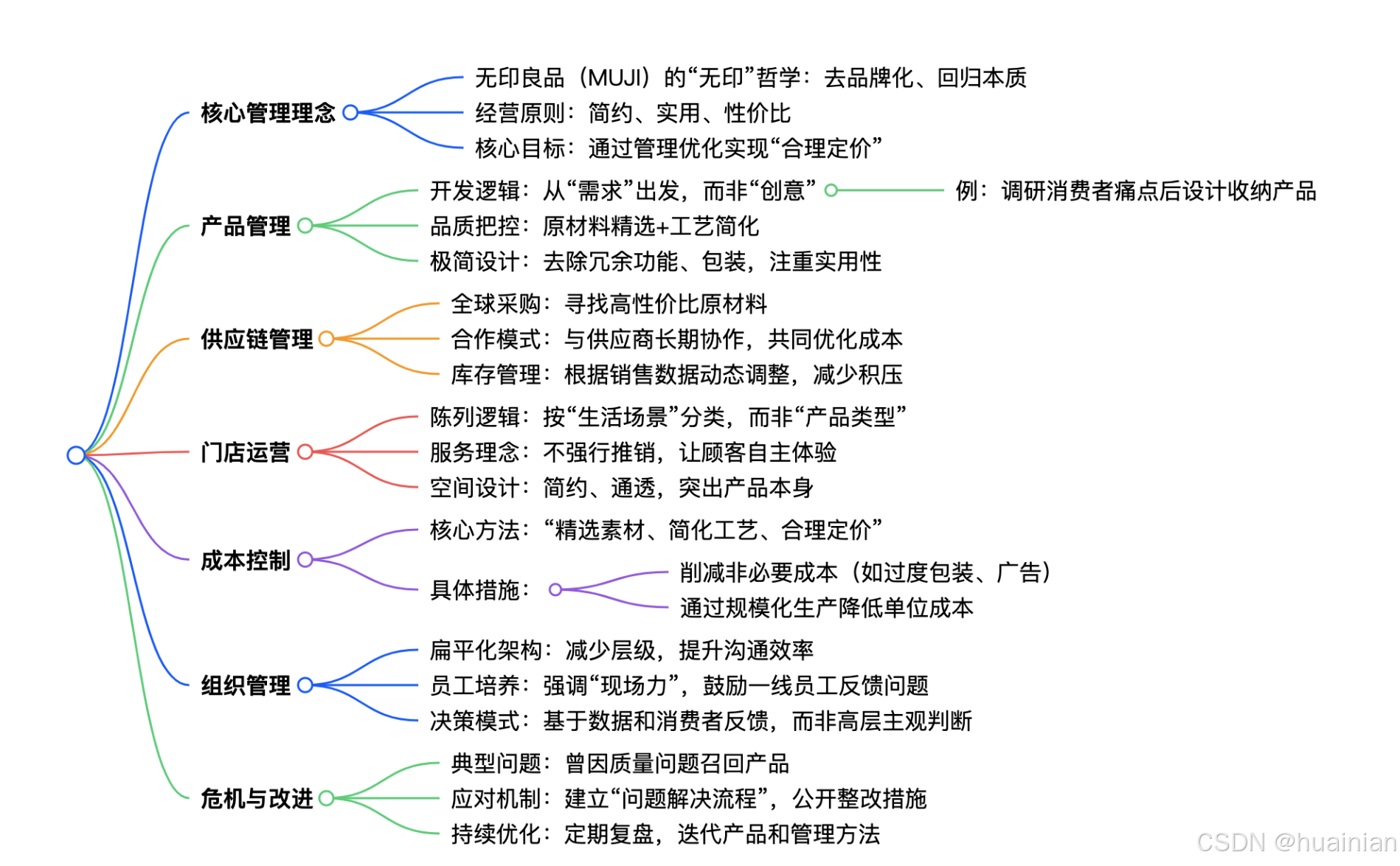
一、底層管理哲學?First, the underlying management philosophy
核心思想:「無印」即「無品牌標識」,回歸產品本質Core idea: "Muji" means "no brand logo", returning to the essence of products.
- 拒絕過度營銷,靠產品價值打動用戶?Refuse excessive marketing and impress users with product value.
- 例:包裝僅標注必要信息,無多余logo?For example: The packaging only marks the necessary information, without any redundant logos.
經營原點:「為生活解決問題」而非「創造需求」Business origin: "Solve problems for life" rather than "Create demand
- 調研方法:走訪用戶家庭,記錄真實使用痛點(如收納死角)Research methods: Visit users' homes and record real pain points in use (such as storage dead corners)
價值觀:「合理就好」—— 不追求極致低價,而是“品質與價格的平衡”Values: "What's reasonable is fine" - Instead of pursuing rock - bottom prices, we aim for "a balance between quality and price".
二、產品開發與管理?II. Product Development and Management
開發流程:「觀察→提案→驗證→量產」四步閉環Development process: A four-step closed loop of "Observation → Proposal → Verification → Mass production
- 觀察:派員工臥底競品門店、菜市場,記錄消費者抱怨Observation: Send employees to infiltrate competitor stores and wet markets to record consumer complaints
- 提案:跨部門(設計+采購+銷售)腦暴解決方案Proposal: Cross - departmental (Design + Procurement + Sales) brainstorming for solutions
- 驗證:制作樣品后在門店試銷,收集顧客試用反饋Verification: After making samples, conduct trial sales in stores and collect customer feedback on trial use.
- 量產:根據試銷數據調整規格(如減少某款杯子的容量)Mass production: Adjust specifications according to test marketing data (such as reducing the capacity of a certain type of cup)
產品標準:「三不原則」?Product Standard: "Three No Principles
- 不使用不必要的材料(如保溫杯去除多余裝飾)Do not use unnecessary materials (such as removing excessive decorations from thermos cups)
- 不采用復雜工藝(如T恤簡化縫線工序)?Do not adopt complex processes (such as simplifying the sewing process of T-shirts)
- 不做華而不實的設計(如手機殼僅保留防摔功能)Don't make flashy and impractical designs (for example, the mobile phone case only retains the anti-drop function)
迭代機制:每年淘汰30%滯銷品,補充20%新品Iteration mechanism: Eliminate 30% of slow-moving products and replenish 20% of new products every year.
- 數據依據:門店銷售排名+用戶差評關鍵詞分析Data basis: Store sales ranking + Keyword analysis of user negative reviews
三、供應鏈與成本控制?III. Supply Chain and Cost Control
全球供應鏈布局:「哪里性價比高,就從哪里采購」Global supply chain layout: "Purchase from wherever offers the best cost - effectiveness.
- 案例:棉花從印度采購(質優價平),拉鏈從日本采購(耐用)Case: Cotton is sourced from India (high quality and reasonable price), and zippers are sourced from Japan (durable).
供應商管理:「伙伴關系」而非「甲乙方」?Supplier Management: "Partnership" rather than "Client - Supplier Relationship
- 共同研發:派技術人員駐廠,協助供應商改進工藝Joint R & D: Assign technicians to the factory to assist suppliers in improving the process
- 成本共擔:原材料漲價時,與供應商協商分攤比例Cost sharing: When raw material prices increase, negotiate the sharing ratio with suppliers.
庫存控制:「Just In Time(準時制)」模式Inventory control: "Just In Time" model
- 數據工具:用POS系統實時追蹤銷售,自動觸發補貨Data tools: Use the POS system to track sales in real time and automatically trigger replenishment.
- 處理滯銷:設立「折扣區」集中清庫存,避免浪費Handling slow - moving products: Set up a "Discount Area" to centrally clear inventory and avoid waste
