一. JDBC式編程
在 jdbc 編程中,我們最常用的是 PreparedStatement 式的編程,我們看下面這個例子;
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement ps = null;
ResultSet rs = null;try {// 1. 注冊驅動Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");// 2. 獲取連接String url = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/zhuce?serverTimezone=UTC";String user = "root";String password = "19991121zq";conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);String sql = "select * from t_user order by id ?";// 3. 獲取數據庫連接對象ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql);ps.setString(1, keyWords);// 4. 執行 sql 語句rs = ps.executeQuery();// 5. 處理查詢結果集while(rs.next()){System.out.println(rs.getInt("id"));}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {throwables.printStackTrace();
} finally {//6.關閉資源if (rs != null) {try {rs.close();} catch (SQLException throwables) {throwables.printStackTrace();}}if (ps != null) {try {rs.close();} catch (SQLException throwables) {throwables.printStackTrace();}}if (conn != null) {try {rs.close();} catch (SQLException throwables) {throwables.printStackTrace();}}
}
二. 解析Configuration
如果我們的 mybatis 配置文件使用 xml 的方式,沒有使用 Spring yaml 配置項的形式,可以通過 XMLMapperBuilder 來看解析 Configuration 的過程;
//---------------------------------XMLConfigBuilder----------------------------
public Configuration parse() {// 確保每個 xml 配置文件只被解析一次if (parsed) {throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");}parsed = true;// 解析 xml 配置文件中的根節點: configurationparseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));return configuration;
}//---------------------------------XMLConfigBuilder-----------------------------
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {try {// 可以看出順序是固定好的propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));loadCustomVfs(settings);loadCustomLogImpl(settings);typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));// 解析 plugins 標簽pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));// 解析 MetaObject 中會使用到的幾個 Factory,了解objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));settingsElement(settings);// 解析 environments 標簽environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));// 解析 mappers 標簽// 我們主要看此處mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));} catch (Exception e) {throw new BuilderException();}
}
1. 解析mappers
我們為什么要重點看解析 mappers 的地方,因為這里有一個很重要的對象 MappedStatement,我們在 Executor 中全程都會使用到該對象;
我們簡單看下:
//-----------------------------XMLMapperBuilder-----------------------------
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {try {String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");}builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));// 解析 mapper 標簽中的 select|insert|update|delete 標簽// 會把每個 select、update 等解析成一個個 MappedStatement 對象buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));} catch (Exception e) {//...}
}//-----------------------------XMLMapperBuilder-----------------------------
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());}buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}//-----------------------------XMLMapperBuilder-----------------------------
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {for (XNode context : list) {XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context);try {// 開始解析 select、update、insert 成 MappedStatementstatementParser.parseStatementNode();} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);}}
}
我們以如下 StudentMapper.xml 為例來看 MappedStatement 的生成;
該 select 標簽的 id 為 “selectStudent”,namespace 為 “com.bjpowernode.dao.StudentDao”;
<mapper namespace="com.bjpowernode.dao.StudentDao"><select id="selectStudent" resultType="com.bjpowernode.domain.Student">select id,name,email,age from student where id=#{id}</select></mapper>
解析如上的 select 標簽如下:
// --------------------------- XMLStatementBuilder -------------------------
public void parseStatementNode() {// 1. 此時該 id = "selectStudent"String id = context.getStringAttribute("id");// ...// 2. 生成 SqlSource 對象// 該 sqlSource 包含了原始sql、參數映射等SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, context, parameterTypeClass);Integer fetchSize = context.getIntAttribute("fetchSize");Integer timeout = context.getIntAttribute("timeout");String parameterMap = context.getStringAttribute("parameterMap");String resultType = context.getStringAttribute("resultType");Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveClass(resultType);String resultMap = context.getStringAttribute("resultMap");String resultSetType = context.getStringAttribute("resultSetType");ResultSetType resultSetTypeEnum = resolveResultSetType(resultSetType);String keyProperty = context.getStringAttribute("keyProperty");String keyColumn = context.getStringAttribute("keyColumn");String resultSets = context.getStringAttribute("resultSets");// 3. 調用 builderAssistant 協助創建 MappedStatement 對象builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id, sqlSource, statementType, sqlCommandType, fetchSize, timeout, parameterMap, parameterTypeClass, resultMap, resultTypeClass,resultSetTypeEnum, flushCache, useCache, resultOrdered,keyGenerator, keyProperty, keyColumn, databaseId, langDriver, resultSets);
