React Native 入門 jsx 基礎語法
JSX 介紹
JSX (JavaScript XML) 是一種 JavaScript 的語法擴展,允許你在 JavaScript 文件中編寫類似 HTML 的代碼。它是 React 和 React Native 應用程序中用來描述 UI 的主要方式。
JSX 的特點
- JSX 看起來像 HTML,但實際上是 JavaScript 的語法糖
- JSX 讓你可以在 JavaScript 代碼中直接編寫標簽結構
- JSX 通過轉譯器(如 Babel)被轉換為純 JavaScript 函數調用
- JSX 使組件的結構和行為可以寫在一起,提高代碼的可讀性和維護性
TSX 與 JSX 的區別
TSX 是 TypeScript 與 JSX 的結合:
- TSX = TypeScript + JSX
- 在
.tsx文件中,你可以使用 JSX 語法,同時享受 TypeScript 的類型檢查 - TypeScript 為 JSX 元素和組件提供了類型安全,幫助開發者在編譯時發現潛在問題
- TSX 文件中可以定義接口、類型和類型注解,增強代碼的可維護性和可靠性
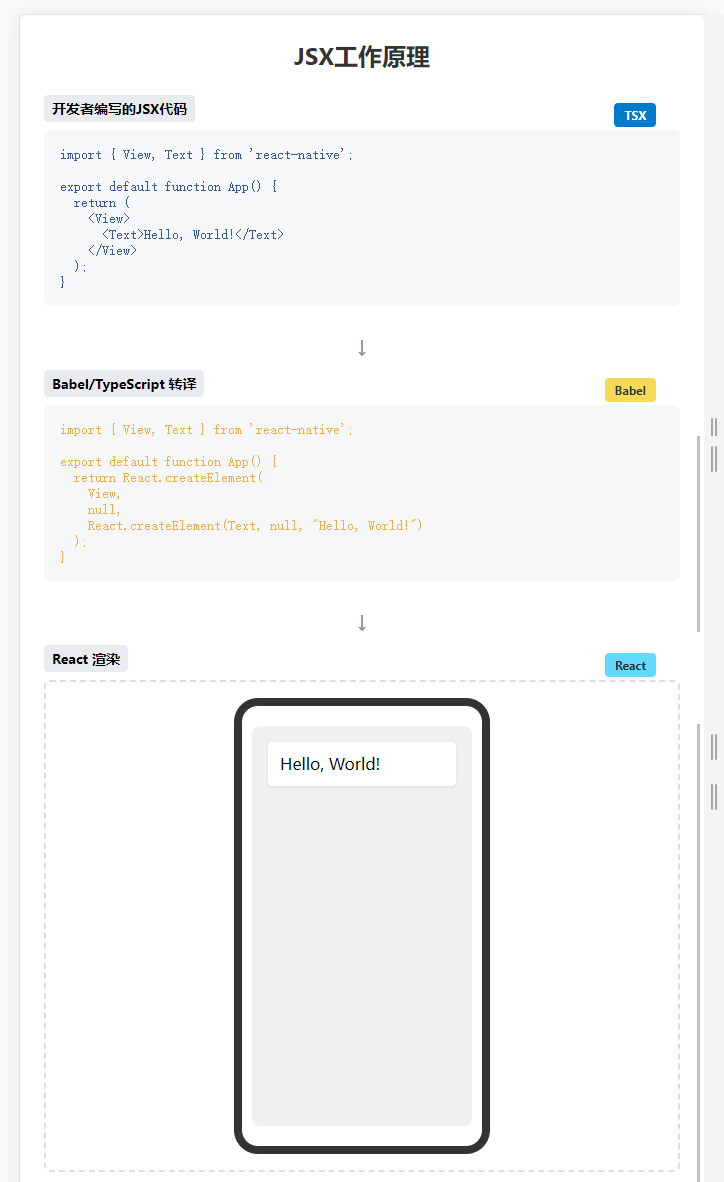
JSX 和 TSX 的工作原理
當你寫下:
<View><Text>Hello, World!</Text>
</View>
它會被轉譯為:
React.createElement(View,null,React.createElement(Text, null, "Hello, World!")
