上篇介紹了read的操作類型,本篇我們來介紹一下dataless
目錄
一、dataless操作概覽
二、Non-CMO (Non-Cache Maintenance Operation)
1、CleanUnique
2、StashOnce and StashOnceSep
3、Evict
三、CMO (Cache Maintenance Operation)
一、dataless操作概覽
| 名稱(non-CMO) | 描述 |
| CleanUnique | 對snoopable地址區域的請求,將Requester的cache line狀態更改為“Unique”,以便對該cache line執行寫操作。對其他的master的cache clean,并且invalid,其他cache line dirty的數據需要寫入main memory |
| MakeUnique | 同CleanUnique,但是dirty cacheline直接丟棄。 |
| Evict | 用于告訴ICN,該RN-F不再緩存這個cacheline(類似于CPU知會HNF某一條cacheline已經被逐出了,本地已經沒有了) |
| StashOnceUnique, StashOnceSepUnique | 對snoopable地址區域的請求,以嘗試將被尋址的cacheline移動到目標緩存,以使目標能夠存儲該行。被尋址的RN可以按照ReadUnique來處理 |
| StashOnceShared, StashOnceSepShared. | 同上,被尋址的RN可以按照ReadNotSharedDirty 來處理 |
| 名稱 (CMO) | 描述 |
| CleanShared | 對snoopable地址區域的請求,所有緩存副本都更改為非dirty狀態,并且任何dirty的副本都會寫回main memory |
| CleanSharedPersist | 同上,但是dirty數據寫入PoP(Point of Persistence ). PoP是內存系統中的一個點,當系統電源斷開時,會保持對內存的寫入,當電源恢復時,會可靠的恢復對內存的寫入 |
| CleanSharedPersistSep | 同上,但是對requester需要有2個response,Comp response 表示請求到達HN;Persist response表示請求已到達PoP |
| CleanInvalid | requester為I態時才能發此請求, 將擁有此 cacheline的 副本invalidate,dirty的寫回main memory |
| MakeInvalid | 同上,dirty的丟棄 |
CleanSharedPersistSep 的功能與leanSharedPersist 類似,但需要對請求者進行兩個單獨的響應:
1、Comp 響應,表明請求已達到一致性點(PoC),并且可以在請求者處消除危險。
2、持久響應,表明請求已到達PoP 或最終目的地。
PoC (Point of Coherence) :?A point at which all agents that can access memory are guaranteed to see the same copy of a memory location. In a typical CHI based system it is the HN-F in the interconnect.
保證所有可以訪問內存的代理都能看到內存位置的相同副本的點。 在典型的基于 CHI 的系統中,它是互連中的 HN-F。
Dataless transaction可分為Non-CMO (Non-Cache Maintenance Operation) 和 CMO (Cache Maintenance Operation)
第一個表為non-CMO的操作,第二個表為CMO操作
二、Non-CMO (Non-Cache Maintenance Operation)
支持的操作有:
? CleanUnique.?
? MakeUnique.?
? Evict.
? StashOnceUnique, StashOnceSepUnique.
? StashOnceShared, StashOnceSepShared.

步驟如下:
1、The Requester sends a Snoopable Read request on the REQ channel?
2、The Completer returns the read data and any associated transaction response with the CompData opcode on the RDAT channel
3、Requester must return an acknowledgement, using the CompAck opcode on the SRSP channel to indicate that the transaction has completed.?