}// --------------------------- XMLStatementBuilder -------------------------
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(String id, SqlSource sqlSource, StatementType statementType,SqlCommandType sqlCommandType, Integer fetchSize, Integer timeout,String parameterMap, Class<?> parameterType, String resultMap,Class<?> resultType, ResultSetType resultSetType, boolean flushCache,boolean useCache, boolean resultOrdered, KeyGenerator keyGenerator,String keyProperty, String keyColumn, String databaseId,LanguageDriver lang, String resultSets) {// 1. 重新生成 id// 此時的 id = id + namespace// 也就是 id = "com.bjpowernode.dao.StudentDao.selectStudent"id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlSource, sqlCommandType).resource(resource).fetchSize(fetchSize).timeout(timeout).statementType(statementType).keyGenerator(keyGenerator).keyProperty(keyProperty).keyColumn(keyColumn).databaseId(databaseId).lang(lang).resultOrdered(resultOrdered).resultSets(resultSets).resultMaps(getStatementResultMaps(resultMap, resultType, id)).resultSetType(resultSetType).flushCacheRequired(valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect)).useCache(valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect)).cache(currentCache);ParameterMap statementParameterMap = getStatementParameterMap(parameterMap, parameterType, id);if (statementParameterMap != null) {statementBuilder.parameterMap(statementParameterMap);}// 2. 創建出 MappedStatement 對象MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();// 3. 將當前 MappedStatement 對象加入到 configuration 配置類中configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);return statement;
}// ----------------------------- Configuration --------------------------------
public void addMappedStatement(MappedStatement ms) {// 將 MappedStatement 對象放入到 configuration 中的 mappedStatements 中// mappedStatements 是一個 Map 對象,可以看到 key 是 MappedStatement.idmappedStatements.put(ms.getId(), ms);
}
可以把 MappedStatement 認為是一條 select、insert、update 等標簽的映射對象;
我們看下 SqlSource 和 MappedStatement 對象,MappedStatement 對象中聚合了 SqlSource 對象;共同點是兩個對象中都聚合了 Configuration 對象;
SqlSource;

MappedStatement;

三. Executor執行器
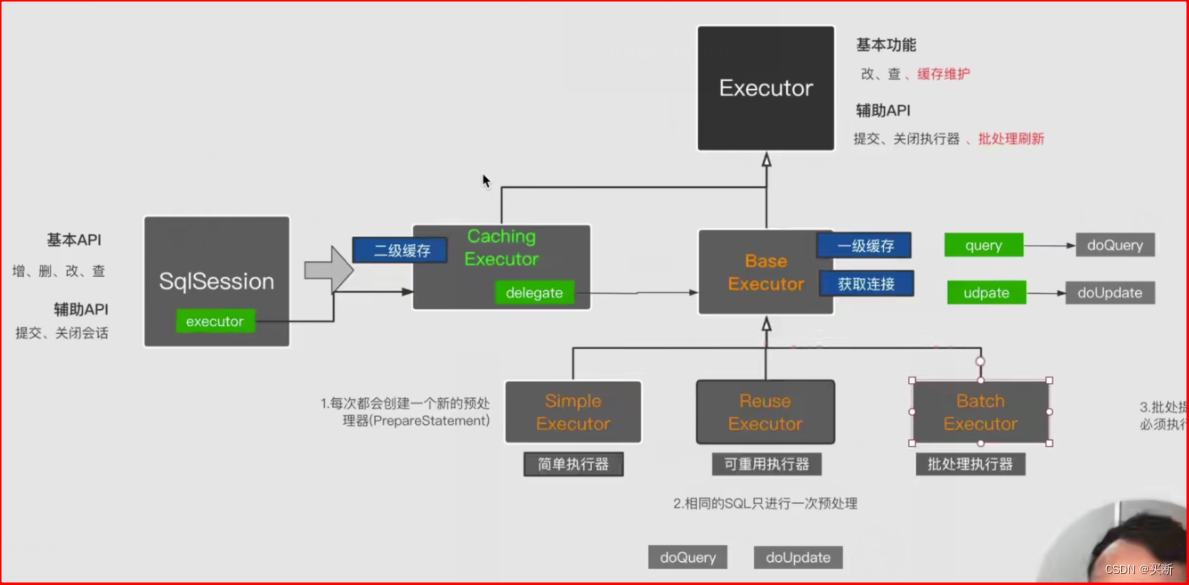
1. Executor執行器的種類
對于 Executor,我們需要知道一點,SqlSession 只是門面而已,它聚合了一個 Executor 對象,真正執行 sql 的是 Executor 而非 SqlSession;
- CachingExecutor:處理二級緩存,采用了裝飾者模式;CachingExecutor 也實現了 Executor 接口,并且內部聚合了一個 BaseExecutor 的實現類;
- BaseExecutor:處理一級緩存,它是一個抽象類,其他的 Executor 都是繼承自該類;
- 該類定義了一個抽象方法如 query(),真正執行查詢邏輯的是子類的 doQuery();
- 該類最大的作用就是用來執行一級緩存的查詢,該執行器聚合了一個一級緩存 Cache;
- SimpleExecutor:簡單執行器,默認使用的是這個執行器,我們重點關注這個;
- ReuseExecutor:可重用的執行器;
- BatchExecutor:批處理的執行器;
類圖如下:
2. Executor和SqlSession的對應關系
一個 SqlSession 對應一個 Executor;每創建一個 SqlSession,都會創建一個對應的 Executor 對象;
這時為啥呢?我們直接看 DefaultSqlSessionFactory.openSession() 創建 SqlSession 對象的方法就知道了;
// ------------------------ DefaultSqlSessionFactory -------------------------
public SqlSession openSession(ExecutorType execType) {return openSessionFromDataSource(execType, null, false);
}// ------------------------ DefaultSqlSessionFactory -------------------------
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);Transaction tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);// 1. 通過 configuration 創建出 Executor 對象Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);// 2. 根據 executor 創建出 SqlSession 對象return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
}// ----------------------------- Configuration -------------------------------
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;Executor executor;// 1. 根據 executorType 的類型創建出不同的 Executor 對象if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);} else {executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);}// 如果開啟了二級緩存的話,還會包裝一層,包裝為 CachingExecutorif (cacheEnabled) {executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);}// 2. 如果需要插件增強的話,給 executor 做一層增強,并返回增強后的 executor 對象executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);return executor;
}
四. 一級緩存
1. 一級緩存PerpetualCache
一級緩存是在 BaseExecutor 類中作為成員變量存在的;
// ------------------------- BaseExecutor -----------------------------
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(BaseExecutor.class);protected Transaction transaction;protected Executor wrapper;protected ConcurrentLinkedQueue<DeferredLoad> deferredLoads;// localCache 就是我們常說的一級緩存// 可以看到它是一個 PerpetualCache 類對象protected PerpetualCache localCache;protected PerpetualCache localOutputParameterCache;protected Configuration configuration;protected int queryStack;private boolean closed;// ...
