0 布局的定義
布局可以理解為一種??容器??,用于??組織與排列界面上的控件??。
-
布局是一個相框,控件就是你要展示的照片。?
-
你(布局規則)決定這些照片怎么排列:是從上到下整齊放(LinearLayout),還是自由定位(ConstraintLayout),還是全部疊在一起(FrameLayout)。
🔹 ??布局的本質是樹狀結構??:一個布局可以包含多個子布局或控件,子布局又可以繼續嵌套,從而形成復雜的 UI 結構。
🧠 ??常見問題:為什么別人寫的布局能實現效果,我的卻不行???
很多時候是因為對??布局類型及其屬性規則??不了解,尤其是某些屬性是由??父布局決定的??,而不是通用的。
一、布局中的屬性來源分類
我們在 XML 布局文件中寫的各種屬性,大致可以分為以下兩類:
? 1. 來自 ??View 本身?? 的屬性(通用屬性,大多數控件都支持)
這些屬性是 ??Android 控件共有的基本屬性??,比如:
android:id:為控件設置唯一標識符
android:layout_width:控件的寬度(如?match_parent,?wrap_content)
android:layout_height:控件的高度
android:text:文本內容(TextView、Button 等)
android:textSize:字體大小
android:background:背景顏色或圖片
android:padding/?android:margin:內邊距和外邊距
android:textColor:文字顏色
📌 這些屬性在任何控件中基本都有效,因為它們定義在?
android.view.View或其子類中。
