一.繼承
Java語言的繼承:單繼承
1.類和類之間的關系
(1)組合關系
公司和員工,學校和學生
(2)繼承關系
學生和人
二.Object類
public class Object {private static native void registerNatives();static {registerNatives();}1.finalize()
對象被JVM回收的一定會自動調用。
~當對象已滿
while (true) {A a = new A();
}規則:當對象沒有任何引用何其關聯
A a = new A();
a = null;
package com.ffyca.entity;public class A {public void finalize() throws Throwable {System.out.println("我悄悄的走了,不帶走一片樹葉...");}
}package com.ffyca.Test;import com.ffyca.entity.A;public class TestA {public static void main(String[] args) {A a = new A();a = null;System.gc();}
}
2.toString()
Returns a string representation of the object. In general, the toString method returns a string that "textually represents" this object. The result should be a concise but informative representation that is easy for a person to read. It is recommended that all subclasses override this method.
System.out.println(c1);
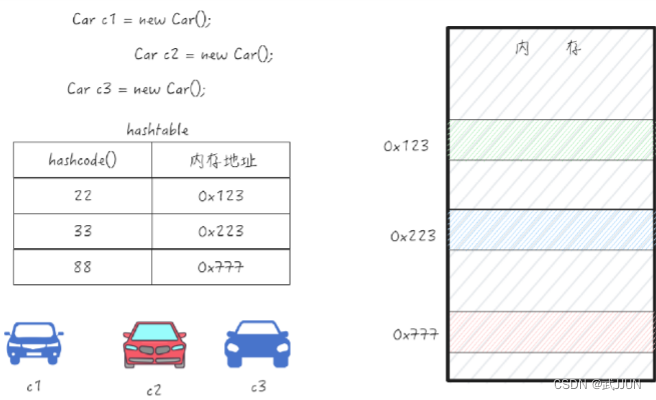
System.out.println(c1.toString());3.hashcode()
對象的一個唯一值,用來快速定位內存地址
Returns a hash code value for the object. This method is supported for the benefit of hash tables such as those provided by java.util.HashMap. The general contract of hashCode is: Whenever it is invoked on the same object more than once during an execution of a Java application, the hashCode method must consistently return the same integer, provided no information used in equals comparisons on the object is modified. This integer need not remain consistent from one execution of an application to another execution of the same application. If two objects are equal according to the equals(Object) method, then calling the hashCode method on each of the two objects must produce the same integer result. It is not required that if two objects are unequal according to the equals(Object) method, then calling the hashCode method on each of the two objects must produce distinct integer results. However, the programmer should be aware that producing distinct integer results for unequal objects may improve the performance of hash tables. As much as is reasonably practical, the hashCode method defined by class Object does return distinct integers for distinct objects. (This is typically implemented by converting the internal address of the object into an integer, but this implementation technique is not required by the Java? programming language.)
4.==
判斷兩個引用是否指向同一個對象。
5.equals
public boolean equals(Object obj) {return (this == obj);}判斷內容相等
==比較的是字符串的地址,但因為有字符串常量池的存在,故str1,str2指向的地址是相同的,所以返回true
如果是以new String("java")的方式創建對象,那么無論內容是否相等,==判斷返回的都是false
改寫equals()
寫一個汽車類:汽車牌號,品牌,價格,顏色
我們認為:如果兩個汽車的牌號相同那么汽車相等
a.equals(b)
?Tip:盡量不要手寫equals和hashcode
 ?
?
package com.ffyca.entity;import java.util.Objects;public class Car {private String num;private String brand;private double price;private String color;public String getNum() {return num;}public void setNum(String num) {this.num = num;}public String getBrand() {return brand;}public void setBrand(String brand) {this.brand = brand;}public double getPrice() {return price;}public void setPrice(double price) {this.price = price;}public String getColor() {return color;}public void setColor(String color) {this.color = color;}public Car(String num, String brand, double price, String color) {this.num = num;this.brand = brand;this.price = price;this.color = color;}@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object obj) {Car c2 = (Car)obj;String s1 = this.getNum();String s2 = c2.getNum();return s1.equals(s2);}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Car{" +"num='" + num + '\'' +", brand='" + brand + '\'' +", price=" + price +", color='" + color + '\'' +'}';}
}package com.ffyca.Test;import com.ffyca.entity.Car;public class TestCar {public static void main(String[] args) {Car car1 = new Car("陜F12345","BWM",2000000.0,"綠色");Car car2 = new Car("陜F12345","BWM",2000000.0,"綠色");System.out.println(car1.equals(car2));}
}
四.final關鍵詞
1.修飾引用
c永遠綁定此對象
final Car c = new Car();2.變量
a永遠是3
final int a = 3;
3.屬性
只能通過構造器,或者屬性直接給值
public class E{private final int a;
}4.class
不能被繼承
public final class E {
}5.方法
子類,實現類不能重寫的方法
public final void run(){}五.接口企業中的應用
1.定規則
2.常量
public interface Constants {int SUNDAY = 7;int LAST_MONDAY = 1;
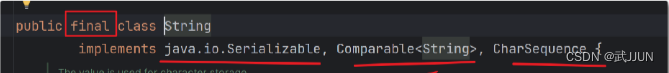
}六.String
1.包
java.lang包下的類會自動引用
2.類
3.內部實現