non-CMO的操作本文會舉3個例子:CleanUnique、StashOnceShared、Evict
1、CleanUnique
CleanUnique : CleanUnique是將其他的master的cache clean,并且invalid,只保留當前master的cache(此cache可以是clean,也可以是dirty); 其他cache line dirty的數據需要寫入main memory
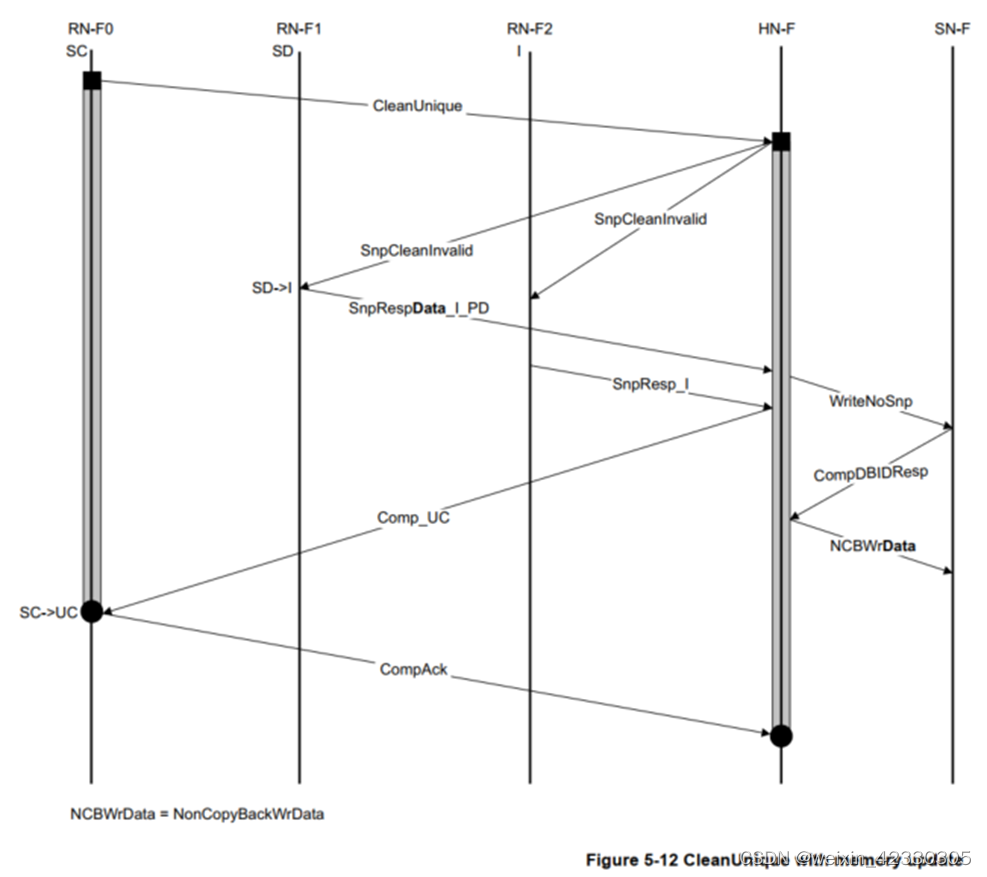
1、RN-F1 has the cache line in SD state and responds to the snoop with a snoop response with data and PD asserted.
2、HN-F waits for all snoop responses and then sends a Comp_UC response to the Requester.
3、HN-F sends a Write request to update memory with the data received from RN-F1.
SnpRespData_I_PD后綴為PD,PD ( pass dirty )?,表示更新內存的責任已傳遞給請求者或 ICN。只能為帶有數據的 Snoop 響應聲明 Pass Dirty。
Comp_UC : CleanUnique、 MakeUnique的comp response
MakeUnique相比cleanunique,沒有寫入main memory的操作,且不管其他cacheline的狀態,dirtys數據會丟棄
2、StashOnce and StashOnceSep
Cache stashing機制可將數據存在系統中特定cache中,確保data靠近使用的節點,因此可以提高系統性能。Cache stashing只支持Snoopable memory空間。
相關的操作有:
? StashOnceUnique,
? StashOnceSepUnique.
? StashOnceShared,
? StashOnceSepShared.