}
我們看下這個 PerpetualCache 類;
可以看到它內部有一個 HashMap,非常簡單,Mybatis 的一級緩存可以看做就是一個簡單的 HashMap;
public class PerpetualCache implements Cache {private final String id;private Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<>();public PerpetualCache(String id) {this.id = id;}@Overridepublic void putObject(Object key, Object value) {cache.put(key, value);}@Overridepublic Object getObject(Object key) {return cache.get(key);}@Overridepublic Object removeObject(Object key) {return cache.remove(key);}@Overridepublic void clear() {cache.clear();}
}
2. 一級緩存的命中場景
一級緩存生效的幾個條件,其實和 CacheKey 有關:
1、mappedStatementId 必須一樣;
2、sql 必須一樣;
3、RowBounds.offset 分頁 offset 必須一樣;
4、RowBounds.limit 分頁 limit 必須一樣;
5、查詢參數 param 必須一樣;
6、enviroment 環境參數必須一樣,Mybatis 配置文件里的 enviroment,一般都是唯一值;
舉例如下:
public static void test1(){StudentDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);// 1. sql和參數相同Student student = mapper.selectStudent(1001);Student student1 = mapper.selectStudent(1001);System.out.println(student == student1); //true// 2. 必須是相同的 statementId// com.bjpowernode.dao.StudentDao.selectById// com.bjpowernode.dao.StudentDao.selectById3Student student2 = mapper.selectById(1001);Student student3 = mapper.selectById3(1001);System.out.println(student2 == student3); //false// 3. sqlSession 必須一樣// 嚴格來說應該是 sqlSession 里的 Executor 必須一樣// 因為一級緩存 cache 是在 Executor 里的// 調用 openSession() 會創建出新的 DefaultSqlSession 和 Executor 對象Student s4 = mapper.selectById(1001);Student s5 = factory.openSession().getMapper(StudentDao.class).selectById3(1001);System.out.println(s4 == s5); //false// 4. RowBounds 返回行的范圍必須相同// RowBounds 的默認值是:RowBounds.DEFAULTStudent student6 = mapper.selectById(1001);String statementId = "com.bjpowernode.dao.StudentDao.selectById";RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(0, 10);List<Student> stus = sqlSession.selectList(statementId, 1001, rowBounds);System.out.println(student6 == stus.get(0)); //false
}
2.1 CacheKey
我們上面講的緩存命中場景,其實都是和 CacheKey 有關的,下面我們簡單看下這個生成 CacheKey 類對象的地方;
// ------------------------------ BaseExecutor --------------------------------
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);// 生成 CacheKey 對象CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}// ------------------------------ BaseExecutor --------------------------------
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();// 1. mappedStatementIdcacheKey.update(ms.getId());// 2. RowBounds.offsetcacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());// 3. RowBounds.limitcacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());// 4. sqlcacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());// ....// 5. 參數 paramsif (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {// 6. environmentcacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());}return cacheKey;
}
可以看到 CacheKey 和 6 個變量的值有關,我們舉一個例子看看:

3. 一級緩存的失效場景
一級緩存的失效,大致有以下幾種場景:
1、手動清空了一級緩存 cache:sqlSession 的 clearCache()、commit()、rollback() 都會清空一級緩存;
2、執行了 sqlSession.update(),只要執行了 sqlSession.update(),都會清空一級緩存,因為 update() 方法中會做一個清空一級緩存的動作;
3、全局將一級緩存的作用域改為了 STATEMENT,默認是 SESSION 級別的,也就是默認是 SqlSession 級別的;了解即可;
舉例如下:
