

目錄
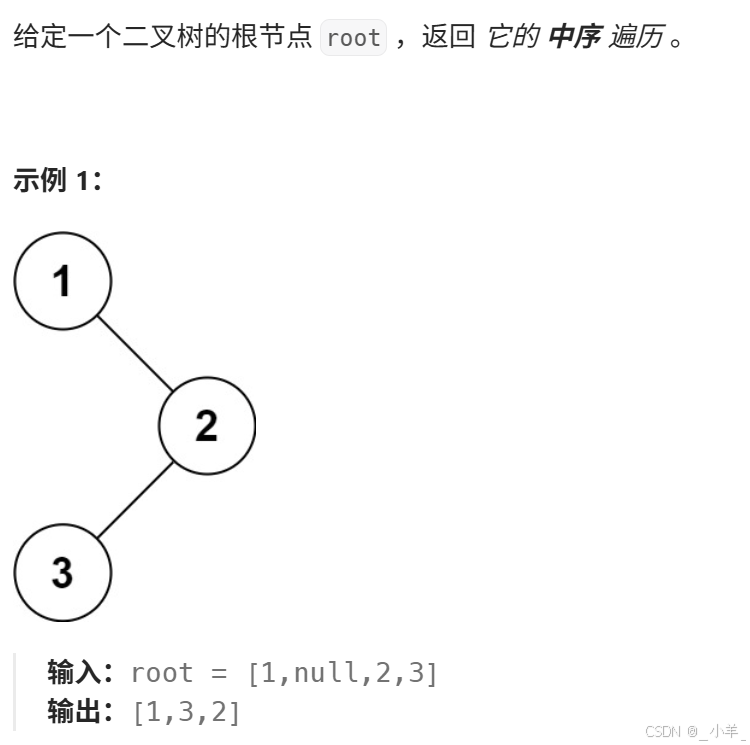
二叉樹的中序遍歷
- 二叉樹的中序遍歷
class Solution {vector<int> res;
public:vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {dfs(root);return res;}void dfs(TreeNode* root){if (root == nullptr) return;dfs(root->left);res.push_back(root->val);dfs(root->right);}
};
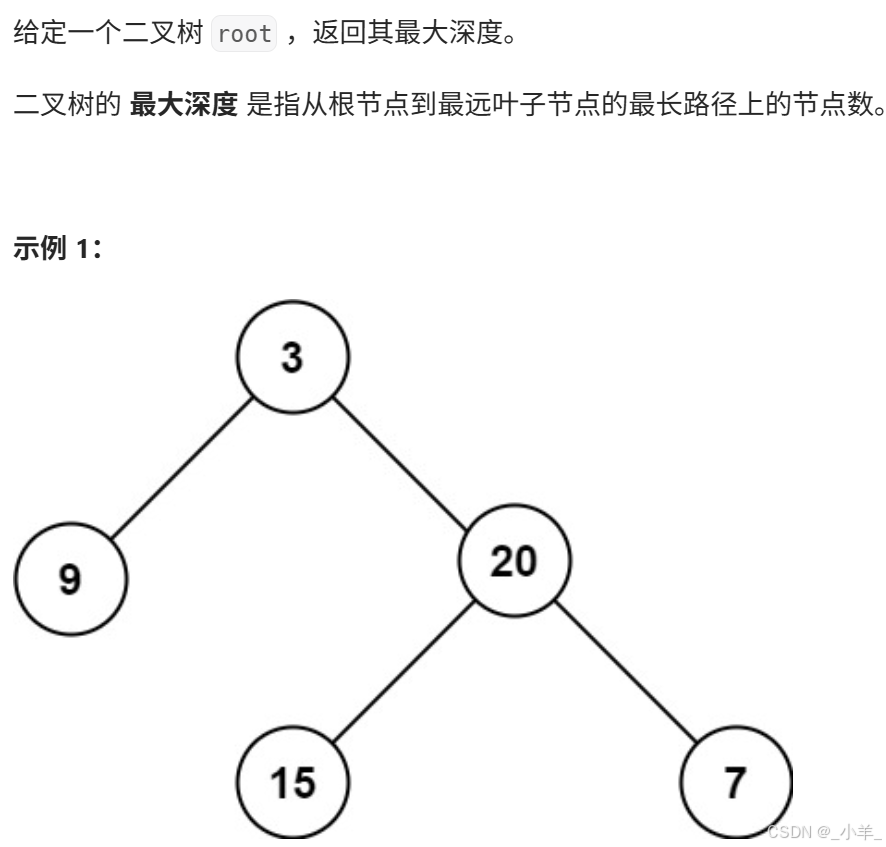
二叉樹的最大深度
- 二叉樹的最大深度
class Solution {
public:int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {if (root == nullptr) return 0;int left = maxDepth(root->left);int right = maxDepth(root->right);return left > right ? left + 1 : right + 1;}
};
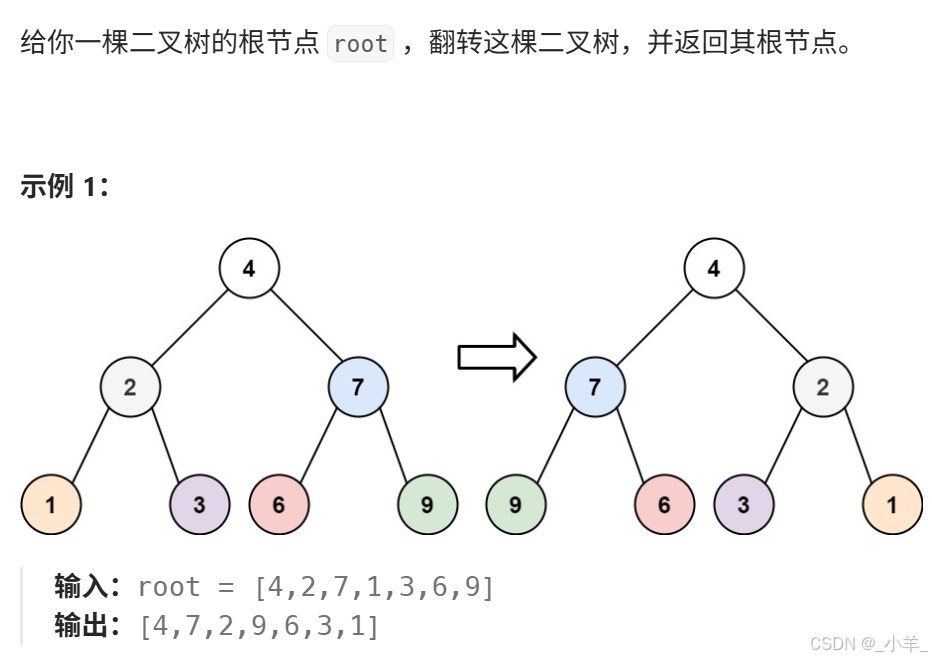
翻轉二叉樹
- 翻轉二叉樹
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {if (root == nullptr) return nullptr;TreeNode *left = invertTree(root->left);TreeNode *right = invertTree(root->right);root->left = right;root->right = left;return root;}
};