);
TypeScript 會在這個過程中進行類型檢查,確保你使用的組件和屬性都符合預期的類型定義。
目錄結構
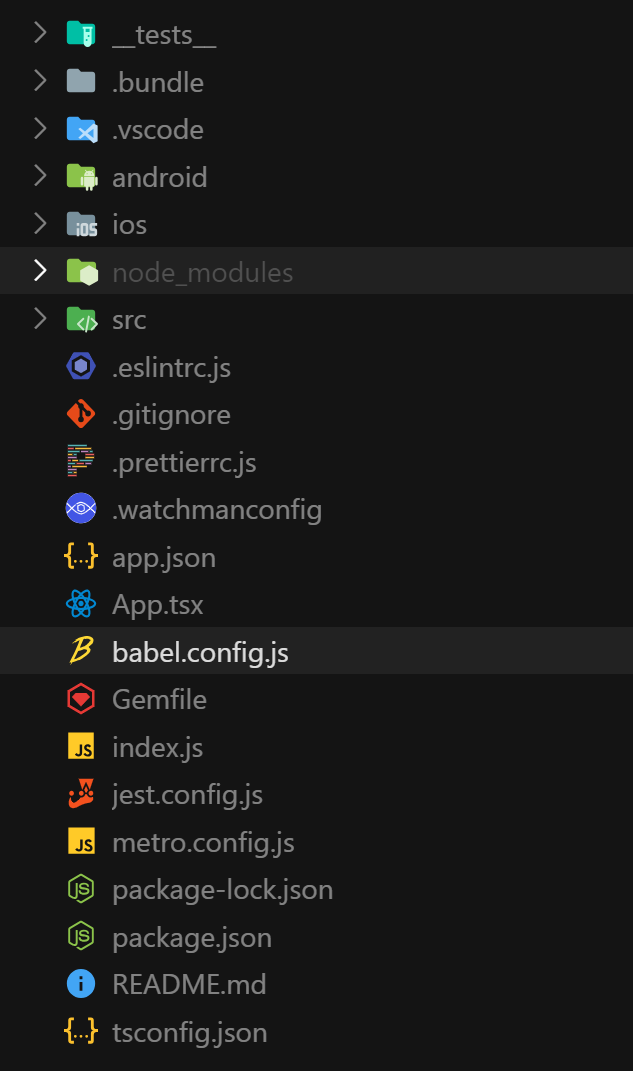
├── android/ # Android平臺相關文件
│ ├── app/ # Android應用特定配置
│ ├── build.gradle # Android項目構建配置
│ ├── settings.gradle # Android項目設置
│ ├── gradle.properties # Gradle屬性配置
│ ├── gradlew # Gradle包裝器腳本(Unix)
│ └── gradlew.bat # Gradle包裝器腳本(Windows)
│
├── ios/ # iOS平臺相關文件
│ ├── AwesomeProject1/ # iOS應用特定文件
│ ├── Podfile # iOS依賴管理配置
│ └── AwesomeProject1.xcodeproj/ # Xcode項目文件
│
│
├── __tests__/ # 測試文件目錄
│ └── App.test.tsx # App組件的測試文件
│
├── node_modules/ # npm依賴包安裝目錄
│
├── App.tsx # 應用主要組件,定義UI和邏輯
├── index.js # 應用入口文件,注冊應用組件
│
├── package.json # 項目信息和npm依賴配置
├── package-lock.json # npm依賴版本鎖定文件
├── app.json # React Native應用配置
│
├── babel.config.js # Babel轉譯器配置
├── metro.config.js # Metro打包器配置
├── .eslintrc.js # ESLint代碼檢查配置
├── .prettierrc.js # Prettier代碼格式化配置
├── .watchmanconfig # Watchman文件監控配置
├── jest.config.js # Jest測試框架配置
├── tsconfig.json # TypeScript配置
│
├── Gemfile # Ruby gems依賴配置(iOS構建相關)
├── .bundle/ # Ruby bundle安裝目錄
│
└── README.md # 項目說明文檔
JSX 介紹
JSX and React 是相互獨立的 東西。但它們經常一起使用,但你 可以 單獨使用它們中的任意一個,JSX 是一種語法擴展,而 React 則是一個 JavaScript 的庫。
JSX 是 JavaScript 語法擴展,可以讓你在 JavaScript 文件中書寫類似 H 標簽。
javascript xml 在書寫 js 的時候,直接寫標簽 把標簽也看成 js 中的一種 類型
tsx typescript +xml
最簡結構
import { Text, View } from "react-native";export default function App() {return (<View><Text>jsx語法</Text></View>);
}
JSX 規則

只能返回一個根元素
import { Text, View } from "react-native";export default function App() {return (<View><Text>jsx語法</Text></View>);
}
如果你想要同時返回多個結構,可以使用 <></>語法把他們包裹起來
import React from "react";
import { Text } from "react-native";export default function App() {return (<><Text>jsx語法1</Text><Text>jsx語法2</Text></>);
}
標簽必須閉合
不管單標簽還是雙標簽都必須閉合
import { Button } from "react-native";export default function App() {return <Button title="點我" />;
}
使用駝峰式命名法給 大部分屬性命名!