成本壓縮技巧:?Cost compression techniques:
- 包裝:用再生紙、無印刷塑料袋?Packaging: Use recycled paper and unprinted plastic bags
- 物流:合并同區域訂單,減少運輸頻次?Logistics: Combine orders in the same region to reduce the frequency of transportation
四、門店運營與用戶體驗?IV. Store Operations and User Experience
陳列邏輯:「生活場景化」而非「品類堆砌」Display logic: "Life scene-based" rather than "category stacking
- 案例:臥室區同時擺放床品、臺燈、收納盒,模擬真實臥室Case: In the bedroom area, bedding, table lamps, and storage boxes are placed simultaneously to simulate a real bedroom.
動線設計:「無引導式」布局?Moving line design: "Non-guided" layout
- 入口無導購攔截,讓顧客自由逛覽?There is no shopping guide intercepting at the entrance, allowing customers to browse freely.
- 貨架高度統一(1.5米),確保視線通透?The shelf height is unified (1.5 meters) to ensure unobstructed sightlines.
服務準則:「適度干預」?Service criteria: "Moderate intervention
- 顧客提問才上前,不推銷“會員”“滿減”?Only approach customers when they have questions. Do not promote "memberships" or "discounts for reaching a certain amount".
- 試用品充足(如香薰可開蓋聞,衣服可直接試穿)
門店數字化:
- 用APP記錄用戶瀏覽軌跡,優化陳列
- 自助結賬占比超60%,減少排隊
五、組織與人才管理?V. Organization and Talent Management
架構:「扁平化」三級體系?Architecture: "Flat" three - level system
- 總部(決策)→區域經理(協調)→門店(執行),無中間層級Headquarters (Decision - making) → Regional Manager (Coordinating) → Store (Execution), with no intermediate levels
- 好處:一線問題24小時內直達總部?Benefits: Frontline issues can reach the headquarters within 24 hours.
員工培養:「現場力至上」?Employee Training: "On-site Capability First
- 新人必輪崗3個月(采購+門店+倉庫),了解全流程Newcomers must rotate positions for 3 months (purchasing + store + warehouse) to understand the whole process.
- 鼓勵員工提改進建議,被采納者獲“改善獎”(如調整貨架角度)Encourage employees to put forward improvement suggestions, and those whose suggestions are adopted will receive the "Improvement Award" (such as adjusting the angle of the shelves).
考核標準:「用戶滿意度」優先于「銷售額」Assessment criteria: "Customer satisfaction" takes precedence over "Sales volume
- 定期電話回訪顧客,差評由店長親自跟進整改Regularly conduct telephone follow - up with customers. The store manager will personally follow up and rectify negative reviews.
六、危機應對與持續進化?VI. Crisis Response and Continuous Evolution
典型危機案例:2017年“甲醛超標”事件?Typical crisis case: the "formaldehyde exceeding standard" incident in 2017
應對步驟:?Response steps:
- 24小時內公開召回涉事產品?Publicly recall the products involved within 24 hours
- 成立第三方檢測小組徹查原因?Establish a third-party inspection team to thoroughly investigate the causes.
- 在門店張貼整改報告,透明化處理過程?Post the rectification report in the store to make the handling process transparent.
自我革新機制:「MUJI會議」?Self-innovation mechanism: "MUJI Meeting
- 每月跨部門復盤會,用數據暴露問題(如“某款筆退貨率高”)Monthly cross - departmental review meeting, expose problems with data (such as "the return rate of a certain pen is high")
- 每年發布《MUJI報告》,公開經營問題及改進方案Release the "MUJI Report" every year, disclosing operational issues and improvement plans.
創新方向:從“賣產品”到“賣生活方式”?Innovation direction: From "selling products" to "selling a lifestyle
- 延伸業務:MUJIcom(便利店)、MUJI INFILL(家裝服務)





寄存器映射)





)


)
html、css、js)
)


