目錄
1、堆的概念與結構
2、堆的實現
2.1 向上調整算法(堆的插入)
2.2 向下調整算法(堆的刪除)?
?2.3 完整代碼
3、堆的應用
3.1 堆排序
3.2 Top-K問題
1、堆的概念與結構
堆是一種特殊的二叉樹,根結點最大的堆稱為大根堆(也叫最大堆),根結點最小的堆稱為小根堆(也叫最小堆)
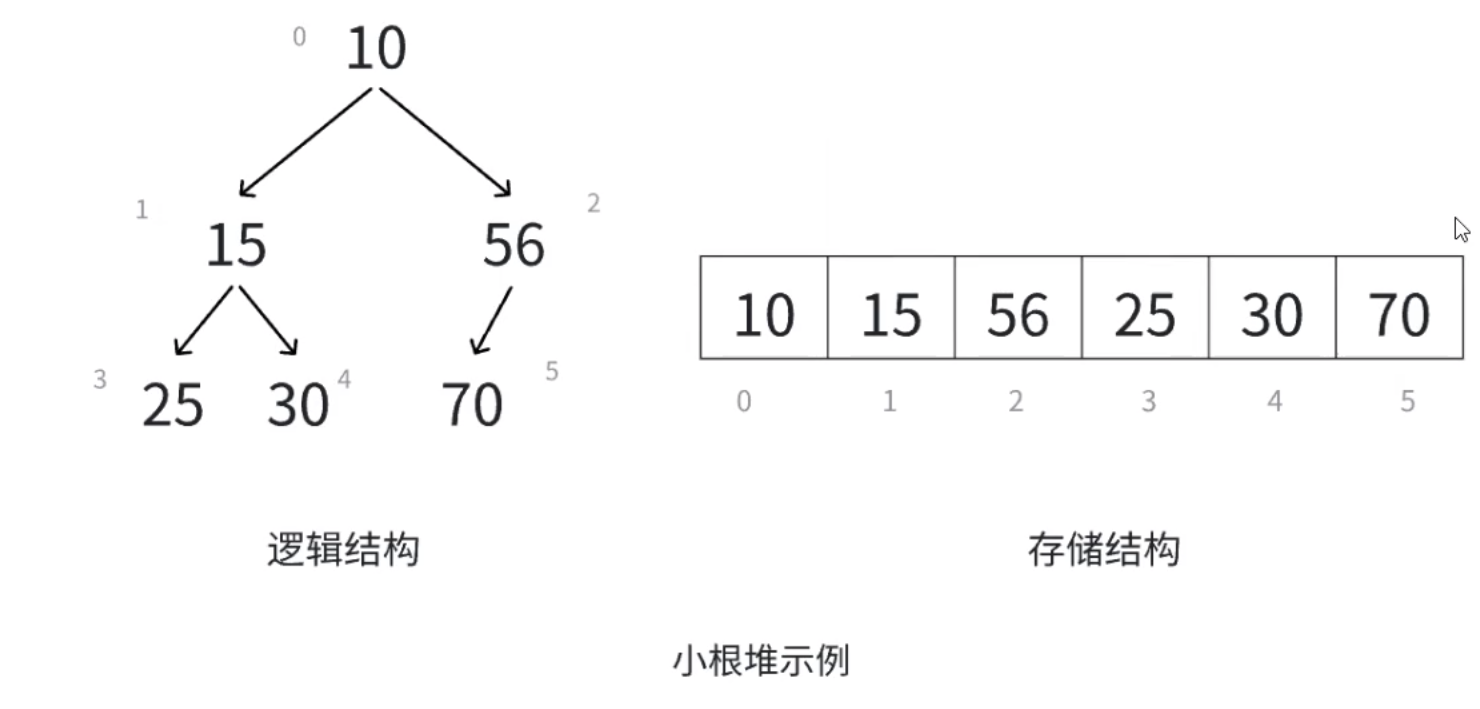
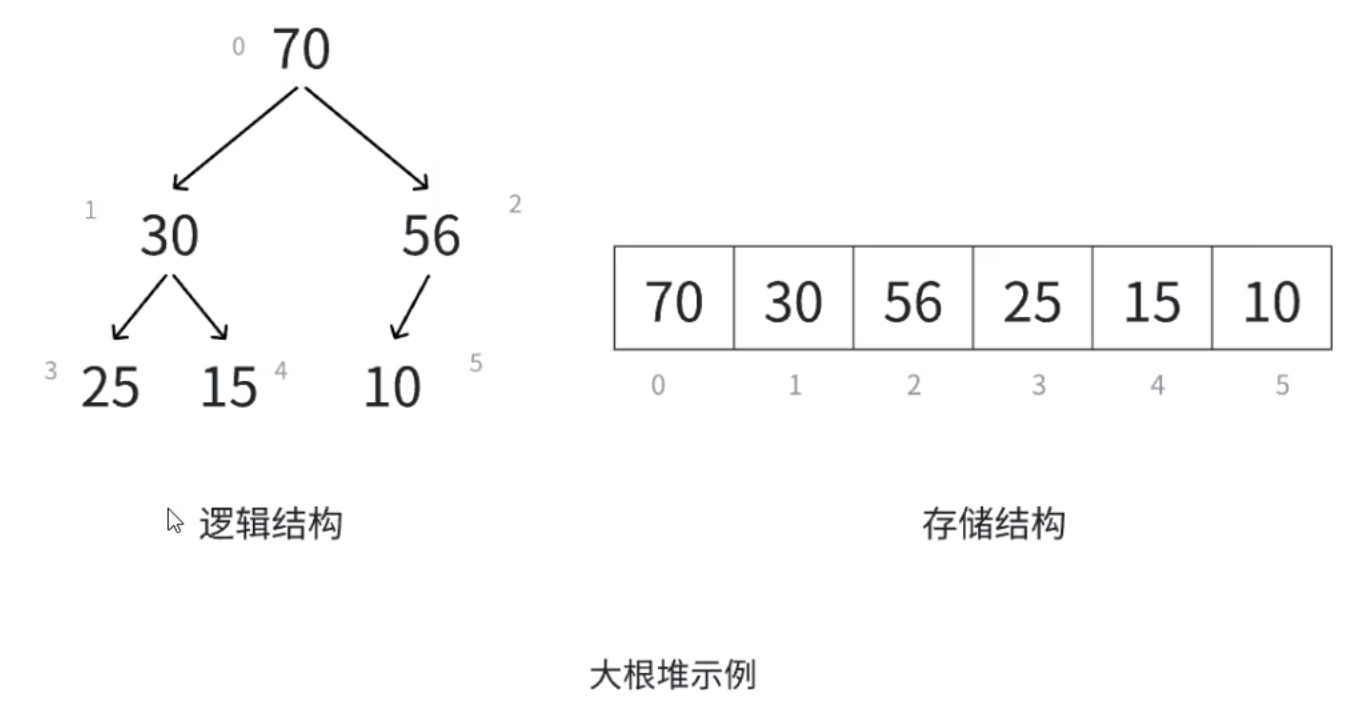
堆具有以下性質:(1)堆中某個結點的值總是不大于或不小于其父結點的值
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?(2)堆總是一棵完全二叉樹
二叉樹的性質
對于具有n個結點的完全二叉樹,如果從上至下從左至右的數組順序對所有結點從0開始編號,對于序號為i的結點有:
1. 若 i > 0,i 位置的雙親結點序號:(i - 1)/ 2;i = 0,i 為根結點,無雙親結點
2. 若 2i + 1 < n,左孩子序號:2i + 1,若 2i + 1 >= n,則沒有左孩子
3. 若 2i + 1 < n,右孩子序號:2i + 2,若 2i + 2?>= n,則沒有右孩子
2、堆的實現
2.1 向上調整算法(堆的插入)
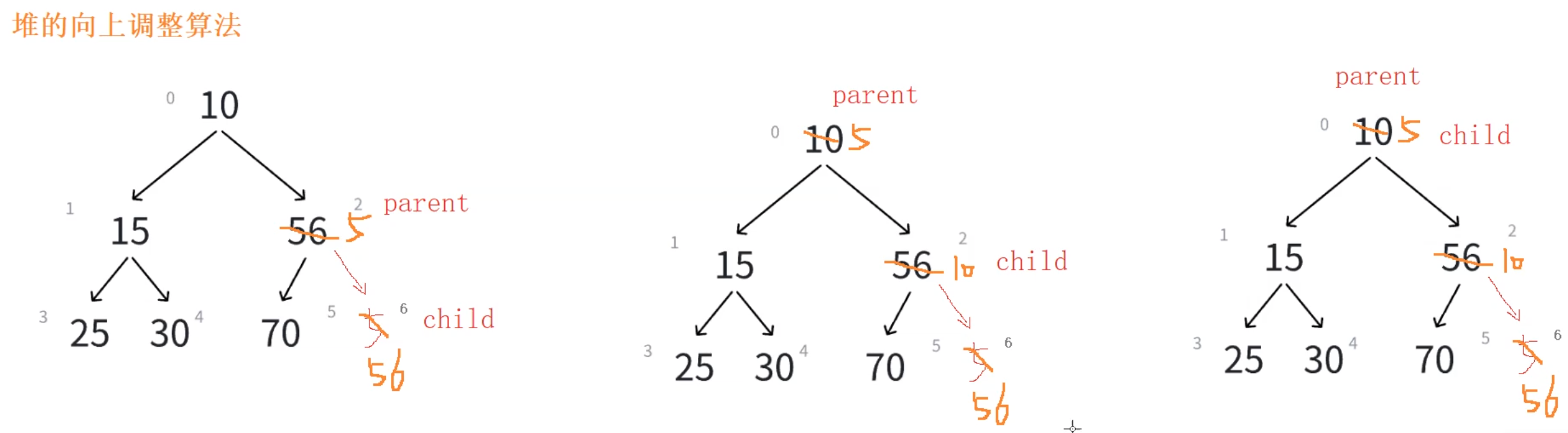
將新數據插入到數組的尾上,再進行向上調整算法,直到滿足堆。
向上調整算法
1、先將元素插入到堆的末尾,即最后一個孩子之后
2、插入之后如果堆的性質遭到破壞,將新插入節點順著其雙親往上調整到合適位置即可
void Swap(HPDataType* x, HPDataType* y)
{HPDataType tmp = *x;*x = *y;*y = tmp;
}void AdjustUp(HPDataType* arr, int child)
