本文參考FastAPI教程https://fastapi.tiangolo.com/zh/tutorial
第一步
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/")
async def root():return {"message": "Hello World"}if __name__ == '__main__':uvicorn.run("test:app", host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True)
$ uvicorn main:app --reload
- 導入
FastAPI:FastAPI是一個為你的API提供了所有功能的Python類 app = FastAPI()創建一個FastAPI實例,這個實例將是創建你所有API的主要交互對象。這個app同樣在如下命令中被uvicorn所引用。- 創建一個路徑操作。
【路徑】:這里的【路徑】指的是從URL中第一個/起的后半部分,比如在https://example.com/items/foo中,路徑是/items/foo,【路徑】也通常被稱為【端點】或【路由】。
【操作】:這里的【操作】是指一種HTTP【方法】,如POST——創建數據,GET——讀取數據,PUT——更新數據,DELETE——刪除數據,以及更少見的幾種OPTIONS,HEAD,PATCH,TRACE,在HTTP協議中,你可以使用以上的其中一種(或多種)【方法】與每個路徑進行通信。 - 定義一個路徑操作裝飾器:
@app.get("/")告訴FastAPI在它下方的函數負責處理如下訪問請求:請求路徑為/,使用get操作。(@something語法在Python中被稱為【裝飾器】,接收位于其下方的函數并且用它完成一些工作,這里是路徑操作裝飾器。) - 定義路徑操作函數:位于路徑操作裝飾器下的函數,這里是
async def root(),這個例子用的是async函數,其作用在后面講。 - 返回內容:可以返回一個
dict、list,像str、int一樣的值,等等。還可以返回Pydanic模型(后面會說),還有許多其他將會自動轉換為JSON的對象和模型(包括ORM對象等)。
查看運行結果
- 打開瀏覽器訪問 http://127.0.0.1:8000。講看到如下的JSON相應:
{"message": "Hello World"}
交互式API文檔
- 跳轉到 http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs。你將會看到自動生成的交互式API文檔(由
Swagger UI提供)。
可選的API文檔
- 前往 http://127.0.0.1:8000/redoc。你將會看到可選的自動生成文檔(由
ReDoc提供)。
路徑參數
FastAPI支持以下路徑模板語法定義動態路由,聲明路徑參數(變量):
import uvicorn
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}/{go}")
async def read_item(go):return {"item_id": go}if __name__ == '__main__':uvicorn.run("test:app", host="127.0.0.1", port=8000, reload=True)
這段代碼聲明了相應位置上的路徑參數item_id和go,并把go的值傳遞給路徑函數的參數go。
運行示例并訪問http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/para1/para2可獲得如下相應:
{"item_id":"para2"}
聲明路徑參數的類型
使用Python標準類型注釋,聲明路徑操作函數中路徑參數的類型。
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: int):return {"item_id": item_id}
上例把item_id的類型聲明為int。
檢查:類型聲明將為函數提供錯誤檢查、代碼補全等編輯器支持
數據轉換
運行上述聲明item_id的類型為int的例子并訪問 http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/3,返回的相應如下:
{"item_id":3}
可見,函數接收并返回的值是3(int),不是"3"(str)。FastAPI通過類型聲明自動解析請求中的數據。
數據校驗
如果通過瀏覽器訪問http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/foo,將會接收如下HTTP錯誤信息:
{"detail": [{"type": "int_parsing","loc": ["path","item_id"],"msg": "Input should be a valid integer, unable to parse string as an integer","input": "foo"}]
}
因為路徑參數item_id的值("foo")的類型不是int。
檢查:FastAPI使用Python類型聲明實現了數據校驗,上面的錯誤清晰的指出了未通過校驗的具體原因,這在開發調試與API交互的代碼時非常有用。
查看文檔
訪問 http://127.0.0.1:8000/docs,查看自動生成的 API 文檔:
Pydantic
FastAPI可以充分利用Pydanic的優勢,用它在后臺校驗數據。
路徑操作的順序
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/users/me")
async def read_user_me():return {"user_id": "the current user"}@app.get("/users/{user_id}")
async def read_user(user_id: str):return {"user_id": user_id}
/users/me和/users/{user_id}不能反過來,否則/users/me的路徑會被/users/{user_id}接收。
預設值
路徑操作使用Python的Enum類型接收預設的路徑參數。
from enum import Enumfrom fastapi import FastAPIclass ModelName(str, Enum):alexnet = "alexnet"resnet = "resnet"lenet = "lenet"app = FastAPI()@app.get("/models/{model_name}")
async def get_model(model_name: ModelName):if model_name is ModelName.alexnet:return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "Deep Learning FTW!"}if model_name.value == "lenet":return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "LeCNN all the images"}return {"model_name": model_name, "message": "Have some residuals"}
