前言
最近和朋友討論oracle行級安全策略(VPD)時,查看了下官方文檔,看起來VPD的原理是針對應用了Oracle行級安全策略的表、視圖或同義詞發出的 SQL 語句動態添加where子句。通俗理解就是將行級安全策略動態添加為where 條件。那么PG中的行級安全策略是怎么處理的呢?
行級安全簡介
行級安全策略(Row Level Security)是更細粒度的數據安全控制策略。行級策略可以根據每個用戶限制哪些行可以通過常規查詢返回,哪些行可以通過數據修改命令插入、更新或刪除。默認情況下,表沒有任何行級安全策略,因此如果用戶根據 SQL 權限系統具有表的訪問權限,則其中的所有行都可以平等地用于查詢或更新。
在PG中我們可以創建行級策略,在SQL執行時行級策略表達式將作為查詢的一部分運行。
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/16/ddl-rowsecurity.html
行級安全演示
創建3個用戶
postgres=# create user admin;
CREATE ROLE
postgres=# create user peter;
CREATE ROLE
postgres=# create user bob;
CREATE ROLE
創建一個rlsdb數據庫
postgres=# create database rlsdb owner admin;
CREATE DATABASE在rlsdb中使用admin用戶創建表employee,并插入3個用戶對應的數據
postgres=# \c rlsdb admin
You are now connected to database "rlsdb" as user "admin".
rlsdb=> create table employee ( empno int, ename text, address text, salary int, account_number text );
CREATE TABLE
rlsdb=> insert into employee values (1, 'admin', '2 down str', 80000, 'no0001' );
INSERT 0 1
rlsdb=> insert into employee values (2, 'peter', '132 south avn', 60000, 'no0002' );
INSERT 0 1
rlsdb=> insert into employee values (3, 'bob', 'Down st 17th', 60000, 'no0003' );
INSERT 0 1
rlsdb=>
授權后,三個用戶都能看到employee表的所有數據
rlsdb=> grant select on table employee to peter;
GRANT
rlsdb=> grant select on table employee to bob;
GRANT
rlsdb=> select * from employee;empno | ename | address | salary | account_number
-------+-------+---------------+--------+----------------1 | admin | 2 down str | 80000 | no00012 | peter | 132 south avn | 60000 | no00023 | bob | Down st 17th | 60000 | no0003
(3 rows)rlsdb=>
rlsdb=> \c rlsdb peter
You are now connected to database "rlsdb" as user "peter".
rlsdb=> select * from employee;empno | ename | address | salary | account_number
-------+-------+---------------+--------+----------------1 | admin | 2 down str | 80000 | no00012 | peter | 132 south avn | 60000 | no00023 | bob | Down st 17th | 60000 | no0003
(3 rows)rlsdb=> \c rlsdb bob
You are now connected to database "rlsdb" as user "bob".
rlsdb=> select * from employee;empno | ename | address | salary | account_number
-------+-------+---------------+--------+----------------1 | admin | 2 down str | 80000 | no00012 | peter | 132 south avn | 60000 | no00023 | bob | Down st 17th | 60000 | no0003
(3 rows)
使用admin用戶創建行級安全策略,對于peter和bob就只能看到自己的數據了。
rlsdb=> \c rlsdb admin
You are now connected to database "rlsdb" as user "admin".
rlsdb=> CREATE POLICY emp_rls_policy ON employee FOR ALL TO PUBLIC USING (ename=current_user);
CREATE POLICY
rlsdb=> ALTER TABLE employee ENABLE ROW LEVEL SECURITY;
ALTER TABLE
rlsdb=> \c rlsdb peter
You are now connected to database "rlsdb" as user "peter".
rlsdb=> select * from employee;empno | ename | address | salary | account_number
-------+-------+---------------+--------+----------------2 | peter | 132 south avn | 60000 | no0002
(1 row)rlsdb=> \c rlsdb bob
You are now connected to database "rlsdb" as user "bob".