import { Alert, Button } from "react-native";export default function App() {return (<Buttontitle="點我"onPress={() => {Alert.alert("被征用");}}/>);
}
JSX 注釋
{// 這里是單行注釋
}
{/*這里是多行注釋這里是多行注釋這里是多行注釋這里是多行注釋*/
}
JSX 表達式
jsx 表達式可以讓我在標簽中嵌入表達式
import { Text, View } from "react-native";export default function App() {const msg = "我們的rn";const getNum = () => 100;return (<View>{/* 普通標簽 */}<Text>普通標簽</Text>{/* 數學運算 */}<Text>{1 + 1}</Text>{/* 字符串 */}<Text>{"a" + "b"}</Text>{/* 變量 */}<Text>{msg}</Text>{/* 三元表達式 */}<Text>{1 + 1 === 2 ? "對了" : "錯誤"}</Text>{/* 函數調用 */}<Text>{getNum()}</Text></View>);
}
屬性上使用表達式
import { Button } from "react-native";export default function App() {const title = "登錄";const showMsg = () => {};return <Button onPress={showMsg} title={title} />;
}
JSX 嵌套 JSX
可以把標簽也看成是一種特殊的變量來理解以下代碼
import { Text, View } from "react-native";export default function App() {return (<View style={{ padding: 10, backgroundColor: "yellow" }}>{<View style={{ padding: 10, backgroundColor: "blue" }}>{<Text style={{ padding: 10, backgroundColor: "orange" }}>哈哈</Text>}</View>}</View>);
}

JSX 條件渲染
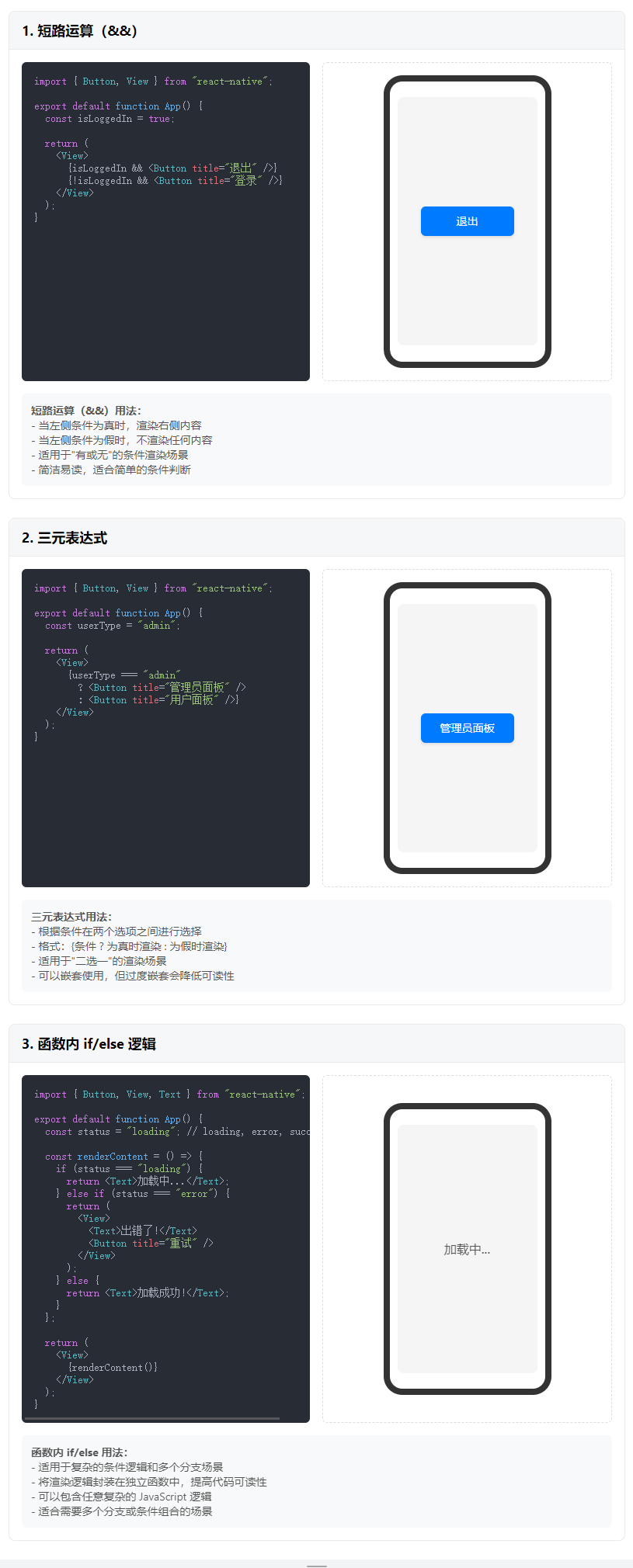
JSX 中實現條件渲染,可以三種方式
- 短路運算
- 三元表達式
- 如果是更加復雜的結構,函數中結合 if/else 來實現
短路運算
import { Button, View } from "react-native";export default function App() {return (<View><View>{true && <Button title="男" />}</View>;<View>{false && <Button title="女" />}</View>;</View>);
}
三元表達式
