本節目標:
- 認識并且能夠實現一個雙鏈表
- 認識LinkedList類并且知道如何去使用
1.雙鏈表
概念
在數據結構中,雙鏈表(Doubly Linked List)?是一種常見的線性數據結構,它由一系列節點組成,每個節點不僅包含數據域,還包含兩個指針域,分別指向其前驅節點(前一個節點)?和后繼節點(后一個節點)。這種結構相比單鏈表(僅含后繼指針),在節點訪問和操作上更加靈活,可以表示成這樣:
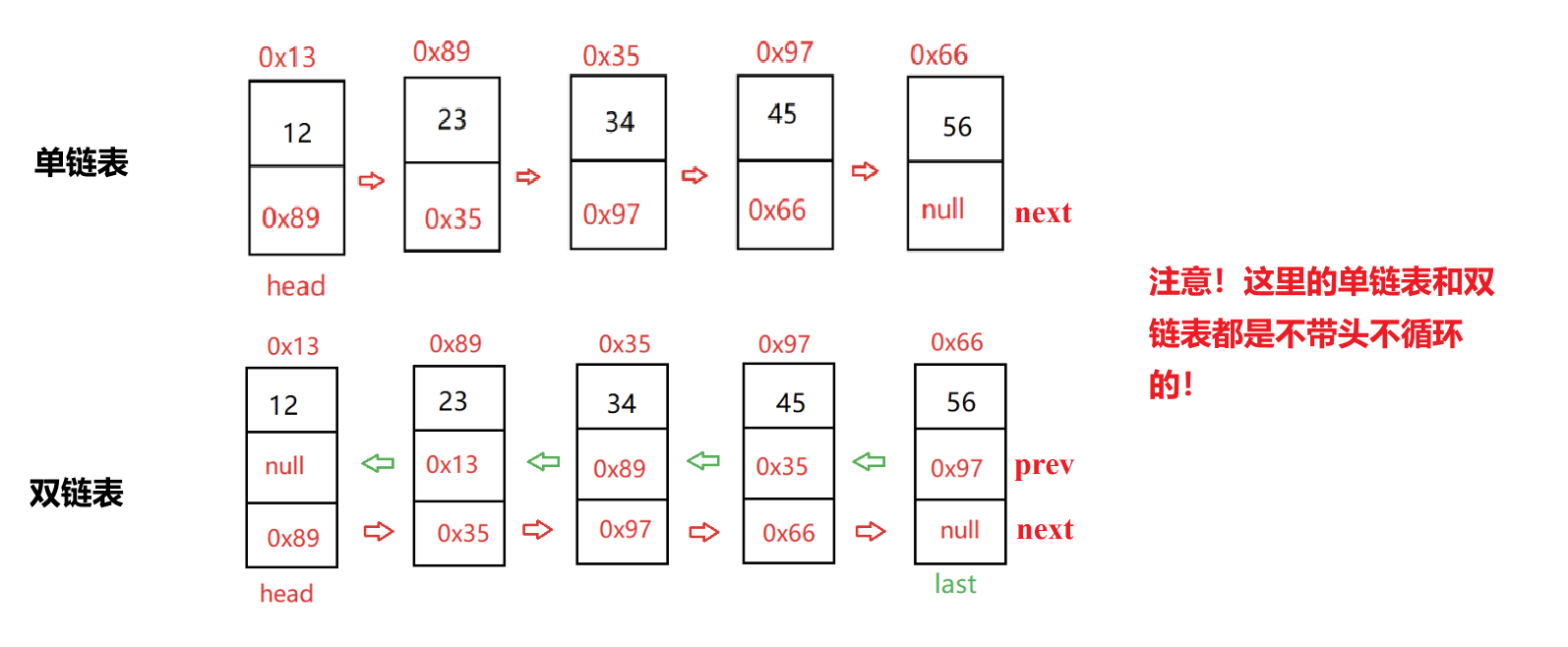
相較于單鏈表,雙鏈表多了一個前驅節點prev,它儲存的是這個節點的前一個節點的地址,即它指向這個節點的前一個節點。
實現雙鏈表
在上一節中,我們已經實現不帶頭不循環的單鏈表了,那么這里實現的是不帶頭不循環的雙鏈表。以下是這個雙鏈表包含的一些操作方法:
// 不帶頭雙向鏈表實現
public class MyLinkedList {
????????//頭插法
????????public void addFirst(int data){ }
????????//尾插法
????????public void addLast(int data){}
????????//任意位置插入,第一個數據節點為0號下標
????????public void addIndex(int index,int data){}
????????//判斷雙鏈表當中是否有包含key節點
????????public boolean contains(int key){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? return false;
????????}
????????//刪除第一次出現關鍵字為key的節點
????????public void remove(int key){}
????????//刪除所有值為key的節點
????????public void removeAllKey(int key){}
????????//得到雙鏈表的長度
????????public int size(){
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? return -1;
????????}
? ? ? ? //打印雙鏈表中的數據
????????public void display(){}
????????//清空雙鏈表
????????public void clear(){}
在實現這些操作之前,先創建節點類 ListNode:
public class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode prev;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}
還是老規矩,實現順序由簡到繁。
(1) 打印雙鏈表中的數據
要求:將雙鏈表中的數據一個個打印出來。
思路:實現方式與單鏈表的打印一樣,通過遍歷的方式,一個個去打印。
public class MyLinkedList {ListNode head;ListNode last;//打印雙鏈表中的數據public void display() {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}
}
因為雙鏈表中前驅結點指向該節點的前一個節點,因此它能夠從后往前訪問,所以用 last
來表示雙鏈表的尾節點。
(2) 得到雙鏈表的長度
要求:通過這個方法獲得雙鏈表的長度。
思路:定義一個變量用于計數,通過遍歷的方式進行計數,最后返回這個變量。
//得到雙鏈表的長度public int size() {ListNode cur = this.head;int size = 0; while (cur != null) {size++;cur = cur.next;}return size;}(3) 判斷雙鏈表當中是否有包含key節點
