正則表達式基礎語法
Java正則表達式基于java.util.regex包,核心類是Pattern和Matcher。基本語法遵循標準正則規范:
.匹配任意單個字符(除換行符)\d匹配數字,等價于[0-9]\w匹配單詞字符,等價于[a-zA-Z0-9_]\s匹配空白字符(空格、制表符等)[]字符集合,如[abc]匹配a、b或c^在字符集中表示否定,如[^abc]匹配非a/b/c的字符*匹配前一個元素0次或多次+匹配前一個元素1次或多次?匹配前一個元素0次或1次{n}精確匹配n次{n,}匹配至少n次{n,m}匹配n到m次- | 寫在方括號外面,表示或
- && 交集,表示與
- (?!) 忽略后面字符的大小寫
常用預定義字符類
\\d 數字 [0-9]
\\D 非數字 [^0-9]
\\s 空白字符 [ \\t\\n\\x0B\\f\\r]
\\S 非空白字符 [^\\s]
\\w 單詞字符 [a-zA-Z_0-9]
\\W 非單詞字符 [^\\w]
邊界匹配符
^匹配行首$匹配行尾\b匹配單詞邊界\B匹配非單詞邊界
Java中的特殊處理
在Java字符串中需要使用雙反斜杠轉義:
// 匹配數字的正則表達式
String regex = "\\d+"; // 實際表示 \d+
Pattern和Matcher使用示例
import java.util.regex.*;String text = "Hello 123 World";// Pattern:表示正則表達式
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\\d+");
// Matcher:文本匹配器,從頭開始讀取,直到讀取到匹配的字符串
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(text);// 查找匹配
while (matcher.find()) {System.out.println("Found: " + matcher.group());
}// 匹配整個字符串
boolean isMatch = Pattern.matches("Hello.*", text);
- 貪婪爬取:用+,*,表示盡可能多的獲取數據
- 非貪婪爬取:在+,*后面加上?,表示盡可能少的獲取數據
String str = "aaaaaaaaaabbbbbbbbaaaaaaaaa";System.out.println("--------- 貪婪匹配 ---------");// 貪婪匹配Pattern p = Pattern.compile("ab+");Matcher m = p.matcher(str);while (m.find()) {System.out.println(m.group());}System.out.println("--------- 懶惰匹配 ---------");// 懶惰匹配Pattern p1 = Pattern.compile("ab+?");Matcher m1 = p1.matcher(str);while (m1.find()) {System.out.println(m1.group());}效果圖:

分組和捕獲
使用()創建捕獲組:
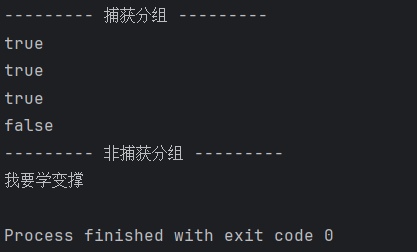
String str = "a123a";String str1 = "abc123abc";String str2 = "1117891111";String str3 = "aa7879a";// 捕獲分組System.out.println("--------- 捕獲分組 ---------");String regex = "(.).+\\1";String regex1 = "(.+).+\\1";String regex2 = "((.)\\2).+\\1";System.out.println(str.matches(regex));System.out.println(str1.matches(regex1));System.out.println(str2.matches(regex2));System.out.println(str3.matches(regex2));// 非捕獲分組System.out.println("--------- 非捕獲分組 ---------");String str4 = "我要學學變變變變撐撐撐撐撐";str4 = str4.replaceAll("(.)\\1+", "$1");// replaceAll() 方法用于把所有滿足匹配的字符串替換成指定的字符串System.out.println(str4);效果圖:
- 從1開始,連續不斷
- 以左括號為基準
- 捕獲分組(默認):① 內部:\\組號?② 外部:$組號(組號會保留下來)
- 非捕獲分組:使用條件,不占組號
- "?=":表示任一數據
- "?:":表示所有數據
- "?!":表示不包含這些數據
常用正則表達式示例
- 郵箱驗證:
String emailRegex = "^[\\w-_.+]*[\\w-_.]@([\\w]+\\.)+[\\w]+[\\w]$";
- 手機號驗證(中國大陸):
String phoneRegex = "^1[3-9]\\d{9}$";
- 身份證號驗證(簡易版):
String idCardRegex = "^[1-9]\\d{5}(18|19|20)\\d{2}(0[1-9]|1[0-2])(0[1-9]|[12]\\d|3[01])\\d{3}[0-9Xx]$";
- URL驗證:
String urlRegex = "^(https?://)?([\\w-]+\\.)+[\\w-]+(/[\\w-./?%&=]*)?$";
特殊匹配模式
通過Pattern的常量設置匹配模式:
// 不區分大小寫匹配
Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE // 多行模式(^和$匹配每行的開頭和結尾)
Pattern.MULTILINE// 示例:不區分大小寫匹配
Pattern.compile("hello", Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE).matcher("Hello").find(); // true
字符串替換
使用正則表達式進行字符串替換:
String text = "a1b2c3";
String replaced = text.replaceAll("\\d", "-"); // a-b-c-
性能優化建議
- 預編譯常用正則表達式:
private static final Pattern EMAIL_PATTERN = Pattern.compile(emailRegex);
避免過度使用
.通配符,盡可能明確匹配范圍對于簡單固定字符串匹配,優先使用
String.contains()或String.startsWith()等原生方法謹慎使用回溯量大的表達式(如嵌套的量詞)













)


)