import { Button, View } from "react-native";export default function App() {return (<View><View>{true ? <Button title="男" /> : <Button title="女" />}</View>;</View>);
}
函數內 if/else
import { Button, View } from "react-native";export default function App() {const showBtn = () => {if (1 === 1) {return <Button title="111" />;} else {return <Button title="222" />;}};return (<View><View>{showBtn()}</View>;</View>);
}
jSX 列表渲染
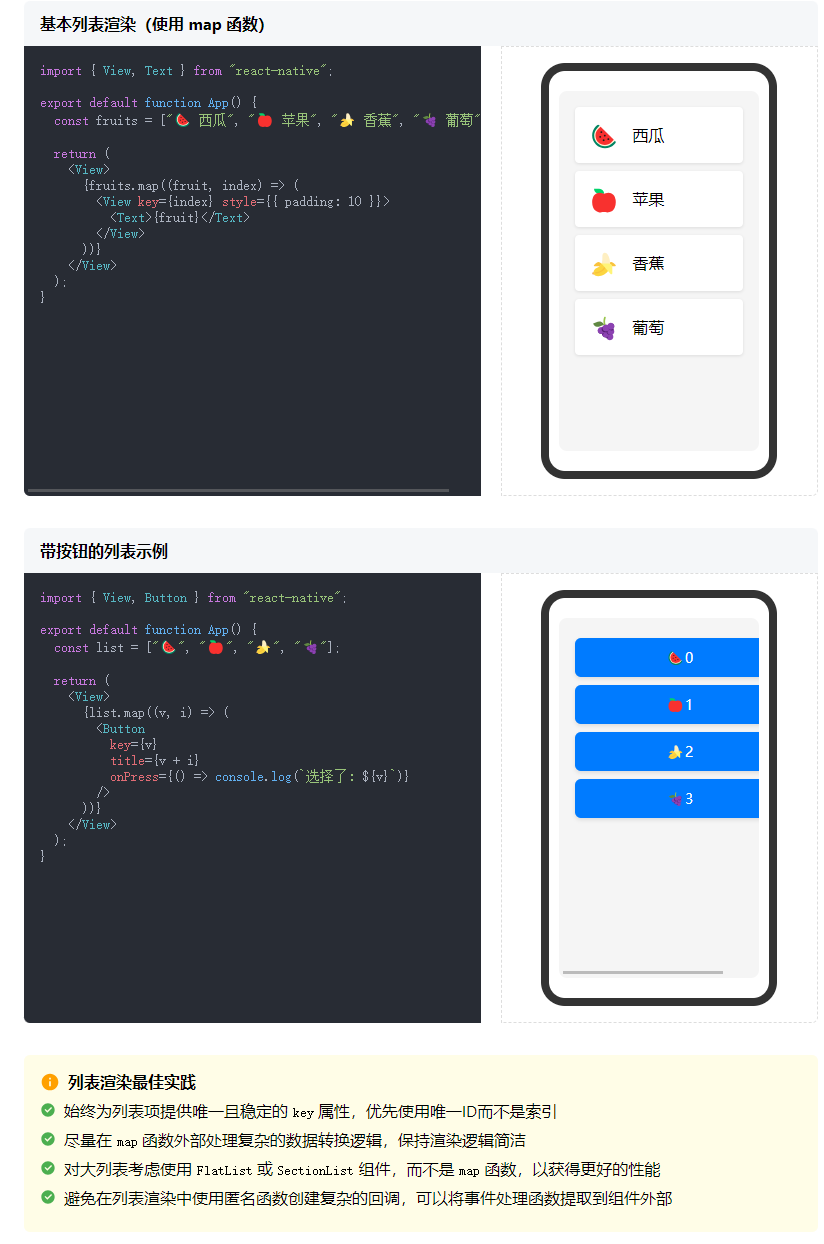
主要通過數組的 map 函數來實現
import { Button, View } from "react-native";export default function App() {const list = ["🍉", "🍎", "🍌", "🍇"];return (<View>{list.map((v, i) => (<Button title={v + i} key={v} />))}</View>);
}
樣式
React Native 中,推薦組件和組件樣式分離的寫法 StyleSheet.create
import { Text, View, StyleSheet } from "react-native";export default function App() {return (<View style={styles.container}><Text>樣式</Text></View>);
}const styles = StyleSheet.create({container: {backgroundColor: "blue",padding: 10,},
});
自定義組件 基本使用
后期可以根據需求,對組件進行導入、導出使用
import { Text, View } from "react-native";export default function App() {return (<View><Text>父組件</Text><Child /></View>);
}function Child() {return <Text>子組件</Text>;
}
useState
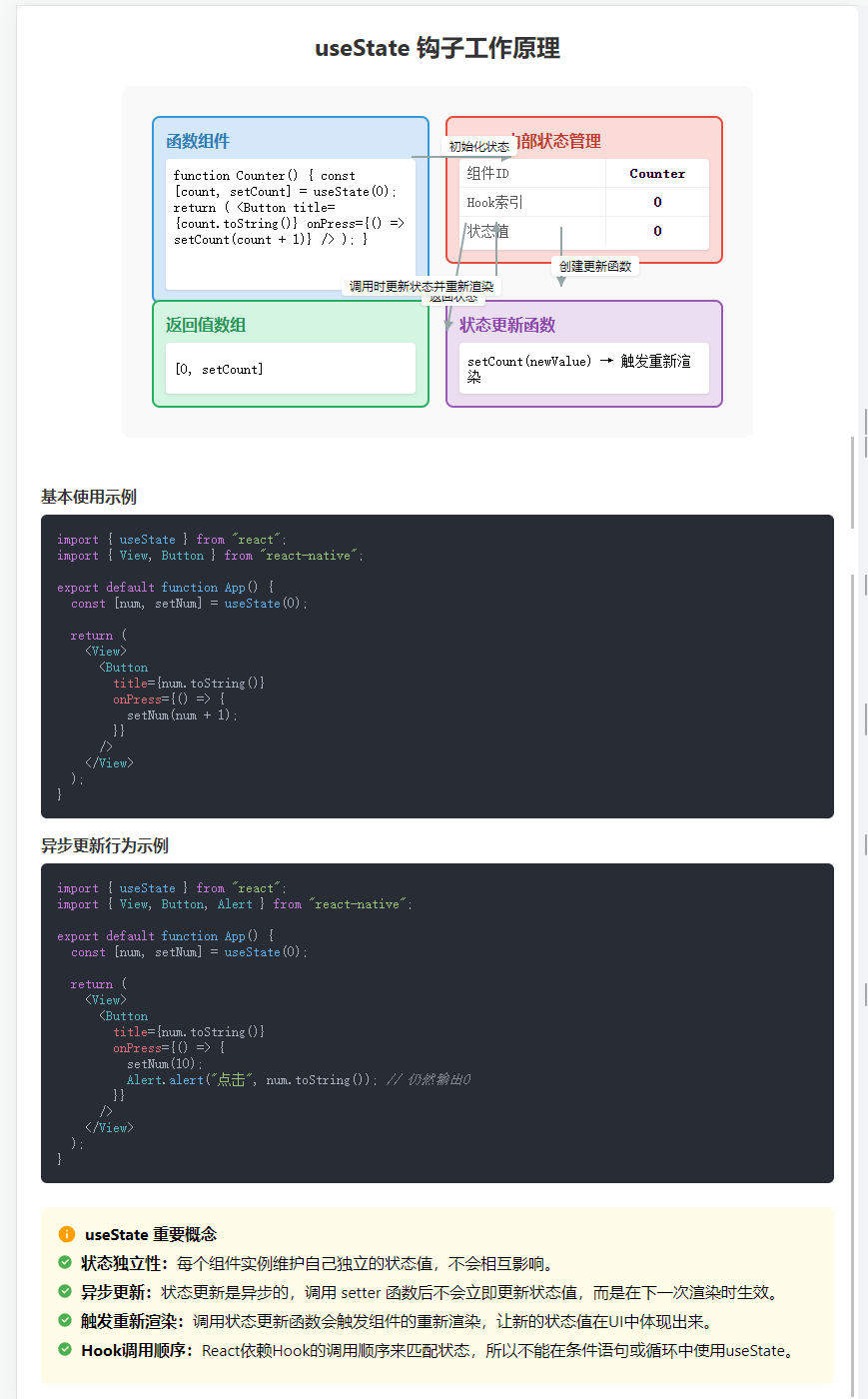
useState 是 React 中用于更新狀態的技術
useState 是一個函數,傳入要設置的狀態的初始值,返回一個數組,第一個元素是數據本身,第二個元素是修改元素的函數。
import { useState } from "react";
import { View, Button } from "react-native";export default function App() {const [num, setNum] = useState(0);return (<View><Buttontitle={num.toString()}onPress={() => {setNum(num + 1);}}/></View>);