rlsdb=> select * from employee;empno | ename | address | salary | account_number
-------+-------+--------------+--------+----------------3 | bob | Down st 17th | 60000 | no0003
(1 row)rlsdb=>
行級安全原理
先看下行級安全策略在數據庫中的呈現是什么樣的。
查看pg_policy表,可以看到我們創建的emp_rls_policy這個策略,具體的策略polqual是一串字符,熟悉parsetree結構的朋友能關注到這是一個OPEXPR node。我們常見的where 條件也是類似的結構。
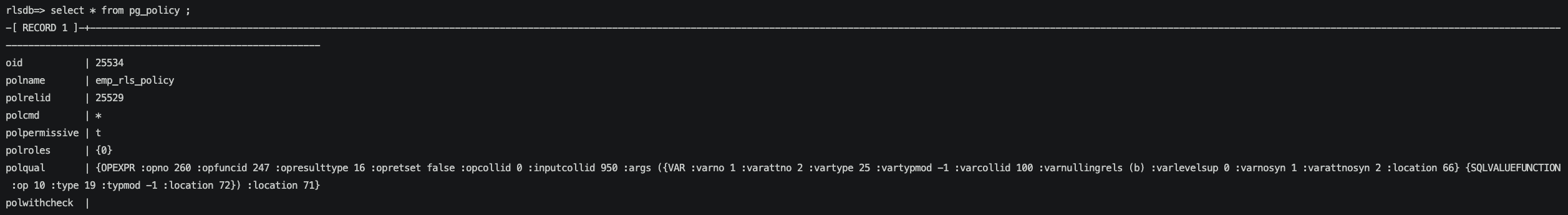
我們可以使用函數讓polqual以更適合人閱讀的方式來展示。
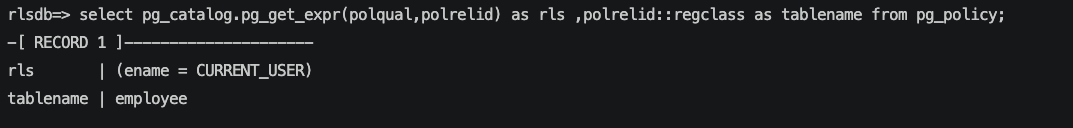
創建策略時,其實是將策略轉換為where子句存到pg_policy表中。
ObjectAddress
CreatePolicy(CreatePolicyStmt *stmt)
{
/*省略部分代碼行*/
/*將策略轉化為where子句*/qual = transformWhereClause(qual_pstate,stmt->qual,EXPR_KIND_POLICY,"POLICY");with_check_qual = transformWhereClause(with_check_pstate,stmt->with_check,EXPR_KIND_POLICY,"POLICY");/* Fix up collation information */assign_expr_collations(qual_pstate, qual);assign_expr_collations(with_check_pstate, with_check_qual);