- 導入
Enum并創建繼承自str和Enum的子類。通過從str繼承,API文檔就能把值的類型定義為字符串,并且能正確渲染。然后創建包含固定值的類屬性,這些固定值是可用的有效值。 - 使用
Enum類(ModelName)創建使用類型注解的路徑參數。 - API文檔會顯示預定義路徑參數的可用值。
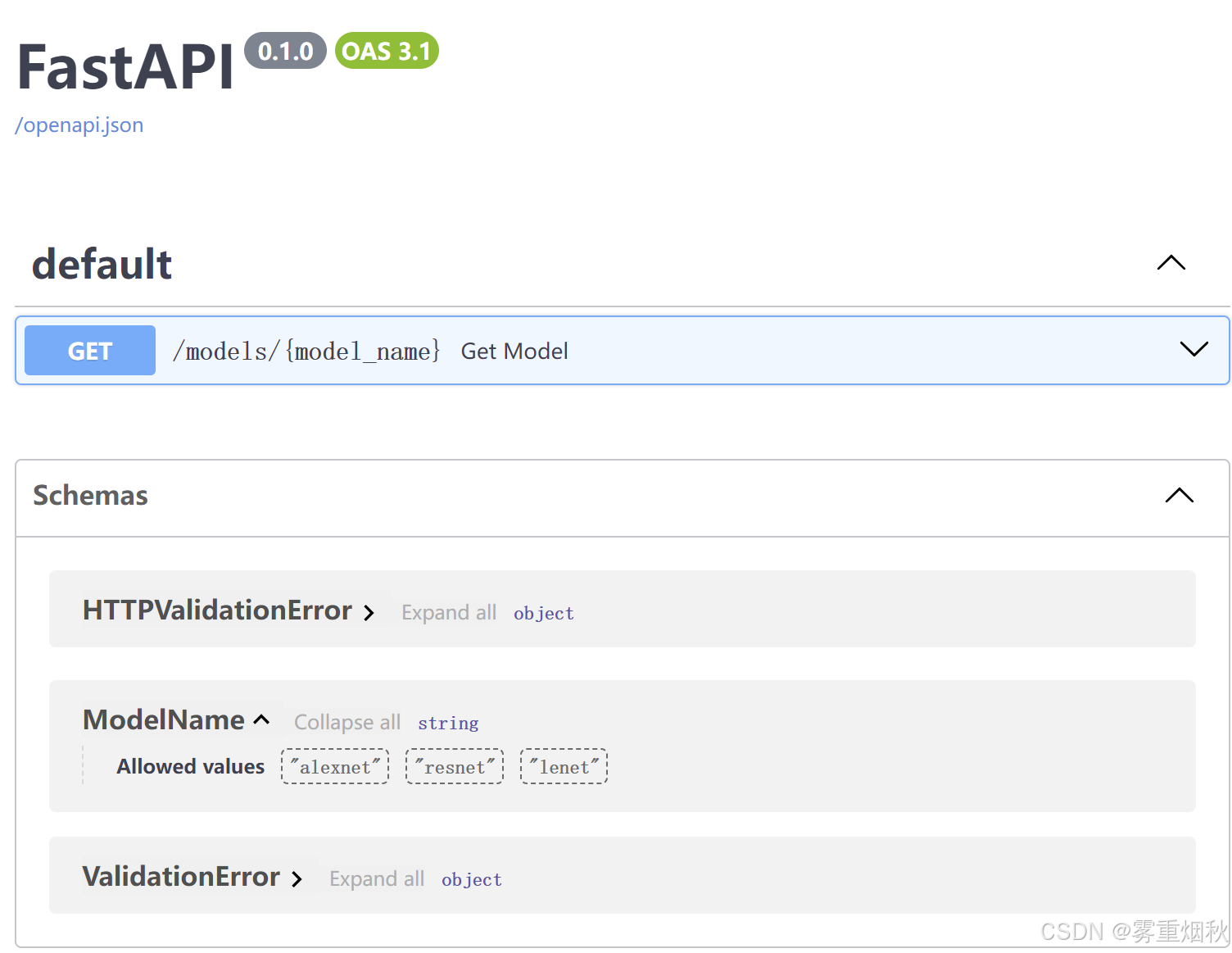
- 使用Python枚舉類型:路徑參數的值是枚舉的元素。枚舉類
ModelName中的枚舉元素支持比較操作(if model_name is ModelName.alexnet),使用model_name.value獲取枚舉值。 - 返回枚舉元素:即使嵌套在JSON請求體里(例如,
dict),也可以從路徑操作返回枚舉元素。
包含路徑的路徑參數
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/files/{file_path:path}")
async def read_file(file_path: str):return {"file_path": file_path}
參數名為file_path,結尾部分的:path說明該參數應匹配路徑。
查詢參數
聲明的參數不是路徑參數時,路徑操作函數會把該參數自動解釋為查詢參數。
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()fake_items_db = [{"item_name": "Foo"}, {"item_name": "Bar"}, {"item_name": "Baz"}]@app.get("/items/")
async def read_item(skip: int = 0, limit: int = 10):return fake_items_db[skip : skip + limit]
查詢字符串是鍵值對的集合,這些鍵值對位于URL的?之后,以&分隔。
例如,以下URL中:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?skip=0&limit=2
查詢參數為:skip: 0,limit: 2
這些值都是URL的組成部分,因此它們的類型本應是字符串。
但聲明Python類型(上例中為int)之后,這些值就會轉換為聲明的類型,并進行類型校驗。
所有應用于路徑參數的流程也適用于查詢參數。
默認值
查詢參數由默認值,如上例。
可以進行如下URL訪問:
- http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/
- http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?skip=0&limit=10
- http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?skip=20
可選參數
把默認值設為None即可聲明可選的查詢參數:
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: str, q: str | None = None):if q:return {"item_id": item_id, "q": q}return {"item_id": item_id}
檢查:注意,FastAPI 可以識別出 item_id 是路徑參數,q 不是路徑參數,而是查詢參數。
查詢參數類型轉換
FastAPI會自動轉換參數類型:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_item(item_id: str, q: Union[str, None] = None, short: bool = False):item = {"item_id": item_id}if q:item.update({"q": q})if not short:item.update({"description": "This is an amazing item that has a long description"})return item
在本例中訪問:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/foo?short=1
或
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/foo?short=True
或short=on,short=true,short=yes或其它任意大小寫形式,函數接收到的short參數都是布爾值True。False同理(0,false,off,no)。
多個路徑和查詢參數
FastAPI可以識別同時聲明的多個路徑參數和查詢參數,而且聲明查詢參數的順序并不重要,FastAPI通過參數名進行檢測:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/users/{user_id}/items/{item_id}")
async def read_user_item(user_id: int, item_id: str, q: Union[str, None] = None, short: bool = False
):item = {"item_id": item_id, "owner_id": user_id}if q:item.update({"q": q})if not short:item.update({"description": "This is an amazing item that has a long description"})return item
把不是路徑參數的參數(至此只有查詢參數)聲明為默認值,或者是吧默認值設為None,這樣參數就不是必選的,否則是必選的。
上述代碼可以用以下URL進行測試:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/users/2/items/item_id?q=test&short=0
將會得到這樣的相應:
{"item_id":"item_id","owner_id":2,"q":"test","description":"This is an amazing item that has a long description"}
再比如:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_user_item(item_id: str, needy: str, skip: int = 0, limit: Union[int, None] = None
):item = {"item_id": item_id, "needy": needy, "skip": skip, "limit": limit}return item
上例中有3個查詢參數:needy,必選的str類型參數,skip,默認值為0的int類型參數,limit,可選的int類型參數。
請求體
FastAPI使用請求體從客戶端(例如瀏覽器)向API發送數據。
請求體是客戶端發送給API的數據。響應體是API發送給客戶端的數據。