public static void test2(){StudentDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);// 1. 手動清空一級緩存Student student = mapper.selectById(1001);sqlSession.clearCache();// sqlSession.commit();// sqlSession.rollback();Student student1 = mapper.selectById(1001);System.out.println(student == student1); // false// 2.執行了 sqlSession.update()// 只要執行過 update 語句,都會清空當前一級緩存Student student2 = mapper.selectById3(1001);mapper.updateStudent(1002,"zq");Student student3 = mapper.selectById3(1001);System.out.println(student2 == student3; // false
}
4. 一級緩存的調用流程
從上面我們知道一級緩存是在 BaseExecutor 中的,我們直接看 BaseExecutor 的 query();
// ------------------------------ BaseExecutor --------------------------------
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {// 如果當前為第一次調用,且當前 MappedStatement 需要清空緩存,則清空一級緩存// queryStack 是用于嵌套子查詢的,后面會講clearLocalCache();}List<E> list;try {queryStack++;// 1. 先去一級緩存中查,如果緩存中有值直接返回list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;if (list != null) {handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);} else {// 2. 一級緩存中沒有值,去查數據庫list = queryFromDatabase(ms,parameter,rowBounds,resultHandler,key, boundSql);}} finally {queryStack--;}if (queryStack == 0) {if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {// 如果當前的緩存范圍是 STATEMENT, 執行完查詢后清空緩存clearLocalCache();}}return list;
}// ------------------------------ BaseExecutor --------------------------------
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {List<E> list;// 1. 將 key 和對應的占位符放入一級緩存localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);try {// 2. 調用 doQuery() 獲取查詢結果list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);} finally {// 3. 將 key 對應的占位符移除localCache.removeObject(key);}// 4. 將查詢結果放入一級緩存localCache.putObject(key, list);// 5. 返回查詢結果return list;
}// ------------------------------ BaseExecutor --------------------------------
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {// 1. 先清空一級緩存// 為什么說執行了 sqlSession.update() 一級緩存會失效,因為會先清空一級緩存clearLocalCache();// 2. 執行 doUpdate() 并返回值return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
五. 二級緩存
二級緩存是在 CachingExecutor 中的,二級緩存和一級緩存不一樣,二級緩存需要開啟才會使用;
我們暫時不去看二級緩存,了解即可;
六. StatementHandler
1. 種類和結構
StatementHandler 的種類和結構大致如下:
我們主要看 PreparedStatementHandler 這個對象:創建 PreparedStatement、設置參數,執行 sql 都是咋 StatementHandler 中執行的;

2. 分析
我們直接進入到 SimpleExecutor 的 doQuery();
// ------------------------- SimpleExecutor -------------------------------
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter,RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {Statement stmt = null;try {Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();// 1. 創建出 StatementHandler 對象StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);// 2. 得到預編譯對象 PreparedStatement// 該方法還會進行參數的映射和設置stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());// 3. 通過 statementHandler.query() 執行 sqlreturn handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);} finally {closeStatement(stmt);}
}
下面我們對 doQuery() 中三個步驟做簡要分析;
2.1 創建出StatementHandler對象
通過 Configuration 對象創建出 StatementHandler 對象;
// ------------------------- Configuration -------------------------------
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {// 1. 創建出 RoutingStatementHandler// 這里又是裝飾器模式// 其實 RoutingStatementHandler 中真正作用的是 PreparedStatementHandlerStatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);// 2. 插件增強statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);return statementHandler;
}// ------------------------- RoutingStatementHandler -----------------------------