? 2. 來自 ??父布局的 LayoutParams??(布局參數,取決于當前控件所在的父布局類型)
這些屬性 ??不是控件本身的屬性,而是由父布局決定的布局行為??,比如:
layout_gravity(在某些布局中控制控件在其父容器中的對齊方式)
layout_centerInParent(居中,但只有特定父布局支持)
layout_weight(權重,LinearLayout 特有)
layout_below,?layout_toRightOf(RelativeLayout 特有)
app:layout_constraintXXX(ConstraintLayout 特有)
?? ??重要提醒:??
如果你在一個布局中使用了 ??只屬于某種父布局的屬性,但該控件的實際父布局并不支持它,那么這個屬性雖然不會報錯,但也不會生效!??
例如:在?
ConstraintLayout中使用?layout_centerInParent是無效的,因為它是?RelativeLayout的屬性
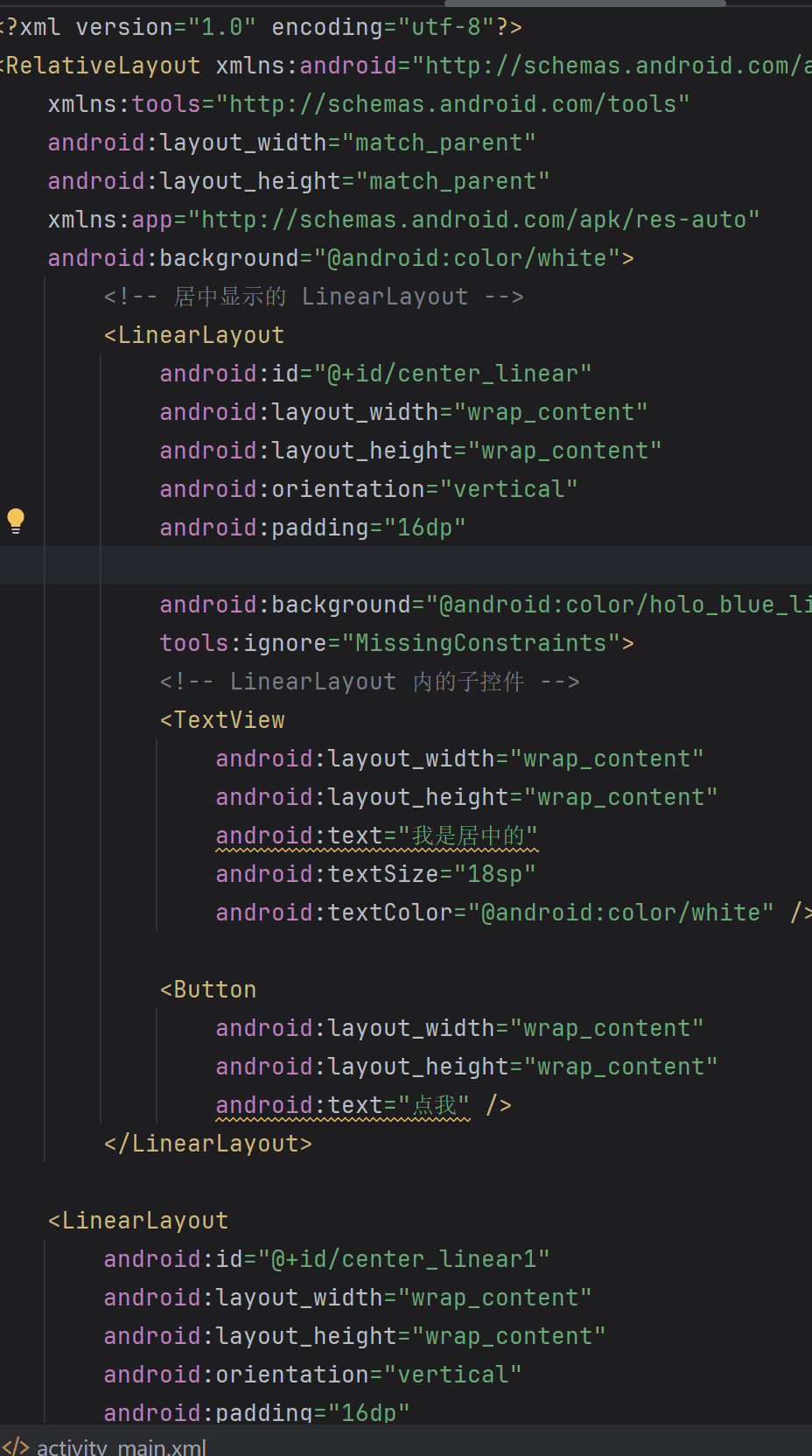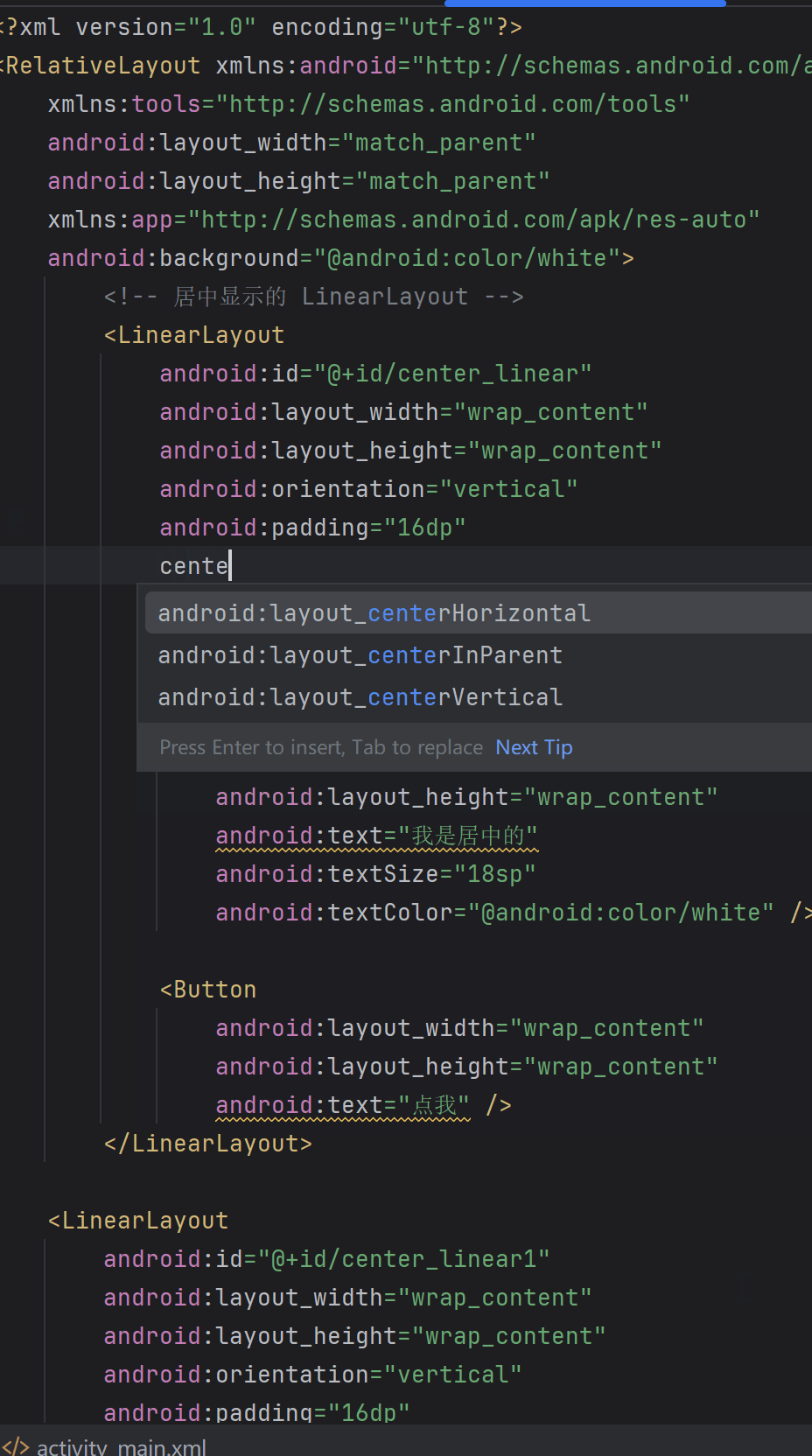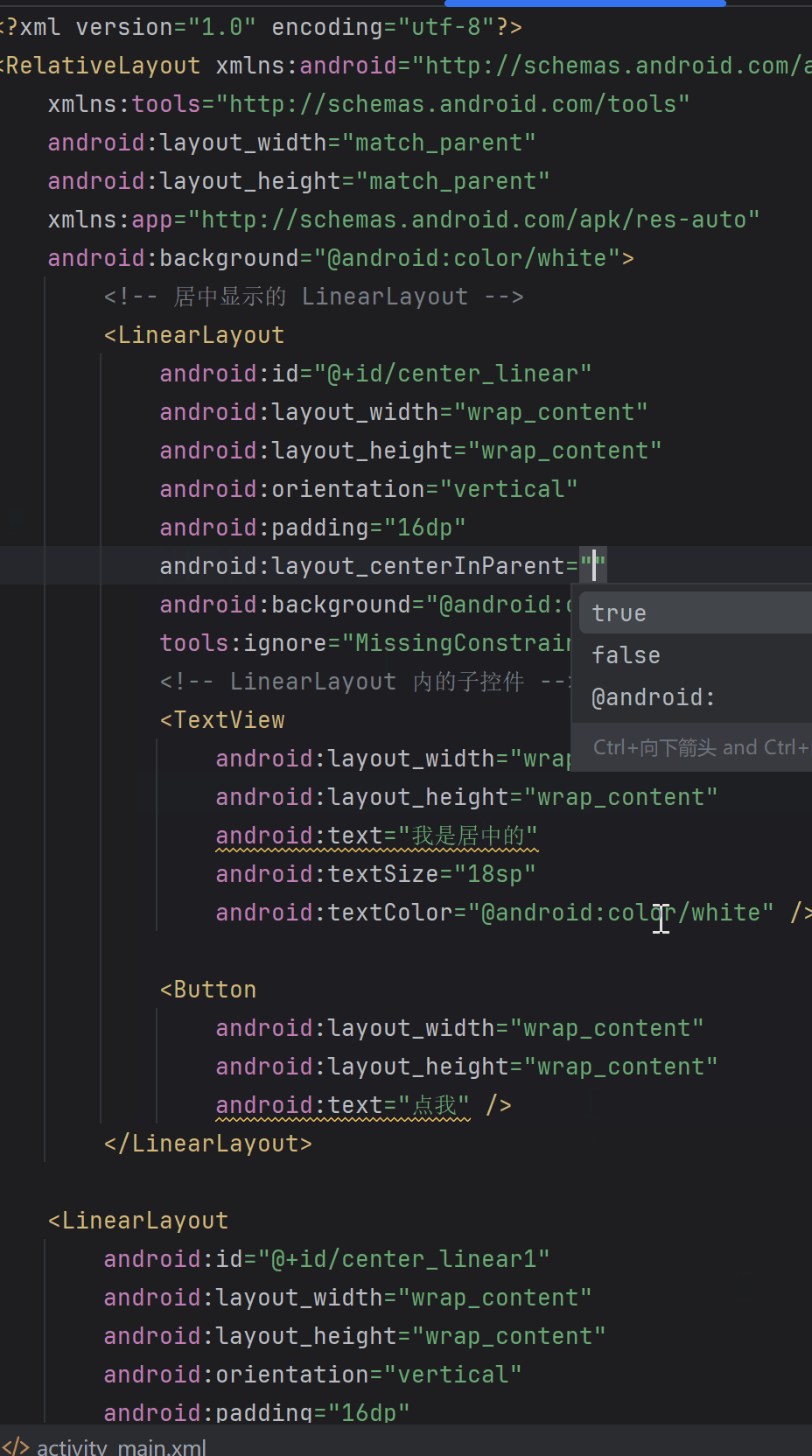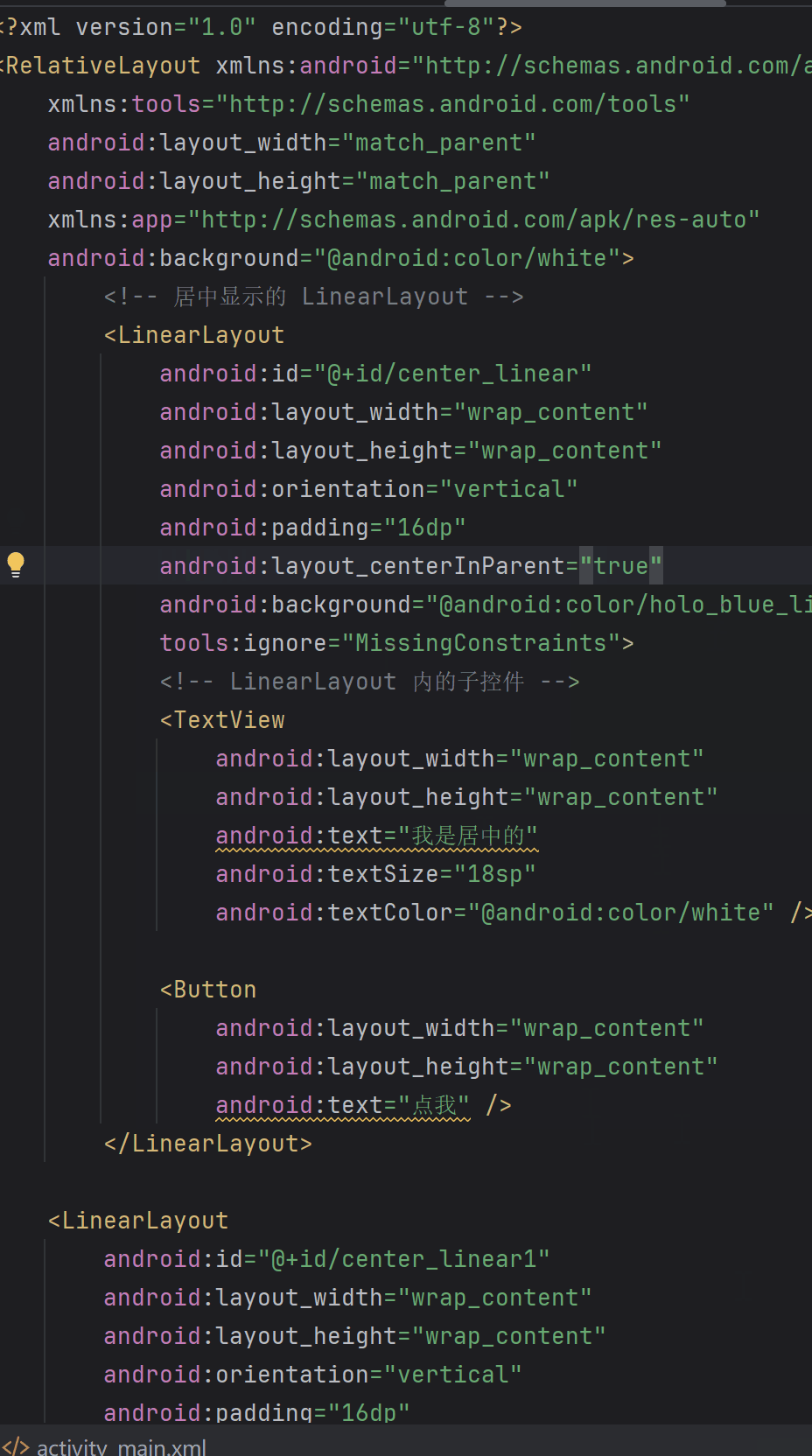
如下面兩張圖,layout_centerInParent在父布局RelativeLayout中是生效的,但是在ConstraintLayout中不會報錯,但是不會生效。
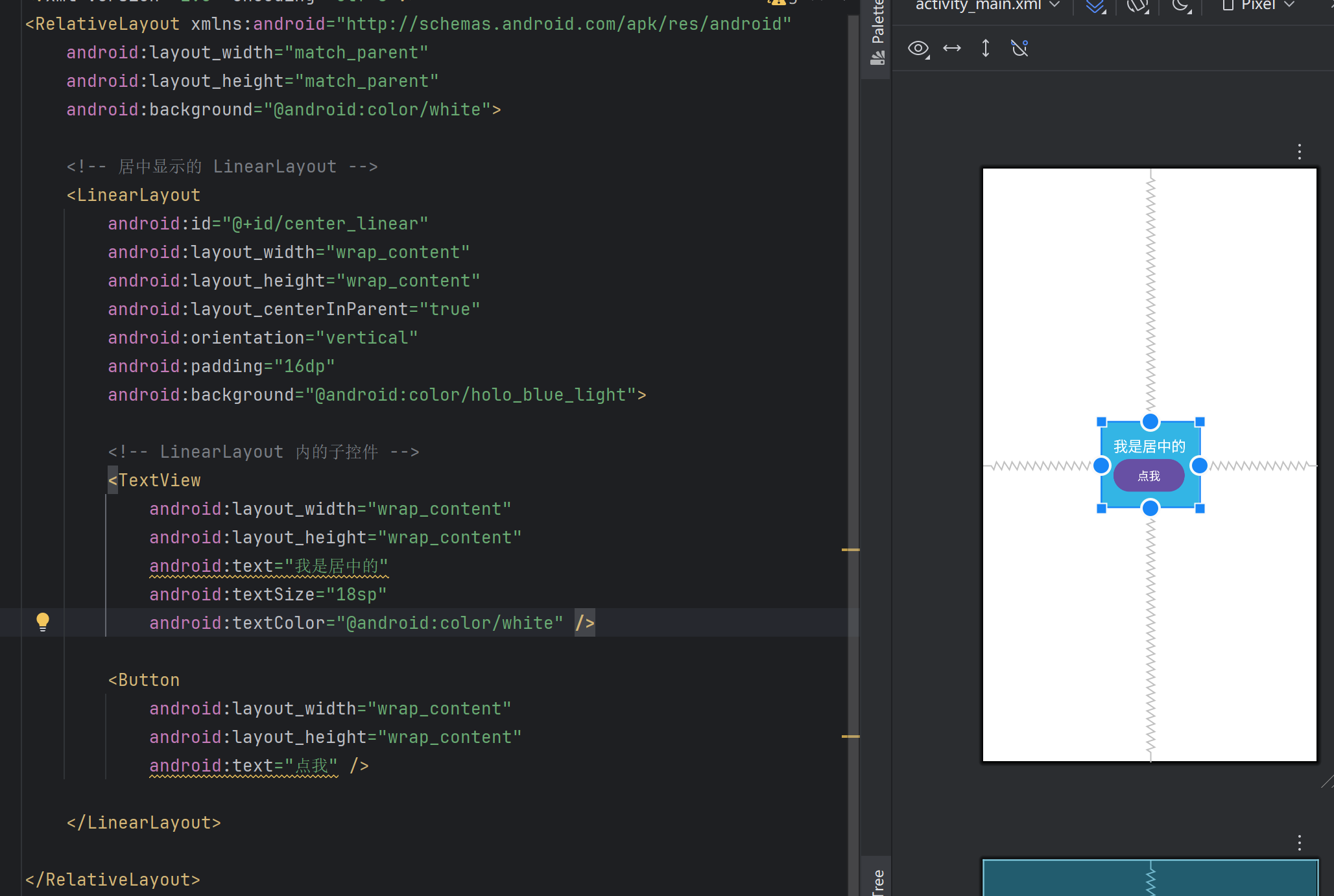