API基本上肯定要發送響應體,但是客戶端不一定發送請求體。
使用Pydantic模型聲明請求體,能充分利用它的功能和優點。
使用Pydantic聲明請求體
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/items/")
async def create_item(item: Item):return item
步驟如下:
- 從
pydantic中導入BaseModel - 創建數據類型:把數據模型聲明為繼承
BaseModel的類。使用Python標準類型聲明所有屬性。 - 聲明請求體參數:使用與聲明路徑和查詢參數相同的方式聲明請求體,把請求體添加至路徑操作,
@app.post()及其下面的函數async def create_item(item: Item):...,此處請求體參數的類型為Item類型。
使用如下代碼進行測試:
import requests# 定義請求的 JSON 數據
item_data = {"name": "Item1","description": "This is item 1","price": 19.99,"tax": 2.00
}# 發送 POST 請求
response = requests.post("http://localhost:8000/items/", json=item_data)# 打印返回的 JSON 數據
print(response.json())
可以看到,FastAPI接收來自測試代碼的請求,返回:
{'name': 'Item1', 'description': 'This is item 1', 'price': 19.99, 'tax': 2.0}
結論
僅使用Python類型聲明,FastAPI就可以
- 以JSON形式讀取請求體
- (在必要時)把請求體轉換為對應的類型
- 校驗數據:數據無效時返回錯誤信息,并指出錯誤數據的確切位置和內容
- 把接收的數據賦值給參數
item - 為模型生成JSON Schema,在項目中所需的位置使用
使用模型
在路徑操作函數內部直接訪問模型對象的屬性:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/items/")
async def create_item(item: Item):item_dict = item.dict()if item.tax:price_with_tax = item.price + item.taxitem_dict.update({"price_with_tax": price_with_tax})return item_dict
用測試代碼測試結果如下:
{'description': 'Mechanical keyboard','name': 'Keyboard','price': 49.99,'price_with_tax': 54.99,'tax': 5.0}
請求體+路徑參數
FastAPI支持同時聲明路徑參數和請求體。
FastAPI能識別與路徑參數匹配的函數參數,還能識別從請求體中獲取的類型為Pydantic模型的函數參數。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):return {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}
使用如下測試代碼發送PUT請求:
import requests
from pprint import pprint# 定義要發送的 JSON 數據,符合 Item 模型的定義
item_data = {"name": "Mouse","description": "Wireless mouse","price": 19.99,"tax": 1.50
}# 定義要更新的 item_id
item_id = 1# 發送 PUT 請求
response = requests.put(f"http://localhost:8000/items/{item_id}", json=item_data)# 打印返回的 JSON 數據
pprint(response.json())
返回結果為:
{'description': 'Wireless mouse','item_id': 1,'name': 'Mouse','price': 19.99,'tax': 1.5}
請求體+路徑參數+查詢參數
FastAPI支持同時聲明請求體、路徑參數和查詢參數。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneapp = FastAPI()@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item, q: str | None = None):result = {"item_id": item_id, **item.dict()}if q:result.update({"q": q})return result
函數參數按如下規則進行識別:
- 路徑中聲明了相同參數的參數,是路徑參數
- 類型是(
int,float,str,bool等)單類型的參數,是查詢參數 - 類型是Pydantic模型的參數,是請求體
使用如下測試代碼:
import requests
from pprint import pprint# 定義要發送的 JSON 數據,符合 Item 模型的定義
item_data = {"name": "Keyboard","description": "Mechanical keyboard","price": 49.99,"tax": 5.00
}# 定義要更新的 item_id
item_id = 1# 定義查詢參數 q
q_param = "example"# 發送 PUT 請求
response = requests.put(f"http://localhost:8000/items/{item_id}?q={q_param}", json=item_data)# 打印返回的 JSON 數據
pprint(response.json())
可得到返回結果:
{'description': 'Mechanical keyboard','item_id': 1,'name': 'Keyboard','price': 49.99,'q': 'example','tax': 5.0}
查詢參數和字符串校驗
FastAPI允許你為參數聲明額外的信息和校驗。
以下面的應用程序為例:
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str | None = None):results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
查詢參數q的類型為str,默認值為None,因此它是可選的。
額外的校驗
我們打算添加約束條件:即使q是可選的,但只要提供了該參數,則該參數值不能超過50個字符的長度
具體步驟如下:
- 導入
Query:首先從fastapi導入Query。 - 使用
Query作為默認值:將Query用作查詢參數的默認值,并將它的max_length參數設置為50,由于我們必須用Query(default=None)替換默認值None,Query的第一個參數同樣是用于定義默認值。