}
需要注意的是,出于性能考慮,修改狀態是異步的
import { useState } from "react";
import { View, Button, Alert } from "react-native";export default function App() {const [num, setNum] = useState(0);return (<View><Buttontitle={num.toString()}onPress={() => {setNum(10);Alert.alert("點擊", num.toString()); // 輸出0}}/></View>);
}
自定義組件 父子傳參
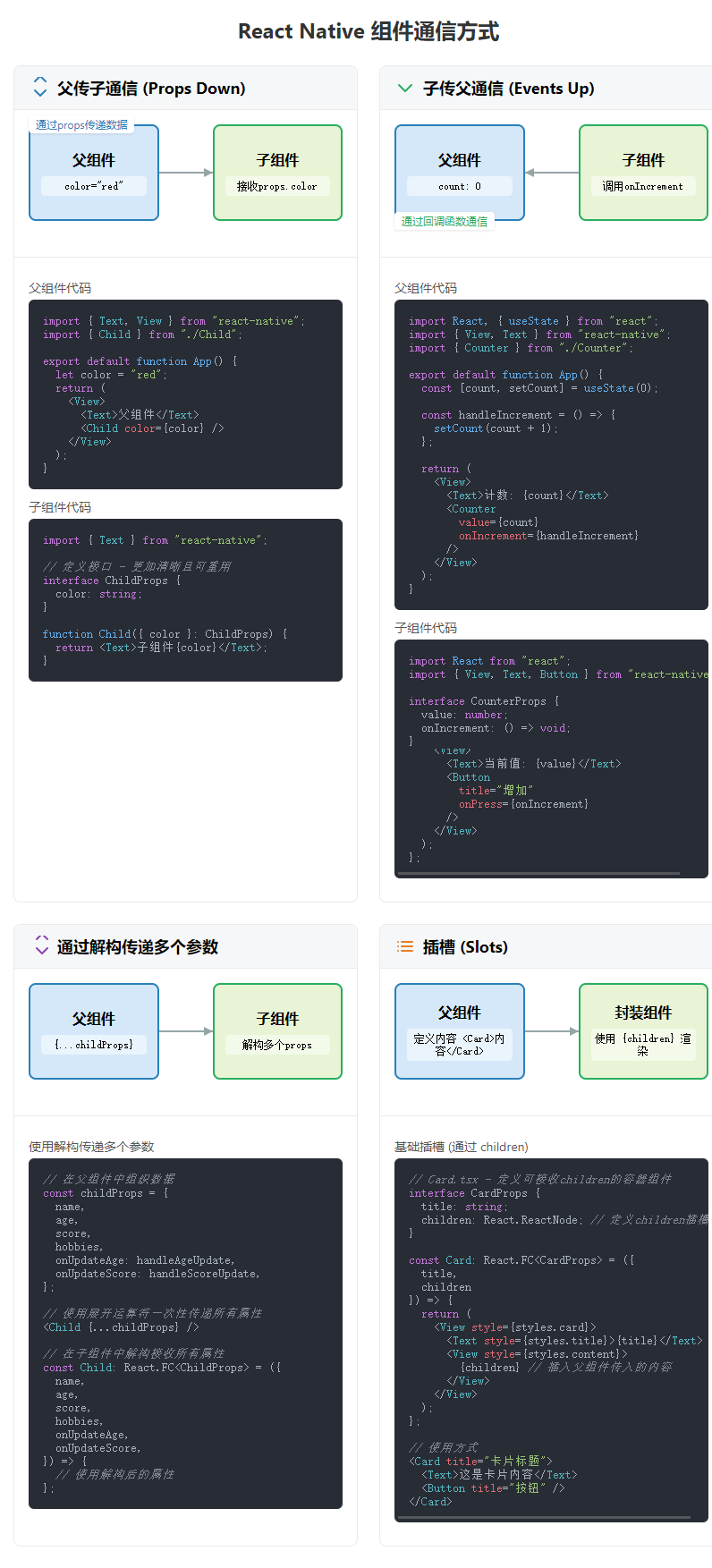
通過普通接口指定參數類型
import { Text, View } from "react-native";// 定義接口 - 更加清晰且可重用
interface ChildProps {color: string;
}export default function App() {let color = "red";return (<View><Text>父組件</Text><Child color={color} /></View>);
}function Child({ color }: ChildProps) {return <Text>子組件{color}</Text>;
}
通過 React.FC 指定參數類型
import React from "react";
import { Text, View } from "react-native";// 定義接口 - 更加清晰且可重用
interface ChildProps {color: string;
}export default function App() {let color = "red";return (<View><Text>父組件</Text><Child color={color} /></View>);
}// 使用React.FC<Props>類型,可以更明確地表明這是一個函數組件
const Child: React.FC<ChildProps> = ({ color }) => {return <Text>子組件{color}</Text>;
};
自定義組件 子父傳參
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { View, Text, Button } from "react-native";// 定義子組件接收的props類型
interface CounterProps {value: number;onIncrement: () => void;
}// 父組件
export default function App() {// 在父組件中維護狀態const [count, setCount] = useState(0);// 定義一個傳遞給子組件的函數const handleIncrement = () => {setCount(count + 1);};return (<View><Text>父組件</Text><Text>父組件中的計數: {count}</Text>{/* 向子組件傳遞屬性和方法 */}<Counter value={count} onIncrement={handleIncrement} /></View>);