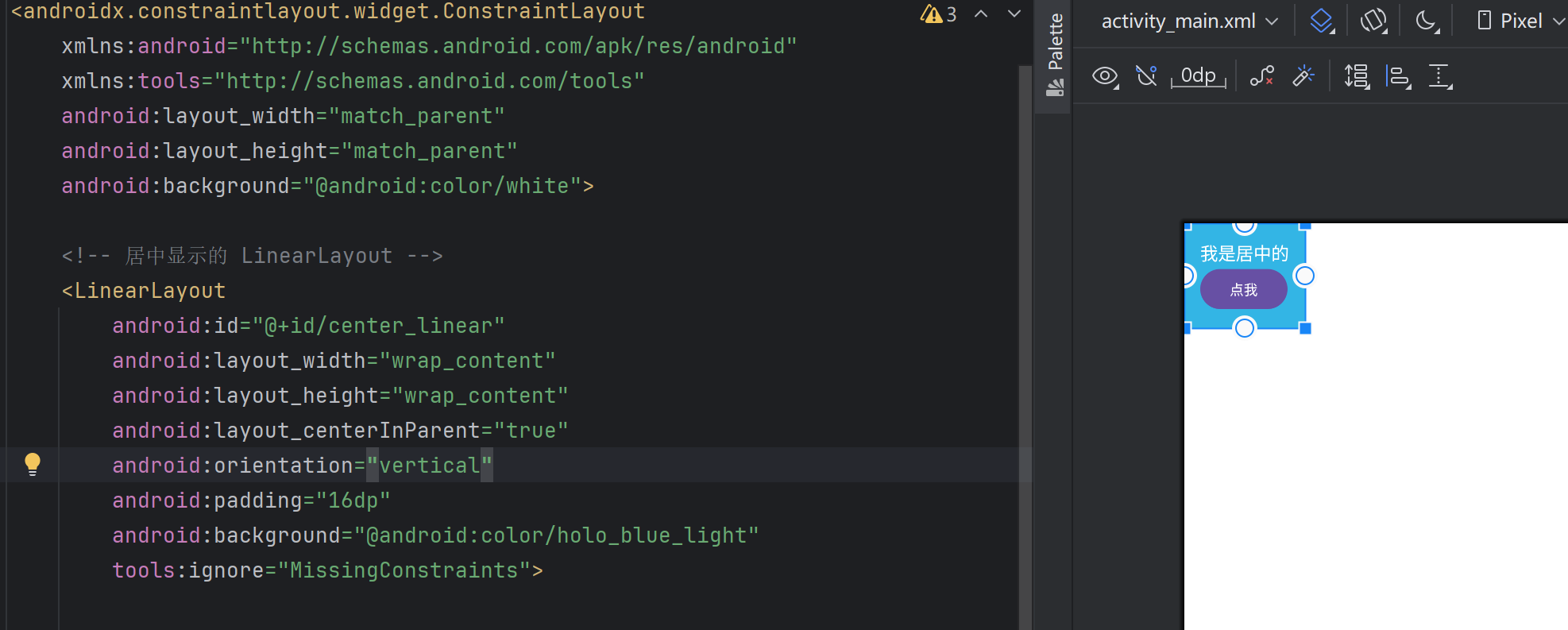
實際中我們在判斷這個布局是否有這個屬性可以通過這個方式,只要在android studio中能顯示,說明就有這個屬性。
二? 常見布局體系總欄(詳細參數去andorid官網學習)
2.1 LinearLayout?(線性疊加布局):
-
垂直方向:下一個子控件從上一個控件的底部開始排列
-
水平方向:下一個子控件從上一個控件的右邊開始排列
方法1:在xml中并且布局,然后直接在代碼中加載
1.1.1 直接在Java中實現布局,不使用xml
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {@Overrideprotected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);// 1. 創建 RelativeLayout 作為根布局RelativeLayout relativeLayout = new RelativeLayout(this);relativeLayout.setLayoutParams(new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT,RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT));relativeLayout.setBackgroundColor(Color.WHITE);// 2. 