目錄
1.知識回顧
2.串聯類和對象的知識重新理解
構造函數
string();
string (const string& str);
string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos);
string (const char* s);
string (size_t n, char c);
append和push_back
string& append (const string& str);?
string& append (const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen);
string& append (const char* s);?
string& append (const char* s, size_t n);
template string& append (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
operator+=
operator[ ]
理解[ ]本質是解引用
上方代碼能否訪問到\0?
方法1:下條件斷點后監視
方法2:反匯編后看內存,手動查找
方法3:直接監視窗口看封裝好的string類的str
缺點
1.知識回顧
之前在C++ Contest專欄提到過string的使用
CC12.【C++ Cont】string類字符串的創建、輸入、訪問和size函數
CC13.【C++ Cont】初識string類字符串的迭代器
CC14.【C++ Cont】string類字符串的push_back、pop_back、字符串+=與+運算和insert
CC15.【C++ Cont】string類字符串的find和substr函數
CC16.【C++ Cont】string類字符串的關系運算和與string有關的函數
2.串聯類和對象的知識重新理解
上方提到的文章講的比較淺,只是介紹了怎么用,本文將用類和對象的思想來理解
以https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/?kw=string網為線索:
構造函數
![]()
 ?下面只講常用的
?下面只講常用的
string();
無參數傳遞,即默認構造,也稱無參構造
string (const string& str);
傳參的類型為const string,為拷貝構造
string (const string& str, size_t pos, size_t len = npos);
傳參的類型為const string,為拷貝構造,只不過是拷貝構造str的子串,顯然第3個參數是缺省參數,如果不寫,默認從pos位置一直截取的string風格的字符串的結尾
string (const char* s);
const char*為C語言風格的字符串類型,因此為使用C風格的字符串構造
string (size_t n, char c);
使用n個字符c來構造
append和push_back
https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/append/

append v.追加 即向原string類字符串后追加字符串,作用類似push_back,只不過push_back只能追加字符
有關push_back成員函數的簡單使用參見CC14.【C++ Cont】string類字符串的push_back、pop_back、字符串+=與+運算和insert文章
此外:如果string的空間不夠,append或push_back會自動擴容,(具體的擴容策略和編譯器的處理有關,沒有統一的規定),C語言strcat,不能自動擴容且找\0耗時
string& append (const string& str);?
向原string類字符串后追加string類字符串(類似push_back)
string& append (const string& str, size_t subpos, size_t sublen);
向原string類字符串后追加string類字符串str的子字符串
string& append (const char* s);?
向原string類字符串后追加C語言風格的字符串
string& append (const char* s, size_t n);
向原string類字符串后追加C語言風格的字符串的前n個字符
代碼示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string str("teststring");str.append("abcdef", 3);cout << str << endl;return 0;
}
運行結果:

template <class InputIterator>
?? string& append (InputIterator first, InputIterator last);
?向原string類字符串后追加范圍為[first,last)的一串字符
代碼示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string str1("teststring");string str2("000abc111");str1.append(str2.begin()+3,str2.begin()+6);cout << str1 << endl;return 0;
}運行結果:

operator+=
參見CC14.【C++ Cont】string類字符串的push_back、pop_back、字符串+=與+運算和insert文章
operator[ ]
https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/operator[]/

給了兩種重載形式,一個可以修改字符串,一個不能修改字符串
可做如下測試:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string str1("helloworld");const string str2("teststring");str1[1];str2[1];return 0;
}寫法等價為:使用點操作符調用成員函數
str1.operator[](1);
str2.operator[](2);從地址上看,調用operator[]的地址不同,因此是不同的重載函數:

如果從operator[]函數的定義上來看:
str1[1]的operator[]沒有有const修飾:

str2[1]的operator[]有const修飾:

理解[ ]本質是解引用
代碼示例:可以像數組一樣訪問
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string str("helloworld");for (size_t i = 0; i < str.size(); i++)cout << str[i];return 0;
}
運行結果:

上方代碼能否訪問到\0?
方法1:下條件斷點后監視

監視窗口查看:

str[i]解引用后是最后一個字母d,不是\0
方法2:反匯編后看內存,手動查找
Debug+x86環境下,for循環的反匯編代碼:

發現ebp-3Ch和ebp-30h高頻出現,由mov dword ptr [ebp-3Ch],0 猜測這是為變量i賦初值,因此[ebp-3Ch]存的是i的值,?由cmp dword ptr [ebp-3Ch],eax和jae 00540BDD猜測這是i < str.size()的條件判斷,因此猜測eax臨時存儲的是str.size的值,可以看看寄存器:

0x0000000A=十進制的10,不帶\0的helloworld恰好占10個字節,因此不會訪問到\0
方法3:直接監視窗口看封裝好的string類的str
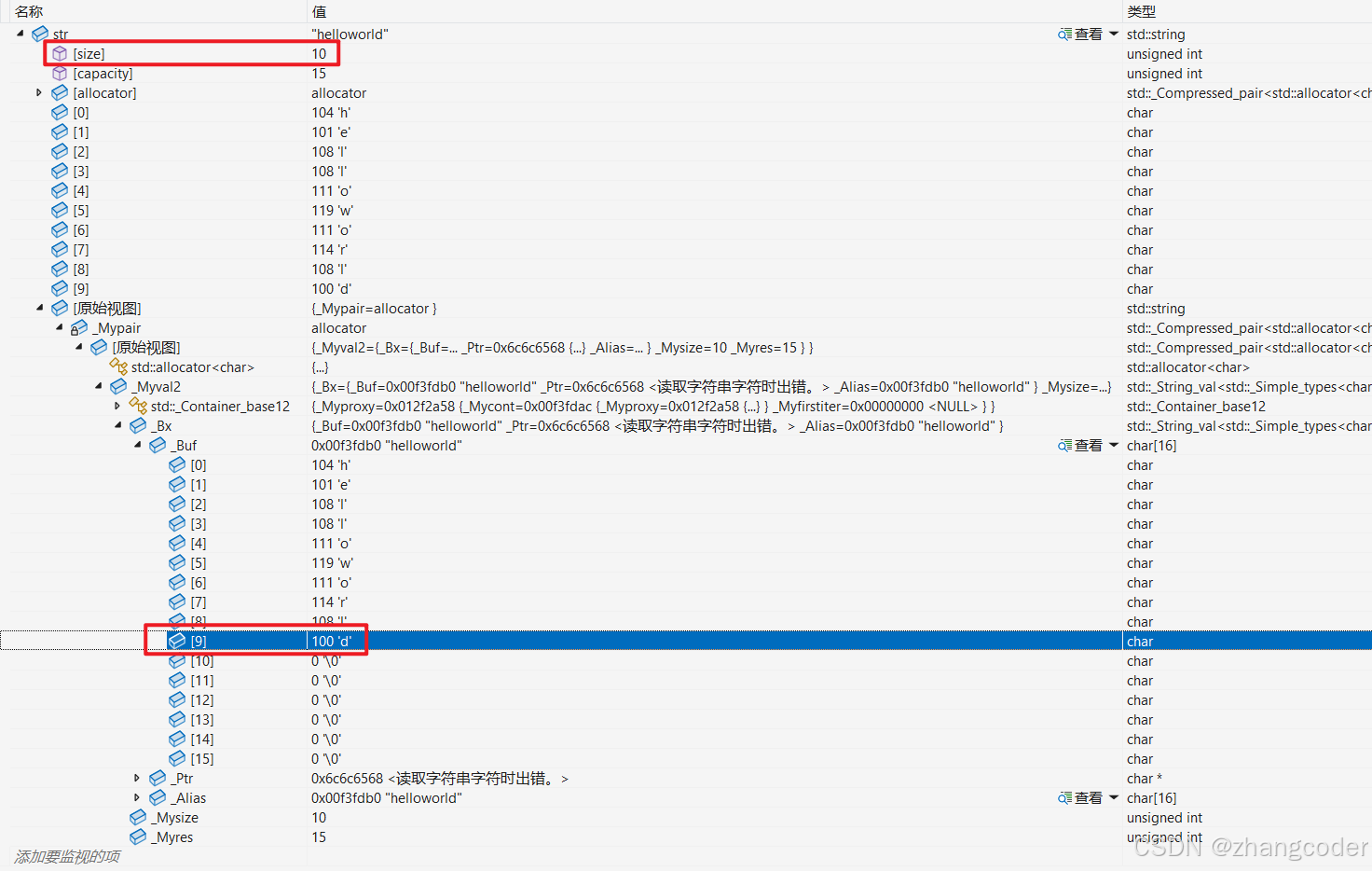
備注:如果想強制打印\0可以將i < str.size()改成i <= str.size()
循環后再打印一個#檢測\0有沒有占位:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{string str("helloworld");for (size_t i = 0; i <= str.size(); i++)cout << str[i];cout << "#";return 0;
}
Visual Studio 2022查看控制臺窗口:

發現\0不顯示,且不占位,因為VS認為str[i]超出界限,因此沒有為\0占位

Dev C++查看控制臺窗口:

發現\0不顯示,且占位
Ubuntu Linux g++運行結果:
![]()
發現\0不顯示,且不占位
發現不同平臺的處理方法不同
缺點
Operator[ ]只有連續的空間才能使用,即非線性結構不能使用[ ]訪問,但一些線性結構和非線性結構都可以使用迭代器訪問,例如鏈表:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ list<int> ls;ls.push_back(1);ls.push_back(3);ls.push_back(13);ls.push_back(0);ls.push_back(43);ls.push_back(546);ls.push_back(9);for (auto i = ls.begin(); i != ls.end(); i++){cout << *i << "-->";}cout << "NULL";return 0;
}
運行結果:




,源碼可白嫖!)





![53.[前端開發-JS實戰框架應用]Day04-Bootstrap入門到項目實戰](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/53.[前端開發-JS實戰框架應用]Day04-Bootstrap入門到項目實戰)

)
)






)