介紹
人工蜂群優化算法(Artificial Bee Colony Algorithm, ABC)是由Dervis Karaboga在2005年提出的一種模擬蜜蜂覓食行為的優化算法。該算法基于蜜蜂群體的分工合作和信息交流機制,通過模擬蜜蜂尋找食物源的過程來解決優化問題。ABC算法因其簡單、靈活和有效的特點,被廣泛應用于各類優化問題,如函數優化、數據挖掘、路徑規劃等
概念
ABC算法主要模擬了三類蜜蜂的行為:雇傭蜂、觀察蜂和偵查蜂。
雇傭蜂(Employed Bees):負責在食物源附近進行局部搜索,并將食物源的信息傳遞給觀察蜂。
觀察蜂(Onlooker Bees):在蜂巢中通過觀察雇傭蜂的舞蹈選擇食物源進行進一步搜索。
偵查蜂(Scout Bees):負責在全局范圍內隨機搜索新的食物源,以替代那些被淘汰的食物源。
步驟
初始化:在搜索空間內隨機生成若干個食物源(即解),并計算其適應度值。
雇傭蜂階段:
每只雇傭蜂在其對應的食物源附近隨機選擇一個新的解。
計算新解的適應度值,如果新解優于當前解,則更新當前解。
觀察蜂階段:
觀察蜂根據雇傭蜂的舞蹈(適應度值)選擇食物源,進行局部搜索。
與雇傭蜂階段類似,計算新解的適應度值并進行更新。
偵查蜂階段:
對于那些長時間未被改進的食物源,由偵查蜂進行全局隨機搜索,以尋找新的潛在食物源。
終止條件:重復上述步驟直到滿足終止條件(如達到最大迭代次數或滿足精度要求)。
本文示例
模擬了機器人在一個二維平面內的路徑規劃問題,目標是找到一條最優路徑,使得機器人能夠從起點移動到終點,避開障礙物
路徑規劃問題定義
假設一個二維平面中有若干障礙物,機器人需要從起點(Start)移動到終點(Goal),避開所有障礙物,找到一條最短路徑
代碼
clc;
clear;% 參數設置
numBees = 50; % 蜂群規模(食物源數量)
maxIter = 1000; % 最大迭代次數
limit = 100; % 限制參數,用于判斷是否需要啟用偵查蜂
dim = 2; % 問題維度
numObstacles = 10; % 障礙物數量
mapSize = [100, 100]; % 地圖大小% 起點和終點位置
startPoint = [10, 10];
endPoint = [90, 90];% 障礙物位置
obstacles = rand(numObstacles, 2) .* repmat(mapSize, numObstacles, 1);% 初始化食物源
foodSources = rand(numBees, dim) .* repmat(mapSize, numBees, 1);
fitness = calculateFitness(foodSources, startPoint, endPoint, obstacles, mapSize);
trials = zeros(numBees, 1);% 繪制地圖
figure;
hold on;
axis([0 mapSize(1) 0 mapSize(2)]);
plot(startPoint(1), startPoint(2), 'go', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'g');
plot(endPoint(1), endPoint(2), 'ro', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'r');
for i = 1:numObstaclesplot(obstacles(i, 1), obstacles(i, 2), 'ks', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'k');
end% 主循環
for iter = 1:maxIter% 雇傭蜂階段for i = 1:numBeesk = randi([1, dim]);phi = rand * 2 - 1;newSolution = foodSources(i, :);newSolution(k) = foodSources(i, k) + phi * (foodSources(i, k) - foodSources(randi([1, numBees]), k));newFitness = calculateFitness(newSolution, startPoint, endPoint, obstacles, mapSize);if newFitness < fitness(i)foodSources(i, :) = newSolution;fitness(i) = newFitness;trials(i) = 0;elsetrials(i) = trials(i) + 1;endend% 觀察蜂階段prob = fitness / sum(fitness);for i = 1:numBeesif rand < prob(i)k = randi([1, dim]);phi = rand * 2 - 1;newSolution = foodSources(i, :);newSolution(k) = foodSources(i, k) + phi * (foodSources(i, k) - foodSources(randi([1, numBees]), k));newFitness = calculateFitness(newSolution, startPoint, endPoint, obstacles, mapSize);if newFitness < fitness(i)foodSources(i, :) = newSolution;fitness(i) = newFitness;trials(i) = 0;elsetrials(i) = trials(i) + 1;endendend% 偵查蜂階段for i = 1:numBeesif trials(i) > limitfoodSources(i, :) = rand(1, dim) .* mapSize;fitness(i) = calculateFitness(foodSources(i, :), startPoint, endPoint, obstacles, mapSize);trials(i) = 0;endend% 繪制當前最優路徑[bestFitness, bestIndex] = min(fitness);bestSolution = foodSources(bestIndex, :);plotPath(startPoint, bestSolution, endPoint, obstacles);drawnow;
end% 計算適應度函數
function fitness = calculateFitness(solutions, startPoint, endPoint, obstacles, mapSize)numSolutions = size(solutions, 1);fitness = zeros(numSolutions, 1);for j = 1:numSolutionssolution = solutions(j, :);path = [startPoint; solution; endPoint];pathLength = 0;for i = 1:(size(path, 1) - 1)pathLength = pathLength + norm(path(i, :) - path(i + 1, :));endfor i = 1:size(obstacles, 1)if min(sqrt(sum((path - obstacles(i, :)).^2, 2))) < 5pathLength = pathLength + 10000; % 懲罰因子endendfitness(j) = pathLength;end
end% 繪制路徑
function plotPath(startPoint, solution, endPoint, obstacles)path = [startPoint; solution; endPoint];plot(path(:, 1), path(:, 2), 'b-o');plot(startPoint(1), startPoint(2), 'go', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'g');plot(endPoint(1), endPoint(2), 'ro', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'r');for i = 1:size(obstacles, 1)plot(obstacles(i, 1), obstacles(i, 2), 'ks', 'MarkerSize', 10, 'MarkerFaceColor', 'k');end
end效果
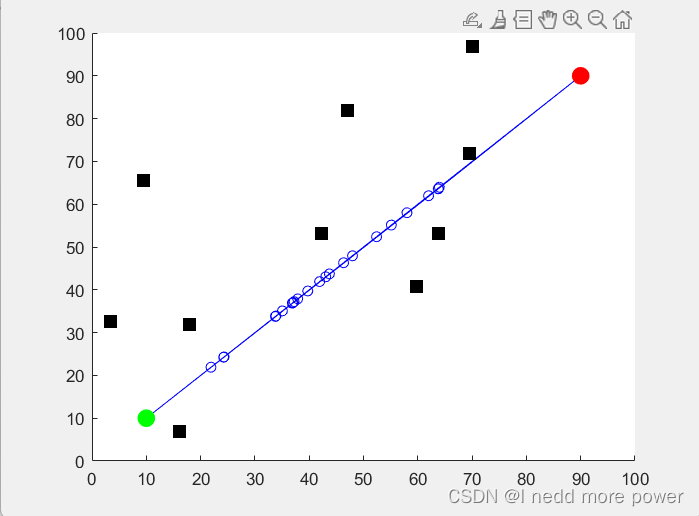
說明
初始化部分:
設置蜂群規模、最大迭代次數等參數。
定義地圖大小、起點和終點的位置,以及障礙物的位置。
初始化食物源(即路徑中的中間點)和計算初始適應度。
主循環部分:
雇傭蜂階段:雇傭蜂在當前食物源附近進行局部搜索,并根據適應度值決定是否更新食物源。
觀察蜂階段:觀察蜂根據雇傭蜂的舞蹈(適應度值)選擇食物源進行進一步搜索。
偵查蜂階段:對長時間未被改進的食物源進行全局隨機搜索,以尋找新的潛在食物源。
實時繪制當前最優路徑,以便觀察算法的收斂過程。
適應度函數:
計算路徑的總長度作為適應度值,同時對路徑經過障礙物的情況進行懲罰,以避免路徑穿越障礙物。
路徑繪制:
繪制當前最優路徑、起點、終點和障礙物,以便觀察路徑規劃的效果



)





,sizeof和strlen的數組計算以及指針運算筆試難題詳解)







 Object Pascal 學習筆記---第14章泛型第2節(Object Pascal中的泛型))