要求:判斷雙鏈表中是否有包含key的節點,如果有就返回true,否則返回false。
思路:依舊通過遍歷的方式去一個個判斷。
//判斷雙鏈表當中是否有包含key節點public boolean contains(int key){ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}(4) 頭插法
要求:在雙鏈表的頭部位置插入一個新節點。
思路:這里與單鏈表不一樣,需要考慮兩種情況:1.插入前鏈表是空的;2.插入前鏈表不為空。
即下圖所示:
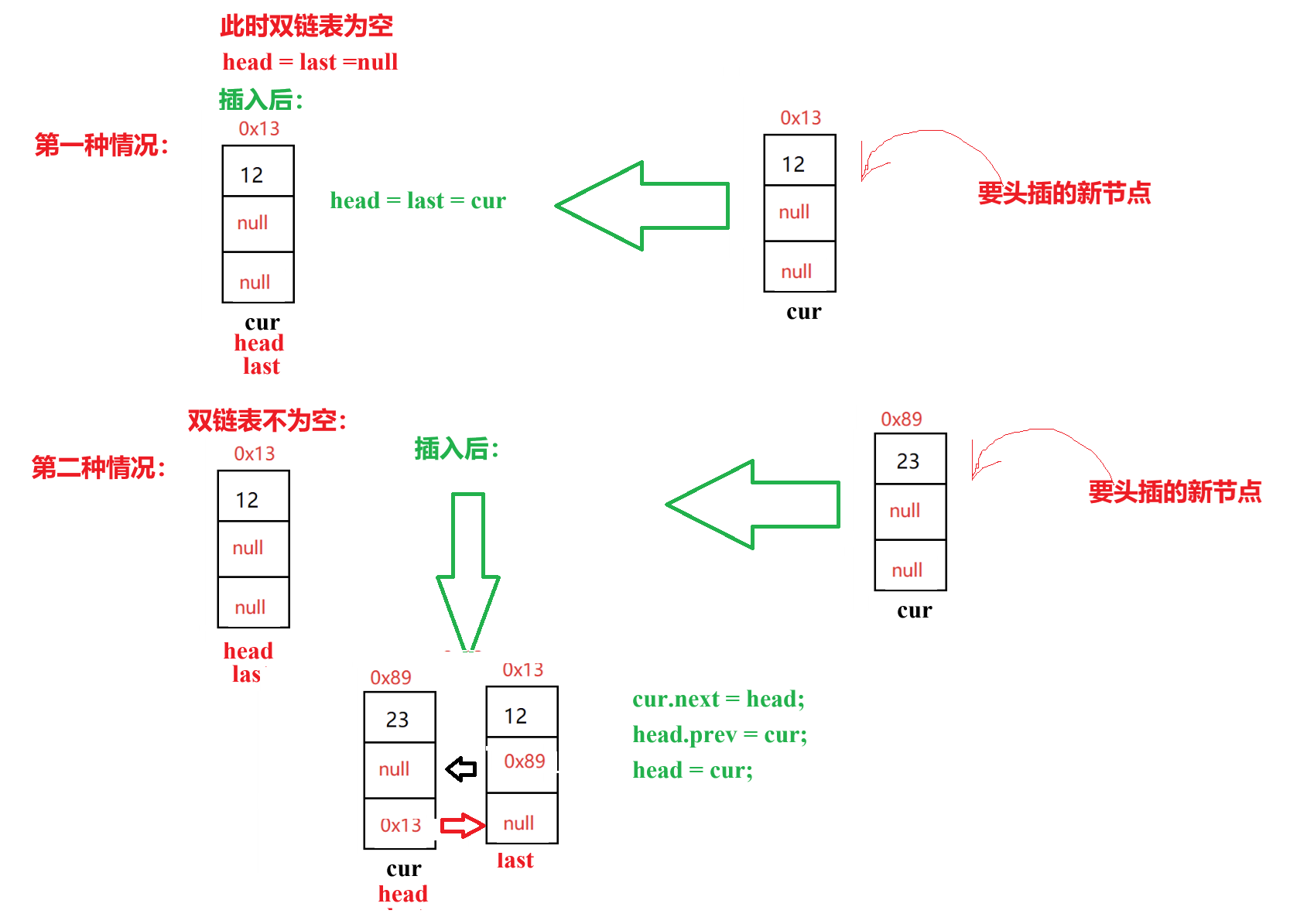
//頭插法public void addFirst(int data){ ListNode cur = new ListNode(data);if (this.head == null) {this.head = this.last = cur;}else {cur.next = this.head;this.head.prev = cur;this.head = cur;}}進行測試:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();myLinkedList.addFirst(1);myLinkedList.addFirst(2);myLinkedList.addFirst(3);myLinkedList.display();}
}//運行結果
3 2 1 符合預期。
(5) 尾插法
要求:在雙鏈表的尾部插入一個新節點。
思路:這里也分兩種情況,與頭插法一樣。需要注意的是,在鏈表不為空的情況下,我們應該對尾節點last進行操作,而不是頭節點head。
//尾插法public void addLast(int data){ListNode cur = new ListNode(data);if (this.head == null) {this.head = this.last = cur;}else {this.last.next = cur;cur.prev = this.last;this.last = cur;}}進行測試:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();myLinkedList.addLast(1);myLinkedList.addLast(2);myLinkedList.addLast(3);myLinkedList.display();}
}//運行結果
1 2 3 符合預期。
(6)?任意位置插入,第一個數據節點為0號下標
要求:在雙鏈表中合法的任一位置插入一個新節點,第一個節點為0號下標。
思路:可以分3種情況處理:頭插、尾插和中間插入。頭插與尾插已經解決了,因此現在只需要解決中間插入即可。如下圖所示:
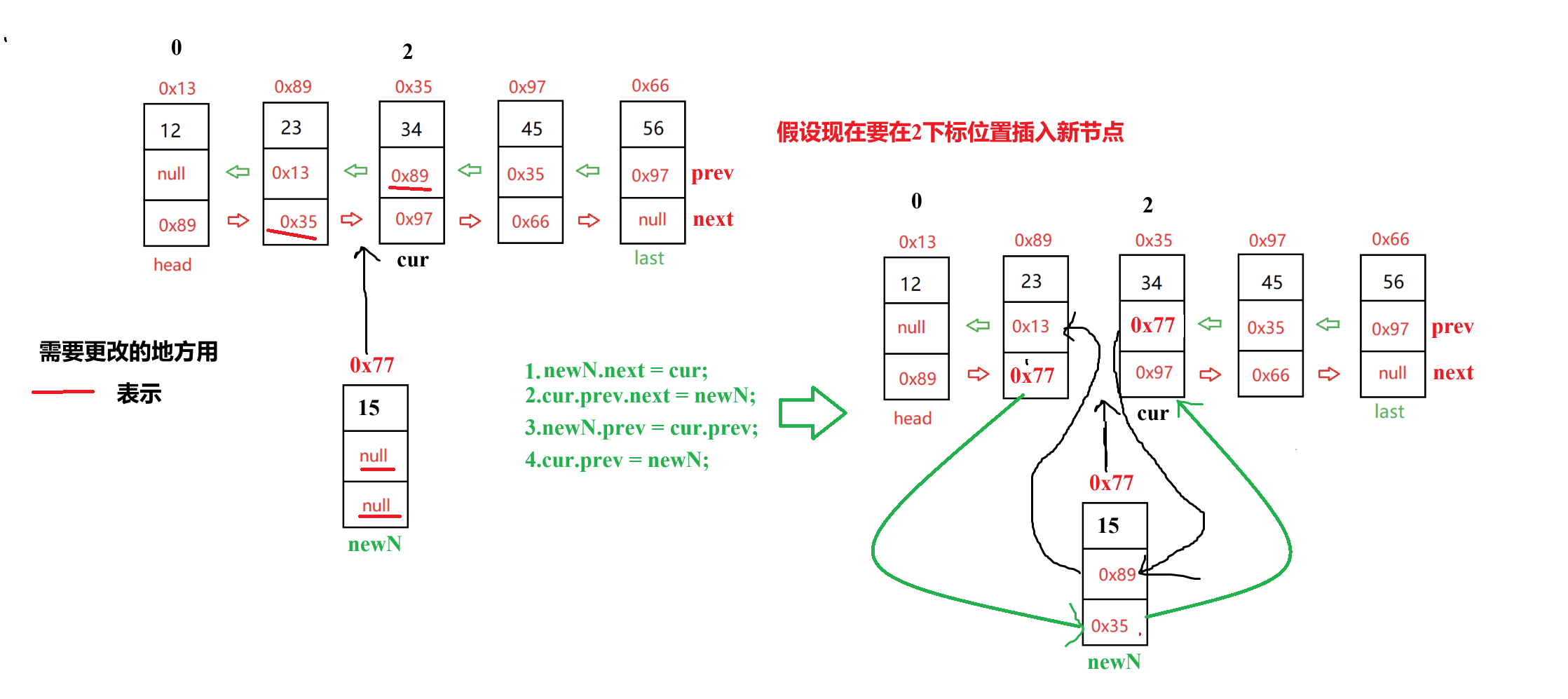
當然,在進行插入操作前,需要判斷插入位置是否合法。
插入位置非法異常類:
public class InsertIllegalException extends RuntimeException {public InsertIllegalException() {}public InsertIllegalException(String str) {super(str);}
}
判斷插入位置是否合法:
//判斷插入位置是否合法private void isIllegal(int index) {if (index < 0 || index > size()) {throw new InsertIllegalException("插入位置不合法!");}}插入操作:
//任意位置插入,第一個數據節點為0號下標public void addIndex(int index,int data){try {isIllegal(index);int len = size();//頭插if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}//尾插if (index == len) {addLast(data);return;}//中間插入ListNode newN = new ListNode(data);ListNode cur = this.head;while (index != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}newN.next = cur;cur.prev.next = newN;newN.prev = cur.prev;cur.prev = newN;}catch (InsertIllegalException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}進行測試:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();myLinkedList.addLast(1);myLinkedList.addLast(2);myLinkedList.addLast(3);myLinkedList.display();myLinkedList.addIndex(1,100);myLinkedList.display();}
}//運行結果
1 2 3
1 100 2 3 符合預期。
(7)?刪除第一次出現關鍵字為key的節點
要求:將雙鏈表中第一次出現包含key的節點刪掉。
思路:這里要分為三種情況:key在鏈表頭部、key在鏈表尾部和key在鏈表中間,但在開始前需要判斷鏈表是否為空。分析如下圖所示:
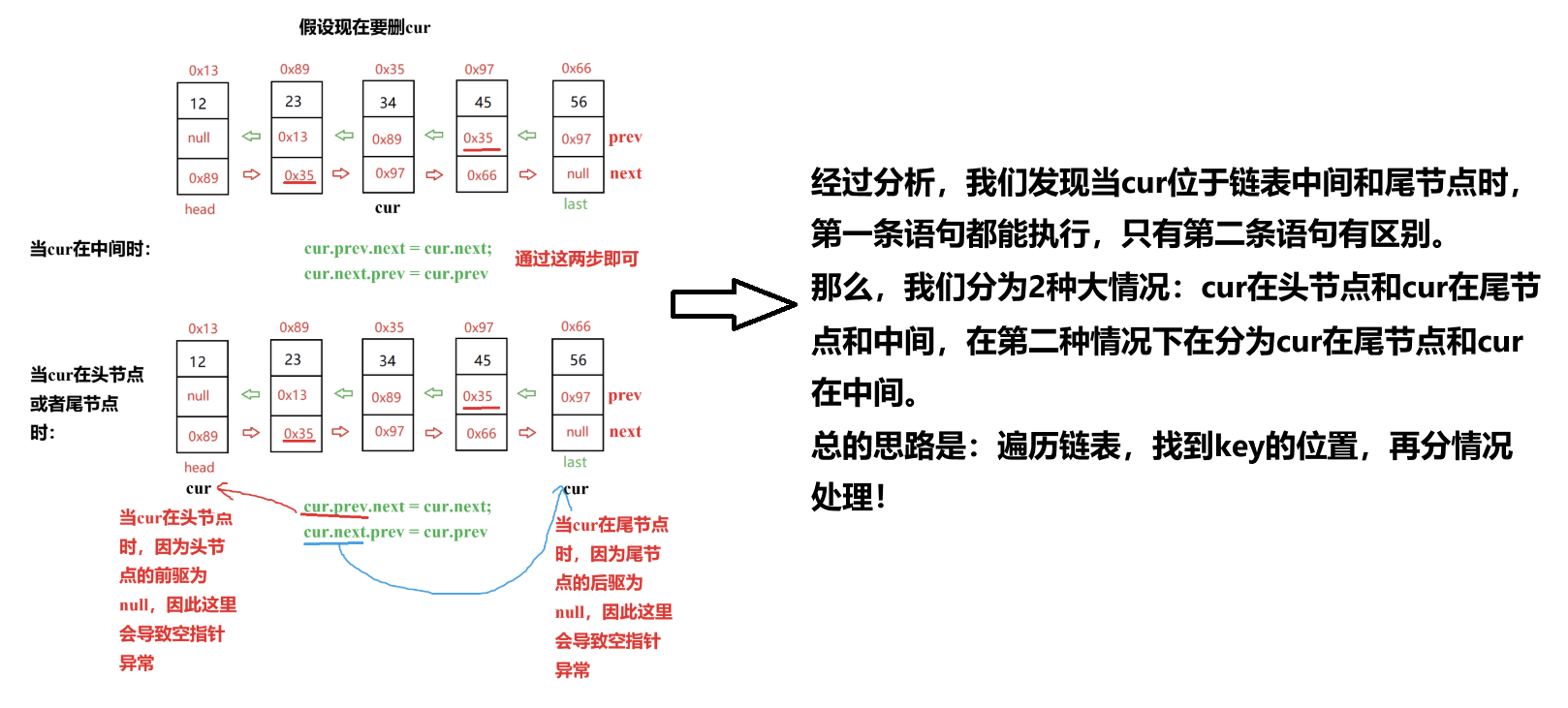
//刪除第一次出現關鍵字為key的節點public void remove(int key){if (this.head == null) {System.out.println("鏈表為空!");return;}ListNode cur = this.head;boolean mark = false; //用于標記鏈表中是否有key,有的話置為truewhile (cur != null) {//先找keyif (cur.val == key) {mark = true;//當cur位于頭節點if (cur == this.head) {this.head = this.head.next;this.head.prev = null;}else {//位于中間或者尾節點cur.prev.next = cur.next;//位于尾節點if (cur.next == null) {this.last = this.last.prev;}else {//位于中間cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}}//刪除完成!return;}cur = cur.next;}if (mark == false) {System.out.println("鏈表中沒有" + key);}}但是這里還有一個不足的地方,就是當鏈表中僅有一個節點時(即head == last且該節點的值為key),這時候 head.prev就會引發空指針異常,所以要對key在頭節點的情況進行補充處理:
