前創建的對象就要被 hand 引用。
代碼如下:
//實現頭插節點public void addFirst(int data) { /* if (hand == null){hand = new Node(data,null);}else {hand = new Node(data,hand);}*///對以上代碼進行簡化得以下代碼:hand = new Node(data,hand);}? ? ? ? 需要注意的時,該 API 是對外訪問。
? ? ? ? 2.2 單鏈表 - 遍歷
? ? ? ? 實現遍歷的方式有三種:
? ? ? ? 第一種方式,使用簡單的 for/while?循環。
????????第二種方式,實現 forEach 方法。
? ? ? ? 第三種方式,實現迭代器的方法。
? ? ? ? 2.2.1?使用簡單的 for/while?循環
? ? ? ? 一般 hand 是不會去移動或者去改變其引用,則需要臨時的變量 p 來指向 hand 的對象。循環的條件為 p != null,每一次循環結束都需要 p 去移動到下一個節點處,p = p.next 。
代碼如下:
//遍歷方式:打印方式public void myPrint(){if (hand == null){throw new RuntimeException("hand is null!!!!");}//第一種: /* Node p = hand;//用while來實現while (p != null){System.out.println(p.data);p = p.next;}*///第二種://用for來實現for (Node p = hand;p !=null;p = p.next){System.out.println(p.data);}}? ? ? ? 還需要注意,for 與 while 這兩種的實現邏輯是一樣的,假如 hand 的引用為空,則沒必要去循環了,直接去拋出錯誤。
? ? ? ? 2.2.2 實現 forEach 方法
? ? ? ? 對于 for/while 的遍歷方法直接把 “方法寫死了”,forEeach 方法是對?for/while 的方法進行了升級。參數為?Consumer<Integer> 內部類,再重寫 accept 方法。
代碼如下:
//遍歷方式:實現forEach,由于跟以下的代碼有沖突,先改名為 myForEach。public void myForEach(Consumer<Integer> consumer){for (Node p = hand; p != null;p = p.next){consumer.accept(p.data);}}具體調用該方法的使用:
singleLists.myForEach(new Consumer<Integer>() {@Overridepublic void accept(Integer integer) {System.out.println(integer);}});? ? ? ? 這樣對外獲取的數據可以自由支配使用,不僅僅打印輸出了。
? ? ? ? 2.2.3?實現迭代器的方法
????????需要實現接口?Iterable<Integer> ,該接口支持泛型,目前先實現整數類型的單鏈表。重寫 hasNext() 與 next() 方法。
代碼如下:
//遍歷方式:使用迭代器循環@Overridepublic Iterator<Integer> iterator() {return new Iterator<Integer>() {Node p = hand;@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return p != null;}@Overridepublic Integer next() {int k = p.data;p = p.next;return k;}};? ? ? ? 重寫完的 hasNext() 這個方法的作用:是判斷當前 p 是否為 null ,如果是就停止遍歷,結束了。反之繼續遍歷下去。
? ? ? ? 重寫之后的 next() 方法的作用:做了兩個動作,第一個動作就是獲取當前的數據;第二個動作就是將 p 移向下一個節點。
具體調用該方法的使用:
for (Integer value:singleLists) {System.out.println(value);}? ? ? ? 同理,這個方式不僅僅只有打印輸出了,自由支配使用。
? ? ? ? 2.3 單鏈表 - 尾插節點
? ? ? ? 找最后的節點后面插入新的節點,如果只有頭節點,需要不斷的遍歷,直到最后一個節點。遍歷的條件為 p.next != null,跟以上的條件需要區別開來,這里需要得到最后的節點,可不能 p !=null 一直下去,這樣就會找不到最后的節點。
代碼如下:
//尾插節點public void addLast(int data) {if (hand == null) {addFirst(data);return;}Node p = hand;while (p.next != null){p = p.next;}p.next = new Node(data,null);}? ? ? ? 需要注意的是,單獨分開當 hand 為 null 時,因為 hand.next == null 了,但是對于hand 為 null 時也可以插入節點呀,所以?當 hand 為 null 時,可以調用頭插節點的方法。
? ? ? ? 2.4 單鏈表 - 通過索引獲取數據
? ? ? ? 單鏈表是不連續的,不用直接通過索引來訪問節點去讀取數據,因此,先獨立設置一個方法,需設置一個 i?記數點,每一個遍歷完 i++ ,直到 i == index 時,先返回該節點。再獨立另一個方法,通過該節點來讀取該數據。
代碼如下:
//根據索引獲取某個節點private Node findNode(int index) {int i = 0;for (Node p = hand ; p != null ; p = p.next,i++){if (i == index) {return p;}}return null;}//根據索引得到對應的數據public int get(int index) {Node p = findNode(index);if (p == null){throw new RuntimeException("找不到該索引!!!");}return p.data;}? ? ? ? 對于找不到的節點,需要拋出異常,需要注意的是,findNode 方法是不對外訪問的,需要封裝起來。
? ? ? ? 2.5 單鏈表 - 通過索引插入數據
? ? ? ? 先獲取插入位置的前一個 prev 節點,然后 prev.next 去指向插入的節點的對象,插入節點的 next 去引用原先 prev.next 的對象。
代碼如下:
//根據索引插入數據public void insert(int index , int data){if (index == 0){addFirst(data);}Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev == null){throw new RuntimeException("index is illegal");}prev.next = new Node(data,prev.next);}? ? ? ? ?需要注意的是,先判斷插入點是否為頭節點,如果是頭節點,則調用頭插的方法。再去判斷其他情況通過 findNode() 方法是否得到 null,如果是,需要拋出異常。
? ? ? ? 2.6 單鏈表 - 頭刪節點
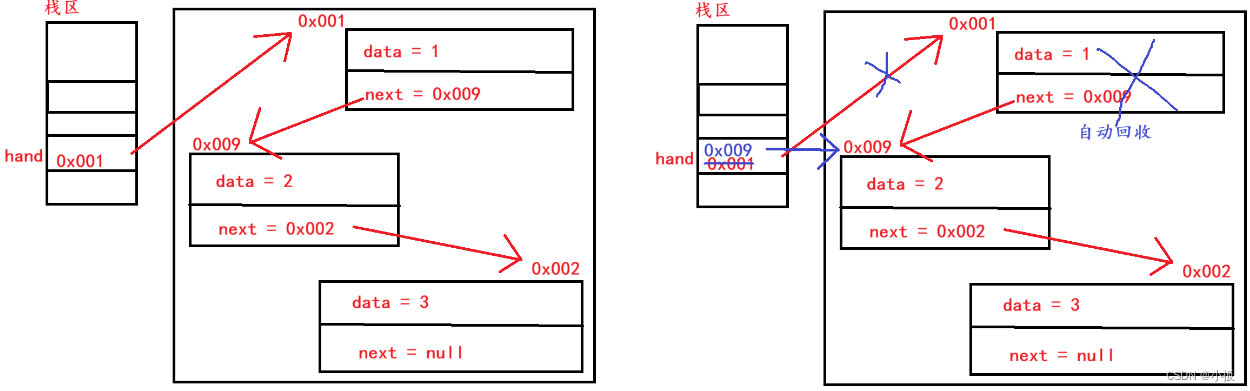
? ? ? ? 顧名思義直接刪除頭節點,思路為: hand 這個引用需要指向 hand.next ,這就是刪除了第一個節點,沒用引用的對象,在 Java 中回自動回收的,不會占內存,這也就是刪除了。
代碼如下:
//頭刪節點public void removeFirst() {if (hand == null){throw new RuntimeException("There are no nodes anymore");}hand = hand.next;}? ? ? ? 需要注意,刪除前先判斷 hand 是否為 null 。
? ? ? ? 2.7 單鏈表 - 根據節點來刪除數據
? ? ? ? 先找到要刪除節點的前一個 prev 節點,然后再去找到 要刪除的節點 move = prev.next ,接著將 prev.next = move.next 即可。
代碼如下:
//根據索引來刪除節點public void remove(int index) {if (index == 0) {removeFirst();return;}Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev == null){throw new RuntimeException("There are no nodes anymore");}Node move = prev.next;if (move == null) {throw new RuntimeException("There are no nodes anymore");}prev.next = move.next;}? ? ? ? 在刪除節點的時候需要先判斷 index 是否為 0,如果是,則調用頭刪的方法,再通過 findNode() 方法來找到刪除節點的前一個節點,如果得到的節點為 null,則需要拋出異常,同樣的如果得到的需要刪除的節點為 null ,則需要拋出異常。
?