{int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){//大堆: >//小堆: <if (arr[child] < arr[parent]){//調整Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);child = parent;parent = (parent - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}
}2.2 向下調整算法(堆的刪除)?
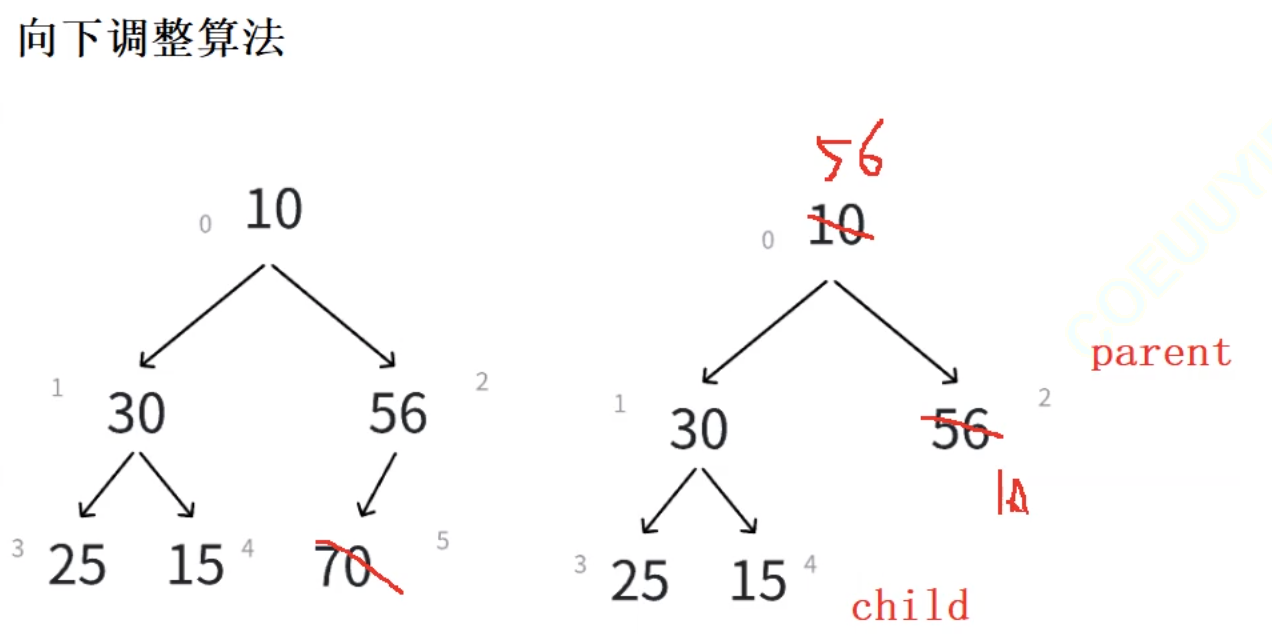
?刪除堆是刪除堆頂的數據,將堆頂數據和最后一個數據交換,然后刪除最后一個數據,再進行向下調整算法。
向下調整算法
1、將堆頂元素與堆中最后一個元素進行交換
2、刪除堆中最后一個元素
3、將堆頂元素向下調整直到滿足堆的特性為止
void AdjustDown(HPDataType* arr, int parent, int n)
{int child = 2 * parent + 1;//左孩子while (child < n){if (child + 1 < n && arr[child] > arr[child + 1]){child = child + 1;}if (arr[child] < arr[parent]){//調整Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);parent = child;child = 2 * child + 1;}else{break;}}
}void HPPop(HP* php)
{assert(!HPEmpty(php));//0 php->size - 1Swap(&php->arr[0], &php->arr[php->size - 1]);php->size--;//向下調整AdjustDown(php->arr, 0, php->size);
}?2.3 完整代碼
Heap.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>//堆的結構
typedef int HPDataType;
typedef struct Heap
{HPDataType* arr;int size; //有效數據個數int capacity; //空間大小
