文章目錄
1、
實現string類的接口,并完成測試,要求利用深拷貝和深賦值實現
MyString.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
class MyString {
private:char* data;//儲存字符串內容
public://默認構造函數MyString(const char* str = nullptr);////拷貝構造函數(深拷貝)MyString(const MyString& other);//析構函數~MyString();// 賦值運算符重載MyString& operator=(const MyString& other);//獲取字符串長度int length() const;//獲取c風格字符串const char* c_str() const;//重載[]運算符char& operator[](int index);//重載==操作符bool operator==(const MyString& other) const;////打印字符串void print() const;// 重載 << 操作符(友元函數)friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const MyString& str);
};
MyString.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"MyString.h"
#include<cstring>
MyString::MyString(const char* str )
{if (str == nullptr){ data = new char[1];data[0] = '\0';}else{data = new char[strlen(str)+1];strcpy(data, str);}
}MyString::MyString(const MyString& other) {// strcpy(data, other.data); // 把 other 的字符串內容復制過來//注意:將對象 other 中的字符串內容(other.data)完整地復制到當前對象的 data 成員變量中。data = new char[strlen(other.data)+1];strcpy(data, other.data);
}MyString::~MyString()
{delete[] data;
}MyString& MyString:: operator=(const MyString& other)
{if (this == &other) return *this;//如果this和other的地址相同,返回other這個值MyString::~MyString();data = new char[strlen(other.data) + 1];strcpy(data, other.data);return *this;
}
void MyString::print() const
{std::cout << data ;
}//獲取字符串長度
int MyString ::length() const
{return static_cast<int>(strlen(data));
}//獲取c風格字符串
const char* MyString::c_str() const
{return data;
}
//重載[]運算符
char& MyString::operator[](int index)
{if (index<0 || index>strlen(data)){throw std::out_of_range("Index out of range");}return data[index];
}
//重載==操作符
bool MyString::operator==(const MyString& other) const
{return strcmp(data, other.data)==0;
}// 重載 << 操作符(友元函數)
std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const MyString& str)
{os << str.data;return os;
}test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"MyString.h"
int main()
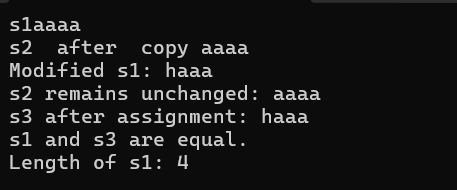
{////默認構造函數MyString s1("aaaa");std::cout << "s1";s1.print();std::cout << std::endl;////拷貝構造函數(深拷貝)MyString s2 = s1;std::cout << "s2 after copy ";s2.print();std::cout << std::endl;// 修改原對象不應影響拷貝對象s1[0] = 'h'; // 使用 [] 運算符修改 s1 的第一個字符std::cout << "Modified s1: " << s1 << std::endl;std::cout << "s2 remains unchanged: " << s2 << std::endl;// 測試賦值操作符MyString s3;s3 = s1;std::cout << "s3 after assignment: " << s3 << std::endl;// 測試比較操作符if (s1 == s3) {std::cout << "s1 and s3 are equal." << std::endl;}// 測試長度std::cout << "Length of s1: " << s1.length() << std::endl;return 0;
}
遇到的問題:
實現MyString
1、data = new char[空間+1](必須是data)
2、strcpy(目標,舊文件)
3、 析構 delete[] data;
4、 strcpy(data, other.data); // 把 other 的字符串內容復制過來
注意:將對象 other 中的字符串內容(other.data)完整地復制到當前對象的 data 成員變量中。
5、return static_cast(strlen(data));
static_cast 的作用
static_cast 是 C++ 的顯式類型轉換運算符,用于在編譯時進行安全的類型轉換。
這里將 size_t(無符號)轉換為 int(有符號),可能出于以下原因:
兼容性:某些舊代碼或接口可能要求 int 類型的長度。
明確意圖:開發者明確知道字符串長度不會超過 INT_MAX(int 的最大值),并希望消除編譯器關于有符號/無符號比較的警告。
6、const char* MyString::c_str() const {
return data;
}
返回類型 const char*
返回一個指向常量字符(const char)的指針,意味著調用者不能通過該指針修改字符串內容。
這是為了保護 MyString 內部數據(data)不被意外修改。
函數名 c_str()
模仿 C++ 標準庫 std::string 的接口,用于返回一個 C 風格字符串(以 \0 結尾的字符數組)。
通常用于與其他 C 風格字符串接口兼容(如 printf、文件操作等)。
const 修飾符(函數末尾)
表示這是一個常量成員函數,即該函數不會修改類的任何成員變量(除非成員被聲明為 mutable)。
允許在 const MyString 對象上調用此函數。
7、throw std::out_of_range(“Index out of range”); 的作用是 拋出一個 C++ 標準庫中的 std::out_of_range 異常,通常用于表示某個索引(下標)超出了有效范圍。
8、 os << str.data; // 將 MyString 內部的字符數據(data)輸出到流 os
return os; // 返回流對象,支持鏈式調用(如 cout << a << b)
9.友元函數// 重載 << 操作符(友元函數)
friend std::ostream& operator<<(std::ostream& os, const MyString& str);
以上就是今天練習的內容。。



 原型與原型鏈)














)