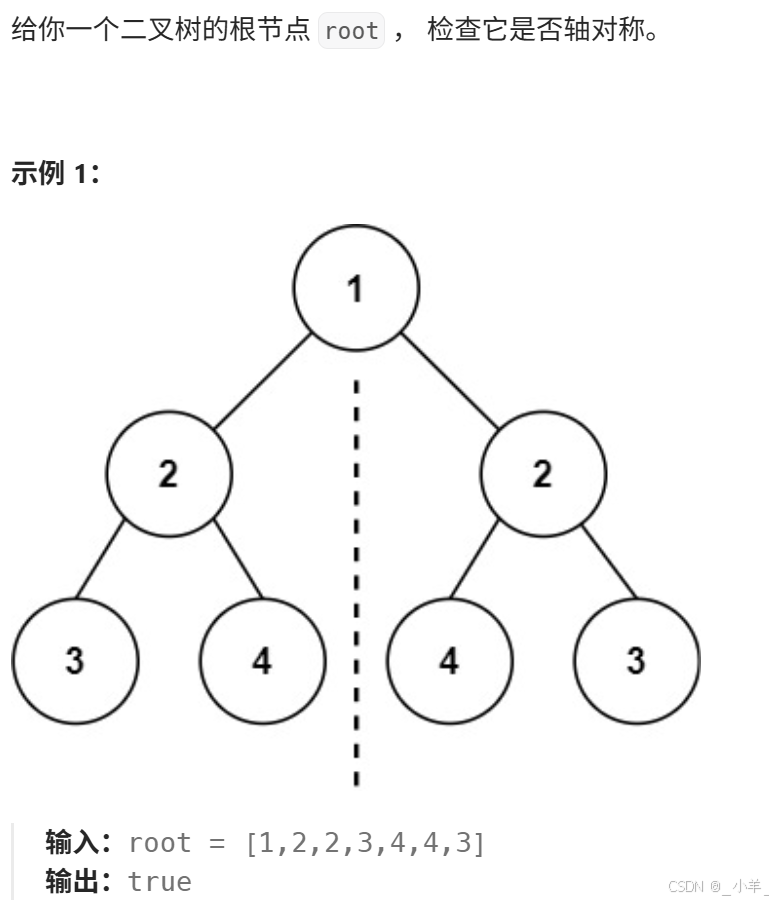
對稱二叉樹
- 對稱二叉樹
class Solution {
public:bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {return dfs(root->left, root->right);}bool dfs(TreeNode* left, TreeNode* right){if (left && right){if (left->val != right->val) return false;return dfs(left->left, right->right) && dfs(left->right, right->left);}else if (left != right) return false;else return true;}
};
二叉樹的直徑
- 二叉樹的直徑
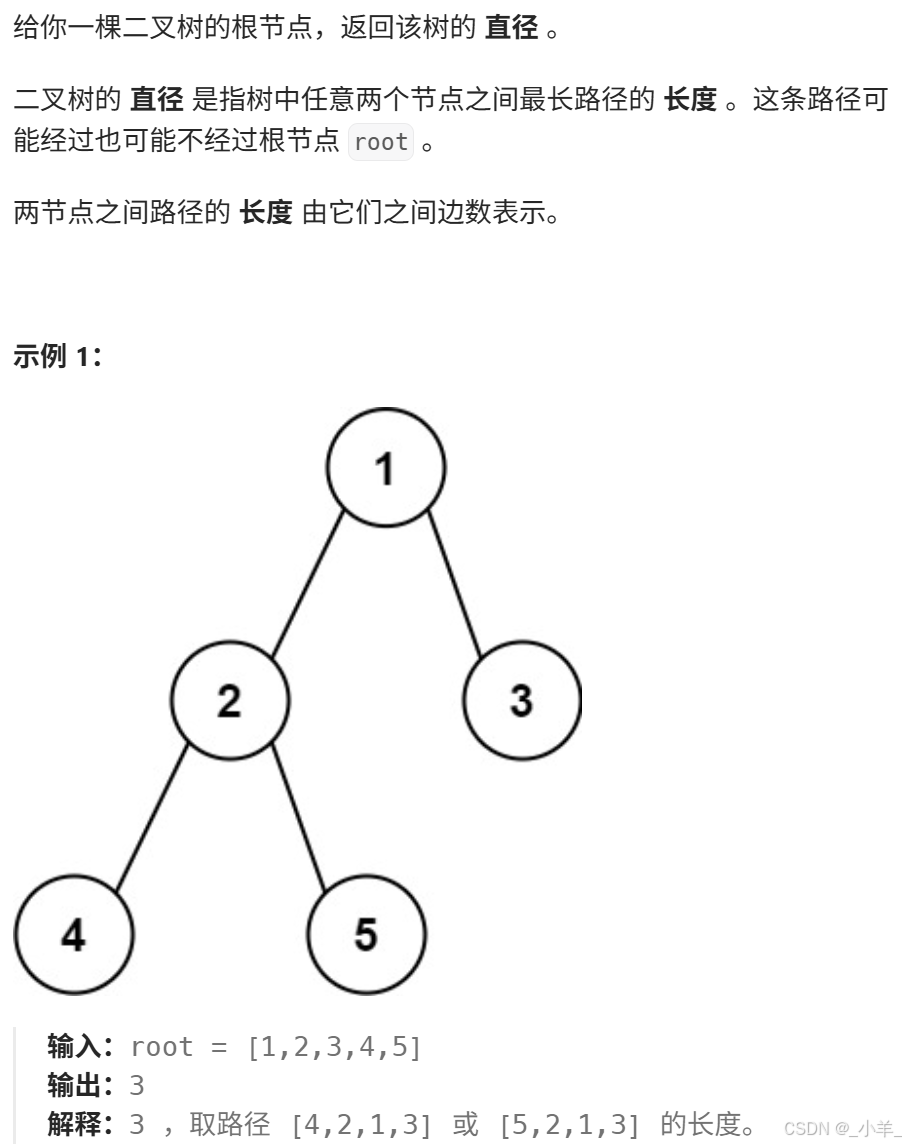
class Solution {int depth;
public:int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {dfs(root);return depth - 1;}int dfs(TreeNode* root){if (root == nullptr) return 0;int left = dfs(root->left);int right = dfs(root->right);depth = max(depth, left + right + 1);return max(left, right) + 1;}
};
二叉樹的層序遍歷
- 二叉樹的層序遍歷
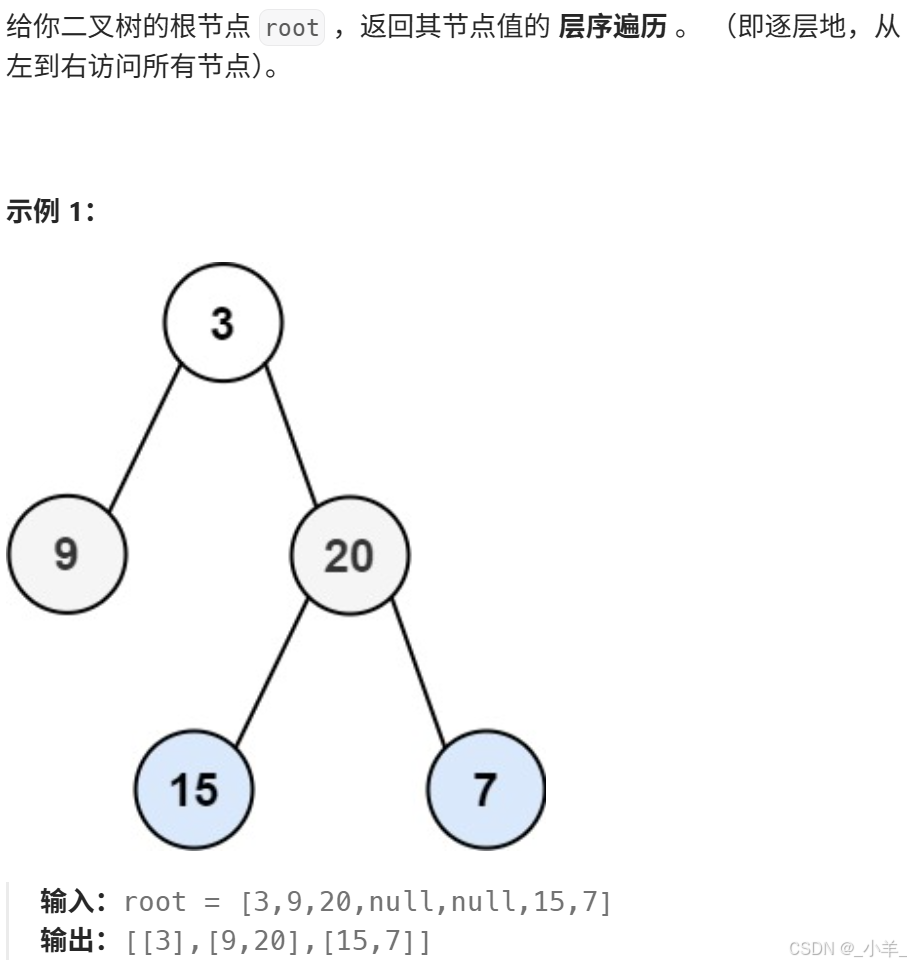
class Solution {
public:vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {vector<vector<int>> res;queue<TreeNode*> q;if (root == nullptr) return res;q.push(root);while (q.size()){int sz = q.size();vector<int> tmp;while (sz--){TreeNode *node = q.front();tmp.push_back(node->val);q.pop();if (node->left) q.push(node->left);if (node->right) q.push(node->right);}res.push_back(tmp);}return res;}
};
將有序數組轉換為二叉搜索樹
- 將有序數組轉換為二叉搜索樹
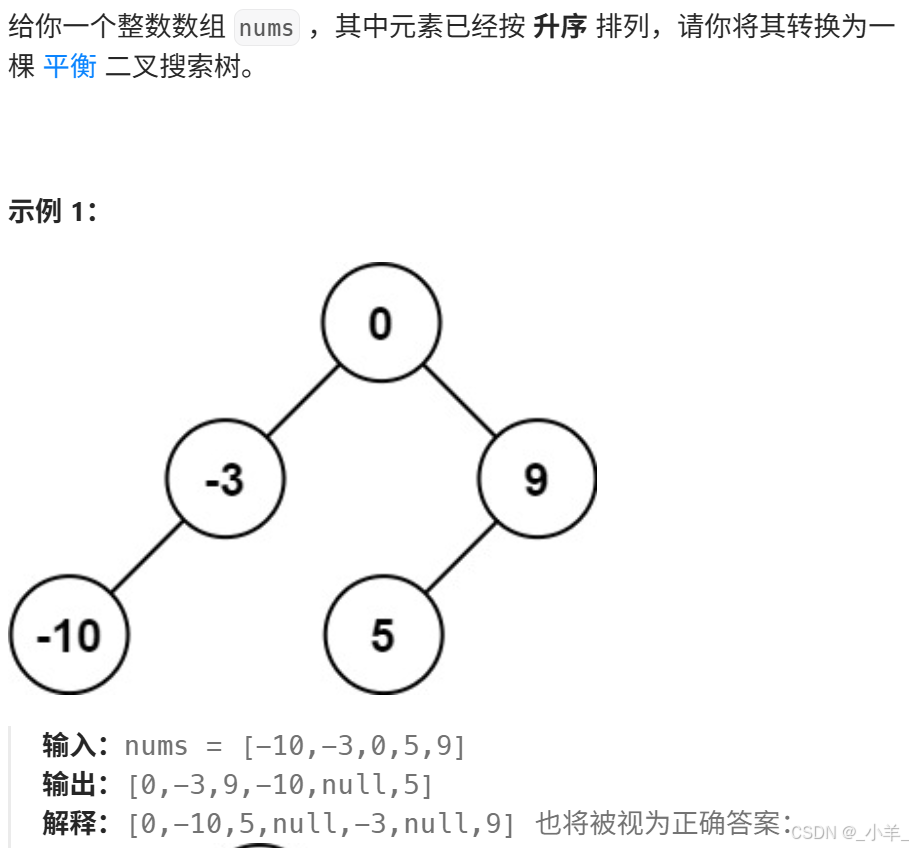
class Solution {
public:TreeNode* sortedArrayToBST(vector<int>& nums) {return dfs(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);}TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>& nums, int l, int r){if (l > r) return nullptr;int mid = l + (r - l) / 2;TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);node->left = dfs(nums, l, mid - 1);node->right = dfs(nums, mid + 1, r);return node;}
};
驗證二叉搜索樹
- 驗證二叉搜索樹
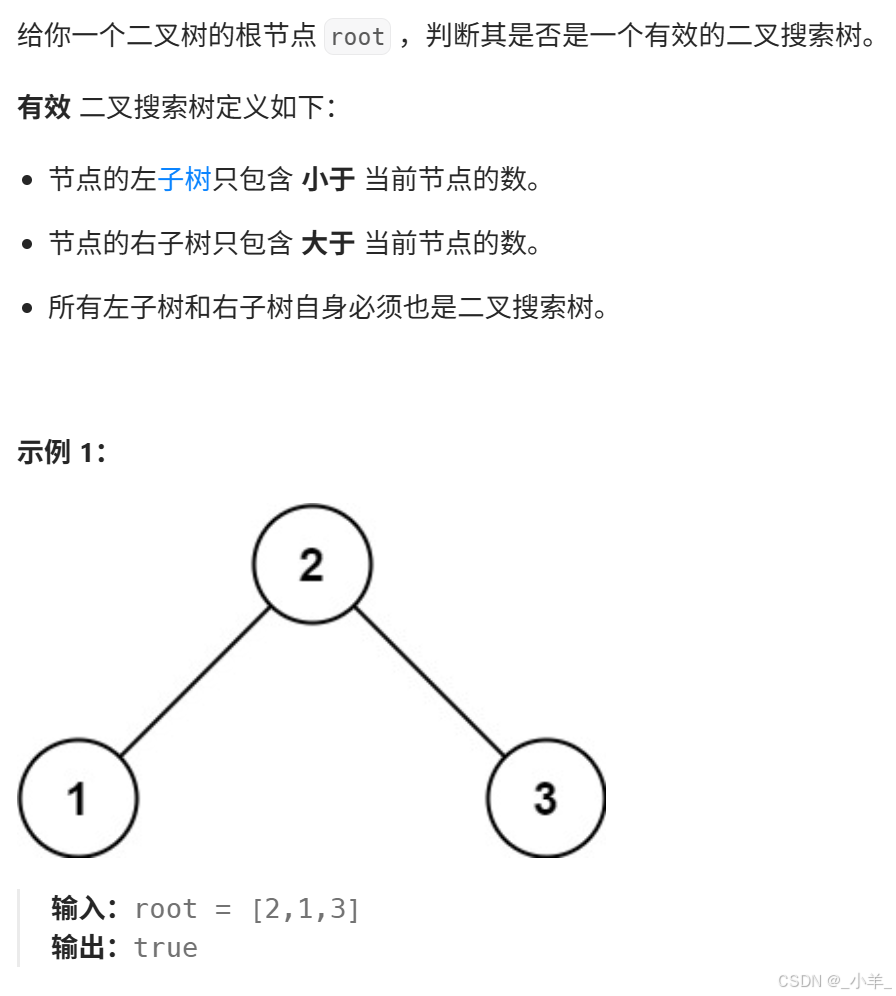
遞歸遍歷。
class Solution {
public:bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {return dfs(root, LONG_MIN, LONG_MAX);}bool dfs(TreeNode* root, long min_val, long max_val){if (root == nullptr) return true;if (root->val <= min_val || root->val >= max_val) return false;return dfs(root->left, min_val, root->val) && dfs(root->right, root->val, max_val);}
};
前序遍歷。
class Solution {long prev = LONG_MIN;
public:bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {if (root == nullptr) return true;if (isValidBST(root->left) == false) return false;if (root->val <= prev) return false;prev = root->val; return isValidBST(root->right);}
};
二叉搜索樹中第 K 小的元素
- 二叉搜索樹中第 K 小的元素
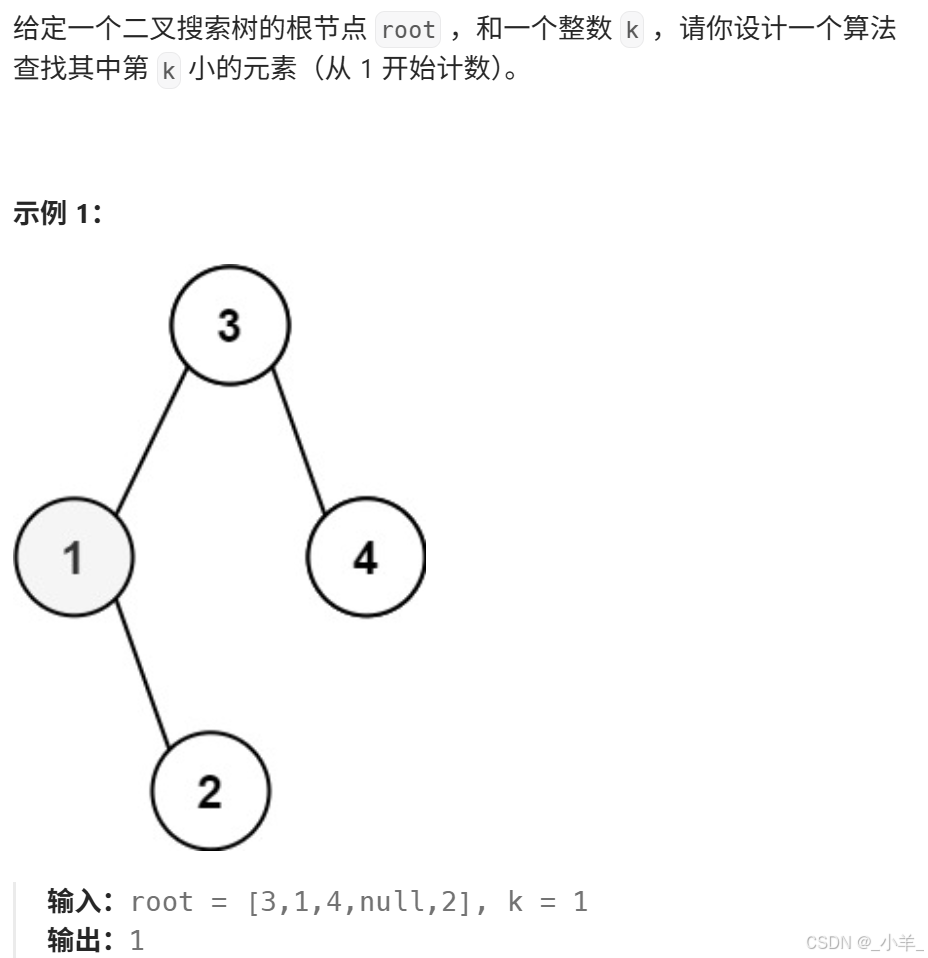
class Solution {int res, cnt;
public:int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {cnt = k;dfs(root);return res;}void dfs(TreeNode* root){if (root == nullptr) return;dfs(root->left);if (--cnt == 0) {res = root->val;return;}dfs(root->right);}