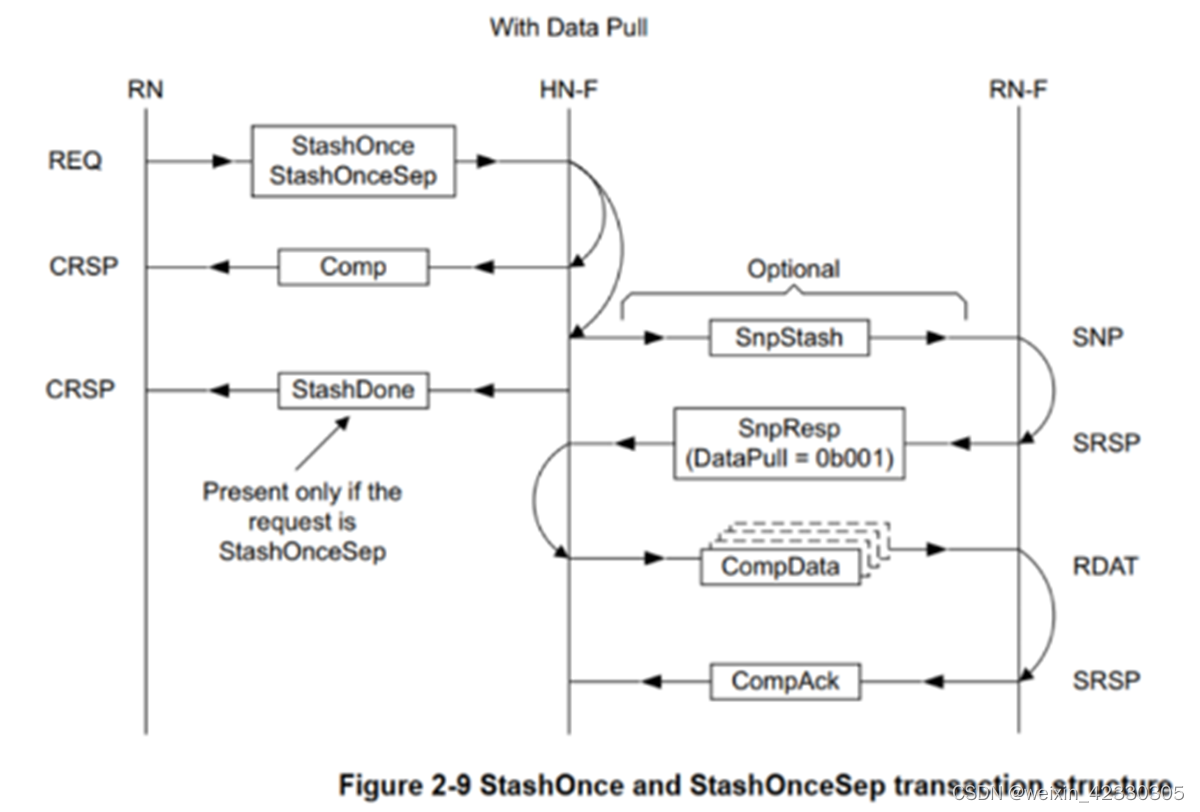
步驟如下:
1、RN在REQ channnel發送request
2、ICN返回 comp response
3、如果是StashOnceSep request,Home返回StashDone響應,表示request已經被保序
4、Home還可以選擇是否在SNP channel上snoop 目標RN-F
5、目標RN-F發送SnpResp響應,可以選擇是否包含DataPull( DataPull =0b001表示響應包含讀請求)
6、如果DataPull =0b001,則Home發送CompData響應
7、目標RN-F收到CompData后,返回CompAck
Datapull[2:0]==0b001?: Inclusion of Data Pull in the Snoop response(在 Snoop 響應中包含數據拉取)
Data Pull. Indicates the inclusion of an implied Read request in the Data response. (數據拉取。 指示在數據響應中包含隱含的讀取請求)
DataPull只能等于0b000、0b001
Comp : Completer接受已經請求,并且不會發送RetryAck相應
StashDone : 后續對于同一內存位置的transaction,該transaction是可被觀察到的(保序)
StashOnce的四種操作的區別在于:
? Sends StashOnce?Unique to Home if the stashed cache line is to be modified.
如果要修改stash的緩存行,則將 StashOnce*Unique 發送到 Home。
? Sends StashOnce?Shared to Home if the stashed cache line is not to be modified.
如果不修改stash的緩存行,則將StashOnce*Shared 發送到Home。
? Sends StashOnceSep only if the Requester is capable of handling the StashDone response.