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {switch (ms.getStatementType()) {case STATEMENT:delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);break;case PREPARED:// 默認創建的就是 PreparedStatementHandler 對象// 這里又是裝飾器模式delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);break;case CALLABLE:delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);break;default:throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type");}}
2.2 得到PreparedStatement對象
我們看一下 prepareStatement() 干了啥;
// ------------------------- SimpleExecutor -------------------------------
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) {Statement stmt;Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);// 1. 執行 PreparedStatementHandler.prepare() 獲得 PreparedStatementHandler 對象stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());// 2. 對參數進行映射處理和設值// 這里后面我們會重點看!!!handler.parameterize(stmt);return stmt;
}// ------------------------- BaseStatementHandler -------------------------------
public Statement prepare(Connection connection, Integer transactionTimeout) throws SQLException {ErrorContext.instance().sql(boundSql.getSql());Statement statement = null;try {// 實例化 statement 對象statement = instantiateStatement(connection);setStatementTimeout(statement, transactionTimeout);setFetchSize(statement);return statement;} catch (Exception e) {closeStatement(statement);throw new ExecutorException("Error preparing statement. Cause: " + e, e);}
}// ------------------------- PreparedStatementHandler -----------------------------
protected Statement instantiateStatement(Connection connection) throws SQLException {String sql = boundSql.getSql();if (mappedStatement.getKeyGenerator() instanceof Jdbc3KeyGenerator) {// ...} else if (mappedStatement.getResultSetType() == ResultSetType.DEFAULT) {// 直接執行 connection.prepareStatement(sql)// 預編譯 sql 得到 PreparedStatement 對象// 這里就是我們 jdbc 中預編譯得到 PreparedStatement 的方式return connection.prepareStatement(sql);} else {// ...}
}
2.3 執行statementHandler.query()
我們簡單看下 statementHandler.query() 干了啥;
public <E> List<E> query(Statement statement, ResultHandler resultHandler) {PreparedStatement ps = (PreparedStatement) statement;// 1. 直接執行 ps.execute()ps.execute();// 2. 通過 resultSetHandler 處理結果集return resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
}
七. Mapper代理類對象
1. UserMapper分析
Spring 為我們生成的 UserMapper 是一個代理類;我們在分析 Mybatis 集成 Spring 后一級緩存失效的場景中已經給 UserMapper 做過一個分析了,我們直接看 UserMapper 的結構;
1、這個 UserMapper 是一個代理類,它的 InvocationHandler 是 MapperProxy 類;
2、MapperProxy 內聚合了一個 SqlSessionTemplate 類,SqlSessionTemplate 實現了 SqlSession 類;
3、MapperProxy 的 invoke() 最終會調用目標類 sqlSessionTemplate 的方法;
4、SqlSessionTemplate 內聚合了一個 sqlSessionProxy,sqlSessionProxy 也是一個代理類,它實現了 SqlSession 類,它的 invocationHandler 是 SqlSessionInterceptor 類;
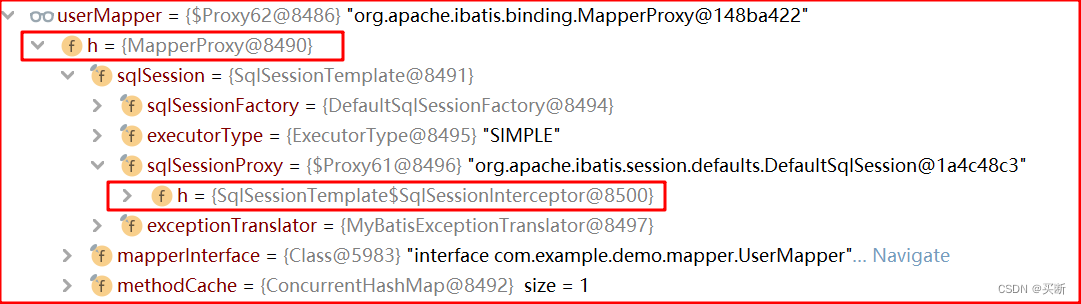
類圖分析如下,其實代理的目標類是 SqlSession,也就是說干活的類是 SqlSession;
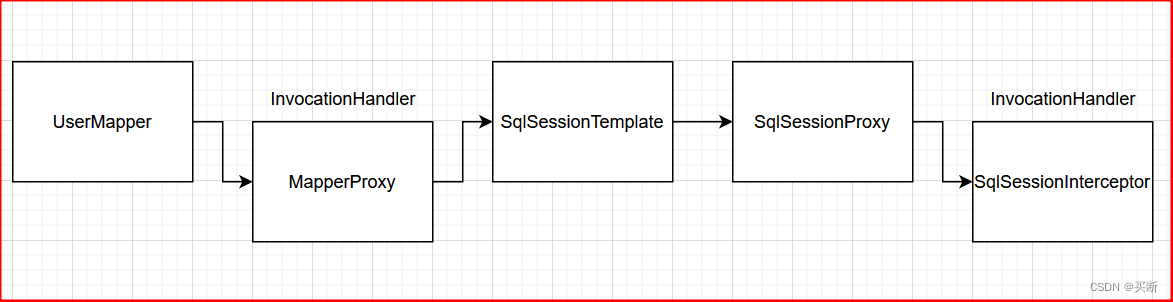
需要注意兩個 InvocationHandler:MapperProxy 和 SqlSessionInterceptor,SqlSessionInterceptor 我們在一級緩存失效的場景中分析過了,這次我們重點看 MapperProxy;
2. MapperProxy
單看 MapperProxy 這個類名,可能認為它是一個代理類對象,其實它是一個 InvocationHandler 對象,我們看下它的 invoke();
// ------------------------------- MapperProxy ---------------------------------
