蘇米特·班迪帕迪亞

照片由Dan Cristian P?dure?在Unsplash上拍攝
一、說明
DATA,通常被稱為原油,需要經過加工和清潔才能有效地用于各種用途。正如我們不直接使用來自其來源的石油一樣,數據也經過類似的處理以提取其真正價值。
二、特征選擇
特征選擇是從數據集中的大量可用特征中選擇相關特征子集的過程。由于以下原因,這是機器學習的重要一步
- 它使機器學習算法能夠更快地訓練。
- 它減少了過度擬合,增強了可解釋性,并降低了計算復雜性。
- 提高模型性能和準確性
特征工程完整指南 - 第一部分-CSDN博客
三、單變量特征選擇:
????????單變量特征選擇方法側重于單獨評估每個特征,而不考慮特征之間的關系。這些方法包括統計檢驗,例如卡方、方差分析或互信息。目標是選擇與目標變量相關性最高的特征,丟棄不相關的特征。
SelectKBest:根據單變量統計測試(例如卡方、f_regression 或mutual_info_regression)選擇前 k 個特征
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest, chi2# Assuming X contains the input features and y contains the target variable# Create an instance of SelectKBest with chi-squared test
selector = SelectKBest(score_func=chi2, k=5)# Fit the selector to the data
selector.fit(X, y)# Get the selected features
X_selected = selector.transform(X)SelectPercentile:使用相同的統計測試,根據得分最高的特征的百分位數選擇排名靠前的特征。
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectPercentile, f_classif# Assuming X contains the input features and y contains the target variable# Create an instance of SelectPercentile with f_classif test and percentile=50
selector = SelectPercentile(score_func=f_classif, percentile=50)# Fit the selector to the data
selector.fit(X, y)# Get the selected features
X_selected = selector.transform(X)四、遞歸特征消除(RFE):
????????RFE 是一種迭代特征選擇技術,從所有特征開始,逐步消除最不重要的特征。它依靠機器學習模型的性能或特征系數來確定特征重要性。通過迭代刪除特征,RFE 可以識別優化模型性能最有影響力的子集。
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression# Assuming X contains the input features and y contains the target variable# Create an instance of Logistic Regression
estimator = LogisticRegression()# Create an instance of RFE with the logistic regression estimator
selector = RFE(estimator, n_features_to_select=3)# Fit the selector to the data
selector.fit(X, y)# Get the selected features
X_selected = selector.transform(X)五、基于模型的特征選擇:
????????基于模型的特征選擇技術使用機器學習模型來評估特征重要性。模型根據系數、特征權重或特征重要性來估計特征重要性。基于 L1 的正則化,例如 Lasso 回歸,可以將不相關的特征系數縮小到零,從而有效地執行特征選擇。
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectFromModel
from sklearn.linear_model import Lasso# Assuming X contains the input features and y contains the target variable# Create an instance of Lasso Regression
estimator = Lasso(alpha=0.1)# Create an instance of SelectFromModel with Lasso estimator
selector = SelectFromModel(estimator)# Fit the selector to the data
selector.fit(X, y)# Get the selected features
X_selected = selector.transform(X)六、基于樹的特征選擇:
????????基于樹的算法,例如隨機森林和梯度提升,提供了內在的特征選擇機制。這些算法根據特征對模型性能的貢獻程度來分配特征重要性。具有較高重要性的特征被認為更相關,并且可以被選擇用于進一步分析。
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectFromModel
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier# Assuming X contains the input features and y contains the target variable# Create an instance of Random Forest Classifier
estimator = RandomForestClassifier()# Create an instance of SelectFromModel with Random Forest estimator
selector = SelectFromModel(estimator)# Fit the selector to the data
selector.fit(X, y)# Get the selected features
X_selected = selector.transform(X)SelectFromModel方法在內部使用 RandomForestClassifier 模型計算的特征重要性來確定要選擇的特征。
SelectFromModel方法根據指定的閾值或預定義的重要性標準自動選擇特征。它根據特征重要性確定重要性閾值,并選擇滿足或超過該閾值的特征。
七、特征重要性
????????特征重要性是一種為數據集中的每個特征分配分數的度量。該分數表示每個特征與目標變量的重要性或相關性級別。