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Queryapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, max_length=50)):results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
添加更多的校驗
- 還可以添加
min_length參數 - 還可以添加正則表達式:定義一個參數值必須匹配的正則表達式
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Queryapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, min_length=3, max_length=50, pattern="^fixedquery$"),
):results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
聲明為必需參數
當我們不需要聲明額外的校驗或元數據時,只需不聲明默認值就可以使q參數成為必需參數,如:
q: str
但是我們現在正在用Query聲明它,如:
q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, min_length=3)
因此,當你在使用Query且需要聲明一個值是必需的時,只需不聲明默認參數:
from fastapi import FastAPI, Queryapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: str = Query(min_length=3)):results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
顯式聲明必需參數的方法
- 使用
(...)聲明:q: str = Query(default=..., min_length=3) - 可以聲明
None為一個有效的類型,仍是必需參數:q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=..., min_length=3) - 使用Pydantic中的
Required代替省略號...:from pydantic import Required,q: str = Query(default=Required, min_length=3)
大多數情況,隱式省略default參數就夠了,通常不必使用顯式聲明...或Required
查詢參數列表/多個值
當你使用Query顯式地定義查詢參數時,你還可以聲明它去接收一組值,或換句話來說,接收多個值。
例如,要聲明一個可在URL中出現多次的查詢參數q,可以這樣寫:
from typing import List, Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Queryapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[List[str], None] = Query(default=None)):query_items = {"q": q}return query_items
然后輸入以下網址:
http://localhost:8000/items/?q=foo&q=bar
你會在路徑操作函數的函數參數q中以一個Pythonlist的形式接收到查詢參數q的多個值:
{"q":["foo","bar"]}
要聲明類型為list的查詢參數,需要顯式地使用Query,否則該參數將被解釋為請求體
具有默認值的查詢參數列表/多個值
可以給定默認list值:
from typing import Listfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Queryapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: List[str] = Query(default=["foo", "bar"])):query_items = {"q": q}return query_items
q: List[str] = Query(default=["foo", "bar"])也可以使用list代替,這樣不會檢查列表的內容,如q: list = Query(default=[])。
聲明更多元數據
你可以添加更多有關該參數的信息。
這些信息將包含在生成的OpenAPI模式中,并由文檔用戶界面和外部工具所使用。
- 添加
title:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Queryapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, title="Query string", min_length=3),
):results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
- 添加
description:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Queryapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None,title="Query string",description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",min_length=3,),
):results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
別名參數(alias)
假設你想要查詢參數為item-query,如下:
http://127.0.0.1:8000/items/?item-query=foobaritems
但是item-query不是一個有效的Python變量名稱,這時可以用alias參數聲明一個別名,該別名將用于在URL中查找查詢參數值:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Queryapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None, alias="item-query")):results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
棄用參數(deprecated)
假設你不再喜歡該參數。
你不得不將其保留一段時間,因為有些客戶端正在使用它,但你希望文檔清楚地將其展示為已棄用。
那么將deprecated=True傳入Query:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Queryapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/")
