Android源碼——Handler機制(一)
- Handler機制概述
- 介紹
- Handler機制模型
- Handler機制架構
- Handler機制源碼解析
- ActivityThread
- Looper
- Handler
Handler機制概述
介紹
Handler是Android消息機制的上層接口。Handler可以將一個任務切換到Handler所在的線程中去執行。通常情況下,Handler的使用場景就是更新UI。
如下就是使用消息機制的一個簡單實例:
public class BasicActivity extends AppCompatActivity {private static final String TAG = "BasicActivity";private Handler mHandler = new Handler() {@Overridepublic void handleMessage(Message msg) {super.handleMessage(msg);Log.i(TAG, msg.what);}};@Overridepublic void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState, PersistableBundle persistentState) {super.onCreate(savedInstanceState, persistentState);setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);new Thread(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {// 耗時操作.....Message message = Message.obtain();message.what = 1;mHandler.sendMessage(message);}}).start();}
}
在子線程中,進行耗時操作,執行完操作后,發送消息,通知主線程更新UI。這便是消息機制的典型應用場景。我們通常只會接觸到Handler和Message來完成消息機制,其實內部還有兩大助手來共同完成消息傳遞。
Handler機制模型
消息機制主要包含:MessageQueue,Handler和Looper這三大部分,以及Message。
- Message: 需要傳遞的消息,可以傳遞數據;
- MessageQueue: 消息隊列,但是它的內部實現并不是用的隊列,實際上是通過一個單鏈表的數據結構來維護消息列表,因為單鏈表在插入和刪除上比較有優勢。主要功能向消息池投遞消息
MessageQueue.enqueueMessage和取走消息池的消息MessageQueue.next; - Handler: 消息輔助類,主要功能向消息池發送各種消息事件
Handler.sendMessage和處理相應消息事件Handler.handleMessage; - Looper: 不斷循環執行
Looper.loop,從MessageQueue中讀取消息,按分發機制將消息分發給目標處理者。
Handler機制架構
運行流程:在子線程執行完耗時操作,當Handler發送Message時,會調用MessageQueue.enqueueMessage,向消息隊列中添加Message。當通過Looper.loop開啟循環后,會不斷從線程池中讀取消息,即調用MessageQueue.next,然后調用目標Handler(即發送該消息的Handler)的dispatchMessage方法傳遞消息,然后返回到Handler所在線程,目標Handler收到消息,調用handleMessage方法,接收處理消息。
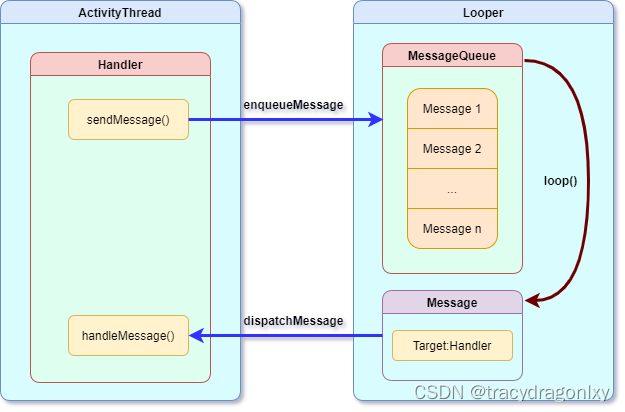
每個線程只能存在一個Looper,Looper保存在ThreadLocal線程中。主線程(UI線程)已經創建了一個Looper,所以在主線程中不需要再創建Looper,但是在其他線程中需要創建Looper。每個線程可以有多個Handler,即一個Looper可以處理來自多個Handler的消息。Looper中維護一個MessageQueue,來維護消息隊列,消息隊列中的Message可以來自不同的Handler。
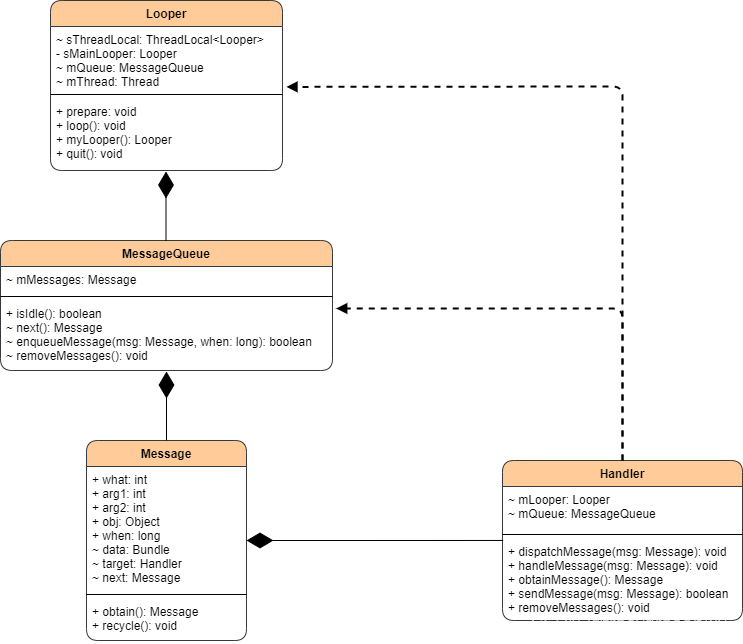
Looper有一個MessageQueue消息隊列,MessageQueue有一組待處理的Message,Message中記錄發送和處理消息的Handler,Handler中有Looper和MessageQueue。
Handler機制源碼解析
ActivityThread
ActivityThread類是用來啟動Android的,在main()函數中準備相關環境,創建并啟動Looper循環。
主線程中不需要自己創建Looper,這是由于在程序啟動的時候,系統已經幫我們自動調用了Looper.prepare()方法。
public static void main(String[] args) {Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");// Install selective syscall interceptionAndroidOs.install();// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);Environment.initForCurrentUser();// Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificatesfinal File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);// Call per-process mainline module initialization.initializeMainlineModules();Process.setArgV0("<pre-initialized>");// 1. 把主線程和消息隊列放進Looper中,同時把Looper放進ThreadLocal(每個線程綁定一個Looper)Looper.prepareMainLooper();// ....// 啟動Looper循環,不斷循環取出消息Looper.loop();throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
Looper