創建 LinearLayout 并設置屬性LinearLayout linearLayout = new LinearLayout(this);linearLayout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL);linearLayout.setPadding(16, 16, 16, 16);linearLayout.setBackgroundColor(0xFF03A9F4); // holo_blue_light// 3. 添加子控件TextView textView = new TextView(this);textView.setText("我是居中的");textView.setTextSize(18);textView.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);linearLayout.addView(textView);Button button = new Button(this);button.setText("點我");linearLayout.addView(button);// 4. 設置 LinearLayout 在 RelativeLayout 中居中RelativeLayout.LayoutParams llParams = new RelativeLayout.LayoutParams(RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,RelativeLayout.LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);llParams.addRule(RelativeLayout.CENTER_IN_PARENT, RelativeLayout.TRUE);linearLayout.setLayoutParams(llParams);// 5. 把 LinearLayout 添加到 RelativeLayoutrelativeLayout.addView(linearLayout);// 6. 設置 Activity 內容為 RelativeLayoutsetContentView(relativeLayout);}
}
方法3:可以在 XML 定義布局基礎結構,然后在 Java 中動態修改或添加控件
1.2 RelativeLayout(相對布局)
? 核心特點:
子控件通過??相對位置??來排列(比如相對于父布局,或相對于其他控件)
支持諸如?layout_alignParentTop,?layout_below,?layout_toRightOf等屬性
??靈活性強,但復雜布局容易難以維護?
1.3 FrameLayout(幀布局)
? 核心特點:
??所有子控件默認都堆疊在左上角(0,0)位置??
后添加的控件會覆蓋在先添加的控件之上(常用于疊加顯示),
-
可以通過
android:layout_gravity或FrameLayout.LayoutParams.gravity控制子控件在父容器中的位置 -
常見值:
center、top|left、bottom|right等
通常用來顯示??單個全屏控件??
🎯 適用場景:
顯示單一內容,比如全屏的圖片、視頻播放器
實現??層疊效果??(比如浮動按鈕蓋在內容上方)