/* 將轉換后的子句寫入pg_policy*//* Open pg_policy catalog */pg_policy_rel = table_open(PolicyRelationId, RowExclusiveLock);/* Set key - policy's relation id. */ScanKeyInit(&skey[0],Anum_pg_policy_polrelid,BTEqualStrategyNumber, F_OIDEQ,ObjectIdGetDatum(table_id));/* Set key - policy's name. */ScanKeyInit(&skey[1],Anum_pg_policy_polname,BTEqualStrategyNumber, F_NAMEEQ,CStringGetDatum(stmt->policy_name));sscan = systable_beginscan(pg_policy_rel,PolicyPolrelidPolnameIndexId, true, NULL, 2,skey);policy_tuple = systable_getnext(sscan);/* Complain if the policy name already exists for the table */if (HeapTupleIsValid(policy_tuple))ereport(ERROR,(errcode(ERRCODE_DUPLICATE_OBJECT),errmsg("policy \"%s\" for table \"%s\" already exists",stmt->policy_name, RelationGetRelationName(target_table))));policy_id = GetNewOidWithIndex(pg_policy_rel, PolicyOidIndexId,Anum_pg_policy_oid);values[Anum_pg_policy_oid - 1] = ObjectIdGetDatum(policy_id);values[Anum_pg_policy_polrelid - 1] = ObjectIdGetDatum(table_id);values[Anum_pg_policy_polname - 