Looper不斷循環執行loop(),從MessageQueue中讀取消息,按分發機制將消息分發給目標處理者。
- 初始化Looper
public final class Looper {// sThreadLocal.get() will return null unless you've called prepare().@UnsupportedAppUsagestatic final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>();@UnsupportedAppUsageprivate static Looper sMainLooper; // guarded by Looper.class@UnsupportedAppUsagefinal MessageQueue mQueue;final Thread mThread;/** Initialize the current thread as a looper.* This gives you a chance to create handlers that then reference* this looper, before actually starting the loop. Be sure to call* {@link #loop()} after calling this method, and end it by calling* {@link #quit()}.*/public static void prepare() {prepare(true);}/*** 創建Looper,并保存在ThreadLocal,不能重復創建Looper,只能創建一個。 */private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {// 不能重復創建否則報錯if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");}// 4. 實例化自己,封裝mQueue和主線程,把自己放入ThreadLocal中sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));}/*** Initialize the current thread as a looper, marking it as an* application's main looper. See also: {@link #prepare()}** @deprecated The main looper for your application is created by the Android environment,* so you should never need to call this function yourself.*/@Deprecatedpublic static void prepareMainLooper() {prepare(false);synchronized (Looper.class) {if (sMainLooper != null) {throw new IllegalStateException("The main Looper has already been prepared.");}sMainLooper = myLooper();}}/*** Return the Looper object associated with the current thread. Returns* null if the calling thread is not associated with a Looper.*/public static @Nullable Looper myLooper() {return sThreadLocal.get();}private Looper(boolean quitAllowed) {// 2. 實例化MessageQueuemQueue = new MessageQueue(quitAllowed);mThread = Thread.currentThread();}}
- 開啟Looper
/*** 5. 調用Looper.loop()方法* Run the message queue in this thread. Be sure to call* {@link #quit()} to end the loop.*/public static void loop() {// 獲取TLS存儲的Looper對象final Looper me = myLooper();if (me == null) {throw new RuntimeException("No Looper; Looper.prepare() wasn't called on this thread.");}if (me.mInLoop) {Slog.w(TAG, "Loop again would have the queued messages be executed"+ " before this one completed.");}me.mInLoop = true;// 獲取Looper對象中的消息隊列final MessageQueue queue = me.mQueue;// Make sure the identity of this thread is that of the local process,// and keep track of what that identity token actually is.Binder.clearCallingIdentity();final long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();// 進入loop()主循環for (;;) {// 消息隊列取出一條消息Message msg = queue.next(); // might blockif (msg == null) {// No message indicates that the message queue is quitting.return;}// 默認為null,可通過setMessageLogging()方法來指定輸出,用于debug功能// This must be in a local variable, in case a UI event sets the loggerfinal Printer logging = me.mLogging;if (logging != null) {logging.println(">>>>> Dispatching to " + msg.target + " " +msg.callback + ": " + msg.what);}// .....try {// 獲取msg的目標Handler,然后用于分發Messagemsg.target.dispatchMessage(msg);// ....