目錄
代碼實現
添加到初始化上
上電看現象
掛載分區可能是一些朋友不理解的——實際上掛載就是將我們的文件系統封裝好了的設備(硬盤啊,SD卡啊,U盤啊等等),掛到我們的默認分區路徑下。這樣我們就能訪問到了(嘿!想象你是一個螞蟻,別人把葡萄掛到了樹枝上,然后你就可以爬著訪問到了)
文件系統的掛載和卸載在Linux中是非常重要的功能,它允許用戶將一個分區的文件系統與另一個分區的目錄樹連接起來。通常情況下,Linux會將根分區作為默認分區,并通過mount命令將其他分區掛載到默認分區的某個目錄上。在這個過程里,分區的根目錄是固定存在的,其他分區盡管有自己的根目錄,但它們的根目錄并不直接與整個系統的文件結構掛鉤。通過mount命令,其他分區可以在需要時被掛載到指定的目錄下,而默認分區的根目錄則作為所有分區的父目錄,掛載后形成一個統一的路徑樹結構。
對于掛載操作系統到裸盤的情況,并沒有現成的分區和文件系統。這時,為了實現文件操作,首先必須在裸盤上創建文件系統,至少要實現基本的文件寫入功能。然后,操作系統可以通過文件系統進行安裝。例如,在Windows或Linux系統安裝過程中,首先會選擇目標分區,格式化并安裝操作系統到文件系統中。對于學習操作系統實現的場景,雖然也可以模仿這一過程,但為了簡化操作,一開始可以避免復雜的分區掛載過程。
實現分區掛載的本質是通過讀取硬盤上的元信息并將其加載到內存中,這樣,所有硬盤資源的使用情況都能通過內存中的元信息進行管理。當執行寫操作時,內存中的數據需要及時同步到硬盤,確保數據的一致性和持久性
代碼實現
/* Finds the partition named 'part_name' in the partition list and assigns its * pointer to 'cur_part' */
static bool mount_partition(list_elem *pelem, int arg) {// Convert the argument to a partition name stringchar *part_name = (char *)arg;// Retrieve the DiskPartition structure from the list elementDiskPartition *part = elem2entry(DiskPartition, part_tag, pelem);
?// If the partition name matches, mount this partitionif (!k_strcmp(part->name, part_name)) {cur_part = part; // Set the current partition to the found partitionDisk *hd = cur_part->my_disk; // Get the disk that contains this partition
?// Allocate a buffer to temporarily store the superblock read from diskSuperBlock *sb_buf = (SuperBlock *)sys_malloc(SECTOR_SIZE);
?// Allocate memory for the superblock of the current partitioncur_part->sb = (SuperBlock *)sys_malloc(sizeof(SuperBlock));if (!cur_part->sb) {KERNEL_PANIC_SPIN("alloc memory failed!"); // Kernel panic if allocation fails}
?// Read the superblock from disk into the bufferk_memset(sb_buf, 0, SECTOR_SIZE);ide_read(hd, cur_part->start_lba + 1, sb_buf, 1);
?// Copy the superblock information from the buffer to the partition's superblockk_memcpy(cur_part->sb, sb_buf, sizeof(SuperBlock));
?/********** Load the block bitmap from disk into memory **********/// Allocate memory for the block bitmapcur_part->block_bitmap.bits = (uint8_t *)sys_malloc(sb_buf->block_bitmap_sects * SECTOR_SIZE);if (!(cur_part->block_bitmap.bits)) {KERNEL_PANIC_SPIN("alloc memory failed!"); // Kernel panic if allocation fails}// Set the length of the block bitmap in bytescur_part->block_bitmap.btmp_bytes_len = sb_buf->block_bitmap_sects * SECTOR_SIZE;// Read the block bitmap from disk into memoryide_read(hd, sb_buf->block_bitmap_lba, cur_part->block_bitmap.bits, sb_buf->block_bitmap_sects);/****************************************************************/