1] = DirectFunctionCall1(namein,CStringGetDatum(stmt->policy_name));values[Anum_pg_policy_polcmd - 1] = CharGetDatum(polcmd);values[Anum_pg_policy_polpermissive - 1] = BoolGetDatum(stmt->permissive);values[Anum_pg_policy_polroles - 1] = PointerGetDatum(role_ids);/* Add qual if present. */if (qual)values[Anum_pg_policy_polqual - 1] = CStringGetTextDatum(nodeToString(qual));elseisnull[Anum_pg_policy_polqual - 1] = true;/* Add WITH CHECK qual if present */if (with_check_qual)values[Anum_pg_policy_polwithcheck - 1] = CStringGetTextDatum(nodeToString(with_check_qual));elseisnull[Anum_pg_policy_polwithcheck - 1] = true;policy_tuple = heap_form_tuple(RelationGetDescr(pg_policy_rel), values,isnull);CatalogTupleInsert(pg_policy_rel, policy_tuple);/* Record Dependencies */target.classId = RelationRelationId;target.objectId = table_id;target.objectSubId = 0;myself.classId = PolicyRelationId;myself.objectId = policy_id;myself.objectSubId = 0;recordDependencyOn(&myself, &target, DEPENDENCY_AUTO);recordDependencyOnExpr(&myself, qual, qual_pstate->p_rtable,DEPENDENCY_NORMAL);recordDependencyOnExpr(&myself, with_check_qual,with_check_pstate->p_rtable, DEPENDENCY_NORMAL);/* Register role dependencies */target.classId = AuthIdRelationId;target.objectSubId = 0;for (i = 0; i < nitems; i++){target.objectId = DatumGetObjectId(role_oids[i]);/* no dependency if public */if (target.objectId != ACL_ID_PUBLIC)recordSharedDependencyOn(&myself, &target,SHARED_DEPENDENCY_POLICY);}InvokeObjectPostCreateHook(PolicyRelationId, policy_id, 0);/* Invalidate Relation Cache */CacheInvalidateRelcache(target_table);/* Clean up. */heap_freetuple(policy_tuple);free_parsestate(qual_pstate);free_parsestate(with_check_pstate);systable_endscan(sscan);relation_close(target_table, NoLock);table_close(pg_policy_rel, RowExclusiveLock);return myself;
}
在SQL執行時,查詢重寫階段會將對應的安全策略拼接到parsetree里,最后生成執行計劃去執行。
從執行計劃來看SQL沒有where條件,但是執行計劃中存在 Filter: (ename = CURRENT_USER),證明了這個過程。