async def read_items(q: Union[str, None] = Query(default=None,alias="item-query",title="Query string",description="Query string for the items to search in the database that have a good match",min_length=3,max_length=50,pattern="^fixedquery$",deprecated=True,),
):results = {"items": [{"item_id": "Foo"}, {"item_id": "Bar"}]}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
文檔會像下面這樣展示它:

總結
你可以為查詢參數聲明額外的校驗和元數據。
通用的校驗和元數據:
aliastitledescriptiondeprecated
特定于字符串的校驗:
min_lengthmax_lengthregex
路徑參數和數值校驗
與使用Query為查詢參數聲明更多的校驗和元數據的方式相同,你也可以使用Path為路徑參數聲明相同類型的校驗和元數據。
具體步驟如下:
- 導入Path:首先從
fastapi導入Path - 聲明元數據:可以聲明與
Query相同的所有參數,例如,要聲明路徑參數item_id的title元數據值,可以輸入item_id: Annotated[int, Path(title="The ID of the item to get")]
from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Path, Queryapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(item_id: Annotated[int, Path(title="The ID of the item to get")],q: Annotated[str | None, Query(alias="item-query")] = None,
):results = {"item_id": item_id}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
路徑參數總是必需的。
按需對參數排序
假設你想要聲明一個必需的str類型查詢參數q。
而且你不需要為該參數聲明任何其他內容,所以實際上并不需要使用Query。
但是你仍然需要使用Path來聲明路徑參數item_id。
如果你將帶有【默認值】的參數放在沒有【默認值】的參數之前,Python將會報錯。
但是你可以對其重新排序,并將不帶默認值的值(查詢參數q)放到最前面。
對FastAPI來說這無關緊要。它將通過參數的名稱、類型和默認值聲明(Query、Path等)來檢測參數,而不在乎參數的順序。
因此可以將函數聲明為:
from fastapi import FastAPI, Pathapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(q: str, item_id: int = Path(title="The ID of the item to get")):results = {"item_id": item_id}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
還可以用*表示后面的所有參數作為關鍵字參數,也被稱為kwargs來調用,即使它們沒有默認值:
from fastapi import FastAPI, Pathapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(*, item_id: int = Path(title="The ID of the item to get"), q: str):results = {"item_id": item_id}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
數值校驗
使用Query和Path(以及后面的其他類)可以聲明字符串約束,也可以聲明數值約束。如下,添加ge=1后,item_id將必須是一個大于(greater than)或等于(equal)1的整數。
- 大于等于
from fastapi import FastAPI, Pathapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(*, item_id: int = Path(title="The ID of the item to get", ge=1), q: str
):results = {"item_id": item_id}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
- 大于:
gt(greater than) - 小于等于:
le(less than or equal)
from fastapi import FastAPI, Pathapp = FastAPI()@app.get("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(*,item_id: int = Path(title="The ID of the item to get", gt=0, le=1000),q: str,
):results = {"item_id": item_id}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
- 浮點數:數值校驗同樣適用于
float值。
請求體-多個參數
既然我們已經知道了如何使用Path和Query,下面讓我們來了解一下請求體聲明的更高級用法。
混合使用Path、Query和請求體參數
你可以隨意混合使用Path、Query和請求體參數聲明。
你還可以通過將默認值設置為None來將請求體參數聲明為可選參數:
from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import FastAPI, Path
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: Annotated[int, Path(title="The ID of the item to get", ge=0, le=1000)],q: str | None = None,item: Item | None = None,
):results = {"item_id": item_id}if q:results.update({"q": q})if item:results.update({"item": item})return results
多個請求體參數
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneclass User(BaseModel):username: strfull_name: str | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item, user: User):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item, "user": user}return results