用作 ??Fragment 的容器?
舉個例子,下面這個就是framelayout從zuos左上角開始疊加的布局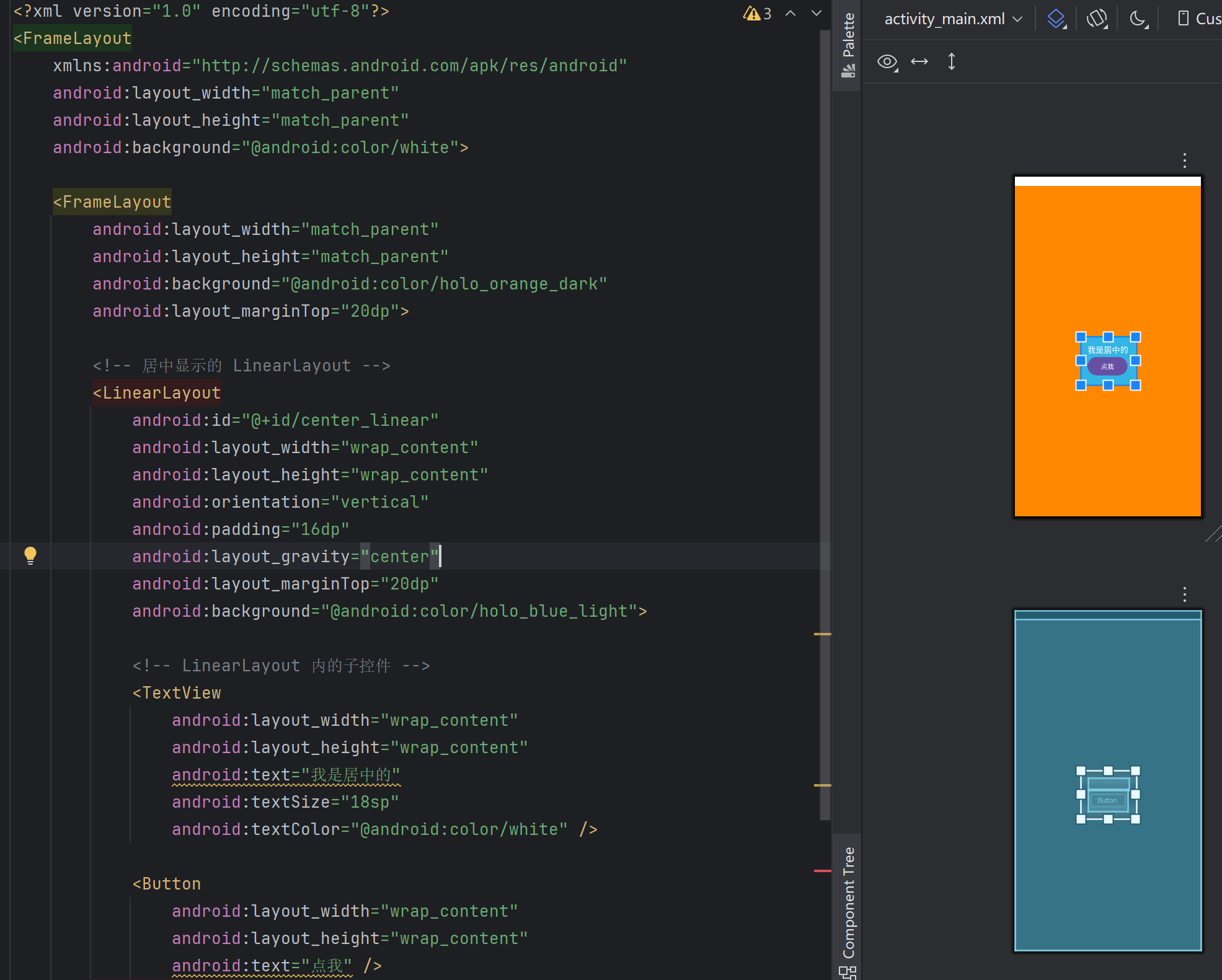
1.4 ConstraintLaout(約束布局)
ConstraintLayout 功能搶到,可以替代 LinearLayout、RelativeLayout、FrameLayout 等組合布局,主要特點如下:
? 核心特點:
通過??控件之間的約束關系(Constraints)??來定位,而不是嵌套
支持百分比定位、居中、偏移、鏈條(Chains)、屏障(Barrier)、Guideline 等高級功能
??官方推薦用于替代多層嵌套的 LinearLayout / RelativeLayout??
支持在 Android Studio 的 ??布局編輯器中可視化拖拽約束??
🎯 適用場景:
構建??復雜且響應式的 UI??
需要精確控制控件位置與對齊
希望減少布局嵌套層級,提升渲染性能
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"android:layout_width="match_parent"android:layout_height="match_parent"xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"android:background="@android:color/white"><!