}
// 子組件
const Counter: React.FC<CounterProps> = ({ value, onIncrement }) => {return (<View><Text>子組件計數器: {value}</Text><Buttontitle="增加計數"onPress={() => {// 調用父組件傳遞的函數onIncrement();}}/></View>);
};
通過解構傳遞多個參數
import React, { useState } from "react";
import { View, Text, Button } from "react-native";// 定義子組件接收的props類型
interface ChildProps {name: string;age: number;score: number;hobbies: string[];onUpdateAge: () => void;onUpdateScore: (newScore: number) => void;
}// 父組件
export default function App() {// 在父組件中維護多個狀態const [name] = useState("張三");const [age, setAge] = useState(25);const [score, setScore] = useState(85);const [hobbies] = useState(["閱讀", "游泳", "編程"]);// 處理年齡更新const handleAgeUpdate = () => {setAge(age + 1);};// 處理分數更新const handleScoreUpdate = (newScore: number) => {setScore(newScore);};// 解構傳遞多個屬性和方法const childProps = {name,age,score,hobbies,onUpdateAge: handleAgeUpdate,onUpdateScore: handleScoreUpdate,};return (<View><Text>父組件</Text><Text>姓名: {name}, 年齡: {age}, 分數: {score}</Text>{/* 方式1: 逐個傳遞屬性 */}<Childname={name}age={age}score={score}hobbies={hobbies}onUpdateAge={handleAgeUpdate}onUpdateScore={handleScoreUpdate}/>{/* 方式2: 使用展開運算符傳遞所有屬性 */}<Child {...childProps} /></View>);
}// 子組件 - 通過解構直接獲取所需的屬性
const Child: React.FC<ChildProps> = ({name,age,score,hobbies,onUpdateAge,onUpdateScore,