在上面的情況下,FastAPI將注意到該函數中有多個請求體參數(兩個Pydantic模型參數)。因此,它將使用參數名稱作為請求體中的鍵(字段名稱),并期望一個類似于以下內容的請求體:
{"item": {"name": "Foo","description": "The pretender","price": 42.0,"tax": 3.2},"user": {"username": "dave","full_name": "Dave Grohl"}
}
FastAPI將自動對請求中的數據進行轉換,因此item參數將接收指定的內容,user參數也是如此。它將執行對復合數據的校驗,并且像現在這樣為OpenAPI模式和自動化文檔對其進行記錄。
請求體中的單一值(Body)
與使用Query和Path為查詢參數和路徑參數定義額外數據的方式相同,FastAPI提供了一個同等的Body,例如上面的模型,除了item和user之外,還想在同一請求體中具有另一個鍵importance,如果按原樣來聲明它,因為它是一個單一值,FastAPI將假定它是一個查詢參數。但是你可以使用Body指示FastAPI將其作為請求體的另一個鍵進行處理。
from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneclass User(BaseModel):username: strfull_name: str | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item, user: User, importance: Annotated[int, Body()]
):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item, "user": user, "importance": importance}return results
在這種情況下,FastAPI將期望這樣的請求體:
{"item": {"name": "Foo","description": "The pretender","price": 42.0,"tax": 3.2},"user": {"username": "dave","full_name": "Dave Grohl"},"importance": 5
}
多個請求體參數和查詢參數
除了請求體參數外,你還可以在任何需要的時候聲明額外的查詢參數。
由于默認情況下單一值被解釋為查詢參數,因此你不必顯式地添加Query。
from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Noneclass User(BaseModel):username: strfull_name: str | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(*,item_id: int,item: Item,user: User,importance: Annotated[int, Body(gt=0)],q: str | None = None,
):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item, "user": user, "importance": importance}if q:results.update({"q": q})return results
嵌入單個請求體參數(Body(embed=True))
假設你只有一個來自Pydantic模型Item的請求體參數item。
默認情況下,FastAPI將直接期望這樣的請求體。
但是,如果你希望它期望一個擁有item鍵并在值中包含模型內容的JSON,就像在聲明額外的請求體參數時所做的那樣,則可以使用一個特殊的Body參數embed:
item: Item = Body(embed=True)
from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Annotated[Item, Body(embed=True)]):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
在這種情況下,FastAPI將期望像這樣的請求體:
{"item": {"name": "Foo","description": "The pretender","price": 42.0,"tax": 3.2}
}
而不是:
{"name": "Foo","description": "The pretender","price": 42.0,"tax": 3.2
}
總結
你可以添加多個請求體參數到路徑操作函數中,即使一個請求只能有一個請求體。
但是 FastAPI 會處理它,在函數中為你提供正確的數據,并在路徑操作中校驗并記錄正確的模式。
你還可以聲明將作為請求體的一部分所接收的單一值。
你還可以指示 FastAPI 在僅聲明了一個請求體參數的情況下,將原本的請求體嵌入到一個鍵中。
請求體-字段(Field)
與在路徑操作函數中使用Query、Path、Body聲明校驗與元數據的方式一樣,可以使用Pydantic的Field在Pydantic模型內部聲明校驗和元數據。
具體步驟如下:
- 導入
Field:首先從Pydantic中導入Field。 - 聲明模型屬性:使用
Field定義模型的屬性。
from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, Fieldapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Field(default=None, title="The description of the item", max_length=300)price: float = Field(gt=0, description="The price must be greater than zero")tax: float | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Annotated[Item, Body(embed=True)]):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
Field的工作方式和Query、Path、Body相同,參數也相同。
請求體-嵌套類型
使用FastAPI,你可以定義、校驗、記錄文檔并使用任意深度嵌套的模型(歸功于Pydantic)。
List字段
你可以將一個屬性定義為擁有子元素的類型。例如Pythonlist:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Nonetags: list = []@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
這將使tags成為一個由元素組成的列表。不過它沒有聲明每個元素的類型。
具有子類型的List字段
但是Python有一種特定的方法來聲明具有子類型的列表:
具體步驟如下:
- 聲明具有子類型的List:從
typing模塊導入它們,使用方括號[和]將子類型作為【類型參數】傳入。 - 在我們的示例中,我們可以將