-- 居中顯示的 LinearLayout --><LinearLayoutandroid:id="@+id/center_linear"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:orientation="vertical"android:padding="16dp"app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"android:background="@android:color/holo_blue_light"tools:ignore="MissingConstraints"><!-- LinearLayout 內的子控件 --><TextViewandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="我是居中的"android:textSize="18sp"android:textColor="@android:color/white" /><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="點我" /></LinearLayout><LinearLayoutandroid:id="@+id/center_linear1"android:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:orientation="vertical"android:padding="16dp"app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="@id/center_linear"app:layout_constraintTop_toBottomOf="@id/center_linear"android:background="@android:color/holo_green_light"><TextViewandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="居中的下面"android:textSize="18sp"android:textColor="@android:color/white" /><Buttonandroid:layout_width="wrap_content"android:layout_height="wrap_content"android:text="點我" /></LinearLayout>
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>

? 提示:
使用?
app:layout_constraintXXX來定義控件間的約束關系
ConstraintLayout強大之處在于不用嵌套也能實現復雜布局
tip:
如果在 XML 和 Java 代碼中都對同一個控件設置了相同屬性,??后設置的會覆蓋前者?
所有的布局與屬性設置,都是在?setContentView()之后才會真正生效嵌套太深會影響性能與渲染速度,
盡量使用?ConstraintLayout減少布局層級


 -- 百度智能云 ASR LIM TTS 語音AI助手源碼)



:二值化)
設計模式(Command))







:實施手冊)