} catch (Exception exception) {// ...} finally {// ...}if (logging != null) {logging.println("<<<<< Finished to " + msg.target + " " + msg.callback);}// Make sure that during the course of dispatching the// identity of the thread wasn't corrupted.final long newIdent = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();// 回收可能正在使用的消息msg.recycleUnchecked();}}
loop()進入循環模式,不斷重復下面的操作,直到消息為空時退出循環:讀取MessageQueue的下一條Message;把Message分發給相應的target。
當next()取出下一條消息時,隊列中已經沒有消息時,next()會無限循環,產生阻塞。等待MessageQueue中加入消息,然后重新喚醒。
Handler
消息輔助類,主要功能向消息池發送各種消息事件(Handler.sendMessage)和處理相應消息事件(Handler.handleMessage)。
- 創建Handler
public class Handler {@UnsupportedAppUsagefinal Looper mLooper;// 這里并沒有實例化,指向Lopper的消息隊列final MessageQueue mQueue;@UnsupportedAppUsagefinal Callback mCallback;final boolean mAsynchronous;@UnsupportedAppUsageIMessenger mMessenger;/*** Callback interface you can use when instantiating a Handler to avoid* having to implement your own subclass of Handler.*/public interface Callback {/*** @param msg A {@link android.os.Message Message} object* @return True if no further handling is desired*/boolean handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg);}/*** Subclasses must implement this to receive messages.*/public void handleMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {}}
構造函數:
@Deprecatedpublic Handler() {this(null, false);}@Deprecatedpublic Handler(@Nullable Callback callback) {this(callback, false);}@UnsupportedAppUsagepublic Handler(boolean async) {this(null, async);}/*** 第一種構造方法:給主線程調用,因為主線程已經調用Looper.prepareMainLooper()*/public Handler(@Nullable Callback callback, boolean async) {if (FIND_POTENTIAL_LEAKS) {final Class<? extends Handler> klass = getClass();if ((klass.isAnonymousClass() || klass.isMemberClass() || klass.isLocalClass()) &&(klass.getModifiers() & Modifier.STATIC) == 0) {Log.w(TAG, "The following Handler class should be static or leaks might occur: " +klass.getCanonicalName());}}// 獲取主線程的LoopermLooper = Looper.myLooper();if (mLooper == null) {throw new RuntimeException("Can't create handler inside thread " + Thread.currentThread()+ " that has not called Looper.prepare()");}// Handler的mQueue指向Looper的mQueuemQueue = mLooper.mQueue;mCallback = callback;mAsynchronous = async;}public Handler(@NonNull Looper looper) {this(looper, null, false);}public Handler(@NonNull Looper looper, @Nullable Callback callback) {this(looper, callback, false);}/*** 第二種構造方法,給在子線程中創建Handler時使用,子線程要自主調用Looper.prepare()*/@UnsupportedAppUsagepublic Handler(@NonNull Looper looper, @Nullable Callback callback, boolean async) {mLooper = looper;mQueue = looper.mQueue;mCallback = callback;mAsynchronous = async;}- 發送消息
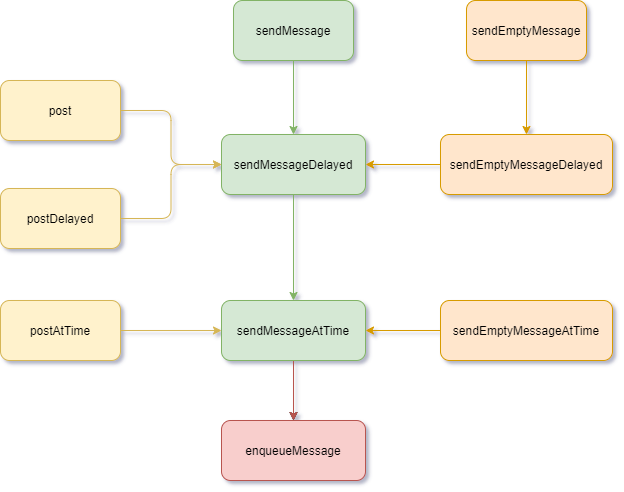