}HP;void HPInit(HP* php);
void HPDestroy(HP* php);
void HPPrint(HP* php);void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x);
void HPPop(HP* php);//判空
bool HPEmpty(HP* php);//取堆頂數據
HPDataType HPTop(HP* php);Heap.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Heap.h"void HPInit(HP* php)
{php->arr = NULL;php->size = php->capacity = 0;
}void HPDestroy(HP* php)
{if (php->arr)free(php->arr);php->arr = NULL;php->size = php->capacity = 0;
}void HPPrint(HP* php)
{for (int i = 0;i < php->size;i++){printf("%d ", php->arr[i]);}printf("\n");
}void Swap(HPDataType* x, HPDataType* y)
{HPDataType tmp = *x;*x = *y;*y = tmp;
}void AdjustUp(HPDataType* arr, int child)
{int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (child > 0){//大堆: >//小堆: <if (arr[child] < arr[parent]){//調整Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);child = parent;parent = (parent - 1) / 2;}else{break;}}
}void HPPush(HP* php, HPDataType x)
{assert(php);if (php->size == php->capacity){int newCapacity = php->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * php->capacity;HPDataType* tmp = (HPDataType*)realloc(php->arr, newCapacity * sizeof(int));if (tmp == NULL){perror("realloc fail!");exit(1);}php->arr = tmp;php->capacity = newCapacity;}php->arr[php->size] = x;//向上調整AdjustUp(php->arr, php->size);php->size++;
}//判空
bool HPEmpty(HP* php)
{assert(php);return php->size == 0;
}void AdjustDown(HPDataType* arr, int parent, int n)
{int child = 2 * parent + 1;//左孩子while (child < n){if (child + 1 < n && arr[child] > arr[child + 1]){child = child + 1;}if (arr[child] < arr[parent]){//調整Swap(&arr[child], &arr[parent]);parent = child;child = 2 * child + 1;}else{break;}}
}void HPPop(HP* php)
{assert(!HPEmpty(php));//0 php->size - 1Swap(&php->arr[0], &php->arr[php->size - 1]);php->size--;//向下調整AdjustDown(php->arr, 0, php->size);
}//取堆頂數據
HPDataType HPTop(HP* php)
{assert(!HPEmpty(php));return php->arr[0];
}test.c?