};
二叉樹的右視圖
- 二叉樹的右視圖
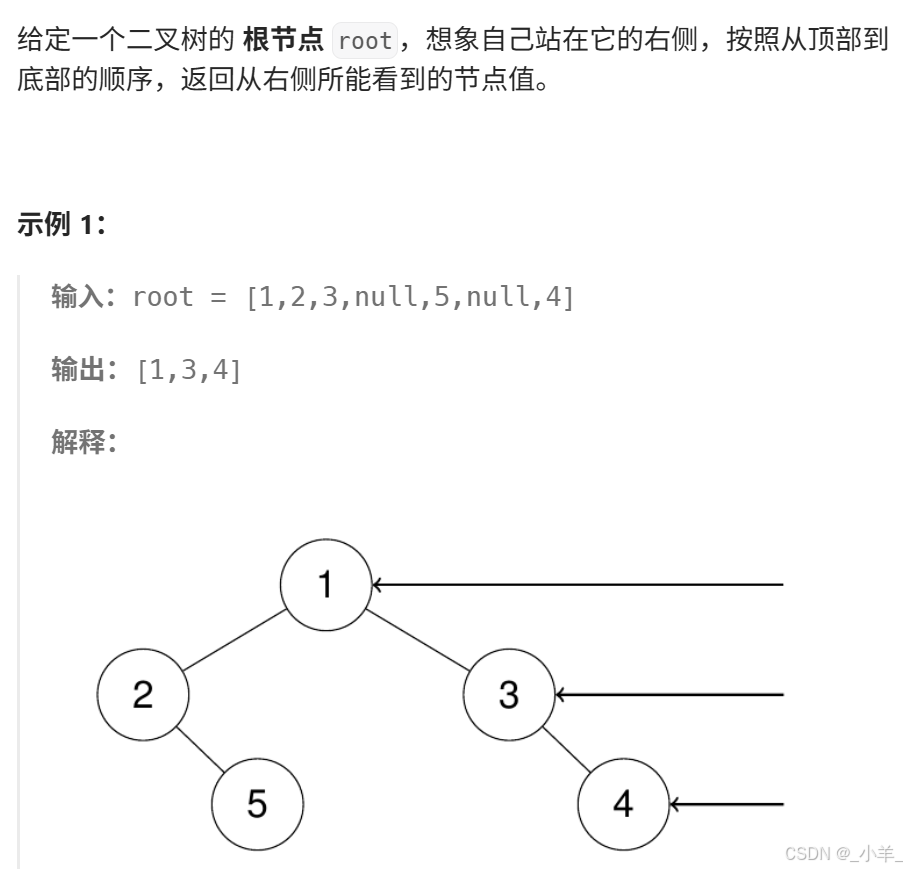
從右往左層序遍歷,每次都只拿隊頭節點的值。
class Solution {
public:vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {vector<int> res;if (root == nullptr) return res;queue<TreeNode*> q;q.push(root);while (q.size()){res.push_back(q.front()->val);int sz = q.size();while (sz--){TreeNode* node = q.front();q.pop();if (node->right) q.push(node->right);if (node->left) q.push(node->left);}}return res;}
};
二叉樹展開為鏈表
- 二叉樹展開為鏈表
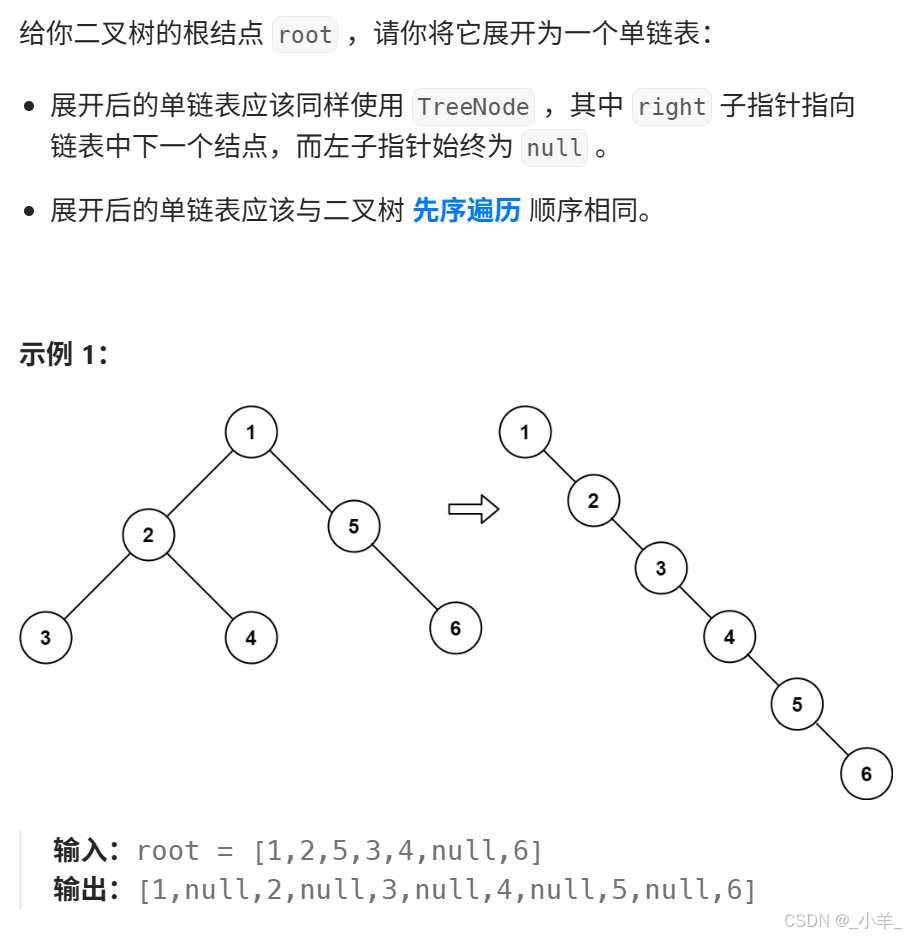
方法一:在前序遍歷的過程中把節點存起來,結束后在處理每個節點的指向。
class Solution {
public:void flatten(TreeNode* root) {vector<TreeNode*> vt;dfs(root, vt);for (int i = 1; i < vt.size(); i++){TreeNode* prev = vt[i - 1], *cur = vt[i];prev->left = nullptr;prev->right = cur;}}void dfs(TreeNode* root, vector<TreeNode*>& vt){if (root){vt.push_back(root);dfs(root->left, vt);dfs(root->right, vt);}}