發送消息有幾種方式,但是歸根結底都是調用了sendMessageAtTime()方法。在子線程中通過Handler的post()方式或send()方式發送消息,最終都是調用了sendMessageAtTime()方法。
post方法:
public final boolean post(@NonNull Runnable r) {return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), 0);}public final boolean postAtTime(@NonNull Runnable r, long uptimeMillis) {return sendMessageAtTime(getPostMessage(r), uptimeMillis);}public final boolean postAtTime(@NonNull Runnable r, @Nullable Object token, long uptimeMillis) {return sendMessageAtTime(getPostMessage(r, token), uptimeMillis);}public final boolean postDelayed(@NonNull Runnable r, long delayMillis) {return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r), delayMillis);}public final boolean postDelayed(Runnable r, int what, long delayMillis) {return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r).setWhat(what), delayMillis);}public final boolean postDelayed(@NonNull Runnable r, @Nullable Object token, long delayMillis) {return sendMessageDelayed(getPostMessage(r, token), delayMillis);}
send方法:
public final boolean sendMessage(@NonNull Message msg) {return sendMessageDelayed(msg, 0);}public final boolean sendEmptyMessage(int what){return sendEmptyMessageDelayed(what, 0);}public final boolean sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what, long delayMillis) {Message msg = Message.obtain();msg.what = what;return sendMessageDelayed(msg, delayMillis);}public final boolean sendEmptyMessageAtTime(int what, long uptimeMillis) {Message msg = Message.obtain();msg.what = what;return sendMessageAtTime(msg, uptimeMillis);}public final boolean sendMessageDelayed(@NonNull Message msg, long delayMillis) {if (delayMillis < 0) {delayMillis = 0;}return sendMessageAtTime(msg, SystemClock.uptimeMillis() + delayMillis);}
就連子線程中調用Activity中的runOnUiThread()更新UI,其實也是發送消息通知主線程更新UI,最終也會調用sendMessageAtTime()方法。
/*** 如果當前的線程不等于UI線程(主線程),就去調用Handler的post()方法,最終會調用sendMessageAtTime()方法。* 否則就直接調用Runnable對象的run()方法。*/
public final void runOnUiThread(Runnable action) {if (Thread.currentThread() != mUiThread) {mHandler.post(action);} else {action.run();}
}
sendMessageAtTime()
public boolean sendMessageAtTime(@NonNull Message msg, long uptimeMillis) {// 其中mQueue是消息隊列,從Looper中獲取的MessageQueue queue = mQueue;if (queue == null) {RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException(this + " sendMessageAtTime() called with no mQueue");Log.w("Looper", e.getMessage(), e);return false;}// 調用enqueueMessage方法return enqueueMessage(queue, msg, uptimeMillis);}private boolean enqueueMessage(@NonNull MessageQueue queue, @NonNull Message msg,long uptimeMillis) {// 把自己(Handler)傳入消息一并發送,因為Looper需要用Handler來執行dispatchMessage()msg.target = this;msg.workSourceUid = ThreadLocalWorkSource.getUid();if (mAsynchronous) {msg.setAsynchronous(true);}// 調用MessageQueue的enqueueMessage方法return queue.enqueueMessage(msg, uptimeMillis);}
可以看到sendMessageAtTime()方法的作用很簡單,就是調用MessageQueue的enqueueMessage()方法,往消息隊列中添加一個消息。
)




)


)





)
)