}) => {return (<View><Text>子組件</Text><Text>姓名: {name}</Text><Text>年齡: {age}</Text><Text>分數: {score}</Text><Text>愛好: {hobbies.join(", ")}</Text><Button title="增加年齡" onPress={onUpdateAge} /><Button title="提高分數" onPress={() => onUpdateScore(score + 5)} /></View>);
};
基礎插槽
往自定義組件中插入我們想要的結構。它有以下常見的使用場景
- 卡片(Card)組件:包裝內容并提供一致的外觀
- 模態框(Modal):包裝彈窗內容,但允許自定義內容
- 面板(Panel):帶標題和可折疊功能的內容容器
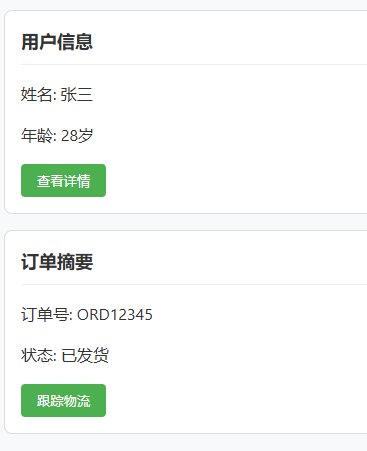
import React from "react";
import { View, Text, Button } from "react-native";// 基礎插槽:使用children
interface CardProps {title: string;children: React.ReactNode; // 定義children插槽
}// 基礎插槽組件
const Card: React.FC<CardProps> = ({ title, children }) => {return (<View><Text>{title}</Text><View>{children}</View></View>);
};// 父組件
export default function App() {return (<View><Text>基礎插槽示例</Text>{/* 基礎插槽用法 */}<Card title="卡片標題"><Text>這是卡片內容</Text><Button title="卡片按鈕" onPress={() => console.log("按鈕點擊")} /></Card></View>);
}
具名插槽
import React from "react";
import { View, Text, Button, StyleSheet } from "react-native";// 具名插槽:使用特定屬性定義多個插槽
interface PanelProps {title: string;header?: React.ReactNode; // 可選的頭部插槽content: React.ReactNode; // 主內容插槽footer?: React.ReactNode; // 可選的底部插槽
}// 具名插槽組件
const Panel: React.FC<PanelProps> = ({ title, header, content, footer }) => {return (<View style={styles.panel}><Text style={styles.panelTitle}>{title}</Text>{/* 頭部插槽 */}{header && <View style={styles.panelHeader}>{header}</View>}{/* 內容插槽 */}<View style={styles.panelContent}>{content}</View>{/* 底部插槽 */}{footer && <View style={styles.panelFooter}>{footer}</View>}</View>);