};
方法二:尋找前驅結點法。
在前序遍歷的過程中,如果當前節點的左子樹不為空,則遍歷到當前節點的右子樹的前一個節點為:當前節點左子樹中最右的那個節點。我們在遍歷的過程中找到這個前驅結點,將當前節點的右子樹拼接到這個前驅節點的右節點上,然后將當前節點的左子樹拼接到當前節點的右子樹上,最后當前節點左子樹置空。
class Solution {
public:void flatten(TreeNode* root) {TreeNode* cur = root;while (cur){if (cur->left){auto prev = cur->left;while (prev->right) prev = prev->right;prev->right = cur->right;cur->right = cur->left;cur->left = nullptr;}cur = cur->right;}}
};
從前序與中序遍歷序列構造二叉樹
- 從前序與中序遍歷序列構造二叉樹
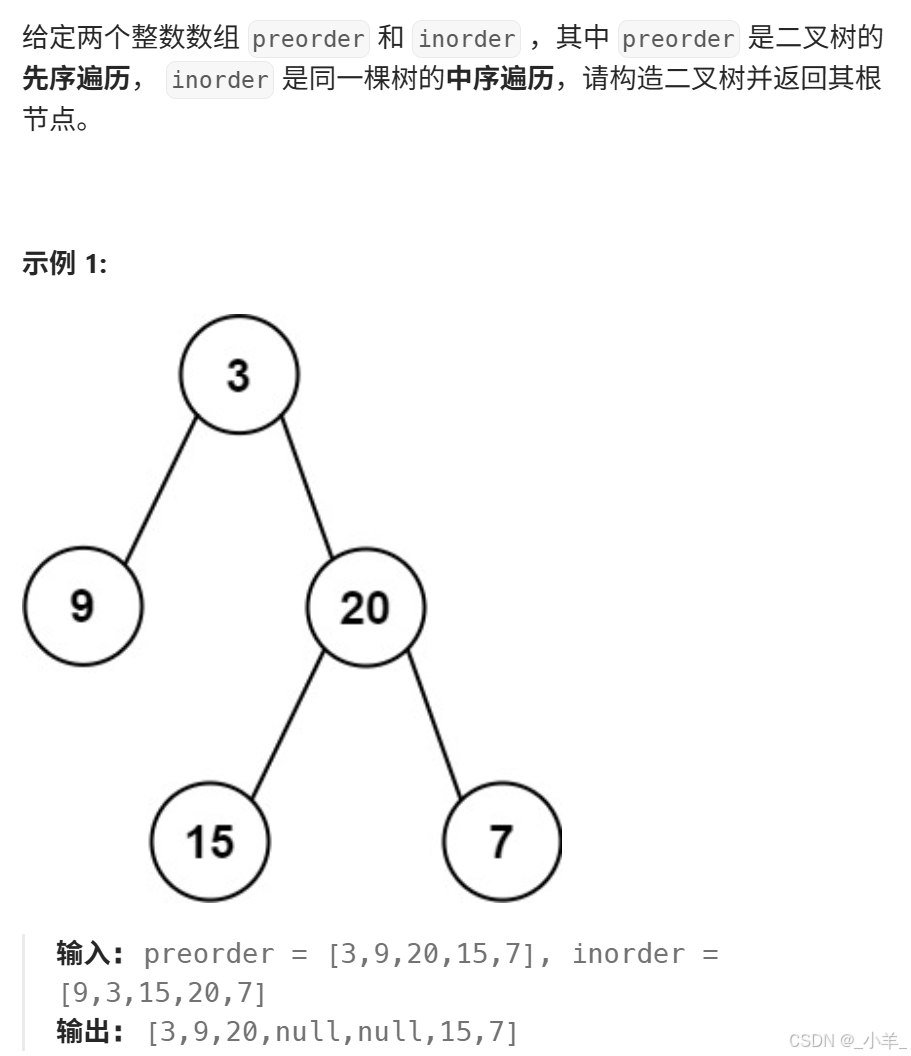
根據前序遍歷依次找到根節點,通過找到的根節點找到中序遍歷中根節點的位置,從而劃分出 [左子樹] [根節點] [右子樹]。
用哈希表存儲中序遍歷的值和下標映射關系,以至于能在找到根節點后直接拿到根節點在中序遍歷中的位置,然后根據中序遍歷的位置遞歸構建左子樹和右子樹。
class Solution {unordered_map<int, int> index;
public:TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {for (int i = 0; i < inorder.size(); i++){index[inorder[i]] = i;}return dfs(preorder, 0, 0, inorder.size() - 