僅當請求者能夠處理StashDone 響應時才發送StashOnceSep。
? The StashOnce? requests provide a Stash target when the data is to be stashed in a peer cache.
當數據要存儲在對等緩存中時,StashOnce* 請求提供存儲目標。
? The StashOnce? requests do not provide a Stash target when the data is to be allocated to the next level cache.
當數據要分配到下一級緩存時,StashOnce* 請求不提供Stash 目標。
以StashOnceShared為例

1、RN sends a StashOnceShared request to HN-F with the Stash target identified as RN-F1.
2、HN-F sends a Comp response after establishing processing order for the received request that is guaranteeing the request is processed before a request to the same address?
此響應是為了保序(該處理request要優先于后續任何request對該地址的請求)
3、HN-F sends a SnpStashShared snoop to RN-F1, and a ReadNoSnp request to SN-F to fetch Data.
4、RN-F1 sends SnpResp_I_Read response to HN-F.
5、HN-F treats the Read request from RN-F1 as a ReadNotSharedDirty, and sends a combined CompData to?RN-F1.
6、?RN-F1 sends CompAck to HN-F to complete the Read transaction.
該操作的目的是,將SN中指定地址的數據,搬到RN-F1。但是在搬運前,要先對RN-F1進行snoop,判斷RN-F1是否已經具有該數據
Snpresp_i_Read, 表示當前state是invalid的,同時帶有read操作,要pull data;
SnpStashShared
Snoop request recommending that the Snoopee obtains a copy of the cache line in a Shared state:
? Permitted to be sent to only one RN-F.?只能發送給RN-F
? This specification recommends not sending the snoop if the cache line is cached at the target.?如果cache line就在target中,則建議不發送snoop
? The Snoopee must not return data with the Snoop response.?該snoop不能返回數據
? Permits the Snoop response to include a Data Pull.?該snoop的response允許包含Data Pull
? Must not change the cache line state at the Snoopee.?不能改變被snoop的cache line狀態
The responses that include Data Pull are:
SnpResp_I_Read.
SnpRespData_I_Read.
SnpRespData_I_PD_Read.
SnpRespDataPtl_I_PD_Read.
3、Evict
告訴HN, 當前RN中的這條cacheline不再進行緩存;類似于CPU知會HNF某一條cacheline已經被逐出了,本地已經沒有了;

RN在發送請求之前,會先將狀態調整到 I
Evict
? ? ? ? --告訴HN, 當前RN中的這條cacheline不再進行緩存;
? ? ? ? --類似于CPU知會HNF某一條cacheline已經被逐出了,本地已經沒有了;
? ? ? ? --RN在發送之前,會先將狀態調整到I;
三、CMO (Cache Maintenance Operation)
支持的操作有:
? CleanShared.?
? CleanSharedPersist.?
? CleanSharedPersistSep.?
? CleanInvalid.? ? MakeInvalid.


步驟如下:
1、The Requester sends a request on the REQ channel
2、The Completer returns a Comp response on the CRSP channel.
3、For the CleanSharedPersistSep transaction the Completer also returns a Persist response to the Requester. The Completer is permitted to combine the Comp and Persist responses into a single CompPersist response.
以CleanSharedPersistSep為例:
要求所有CPU把dirty數據都寫回主存
In this example of CleanSharedPersistSep transaction flow, the Point of Persistence (PoP) is at the SN-F.
