
開始答題
版本一:
/*** @param {Function} fn* @return {Function}*/
var once = function(fn) {let runCount=0return function(...args){runCount++runCount == 1 ? return fn(...args) :return undefined}
};/*** let fn = (a,b,c) => (a + b + c)* let onceFn = once(fn)** onceFn(1,2,3); // 6* onceFn(2,3,6); // returns undefined without calling fn*/
報錯
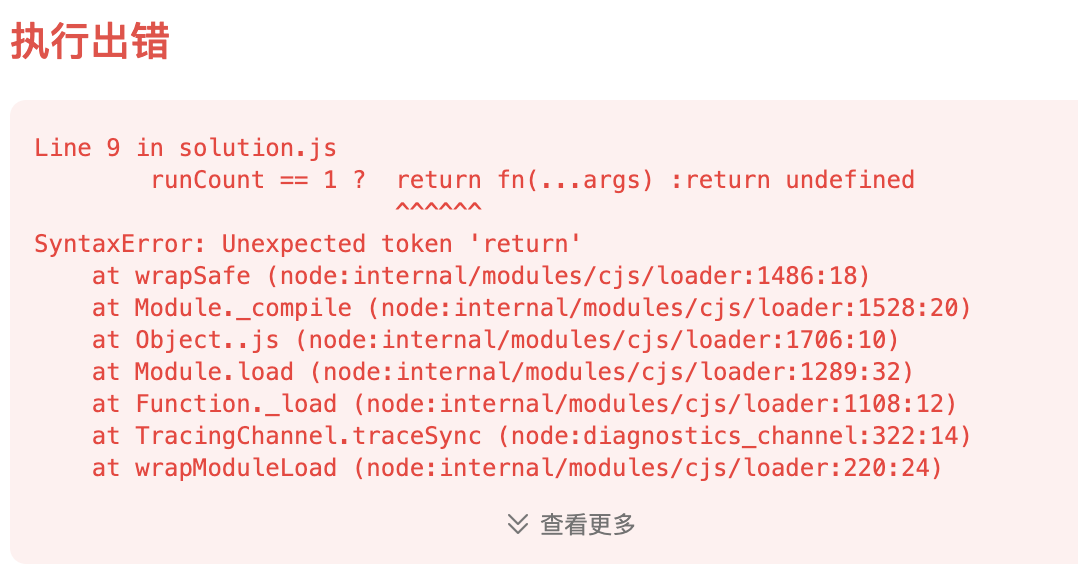
為ai為啥報錯 ai說三木運算符? :后面只能寫表達式不能寫語句。return ?是語句。
語句與表達式的區別
語句是一個動作,不一定有事。表達式一定會得到一個值。
語句:
if (x > 10) { … } // if 語句
while (true) { … } // while 語句
return 5; // return 語句
var a = 1; // 變量聲明語句
表達式:
3 + 4 // 表達式,結果是 7
x > 10 // 表達式,結果是 true 或 false
fn(1, 2) // 表達式,結果是函數返回值
a = 5 // 賦值表達式,結果是 5
即是表達式又是語句
a = 5; // 既是語句(賦值語句),又是表達式(返回 5)
第二版
/*** @param {Function} fn* @return {Function}*/
var once = function(fn) {let runCount=0return function(...args){runCount++return runCount == 1 ? fn(...args) : undefined}
};/*** let fn = (a,b,c) => (a + b + c)* let onceFn = once(fn)** onceFn(1,2,3); // 6* onceFn(2,3,6); // returns undefined without calling fn*/
提交通過了
看官方題解
知識點
- 高階函數
在 JavaScript(以及很多語言)里,如果一個函數滿足下面任意條件之一,就叫高階函數:
- 函數作為參數傳入(參數是函數)
- 函數作為返回值返回(返回函數)
換句話說:操作函數的函數 → 就是高階函數。
- 異步操作 promise 與 async await
- 它倆都是處理異步操作的,async 是promise的語法糖,通過async可以像處理同步那樣處理異步。
- Promise 的基本語法
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {// 做一些異步的事...// 成功時調用 resolve(值)// 失敗時調用 reject(錯誤)
});
new Promise(…) 創建一個 Promise 對象
里面必須傳一個函數,這個函數有兩個參數:resolve 和 reject
resolve(value) → 表示成功,并把結果 value 傳出去
reject(error) → 表示失敗,并把錯誤傳出去
then ,catch 注是 Promise 對象的方法
then作用是:當 Promise 完成后(resolve),執行的回調函數,then里面會自動接收resolve里面傳入的參數。可以使用多個then把異步操作順序串聯,上一個 then 的返回值作為下一個 then 的輸入
catch作用是:處理 Promise 失敗(reject)或者 then 中拋出的異常。
- 實例對比
//promise
const p1 = new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve("A"), 1000));p1.then(console.log); // 1秒后輸出 "A"
//async
const p1 = new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve("A"), 1000));async function run() {const result = await p1; // 等待 p1 完成,拿到值console.log(result); // 輸出 "A"
}run();
- 在原函數外面再包一層函數來修改或擴展函數
- 節流:限制執行頻率
function throttle(fn,delay){let lastTime =0 return function(...args){const now = Date.now()if(now - lastTime > delay){fn(args)lastTime = now}}
}
// 用法:搜索時 500ms 內只發一次請求
const search = (text) => console.log("查詢數據庫:", text);
const throttledSearch = throttle(search, 500);// 模擬用戶頻繁輸入
throttledSearch("a");
throttledSearch("ab");
throttledSearch("abc");
// 最終只會間隔 >= 500ms 時才真的調用一次 search
- 時間限制:如果某一個函數執行了好久還沒成功,給出失敗提示。
function withTimeout(fn, ms) {return function() {return Promise.race([fn(), // 原函數new Promise((_, reject) => setTimeout(() => reject("超時"), ms))]);};
}// 模擬一個耗時很長的異步任務
const longTask = () => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(() => resolve("完成"), 3000));const safeTask = withTimeout(longTask, 1000);safeTask().then(console.log).catch(console.error);
// 1 秒后報 "超時",不會卡住- 記憶化 (Memoization): 有些函數計算量大,但輸入相同 → 結果其實一樣。下次相同輸入就直接返回緩存。
function memoize(fn) {const cache = {};return function(...args) {const key = JSON.stringify(args);if (cache[key] !== undefined) {return cache[key]; // 從緩存取結果}const result = fn(...args);cache[key] = result;return result;};
}const slowSquare = (n) => {console.log("計算中...");return n * n;
};const fastSquare = memoize(slowSquare);console.log(fastSquare(5)); // "計算中..." 然后 25
console.log(fastSquare(5)); // 直接用緩存 → 25


![[Vid-LLM] 數據集 | 基準測試](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Vid-LLM] 數據集 | 基準測試)
 - /物流與倉儲組件/extended-warehouse-management)




)



[條件隨機場]](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/機器學習 [白板推導](十三)[條件隨機場])



git高階命令分析【結合使用場景】)