};// 父組件
export default function App() {return (<View style={styles.container}><Text style={styles.header}>具名插槽示例</Text>{/* 具名插槽用法 */}<Paneltitle="具名插槽"header={<Text style={styles.headerText}>這是自定義頭部區域</Text>}content={<View><Text>這是主要內容區域</Text><Buttontitle="內容區按鈕"onPress={() => console.log("內容區按鈕點擊")}/></View>}footer={<View style={styles.footerButtons}><Button title="取消" onPress={() => console.log("取消")} /><Button title="確定" onPress={() => console.log("確定")} /></View>}/></View>);
}// 樣式
const styles = StyleSheet.create({container: {padding: 16,gap: 16,},header: {fontSize: 20,fontWeight: "bold",marginBottom: 16,},panel: {backgroundColor: "#f9f9f9",borderRadius: 8,borderWidth: 1,borderColor: "#ddd",marginBottom: 16,overflow: "hidden",},panelTitle: {fontSize: 18,fontWeight: "bold",backgroundColor: "#eee",padding: 12,},panelHeader: {padding: 12,backgroundColor: "#f5f5f5",borderBottomWidth: 1,borderBottomColor: "#ddd",},headerText: {fontWeight: "600",},panelContent: {padding: 16,},panelFooter: {padding: 12,backgroundColor: "#f5f5f5",borderTopWidth: 1,borderTopColor: "#ddd",},footerButtons: {flexDirection: "row",justifyContent: "flex-end",gap: 8,},
});
)

)


?)



![每日一題洛谷P8635 [藍橋杯 2016 省 AB] 四平方和c++](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/每日一題洛谷P8635 [藍橋杯 2016 省 AB] 四平方和c++)






-沒有使用演繹推理的必然判斷)