//刪除第一次出現關鍵字為key的節點public void remove(int key){if (this.head == null) {System.out.println("鏈表為空!");return;}ListNode cur = this.head;boolean mark = false; //用于標記鏈表中是否有key,有的話置為truewhile (cur != null) {//先找keyif (cur.val == key) {mark = true;//當cur位于頭節點if (cur == this.head) {this.head = this.head.next;//當刪除后鏈表不為空,即鏈表不僅僅有一個節點if (this.head != null) {this.head.prev = null;}else {//刪除后鏈表為空,即鏈表僅有一個節點,這里更新尾節點lastthis.last = null;}}else {//位于中間或者尾節點cur.prev.next = cur.next;//位于尾節點if (cur.next == null) {this.last = this.last.prev;}else {//位于中間cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}}//刪除完成!return;}cur = cur.next;}if (mark == false) {System.out.println("鏈表中沒有" + key);}}進行測試:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();myLinkedList.addLast(1);myLinkedList.addLast(2);myLinkedList.addLast(3);myLinkedList.addLast(1);myLinkedList.display();myLinkedList.remove(1);myLinkedList.display();}
}//運行結果:
1 2 3 1
2 3 1 符合預期。
(8)?刪除所有值為key的節點
要求:將鏈表中所有值為key的節點都刪掉。
思路:只需要在刪除第一次出現關鍵字為key的節點的方法的基礎上進行修改即可,把return去掉,使得循環繼續進行,繼續找key的節點,繼續刪除,直到遍歷結束,此時已將所有值為key的節點刪除。
//刪除所有值為key的節點public void removeAllKey(int key) {if (this.head == null) {System.out.println("鏈表為空!");return;}ListNode cur = this.head;boolean mark = false; //用于標記鏈表中是否有key,有的話置為truewhile (cur != null) {//先找keyif (cur.val == key) {mark = true;//當cur位于頭節點if (cur == this.head) {this.head = this.head.next;//當刪除后鏈表不為空,即鏈表不僅僅有一個節點if (this.head != null) {this.head.prev = null;} else {//刪除后鏈表為空,即鏈表僅有一個節點,這里更新尾節點lastthis.last = null;}} else {//位于中間或者尾節點cur.prev.next = cur.next;//位于尾節點if (cur.next == null) {this.last = this.last.prev;} else {//位于中間cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}}}cur = cur.next;}if (mark == false) {System.out.println("鏈表中沒有" + key);}}不過這里可能會有一個潛在的問題,就是當我們刪除某一個節點,cur指向的節點已經被移除,此時執行cur = cur.next可能會出現問題。舉個例子:
現在有一個雙鏈表:
2 <-> 3 <-> 2 <-> 4
現在要刪掉所有的2
1.首先,cur指向第一個2,刪除后head變為3節點;
2.接著執行cur = cur.next時,此時的cur仍然指向已經被刪除的第一個 2 節點;
3.這個節點的