public class MapperProxy<T> implements InvocationHandler {private static final long serialVersionUID = -6424540398559729838L;private final SqlSession sqlSession;private final Class<T> mapperInterface;private final Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache;public MapperProxy(SqlSession sqlSession, Class<T> mapperInterface, Map<Method, MapperMethod> methodCache) {this.sqlSession = sqlSession;this.mapperInterface = mapperInterface;this.methodCache = methodCache;}@Overridepublic Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) {try {if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {return method.invoke(this, args);} else if (isDefaultMethod(method)) {return invokeDefaultMethod(proxy, method, args);}} catch (Throwable t) {throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);}// 1. 創建或從緩存中得到 MapperMethod 對象final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);// 2. 執行 mapperMethod.execute()return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);}
}
主要是執行 MapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
我們先看下 MapperMethod 的結構,其中 paramNameResolver 用于解析參數對象,后面我們會重點看;
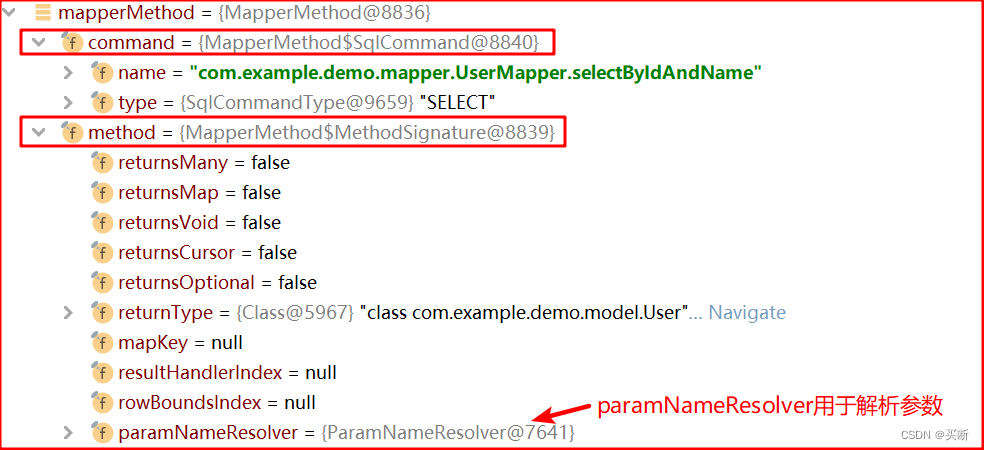
mapperMethod.execute() 如下:
// ------------------------------- MapperMethod ---------------------------------
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {Object result;switch (command.getType()) {case INSERT: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));break;}case UPDATE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));break;}case DELETE: {Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));break;}case SELECT:if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {// ...} else {// 我們直接看這個地方// 1. 處理參數 Object[] args,得到處理后的參數 Object paramObject param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);// 2. 調用 sqlSession.selectxxx() 得到 result// 可以看到參數已經是我們上面得到的 param,不再是 args 了result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);if (method.returnsOptional()&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {result = Optional.ofNullable(result);}}break;case FLUSH:result = sqlSession.flushStatements();break;default:throw new BindingException();}if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {throw new BindingException();}return result;
}// ------------------------------- MethodSignature ---------------------------------
public Object convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(Object[] args) {// 調用 paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args) 解析得到新的參數對象return paramNameResolver.getNamedParams(args);
}
參數解析是在 ParamNameResolver 中做的,我們重點看下 ParamNameResolver;
2.1 參數解析ParamNameResolver
2.1.1 構造函數
我們先看下它的構造函數;
// ------------------------- ParamNameResolver ---------------------------
public ParamNameResolver(Configuration config, Method method) {final Class<?>[] paramTypes = method.getParameterTypes();final Annotation[][] paramAnnotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();final SortedMap<Integer, String> map = new TreeMap<>();int paramCount = paramAnnotations.length;// 輪詢解析方法中的參數for (int paramIndex = 0; paramIndex < paramCount; paramIndex++) {if (isSpecialParameter(paramTypes[paramIndex])) {continue;}String name = null;// 1. 如果該參數前有 @Param 注解,name 值為 @Param 注解的 value 值for (Annotation annotation : paramAnnotations[paramIndex]) {if (annotation instanceof Param) {// 方法參數上有 @Param 注解的情況下,hasParamAnnotation 置為 truehasParamAnnotation = true;name = ((Param) annotation).value();break;}}// 2. 如果參數前沒有 @Param 注解if (name == null) {// 3. 默認情況下 Mybatis 中 config 的 useActualParamName 默認值為 true// 所以默認情況下 name 值為方法參數名if (config.isUseActualParamName()) {name = getActualParamName(method, paramIndex);}if (name == null) {name = String.valueOf(map.size());}}// map 中值的形式如 {{0, "id"}, {1, "name"}}map.put(paramIndex, name);}// 4. names 也是一個 Map,所以 names 中值的形式如 {{0, "id"}, {1, "name"}}names = Collections.unmodifiableSortedMap(map);