????????基于樹的分類器,例如隨機森林分類器和額外樹分類器,具有內置的特征重要性類。此類允許您在數據集(例如虹膜數據集)上訓練模型,然后使用 feature_importance_ 屬性計算每個特征的重要性得分。
????????在下面的示例中,我們將在 iris 數據集中訓練額外的樹分類器,并使用內置類 feature_importance_ 來計算每個特征的重要性。
# Load libraries
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier# Load iris data
iris_dataset = load_iris()# Create features and target
X = iris_dataset.data
y = iris_dataset.target# Convert to categorical data by converting data to integers
X = X.astype(int)# Building the model
extra_tree_forest = ExtraTreesClassifier(n_estimators = 5,criterion ='entropy', max_features = 2)# Training the model
extra_tree_forest.fit(X, y)# Computing the importance of each feature
feature_importance = extra_tree_forest.feature_importances_# Normalizing the individual importances
feature_importance_normalized = np.std([tree.feature_importances_ for tree in extra_tree_forest.estimators_],axis = 0)# Plotting a Bar Graph to compare the models
plt.bar(iris_dataset.feature_names, feature_importance_normalized)
plt.xlabel('Feature Labels')
plt.ylabel('Feature Importances')
plt.title('Comparison of different Feature Importances')
plt.show()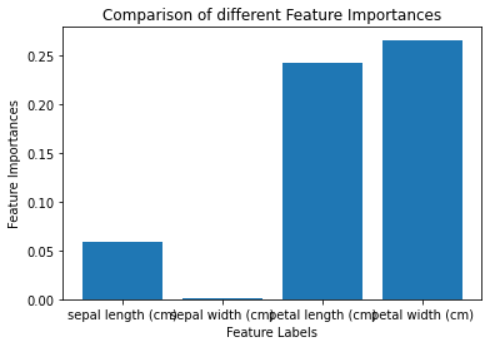
標準化特征重要性
上圖顯示最重要的特征是花瓣長度 (cm)和花瓣寬度 (cm),最不重要的特征是萼片寬度 (cm)。這意味著您可以使用最重要的功能來訓練模型并獲得最佳性能。
八、皮爾遜相關系數矩陣
相關性是一種統計度量,表示兩個變量之間關系的強度。兩種主要類型的相關性是正相關性和負相關性。當兩個變量朝同一方向移動時,就會出現正相關;當一個增加時,另一個也會增加。
兩個變量 X 和 Y 之間的皮爾遜相關系數可以使用以下公式計算
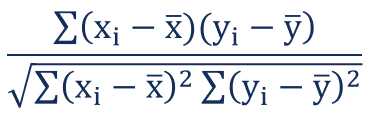
皮爾遜相關系數公式
相關系數的值可以取-1到1之間的任意值。
- 如果值為 1,則表示兩個變量之間呈正相關。這意味著當一個變量增加時,另一個變量也會增加。
- 如果值為 -1,則表示兩個變量之間呈負相關。這意味著當一個變量增加時,另一個變量就會減少。
- 如果值為 0,則兩個變量之間不存在相關性。這意味著變量彼此之間以隨機方式變化。
在下面的示例中,我們將使用 Scikit-learn 庫中的波士頓房價數據集和pandas 中的corr()?方法來查找數據框中所有特征的成對相關性:
# Load libraries
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns# load boston data
boston_dataset = load_boston()# create a daframe for boston data
boston = pd.DataFrame(boston_dataset.data, columns=boston_dataset.feature_names)# Convert to categorical data by converting data to integers
#X = X.astype(int)#ploting the heatmap for correlation
ax = sns.heatmap(boston.corr().round(2), annot=True) 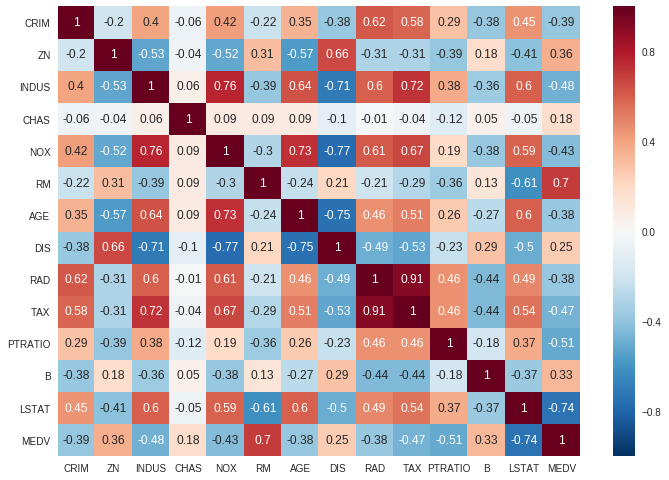
在提供的圖中,很明顯,特征 RAD 和 RAD 表現出顯著的正相關性,而特征 DIS 和 NOX 表現出很強的負相關性。
當您在數據集中發現相關特征時,這表明它們傳達了相似的信息。在這種情況下,建議消除相關特征之一。
九、順序特征選擇:
順序特征選擇方法評估特征子集而不是單個特征。他們根據選定的評估指標(例如模型性能或交叉驗證分數)迭代地添加或刪除功能。前向選擇從空集開始,逐步添加特征,而后向消除則從所有特征開始,一一刪除。
from sklearn.feature_selection import SequentialFeatureSelector
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression# Assuming X contains the input features and y contains the target variable# Create an instance of Logistic Regression
estimator = LogisticRegression()# Create an instance of SequentialFeatureSelector with logistic regression estimator
selector = SequentialFeatureSelector(estimator, direction='forward', k_features=3)# Fit the selector to the data
selector.fit(X, y)# Get the selected features
X_selected = selector.transform(X)十、結論
????????特征選擇是機器學習中提高模型性能、可解釋性和效率的重要技術。通過理解和應用適當的特征選擇技術,您可以識別與模型最相關的特征,減少過度擬合并增強其泛化能力。無論您使用單變量方法、遞歸消除、基于模型的方法、基于樹的技術還是順序選擇,選擇取決于您的特定數據集和問題的要求。
????????通過利用這些特征選擇技術,您可以簡化機器學習流程并構建更準確、更高效、更可解釋的模型。
????????請記住,特征選擇是整個模型開發過程的關鍵部分,應該仔細執行和評估,以確保所選特征真正具有信息性和相關性。


)
應用開發——ArkTs學習準備)



 - 前端)


pipeline)