next雖然可能還指向 3,但這是不安全的(已刪除節點的引用應該被視為無效)
因此出于安全考慮,可以用一個變量記錄cur的=指向的下一個節點。
//刪除所有值為key的節點public void removeAllKey(int key) {if (this.head == null) {System.out.println("鏈表為空!");return;}ListNode cur = this.head;boolean mark = false; //用于標記鏈表中是否有key,有的話置為truewhile (cur != null) {ListNode curN = cur.next;//先找keyif (cur.val == key) {mark = true;//當cur位于頭節點if (cur == this.head) {this.head = this.head.next;//當刪除后鏈表不為空,即鏈表不僅僅有一個節點if (this.head != null) {this.head.prev = null;} else {//刪除后鏈表為空,即鏈表僅有一個節點,這里更新尾節點lastthis.last = null;}} else {//位于中間或者尾節點cur.prev.next = cur.next;//位于尾節點if (cur.next == null) {this.last = this.last.prev;} else {//位于中間cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}}}cur = curN;}if (mark == false) {System.out.println("鏈表中沒有" + key);}}進行測試:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();myLinkedList.addLast(2);myLinkedList.addLast(1);myLinkedList.addLast(2);myLinkedList.addLast(3);myLinkedList.addLast(2);myLinkedList.display();myLinkedList.removeAllKey(2);myLinkedList.display();}
}//運行結果:
2 1 2 3 2
1 3 符合預期。
(9) 清空雙鏈表
要求:將雙鏈表清空。
思路:粗暴的方式就不介紹了(直接將head和last置空),溫柔的方式:通過遍歷,一個個將節點的prev和next置空,最后將head和last置空。
//清空雙鏈表public void clear() {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {ListNode curN = cur.next;cur.prev = null;cur.next = null;cur = curN;}this.head = null;this.last = null;}進行測試:
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyLinkedList myLinkedList = new MyLinkedList();myLinkedList.addLast(2);myLinkedList.addLast(1);myLinkedList.addLast(2);myLinkedList.addLast(3);myLinkedList.addLast(2);myLinkedList.display();myLinkedList.clear();myLinkedList.display();}
}//運行結果:
2 1 2 3 2 符合預期。
到此,我們就成功實現了一個不帶頭不循環的雙鏈表。
完整代碼