}
names 的值跟有無 @Param 注解有關,我們可以看如下場景中 names 的值;
1、沒有 @Param 注解,但是給 Java 加上了 -parameters,names 值為:{{0, “id”}, {1, “username”}}
2、沒有 @Param 注解,沒有給 Java 加上了 -parameters,names 值為:{{0, “arg0”}, {1, “arg1”}}
User selectByIdAndName(int id, String username);
3、有 @Param 注解,names 值為:{{0, “id”}, {1, “name”}}
User selectByIdAndName(int id, @Param("name") String username);
2.1.2 參數解析
我們再看它的參數解析方法:getNamedParams();
// ------------------------- ParamNameResolver ---------------------------
public Object getNamedParams(Object[] args) {int paramCount = names.size();if (args == null || paramCount == 0) {return null;} else if (!hasParamAnnotation && paramCount == 1) {// 1. 如果方法參數沒有 @Param 注解,且只有一個參數// 直接返回該參數,不做任何處理return args[names.firstKey()];} else {// 2. 此時,參數前有 @Param 注解 || 參數不止一個// 創建一個 Map<String, Object> param,該 Map 的類型為 ParamMapfinal Map<String, Object> param = new ParamMap<>();int i = 0;// 3. 遍歷我們構造函數中得到的 names, 構造 paramfor (Map.Entry<Integer, String> entry : names.entrySet()) {// 3.1 給 param 添加值// {names.entry.value0, arg[0]}, {names.entry.value1, arg[1]}param.put(entry.getValue(), args[entry.getKey()]);// 3.2 再往 param 中添加 {"param1":args[0]}, {"param2":args[1]}String genericParamName = "param" + String.valueOf(i + 1);if (!names.containsValue(genericParamName)) {param.put(genericParamName, args[entry.getKey()]);}i++;}// 4. 該情況下,返回得到的 param 對象,該 param 是一個 Map 對象return param;}
}
param 的值跟有無 @Param 注解有關,我們可以看如下場景中 param 的值;
我們默認沒有給 Java 加上 -parameters 參數,看 param 的值:
1、當參數有 @Param 注解標注;此時 param 的 key 列表為 id、name、param1、param2;
// 此時 param 的 key 列表為 id, name, param1, param2
@Select("select * from student where id=#{id} and name=#{name}")
public Student selectByIdAndName(@Param("id") int id, @Param("name") String name);
2、當參數沒有 @Param 注解標注;此時 param 的 key 列表為 arg0、arg1、param1、param2;
// 此時 param 的 key 列表為 arg0, arg1, param1, param2
@Select("select * from student where id=#{param1} and name=#{param2}")
public Student selectByIdAndName(int id, String name);
3、當參數不全有 @Param 注解標注(了解即可,一般我們不會寫這么腦癱的寫法);
// 此時 param 的 key 列表為 id, arg1, param1, param2
@Select("select * from student where id=#{id} and name=#{param2}")
public Student selectByIdAndName(@Param("id") int id, String name);
4、當只有一個參數時,且沒有 @Param 注解,顯然 getNamedParams() 會直接返回該參數;
// 此時參數解析結果就是原參數 Student 對象
// 很顯然不能使用 #{stu.id},因為根本沒有 stu 這個索引,只能使用 #{id}
@Select("select * from student where id=#{id}")
public Student selectByStudentId2(Student stu);
5、當只有一個參數時,且有 @Param 注解;此時 param 的 key 列表為 stu、param1;
// 此時的參數解析結果是 param 對象:{"stu": student, "param1": student}
// 很顯然如果使用 #{id} 來取值的話,Mybatis 不知道該用哪個
// 只有我們明確指出 #{stu.id} 才行,或者也可使用 #{param1.id}
@Select("select * from student where id=#{stu.id}")
public Student selectByStudentId(@Param("stu") Student stu);
此時 param 參數如下:

至此,參數解析完畢;
八. 參數映射處理
我們在第五大點中 prepareStatement() 創建 PreparedStatement 對象中知道,該方法內還會做參數的映射處理;
// ------------------------- SimpleExecutor -------------------------------
private Statement prepareStatement(StatementHandler handler, Log statementLog) {Statement stmt;Connection connection = getConnection(statementLog);// 1. 執行 PreparedStatementHandler.prepare() 獲得 PreparedStatementHandler 對象stmt = handler.prepare(connection, transaction.getTimeout());// 2. 對參數進行映射處理handler.parameterize(stmt);return stmt;