?/********** Load the inode bitmap from disk into memory **********/// Allocate memory for the inode bitmapcur_part->inode_bitmap.bits = (uint8_t *)sys_malloc(sb_buf->inode_bitmap_sects * SECTOR_SIZE);if (!(cur_part->inode_bitmap.bits)) {KERNEL_PANIC_SPIN("alloc memory failed!"); // Kernel panic if allocation fails}// Set the length of the inode bitmap in bytescur_part->inode_bitmap.btmp_bytes_len = sb_buf->inode_bitmap_sects * SECTOR_SIZE;// Read the inode bitmap from disk into memoryide_read(hd, sb_buf->inode_bitmap_lba, cur_part->inode_bitmap.bits, sb_buf->inode_bitmap_sects);/****************************************************************/
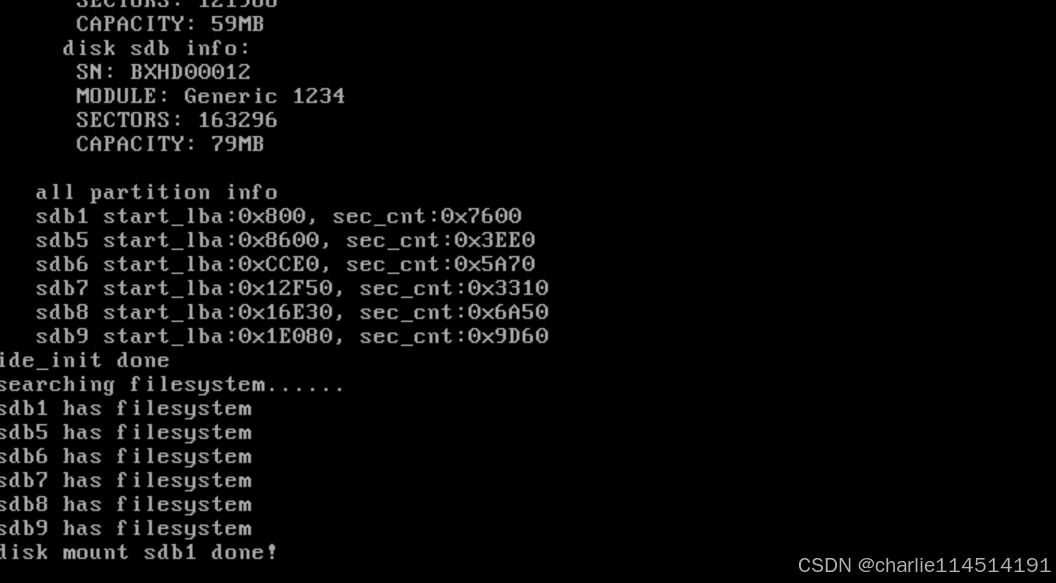
?// Initialize the list of open inodes in this partitionlist_init(&cur_part->open_inodes);verbose_printk("disk mount %s done!\n", part->name); // Print a message indicating successful mounting
?// Return true to stop further traversal, as the partition has been found and mountedreturn true;}return false; // Continue traversing the list if the partition was not found
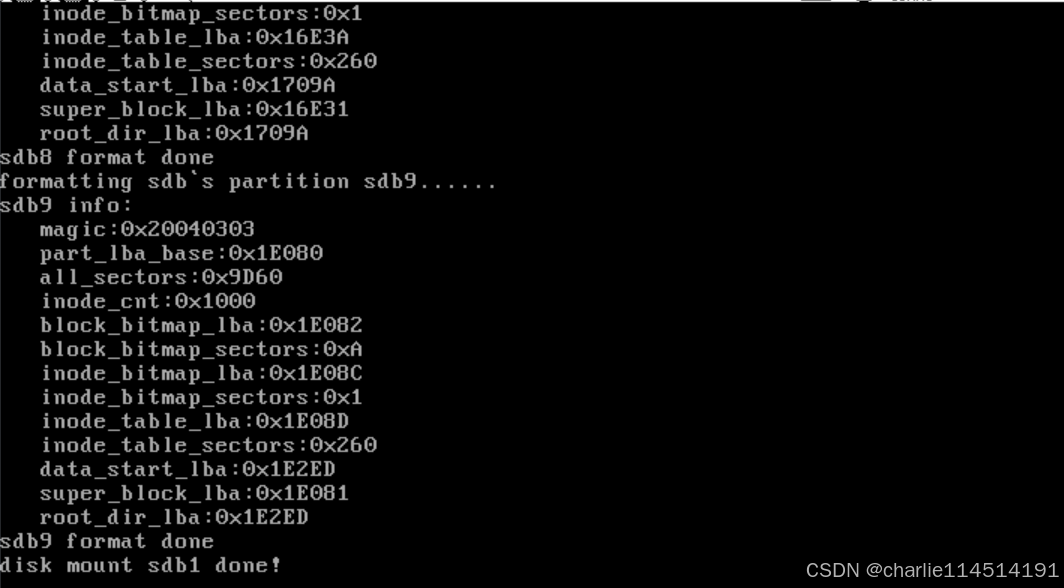
}mount_filesystem函數就是完成了文件系統中掛載默認分區并加載其元信息的過程。默認分區的名稱為 default_part,其值為 sdb1,表示默認操作的分區是 sdb1。分區掛載通過 list_traversal 函數完成,該函數遍歷分區列表 partition_list,并對每個分區調用回調函數 mount_partition,傳入的參數是 default_part 的地址轉換為整型后的值。mount_partition 是 list_traversal 的回調函數,其功能是在分區鏈表中找到與傳入的分區名匹配的分區,并將其指針賦值給全局變量 cur_part,用于記錄當前操作的分區。
在 mount_partition 函數中,首先將傳入的參數 arg 還原為字符指針 part_name,然后通過宏 elem2entry 將 pelem 還原為分區結構體 part。接著,通過 strcmp 比對 part->name 和 part_name,如果匹配則找到目標分區,并將其指針賦值給 cur_part。隨后,獲取該分區所在的硬盤 hd,作為后續硬盤操作的參數。
接下來,系統為超級塊申請內存緩沖區 sb_buf,并從硬盤中讀取超級塊信息到 sb_buf,然后將有用的超級塊信息復制到 cur_part->sb 中,忽略填充部分以節省內存。之后,為塊位圖申請內存,并根據超級塊中的 block_bitmap_sects 初始化塊位圖的大小,最后將硬盤上的塊位圖讀入內存。類似地,系統還會加載 inode 位圖到內存中。整個過程確保了分區的元信息被正確加載,并為后續的文件系統操作做好準備。
添加到初始化上
.../* Determine the default partition for operations */char default_part[8] = "sdb1";/* Mount the partition */list_traversal(&partition_list, mount_partition, (int)default_part);上電看現象
下一篇
從0開始的操作系統手搓教程34:說說文件描述符與常見的操作和文件基本操作-CSDN博客文章瀏覽閱讀614次,點贊4次,收藏13次。我們還需要打開根目錄并初始化文件表// filesystem_init函數下追加:??*/return ret;函數將本地文件描述符轉換為全局文件表索引。首先,它獲取當前任務的文件描述符表,然后根據傳入的本地文件描述符返回對應的全局文件描述符索引。sys_close函數用于關閉文件。首先,它檢查文件描述符是否大于2(標準輸入、輸出和錯誤文件描述符不處理)。然后,調用將本地文件描述符轉換為全局文件描述符,并嘗試關閉文件。如果成功,更新任務的文件描述符表并返回0;否則,返回-1。https://blog.csdn.net/charlie114514191/article/details/146143441











)