tags明確地指定為一個【字符串列表】。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Nonetags: list[str] = []@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
Set類型
標簽不應該重復,所以用Set將tag聲明為一個由str組成的set:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Nonetags: set[str] = set()@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
這樣,即使收到帶有重復數據的請求,這些數據也會被轉換為一組唯一項。
而且,每當你輸出該數據時,即使源數據有重復,它們也將作為一組唯一項輸出。
并且還會被相應地標注/記錄文檔。
嵌套類型
Pydantic模型的每個屬性都具有類型。但是這個類型本身可以是另一個Pydantic模型。因此,你可以聲明擁有特定屬性名稱、類型和校驗的深度嵌套的JSON對象。
例如:
- 定義一個
Image模型 - 將
Image模型用作一個屬性的類型
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Image(BaseModel):url: strname: strclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Nonetags: set[str] = set()image: Image | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
這意味著FastAPI將期望類似于以下內容的請求體:
{"name": "Foo","description": "The pretender","price": 42.0,"tax": 3.2,"tags": ["rock", "metal", "bar"],"image": {"url": "http://example.com/baz.jpg","name": "The Foo live"}
}
特殊的類型和校驗
除了普通的單一值類型(如str、int、float等)外,你還可以使用從str繼承的更復雜的單一值類型。
要了解所有的可用選項,查看來自Pydantic的外部類型的文檔。
例如,在Image模型中我們有一個url字段,我們可以把它聲明為Pydantic的HttpUrl,而不是str:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrlapp = FastAPI()class Image(BaseModel):url: HttpUrlname: strclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Nonetags: set[str] = set()image: Image | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
該字符串將被檢查是否為有效的URL,并在JSON Schema/OpenAPI文檔中進行記錄。
帶有一組子模型的屬性
你還可以將Pydantic模型用作list、set等的子模型:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrlapp = FastAPI()class Image(BaseModel):url: HttpUrlname: strclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Nonetags: set[str] = set()images: list[Image] | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
這將期望(轉換,校驗,記錄文檔等)下面這樣的JSON請求體:
{"name": "Foo","description": "The pretender","price": 42.0,"tax": 3.2,"tags": ["rock","metal","bar"],"images": [{"url": "http://example.com/baz.jpg","name": "The Foo live"},{"url": "http://example.com/dave.jpg","name": "The Baz"}]
}
深度嵌套模型
你可以定義任意深度的嵌套模型:
from typing import Unionfrom fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrlapp = FastAPI()class Image(BaseModel):url: HttpUrlname: strclass Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floattax: Union[float, None] = Nonetags: set[str] = set()images: Union[list[Image], None] = Noneclass Offer(BaseModel):name: strdescription: Union[str, None] = Noneprice: floatitems: list[Item]@app.post("/offers/")
async def create_offer(offer: Offer):return offer純列表請求體
如果你期望的JSON請求體的最外層是一個JSONarray(即Python list),則可以在路徑操作函數的參數中聲明此類型,就像聲明Pydantic模型一樣:
images: List[Image]
例如:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, HttpUrlapp = FastAPI()class Image(BaseModel):url: HttpUrlname: str@app.post("/images/multiple/")
async def create_multiple_images(images: list[Image]):return images
任意dict構成的請求體
你也可以將請求體聲明為使用某類型的鍵和其他類型值的dict。
無需事先知道有效的字段/屬性(在使用Pydantic模型的場景)名稱是什么。
如果你想接收一些尚且未知的鍵,這將很有用。
其他有用的場景是當你想要接收其他類型的鍵時,例如int,如下,你將接受任意鍵為int類型并且值為float類型的dict:
from fastapi import FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.post("/index-weights/")
async def create_index_weights(weights: dict[int, float]):return weights
JSON僅支持將str作為鍵,但是Pydantic具有自動轉換數據的功能。這意味著,即使你的API客戶端只能將字符串作為鍵發送,只要這些字符串內容僅包含整數,Pydantic就會對其進行轉換并校驗。然后你接收的名為weights的dict實際上將具有int類型的鍵和float類型的值。