1);}TreeNode* dfs(vector<int>& preorder, int root, int l, int r){if (l > r) return nullptr;TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(preorder[root]);int id = index[preorder[root]];node->left = dfs(preorder, root + 1, l, id - 1);node->right = dfs(preorder, root + id - l + 1, id + 1, r);return node;}
};
路徑總和
- 路徑總和
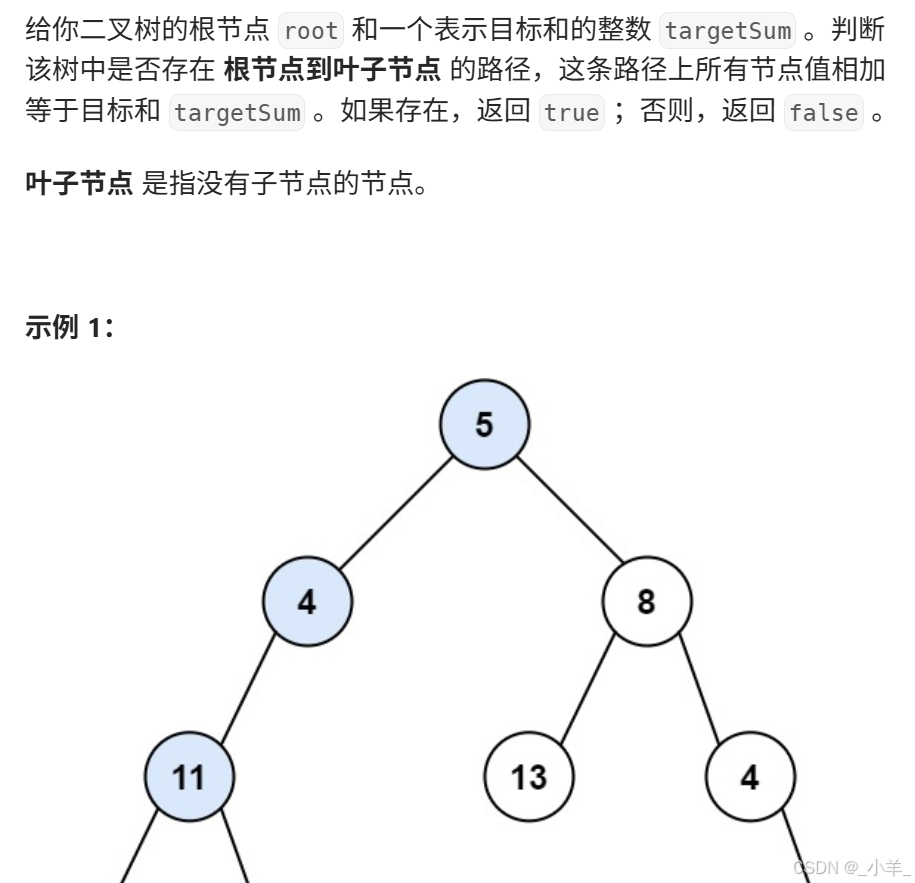
class Solution {
public:bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {if (root == nullptr) return false;if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {return targetSum == root->val;}return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root->right, targetSum - root->val);}
};
路徑總和 II
- 路徑總和 II
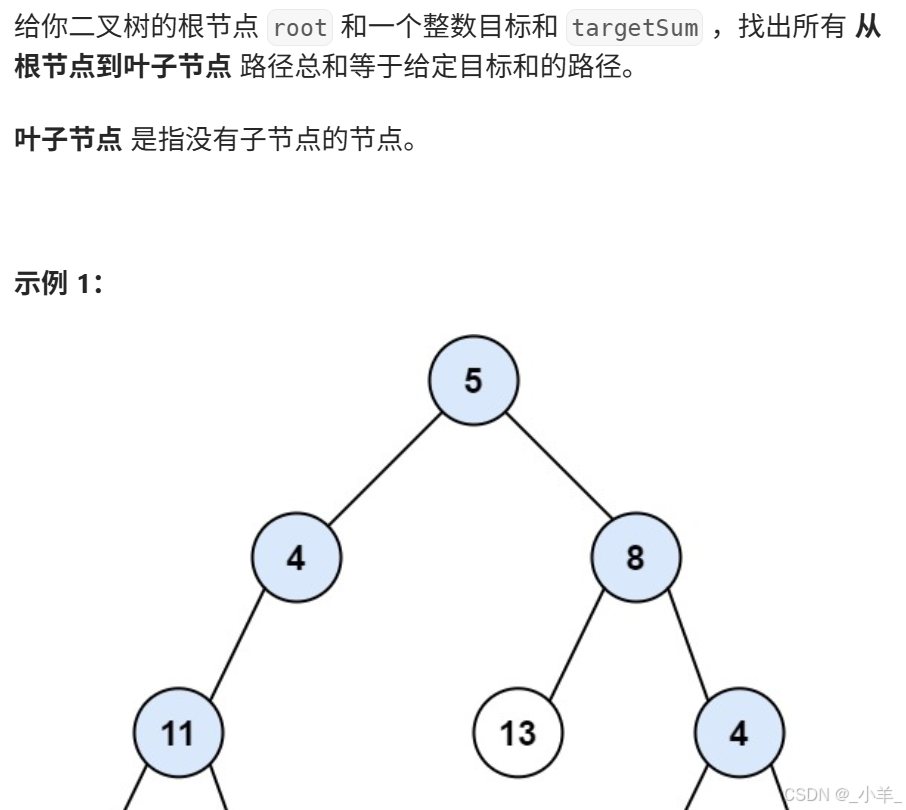
class Solution {vector<vector<int>> res;vector<int> path;
public:vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {dfs(root, targetSum);return res;}void dfs(TreeNode* root, int t){if (root == nullptr) return;path.push_back(root->val);if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr && t == root->val){res.push_back(path);}dfs(root->left, t - root->val);dfs(root->right, t - root->val);path.pop_back(); // 回溯}
};
路徑總和 III
- 路徑總和 III
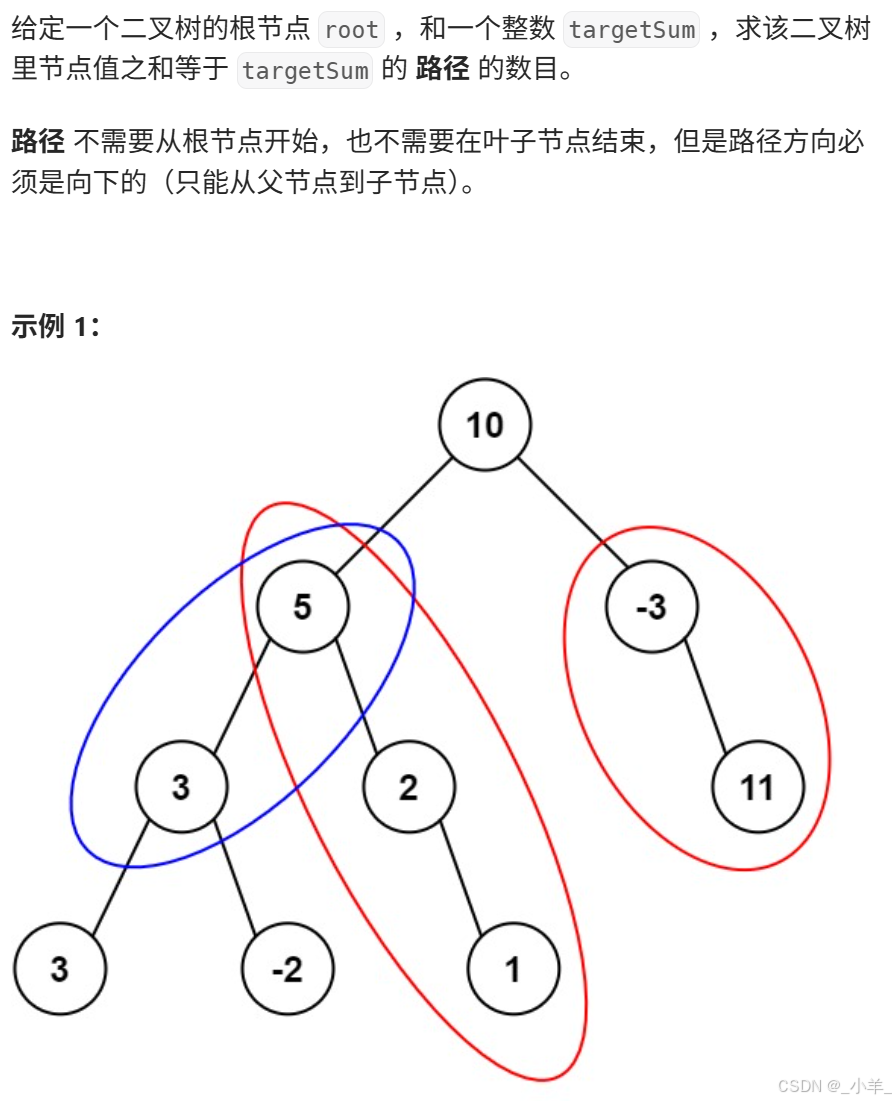
class Solution {using ll = long long;unordered_map<ll, int> pre_cnt; // 記錄前綴和及其出現次數int t;
public:int pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {t = targetSum;pre_cnt[0] = 1; // 前綴和恰好等于目標值return dfs(root, 0);}int dfs(TreeNode* root, ll sum) {if (root == nullptr) return 0;sum += root->val;int count = pre_cnt[sum - t];pre_cnt[sum]++;count += dfs(root->left, sum);count += dfs(root->right, sum);pre_cnt[sum]--;return count;}
};
本篇文章的分享就到這里了,如果您覺得在本文有所收獲,還請留下您的三連支持哦~


LLM數據基礎-分詞算法(2))


Python爬蟲高階:動態頁面處理與云原生部署全鏈路實踐(Selenium、Scrapy、K8s))
——排序)




View相關知識)



發布)