4.StringBuilder
提高字符串的拼接能力
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("hello");long s1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i=0;i<1000000;i++){sb.append(" world");
}
long s2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("時間:"+(s2-s1)+"ms")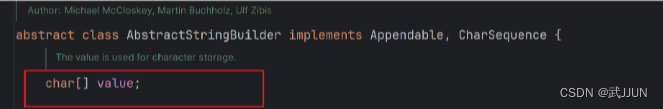
5.String常用的api
(1)將基本類型轉換為字符串
Integer.parseInt(str)
Double.parseDouble(str)

char[] s = {'s','a','p','t'};String t = String.valueOf(s,0,3); System.out.println(t);(2)字符大小轉換,空格處理
(2.1)空格處理
輸入時不小心多輸入空格
username: admin
過濾掉前后空格 trim()
(2.2)大小轉換
String str ="apple";str = str.toUpperCase();System.out.println("str:"+str);3.字符串截取
substring(int,int);
包頭不包尾,索引從0開始
substring(int);
substring(int,int);的重載方法,從當前索引位置一直截取到字符串的末尾
String str = "1000-趙云-蜀國-武將"; System.out.println(str.substring(8)); System.out.println(str.substring(8, 10));4.查找子字符串


5.拆分字符串
把字符串按照某個指定內容分割成多個字符串,返回一個字符串數組

6.startwith
public class StringTest06 {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "hello,this is beautiful HanZhong";String str2 = "xuexiao.jpgx"; System.out.println(str.startsWith("this")); if(str2.endsWith(".jpg")||str.endsWith(".png")||str.endsWith(".bmp")){ System.out.println("是圖片");}else {System.out.println("其它文件");}}
}7.替換
8.正則表達式
(1)[a-z]
a-z的其中一個字符
(2)[0-9]
[0-9]的一個數字
[0-9]{17}[0-9Xx](3){n}
前面的數據出現的次數
[0-9Xx]:數字0-9或者X或者x
(4){m,n}
9.charAt()
獲取某個索引位置的字符
String str = "apple";
System.out.println(str.charAt(3));//"p"10.contains()
判斷字符串中是否包含str
public class StringTest03 {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "01234567";System.out.println(str.contains("2"));}
}11.toCharArray()
將字符串轉換為字符數組
public class StringTest03 {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "01234567";char[] chars = str.toCharArray();for (int i = 0;i < chars.length;i++){System.out.println(chars[i]);}}
}










事件系統)




LRU緩存、)

模型的編輯、軸網和標高)

)