?????????3.0 實現單鏈表的完整代碼
import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.function.Consumer;//整體 public class SingleLists implements Iterable<Integer>{//頭節點private Node hand = null;//節點private static class Node {//數據private int data;//指向下一個節點private Node next;public Node() {}public Node(int data, Node next) {this.data = data;this.next = next;}}//實現頭插節點public void addFirst(int data) { /* if (hand == null){hand = new Node(data,null);}else {hand = new Node(data,hand);}*///對以上代碼進行簡化得以下代碼:hand = new Node(data,hand);}//遍歷方式:打印方式public void myPrint(){if (hand == null){throw new RuntimeException("hand is null!!!!");}//第一種: /* Node p = hand;//用while來實現while (p != null){System.out.println(p.data);p = p.next;}*///第二種://用for來實現for (Node p = hand;p !=null;p = p.next){System.out.println(p.data);}}//遍歷方式:實現forEach,由于跟以下的代碼有沖突,先改名為 myForEach。public void myForEach(Consumer<Integer> consumer){for (Node p = hand; p != null;p = p.next){consumer.accept(p.data);}}//遍歷方式:使用迭代器循環@Overridepublic Iterator<Integer> iterator() {return new Iterator<Integer>() {Node p = hand;@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return p != null;}@Overridepublic Integer next() {int k = p.data;p = p.next;return k;}};}//尾插節點public void addLast(int data) {if (hand == null) {addFirst(data);return;}Node p = hand;while (p.next != null){p = p.next;}p.next = new Node(data,null);}//根據索引獲取某個節點private Node findNode(int index) {int i = 0;for (Node p = hand ; p != null ; p = p.next,i++){if (i == index) {return p;}}return null;}//根據索引得到對應的數據public int get(int index) {Node p = findNode(index);if (p == null){throw new RuntimeException("找不到該索引!!!");}return p.data;}//根據索引插入數據public void insert(int index , int data){if (index == 0){addFirst(data);}Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev == null){throw new RuntimeException("index is illegal");}prev.next = new Node(data,prev.next);}//頭刪節點public void removeFirst() {if (hand == null){throw new RuntimeException("There are no nodes anymore");}hand = hand.next;}//根據索引來刪除節點public void remove(int index) {if (index == 0) {removeFirst();return;}Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev == null){throw new RuntimeException("There are no nodes anymore");}Node move = prev.next;if (move == null) {throw new RuntimeException("There are no nodes anymore");}prev.next = move.next;}}
? ? ? ? 4.0 實現加 "哨兵" 的單鏈表?
????????哨兵是單鏈表中的一個特殊節點,它不在乎存儲什么數據元素,只用于標記鏈表的開始或結束。在單鏈表中,通常有一個頭節點作為鏈表的起始位置。而哨兵節點是在頭節點之前或尾節點之后的一個額外節點,用于簡化鏈表的操作。簡單來說,就是 hand 不在為 null ,始終有節點,這么一來,就會節省了考慮 hand == null 的情況發生了,寫出來的代碼更加簡潔了。
加 "哨兵" 的代碼如下:
import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.function.Consumer;//整體 public class SingleLists implements Iterable<Integer>{//頭節點private final Node hand = new Node(0,null);//節點private static class Node {//數據private int data;//指向下一個節點private Node next;public Node() {}public Node(int data, Node next) {this.data = data;this.next = next;}}//實現頭插節點public void addFirst(int data) {//對以上代碼進行簡化得以下代碼://hand.next = new Node(data,hand.next);insert(0,data);}//遍歷方式:打印方式public void myPrint(){for (Node p = hand.next;p !=null;p = p.next){System.out.println(p.data);}}//遍歷方式:實現forEach,由于跟以下的代碼有沖突,先改名為 myForEach。public void myForEach(Consumer<Integer> consumer){for (Node p = hand.next; p != null;p = p.next){consumer.accept(p.data);}}//遍歷方式:使用迭代器循環@Overridepublic Iterator<Integer> iterator() {return new Iterator<Integer>() {Node p = hand.next;@Overridepublic boolean hasNext() {return p != null;}@Overridepublic Integer next() {int k = p.data;p = p.next;return k;}};}//尾插節點public void addLast(int data) {Node p = hand;while (p.next != null){p = p.next;}p.next = new Node(data,null);}//根據索引獲取某個節點private Node findNode(int index) {int i = -1;for (Node p = hand ; p != null ; p = p.next,i++){if (i == index) {return p;}}return null;}//根據索引得到對應的數據public int get(int index) {Node p = findNode(index);if (p == null){throw new RuntimeException("找不到該索引!!!");}return p.data;}//根據索引插入數據public void insert(int index , int data){Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev == null){throw new RuntimeException("index is illegal");}prev.next = new Node(data,prev.next);}//頭刪節點public void removeFirst() {//hand = hand.next;remove(0);}//根據索引來刪除節點public void remove(int index) {Node prev = findNode(index - 1);if (prev == null){throw new RuntimeException("There are no nodes anymore");}Node move = prev.next;if (move == null) {throw new RuntimeException("There are no nodes anymore");}prev.next = move.next;} }????????需要注意的是,哨兵節點并不是必需的,可以根據具體的需求來決定是否使用哨兵節點。在某些情況下,如果鏈表的操作較為簡單,不涉及插入和刪除等復雜操作,可以不使用哨兵節點來簡化代碼。
?













)