}
下面我們對 PreparedStatementHandler.parameterize() 做一個簡單的分析;
// ----------------------- PreparedStatementHandler -----------------------------
public void parameterize(Statement statement) throws SQLException {// 調用 parameterHandler.setParameters() 對參數進行映射parameterHandler.setParameters((PreparedStatement) statement);
}
Mybatis 中只有一個默認的 ParameterHandler,是 DefaultParameterHandler,我們看下這個類的 setParameters();
1. DefaultParameterHandler
DefaultParameterHandler 的 setParameters() 流程不長,我們直接往下看;
// ------------------------ DefaultParameterHandler ---------------------------
public void setParameters(PreparedStatement ps) {// 1. 獲取 sql 中所有的 parameterMapping// 其實就是我們 sql 中 #{id} 中對應值List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();if (parameterMappings != null) {// 2. 遍歷處理 parameterMappingfor (int i = 0; i < parameterMappings.size(); i++) {ParameterMapping parameterMapping = parameterMappings.get(i);Object value;// 獲取 parameterMapping 的屬性 propertyString propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);} else if (parameterObject == null) {value = null;} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {// 3. parameterObject 就是我們上文解析得到的參數對象// 如果參數只有一個且沒有 @Param 的情況下,value 直接等于 parameterObject// 當然這里是簡單參數的情況// 如果 parameterObject 是 JavaBean 類型,還是會走到第 4 步去解析參數value = parameterObject;} else {// 4. 參數不止一個的情況,parameterObject 是一個 map 對象// 此時需要通過輔助的 MetaObject 根據 propertyName 獲取參數值MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);}// 5. 獲取 parameterMapping 的 TypeHandler// 我們在 sql 中一般不指定 TypeHandler// 此處獲取的 typeHandler 一般都為 UnknownTypeHandlerTypeHandler typeHandler = parameterMapping.getTypeHandler();JdbcType jdbcType = parameterMapping.getJdbcType();if (value == null && jdbcType == null) {jdbcType = configuration.getJdbcTypeForNull();}try {// 6. 通過 typeHandler.setParameter() 給 sql 中參數進行設值typeHandler.setParameter(ps, i + 1, value, jdbcType);} catch (TypeException | SQLException e) {throw new TypeException("Could not set parameters for mapping");}}}
}// -------------------------- UnknownTypeHandler ----------------------------
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Object parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) {// 1. 根據 parameter、jdbcType 獲取一個合適的 TypeHandler// 一般 int 對應 IntegerTypeHandler、String 對應 StringTypeHandlerTypeHandler handler = resolveTypeHandler(parameter, jdbcType);// 2. 再次調用 typeHandler.setParameter()// 我們以 IntegerTypeHandler 為例來看handler.setParameter(ps, i, parameter, jdbcType);
}// -------------------------- IntegerTypeHandler ----------------------------
public class IntegerTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler<Integer> {@Overridepublic void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, Integer parameter, JdbcType jdbcType) {// 調用我們熟悉的 jdbc 中的 ps.setInt()// TypeHandlerRegistry 中有所有注冊的 TypeHandlerps.setInt(i, parameter);}
}
我們舉兩個例子來看 DefaultParameterHandler.setParameters();
1.1 參數只有一個且沒有@Param
parameterObject 是簡單類型,此時 value = parameterObject;parameterMappings 只有一個參數;
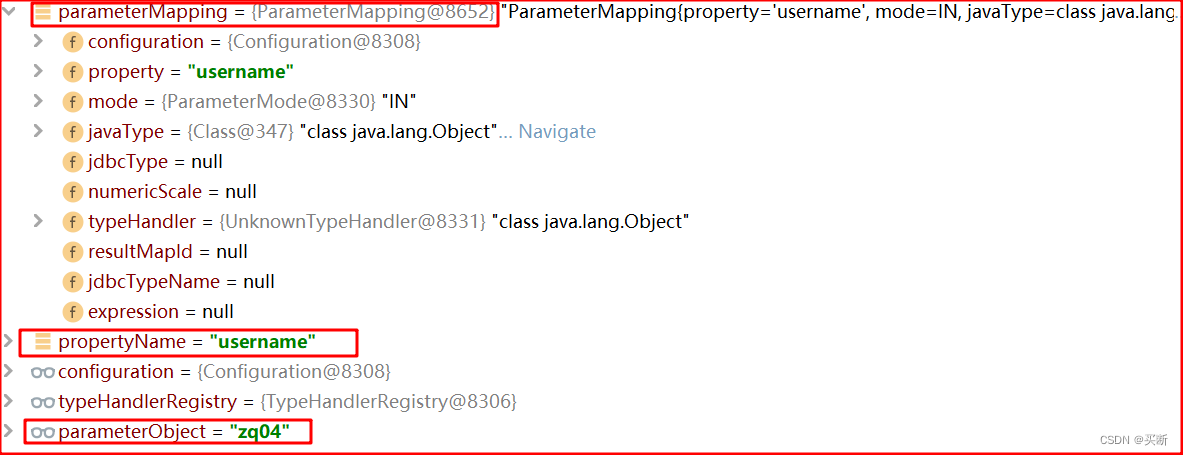
1.2 參數有兩個
此時 parameterObject 是一個 Map 對象,parameterMappings 也有兩個參數,需要輪詢進行處理;
處理邏輯其實就是取 parameterObject 中對應 key 的 value 值;
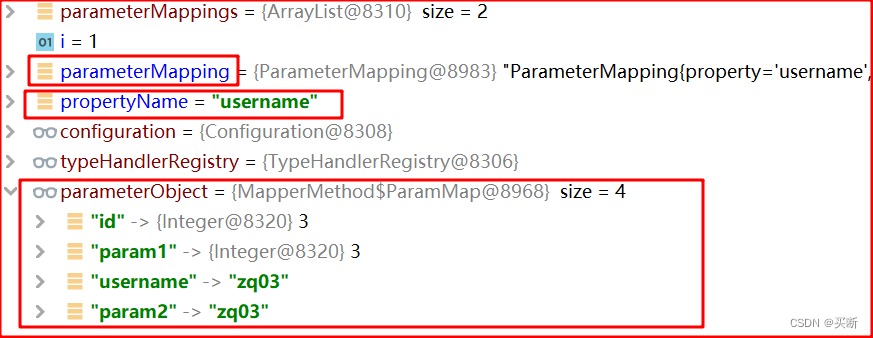
至此,參數映射完畢;





)
)












)