rlsdb=> explain analyze select * from employee ;QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Seq Scan on employee (cost=0.00..19.15 rows=3 width=104) (actual time=0.010..0.012 rows=1 loops=1)Filter: (ename = CURRENT_USER)Rows Removed by Filter: 2Planning Time: 0.416 msExecution Time: 0.036 ms
(5 rows)rlsdb=>
再debug驗證下這個過程。
給fireRIRrules函數設置斷點,進入斷點后從stack可以看到目前是在QueryRewrite階段,結合一些規則進行查詢重寫。
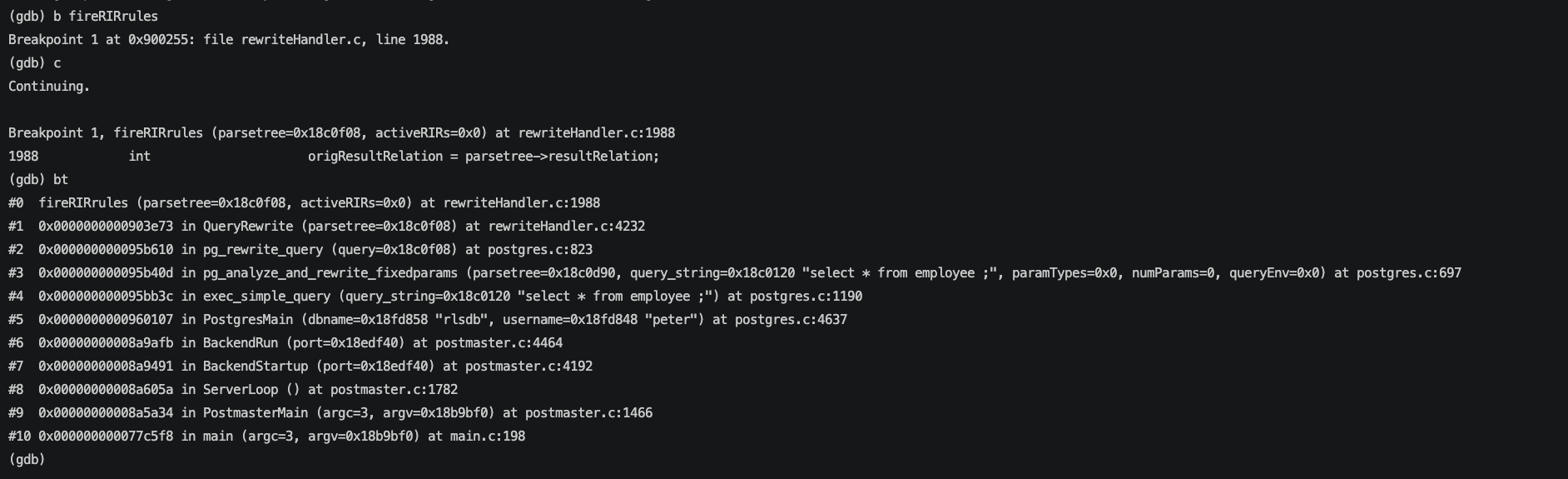
觀察這個時候的parsetree,可以看到還沒有將安全策略對應的OPEXPR拼接進來。
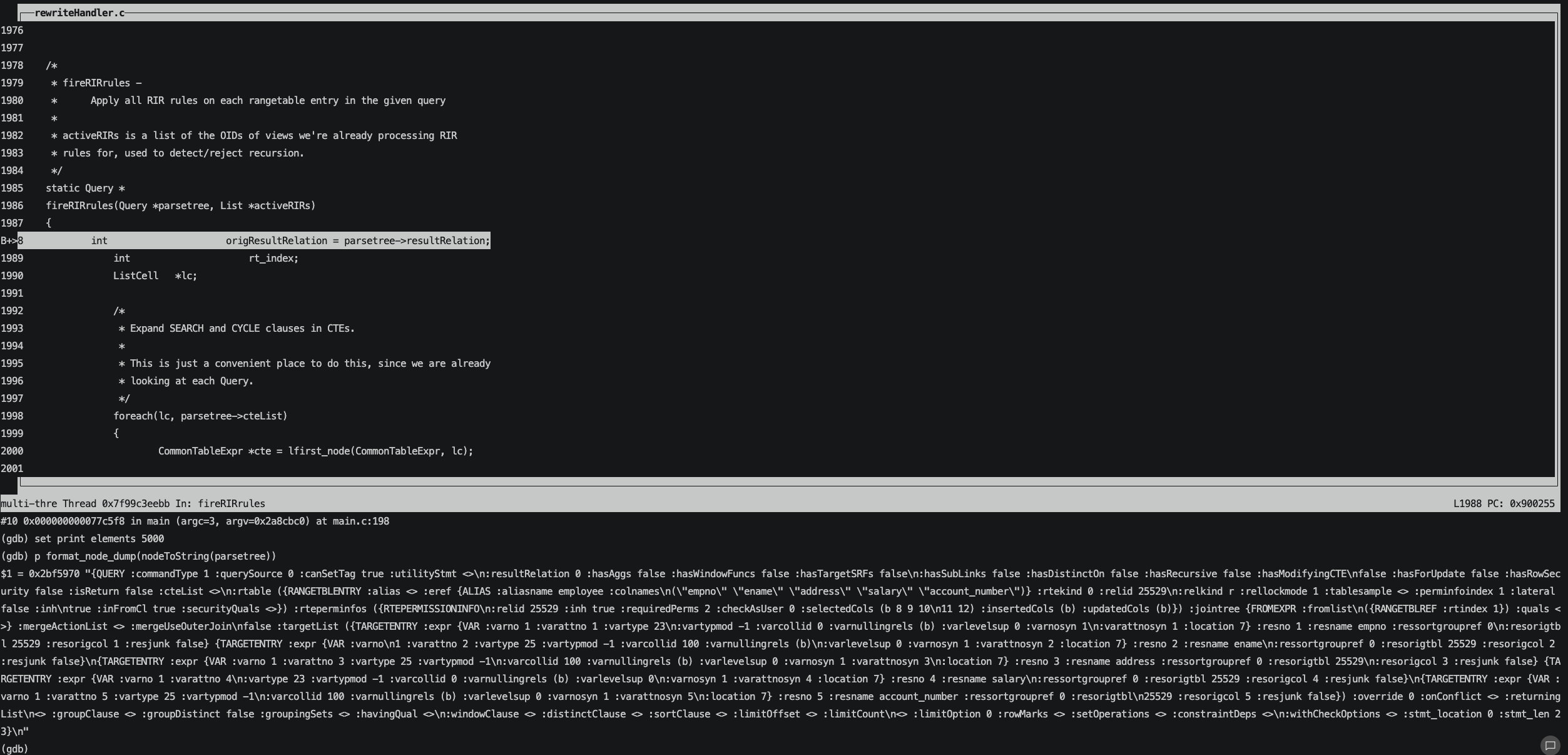
等執行到get_row_security_policies函數已獲取到表對應安全策略securityQuals。
打印securityQuals可以看到和我們查詢pg_policy中的OPEXPR是一致的。
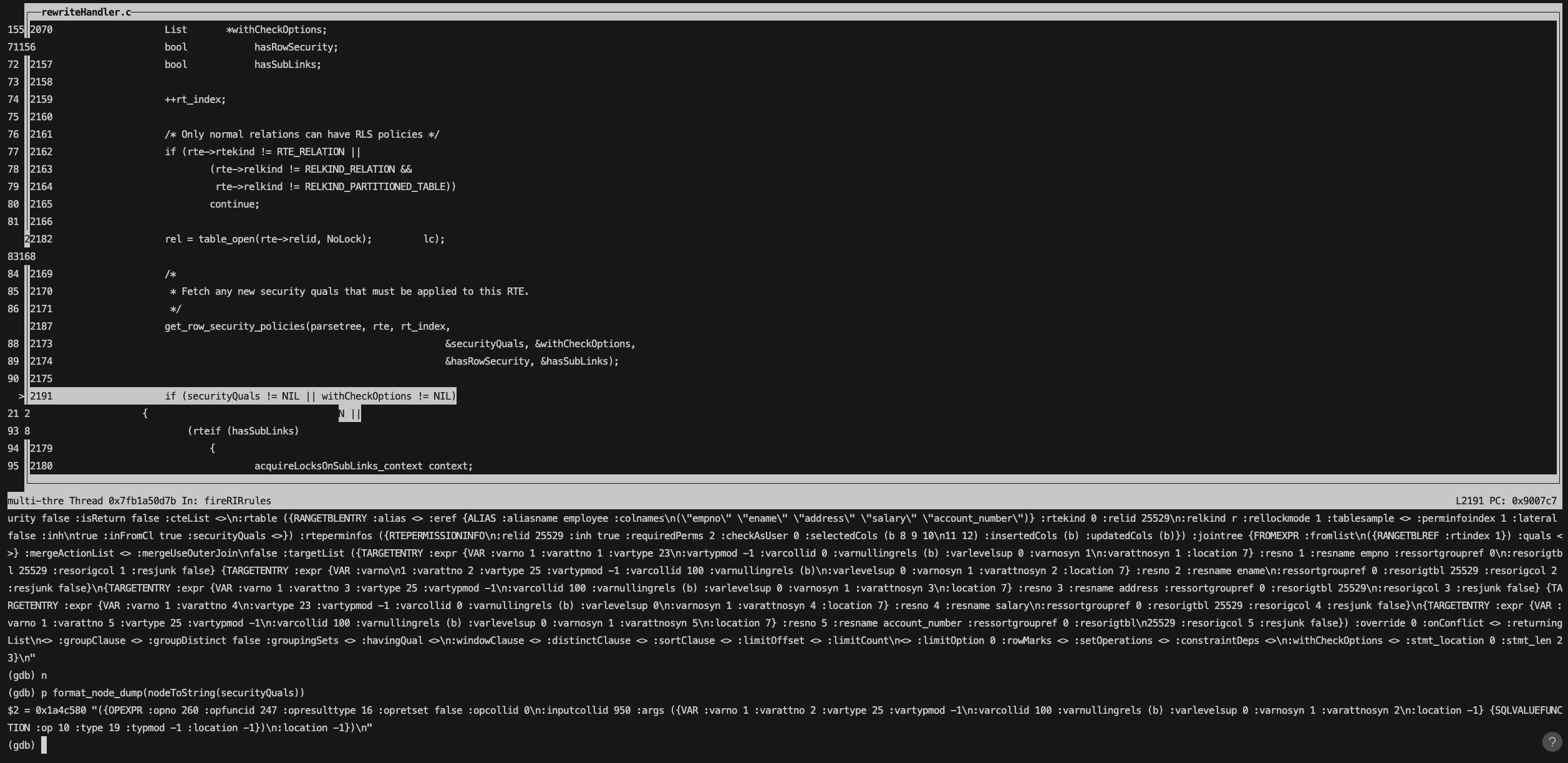
接著將securityQuals加入到rte的list中,這樣我們再去打印parsetree就可以看到安全策略securityQuals對應的OPEXPR已經被拼接進來。
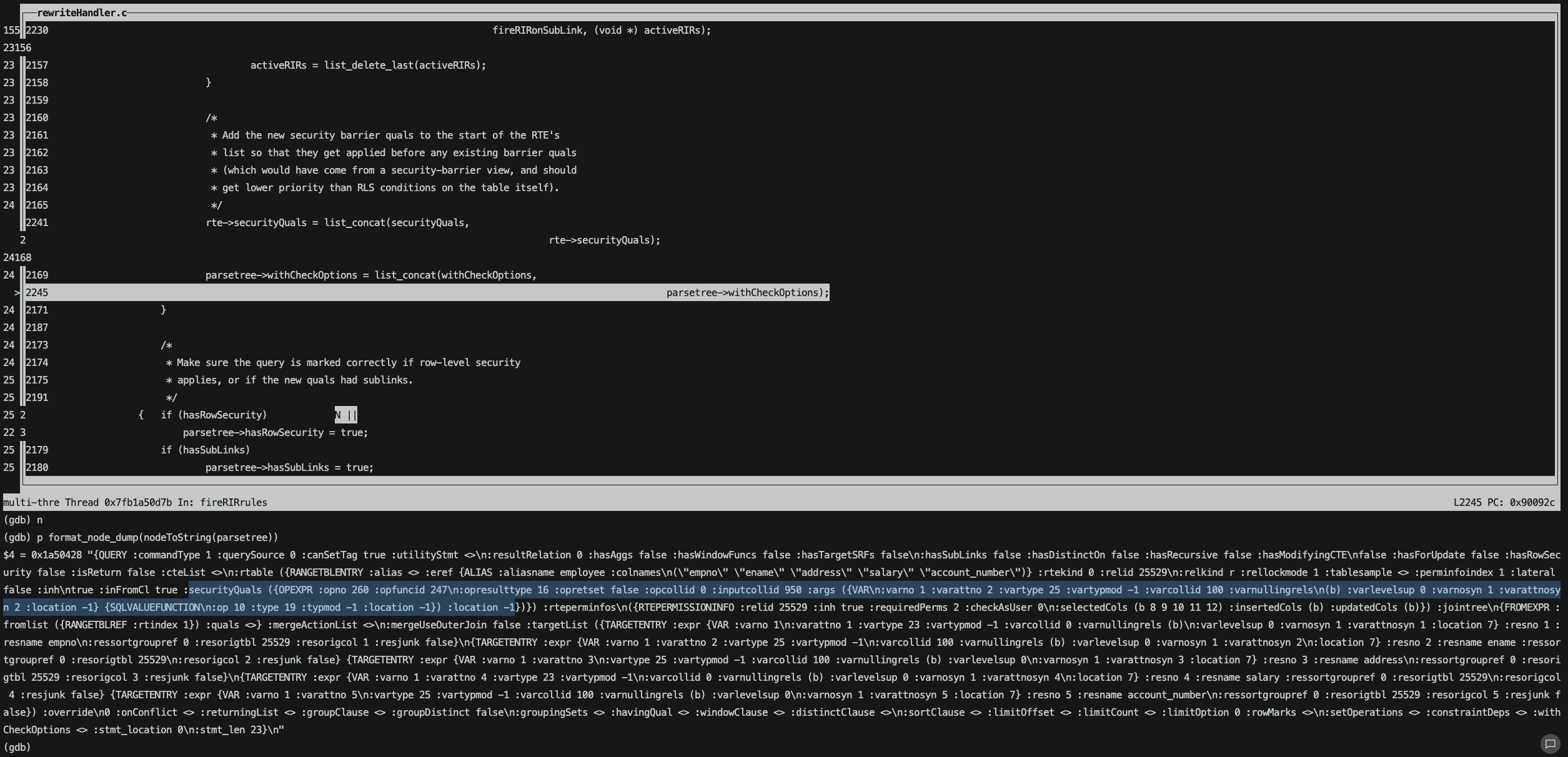
然后就是去生成執行計劃并執行。
小結
PG的RLS也是將對應的策略動態轉換為where子句,在查詢重寫階段將安全策略拼接到parsetree,生成執行計劃去執行。
行級安全策略,可以提供更精細粒度的表數據權限管理,在一定的場景下,比如只讓用戶看到自己對應的數據,能做到更安全的權限把控。











帶寬以及雙機熱備實驗)