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Heap.h"void test01()
{HP hp;HPInit(&hp);HPPush(&hp, 56);HPPush(&hp, 10);HPPush(&hp, 15);HPPush(&hp, 30);HPPush(&hp, 70);HPPush(&hp, 25);HPPrint(&hp);HPPop(&hp);HPPrint(&hp);HPDestroy(&hp);
}void test02()
{HP hp;HPInit(&hp);HPPush(&hp, 56);HPPush(&hp, 10);HPPush(&hp, 15);HPPush(&hp, 30);HPPrint(&hp);while (!HPEmpty(&hp)){int top = HPTop(&hp);printf("%d ", top);HPPop(&hp);}
}int main()
{//test01();test02();return 0;
}3、堆的應用
3.1 堆排序
? ? ? ? 我們發現,依次取出堆頂元素,元素是按照從小到大(或從大到小)的順序排列輸出的,因此,我們可以使用堆這個數據結構來進行排序。
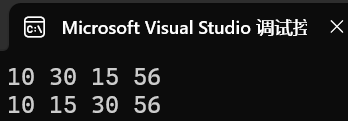
版本一:基于已有數組建堆,取堆頂元素完成排序。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "Heap.h"//堆排序
void HeapSort(int* arr, int n)
{HP hp;HPInit(&hp);for (int i = 0;i < n;i++){HPPush(&hp, arr[i]);}int i = 0;while (!HPEmpty(&hp)){int top = HPTop(&hp);arr[i++] = top;HPPop(&hp);}HPDestroy(&hp);
}int main()
{int arr[6] = { 19,15,20,17,13,10 };HeapSort(arr, 6);for (int i = 0;i < 6;i++){printf("%d ", arr[i]);}printf("\n");return 0;
}該版本有一個前提,那就是必須要借助堆這個數據結構,而我們所說的堆排序,并不是要用對這個數據結構來排序,而是要借助堆的思想。
版本二:根據數組建堆,首尾交換,交換后的堆尾數據從堆中刪掉,將堆頂數據向下調整選出次大的數據。
第一步、根據數組進行建堆?
????????排升序——建大堆
????????排降序——建小堆
第二步、將堆頂和最后一個數據交換位置,--size并向下調整堆,重復該過程
void HeapSort(int* arr, int n)
{//建堆——向下調整算法建堆for (int i = (n - 1 - 1) / 2;i >= 0;i--){AdjustDown(arr, i, n);}//堆排序int end = n - 1;while (end > 0){Swap(&arr[0], &arr[end]);AdjustDown(arr, 0, end);end--;}
}向下調整算法建堆時間復雜度為O(n)?
void HeapSort(int* arr, int n)
{//建堆——向上調整算法for (int i = 0;i < n;i++){AdjustUp(arr, i);}//堆排序int end = n - 1;while (end > 0){Swap(&arr[0], &arr[end]);AdjustDown(arr, 0, end);end--;}
}向上調整算法建堆時間復雜度為O(nlogn)
3.2 Top-K問題
Top-K問題:求數據中前K個最大的元素或者最小的元素,一般情況下數據量都比較大。對于Top-K問題,能想到的對簡單直接的方式就是排序,最佳的方式就是使用堆排序,基本思路如下:
先取前K個數據建堆,遍歷剩下的n - K個數據和堆頂比較。找最大的前K個數據,建小堆,比堆頂數據大就和堆頂元素交換;找最小的前K個數據,建大堆,比堆頂數據小就和堆頂元素交換。
#include "Heap.h"void CreateNData()
{//造數據int n = 100000;srand(time(0));const char* file = "data.txt";FILE* fin = fopen(file, "w");if (fin == NULL){perror("fopen error");return;}for (int i = 0;i < n;i++){int x = (rand() + i) % 100000;fprintf(fin, "%d\n", x);}fclose(fin);
}void TopK()
{printf("請輸入k:");int k = 0;scanf("%d", &k);const char* file = "data.txt";FILE* fout = fopen(file, "r");if (fout == NULL){perror("fopen fail");return;}//找最大的前k個數據,建小堆int* minHeap = (int*)malloc(k * sizeof(int));if (minHeap == NULL){perror("malloc fail");return;}for (int i = 0;i < k;i++){fscanf(fout, "%d", &minHeap[i]);}//minHeap--向下調整建堆for (int i = (k - 1 - 1) / 2;i >= 0;i--){AdjustDown(minHeap, i, k);}//遍歷剩下的n-k個數據,跟堆頂比較int x = 0;while (fscanf(fout, "%d", &x) != EOF){//minHeap-top x if (minHeap[0] < x){minHeap[0] = x;AdjustDown(minHeap, 0, k);}}for (int i = 0;i < k;i++){printf("%d ", minHeap[i]);}fclose(fout);
}int main()
{//CreateNData();TopK();return 0;
}


)


?? 的開源庫詳解)






檢測頭結構創新,實現有效漲點)


AXI協議總線學習)


![[特殊字符]? 整個鍵盤控制無人機系統框架](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[特殊字符]? 整個鍵盤控制無人機系統框架)