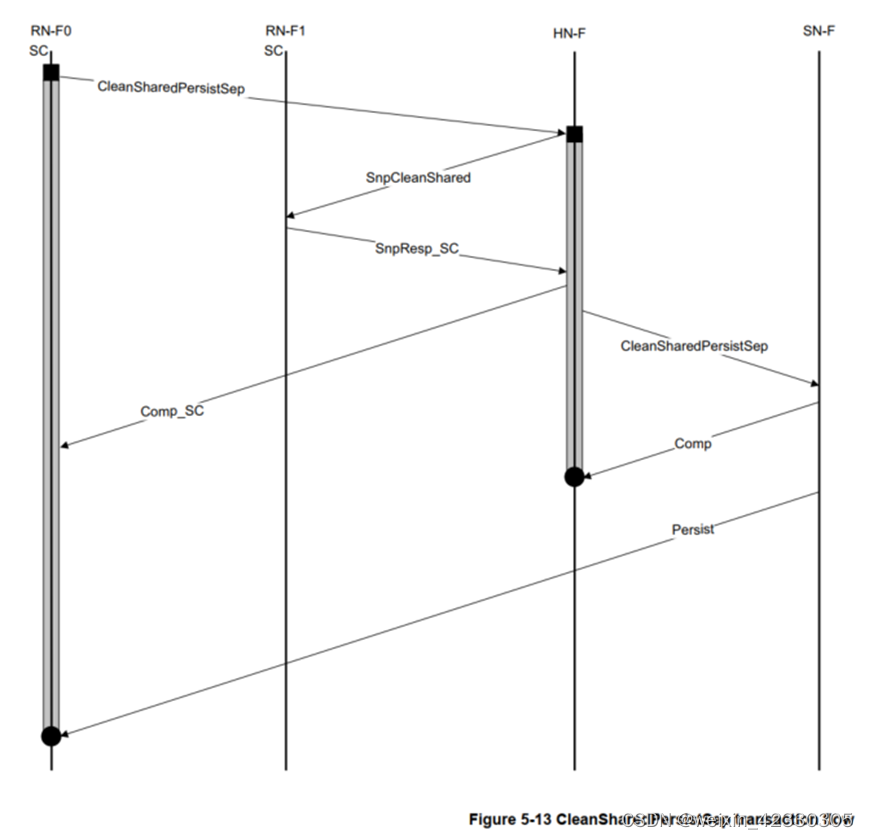 1、RN-F1 has the cache line in SC state. RN-F1 responds to the snoop with a snoop response without data.
1、RN-F1 has the cache line in SC state. RN-F1 responds to the snoop with a snoop response without data.
2、HN-F waits for all snoop responses and then sends a Comp_SC response to the Requester.
3、HN-F sends a CleanSharedPersistSep request to SN-F, only after completing the writing back of all snooped Dirty data, if any, to the SN-F. SN-F responds to the request with Comp
4、SNF sends a Persist response to RN-F0 to indicate that the request has reached the PoP, and data from any prior writes to the same location is pushed to the PoP?
PoP (Point of Persistence) : 系統中用于持久性存儲的特定位置或機制。它表示數據在系統中的存儲狀態,以確保數據在斷電或重啟后仍然可用。通常是將易失性存儲(如cache)復制到非易失性存儲(如硬盤)
圖中,Comp_UC反映了其他master中該cache line的狀態
Comp_UC:
? ? ? ? 1、表明該cache line副本在Requester中至高可以為UC狀態(即可以是UC、UCE、SC、I)。
? ? ? ? 2、不過MakeReadUnique/CleanUnique這兩個“Upgrade”的請求則有所差異,SD收到Comp_UC后進入UD狀態。這在下文關于MakeReadUnique的描述中可以再次看到。
相應的response還有:
Comp_I:
????????表明該cache line副本在Requester中最終需為I狀態。
Comp_SC:
????????表明該cache line副本在Requester中至高可以為SC狀態(即可以是SC、I)。
Comp_UD_PD:
????????表明將更新Memory的責任傳遞給Requester,該cache line副本在Requester中至高可以為UD狀態(即可以是UD、SD)。
對于CleanShared,可能會收到Comp_UC、Comp_SC、Comp_I。CleanShared用于將其他副本的dirty數據寫回,并不會無效化其他副本,所以收到response后緩存行狀態不改變。
對于CleanUnique,只會收到Comp_UC。收到時處于I狀態(出現I狀態的原因是發出CleanUnique后被invalid),則進入UCE;收到時處于SC狀態,則進入UC狀態;收到時處于SD,則進入UD狀態。
對于MakeUnique,只會收到Comp_UC。由于其寫一整行,所以最終進入UD狀態。

)





![虛擬化技術[1]之服務器虛擬化](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/虛擬化技術[1]之服務器虛擬化)
)



—— SpeechRecognition)