public class MyLinkedList {ListNode head;ListNode last;//打印雙鏈表中的數據public void display() {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}System.out.println();}//得到雙鏈表的長度public int size() {ListNode cur = this.head;int size = 0;while (cur != null) {size++;cur = cur.next;}return size;}//判斷雙鏈表當中是否有包含key節點public boolean contains(int key){ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}//頭插法public void addFirst(int data){ListNode cur = new ListNode(data);if (this.head == null) {this.head = this.last = cur;}else {cur.next = this.head;this.head.prev = cur;this.head = cur;}}//尾插法public void addLast(int data){ListNode cur = new ListNode(data);if (this.head == null) {this.head = this.last = cur;}else {this.last.next = cur;cur.prev = this.last;this.last = cur;}}//判斷插入位置是否合法private void isIllegal(int index) {if (index < 0 || index > size()) {throw new InsertIllegalException("插入位置不合法!");}}//任意位置插入,第一個數據節點為0號下標public void addIndex(int index,int data){try {isIllegal(index);int len = size();//頭插if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}//尾插if (index == len) {addLast(data);return;}//中間插入ListNode newN = new ListNode(data);ListNode cur = this.head;while (index != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}newN.next = cur;cur.prev.next = newN;newN.prev = cur.prev;cur.prev = newN;}catch (InsertIllegalException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}//刪除第一次出現關鍵字為key的節點public void remove(int key){if (this.head == null) {System.out.println("鏈表為空!");return;}ListNode cur = this.head;boolean mark = false; //用于標記鏈表中是否有key,有的話置為truewhile (cur != null) {//先找keyif (cur.val == key) {mark = true;//當cur位于頭節點if (cur == this.head) {this.head = this.head.next;//當刪除后鏈表不為空,即鏈表不僅僅有一個節點if (this.head != null) {this.head.prev = null;}else {//刪除后鏈表為空,即鏈表僅有一個節點,這里更新尾節點lastthis.last = null;}}else {//位于中間或者尾節點cur.prev.next = cur.next;//位于尾節點if (cur.next == null) {this.last = this.last.prev;}else {//位于中間cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}}//刪除完成!return;}cur = cur.next;}if (mark == false) {System.out.println("鏈表中沒有" + key);}}//刪除所有值為key的節點public void removeAllKey(int key) {if (this.head == null) {System.out.println("鏈表為空!");return;}ListNode cur = this.head;boolean mark = false; //用于標記鏈表中是否有key,有的話置為truewhile (cur != null) {ListNode curN = cur.next;//先找keyif (cur.val == key) {mark = true;//當cur位于頭節點if (cur == this.head) {this.head = this.head.next;//當刪除后鏈表不為空,即鏈表不僅僅有一個節點if (this.head != null) {this.head.prev = null;} else {//刪除后鏈表為空,即鏈表僅有一個節點,這里更新尾節點lastthis.last = null;}} else {//位于中間或者尾節點cur.prev.next = cur.next;//位于尾節點if (cur.next == null) {this.last = this.last.prev;} else {//位于中間cur.next.prev = cur.prev;}}}cur = curN;}if (mark == false) {System.out.println("鏈表中沒有" + key);}}//清空雙鏈表public void clear() {ListNode cur = this.head;while (cur != null) {ListNode curN = cur.next;cur.prev = null;cur.next = null;cur = curN;}this.head = null;this.last = null;}
}
2.LinkedList
2.1 概念
LinkedList的底層是雙向鏈表結構,由于鏈表沒有將元素存儲在連續的空間中,元素存儲在單獨的節點中,然后通過引用將節點連接起來了,因此在在任意位置插入或者刪除元素時,不需要搬移元素,效率比較高。
在集合框架中,LinkedList也實現了List接口,具體如下:
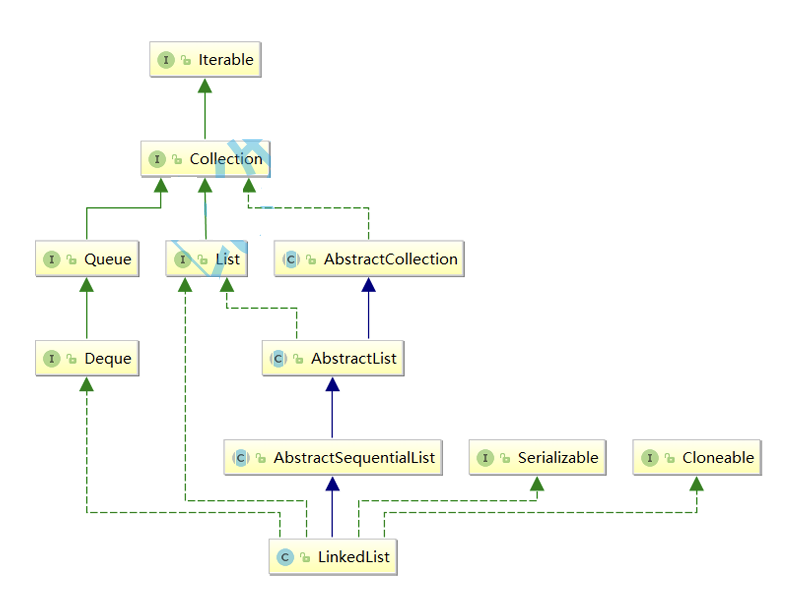
【說明】
- LinkedList實現了List接口
- LinkedList的底層使用了雙向鏈表
- LinkedList沒有實現RandomAccess接口,因此LinkedList不支持隨機訪問
- LinkedList的任意位置插入和刪除元素時效率比較高,時間復雜度為O(1)
- LinkedList比較適合任意位置插入的場景
2.2 使用
構造方法
LinkedList的構造方法:
| 方法 | 解釋 |
|---|---|
| LinkedList() | 無參構造 |
| public LinkedList(Collection <? extends E> c) | 使用其他集合容器中元素構造List |