模式的額外信息-例子
你可以在JSON模式中定義額外的信息。
一個常見的用例是添加一個將在文檔中顯示的example。
有幾種方法可以聲明額外的JSON模式信息。
Pydantic schema_extra
你可以使用Config和schema_extra為Pydantic模型聲明一個示例,如Pydantic文檔:定制Schema中所述。
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = Nonemodel_config = {"json_schema_extra": {"examples": [{"name": "Foo","description": "A very nice Item","price": 35.4,"tax": 3.2,}]}}@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
這些額外的信息將按原樣添加到輸出的JSON模式中。
Field的附加參數
在Field,Path,Query,Body和其他你之后將會看到的工廠函數,你可以為JSON模式聲明額外信息,你也可以通過給工廠函數傳遞其他的任意參數來給JSON模式聲明額外信息,比如增加example:
from fastapi import FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModel, Fieldapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: str = Field(examples=["Foo"])description: str | None = Field(default=None, examples=["A very nice Item"])price: float = Field(examples=[35.4])tax: float | None = Field(default=None, examples=[3.2])@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int, item: Item):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
傳遞的那些額外參數不會添加任何驗證,只會添加注釋,用于文檔的目的。
Body額外參數
from typing import Annotatedfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPI
from pydantic import BaseModelapp = FastAPI()class Item(BaseModel):name: strdescription: str | None = Noneprice: floattax: float | None = None@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def update_item(item_id: int,item: Annotated[Item,Body(examples=[{"name": "Foo","description": "A very nice Item","price": 35.4,"tax": 3.2,}],),],
):results = {"item_id": item_id, "item": item}return results
額外數據類型
到目前為止,一直在使用常見的數據類型,如:
intfloatstrbool
但是也可以使用更復雜的數據類型。
其他數據類型
UUID:
一種標準的 “通用唯一標識符” ,在許多數據庫和系統中用作ID。
在請求和響應中將以str表示。datetime.datetime:
一個 Pythondatetime.datetime.
在請求和響應中將表示為 ISO 8601 格式的str,比如: 2008-09-15T15:53:00+05:00.datetime.date:
Python datetime.date.
在請求和響應中將表示為 ISO 8601 格式的str,比如: 2008-09-15.datetime.time:
一個 Python datetime.time.
在請求和響應中將表示為 ISO 8601 格式的str,比如: 14:23:55.003.datetime.timedelta:
一個 Python datetime.timedelta.
在請求和響應中將表示為float代表總秒數。
Pydantic 也允許將其表示為 “ISO 8601 時間差異編碼”, 查看文檔了解更多信息。frozenset:
在請求和響應中,作為set對待:
在請求中,列表將被讀取,消除重復,并將其轉換為一個set。
在響應中set將被轉換為list。
產生的模式將指定那些set的值是唯一的 (使用 JSON 模式的uniqueItems)。bytes:
標準的 Pythonbytes。
在請求和響應中被當作str處理。
生成的模式將指定這個str是binary“格式”。Decimal:
標準的 PythonDecimal。
在請求和響應中被當做float一樣處理。
您可以在這里檢查所有有效的pydantic數據類型: Pydantic data types.
例子
from datetime import datetime, time, timedelta
from typing import Annotated
from uuid import UUIDfrom fastapi import Body, FastAPIapp = FastAPI()@app.put("/items/{item_id}")
async def read_items(item_id: UUID,start_datetime: Annotated[datetime, Body()],end_datetime: Annotated[datetime, Body()],process_after: Annotated[timedelta, Body()],repeat_at: Annotated[time | None, Body()] = None,
):start_process = start_datetime + process_afterduration = end_datetime - start_processreturn {"item_id": item_id,"start_datetime": start_datetime,"end_datetime": end_datetime,"process_after": process_after,"repeat_at": repeat_at,"start_process": start_process,"duration": duration,}







![[code snippet] 生成隨機大文件](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[code snippet] 生成隨機大文件)







和安卓操作系統(Android)的區別)

)