舉例:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {//使用第一種構造方法,構造一個空的LinkedListLinkedList<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();//List<Integer> linkedList = new LinkedList<>();這種寫法等于上一條語句,//因此LinkedList實現了List接口,因此可以用List去接收//可以插入數據linkedList.addFirst(1);linkedList.addFirst(2);linkedList.addFirst(3);System.out.println(linkedList);System.out.println("=============");//使用第二種構造方法List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); //創建一個ArrayList,并往里面插入一些數據list.add(1);list.add(2);list.add(3);System.out.println(list);System.out.println("=============");//可以ArrayList構造LinkedListList<Integer> list1 = new LinkedList<>(list);System.out.println(list1);}
}//運行結果:
[3, 2, 1]
=============
[1, 2, 3]
=============
[1, 2, 3]其他常用方法
| 方法 | 解釋 |
|---|---|
| boolean add(E e) | 尾插 e |
| void add(int index, E element) | 將 e 插入到 index 位置 |
| boolean addAll(Collection <? extends E> c) | 尾插 c 中的元素 |
| E remove(int index) | 刪除 index 位置元素 |
| boolean remove(Object o) | 刪除遇到的第一個 o |
| E get(int index) | 獲取下標 index 位置元素 |
| E set(int index, E element) | 將下標 index 位置元素設置為 element |
| void clear() | 清空 |
| boolean contains(Object o) | 判斷 o 是否在線性表中 |
| int indexOf(Object o) | 返回第一個 o 所在下標 |
| int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回最后一個 o 的下標 |
| List subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 截取部分 list |
LinkedList的遍歷
LinkedList的遍歷與ArrayList的遍歷一樣,有三種方法,分別是通過for遍歷、通過for-each遍歷和通過迭代器遍歷。具體請看:
數據結構 ArrayList與順序表-CSDN博客
2.3 ArrayList與LinkedList的區別
| 不同點 | ArrayList | LinkedList |
|---|---|---|
| 存儲空間上 | 物理上一定連續 | 邏輯上連續,但物理上不一定連續 |
| 隨機訪問 | 支持:O(1) | 不支持:O(N) |
| 頭插 | 需要搬移元素,效率低O(N) | 只需修改引用的指向,時間復雜度為O(1) |
| 插入 | 空間不夠時需要擴容 | 沒有容量的概念 |
| 應用場景 | 元素高效存儲+頻繁訪問 | 任意位置插入和刪除頻繁 |
到此,雙鏈表與LinkedList的內容完結。感謝您的觀看,如有不對的地方還請指出,謝謝!







版)









)

