Authorize HttpServletRequests
SpringSecurity 允許您在請求級別對授權進行建模。例如,對于 Spring Security,可以說/admin 下的所有頁面都需要一個權限,而其他所有頁面只需要身份驗證。
默認情況下,SpringSecurity 要求對每個請求進行身份驗證。也就是說,任何時候使用 HttpSecurity 實例,都需要聲明授權規則。
無論何時有 HttpSecurity 實例,您至少應該這樣做:
Use authorizeHttpRequests
http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.anyRequest().authenticated())
這告訴 Spring Security,應用程序中的任何端點都需要至少對安全上下文進行身份驗證才能允許它。
在許多情況下,您的授權規則將比這更復雜,因此請考慮以下用例:
- 我有一個使用 AuthorizeRequest 的應用程序,我想將它遷移到 AuthorizeHttpRequest(I have an app that uses
authorizeRequestsand I want to migrate it toauthorizeHttpRequests) - 我想了解 AuthorizationFilter 組件是如何工作的(I want to understand how the
AuthorizationFiltercomponents work) - 我希望根據模式匹配請求,特別是正則表達式(I want to match requests based on a pattern; specifically regex)
- 我想匹配請求,并將 SpringMVC 映射到默認 servlet 之外的其他內容(I want to match request, and I map Spring MVC to something other than the default servlet)
- I want to authorize requests
- 希望以編程方式匹配請求(I want to match a request programmatically)
- 我想以編程方式授權一個請求(I want to authorize a request programmatically)
- 我要將請求授權委托給策略代理(I want to delegate request authorization to a policy agent)
Understanding How Request Authorization Components Work
本節通過深入研究基于 Servlet 的應用程序中的請求級授權如何工作,構建在 Servlet 體系結構和實現的基礎上。
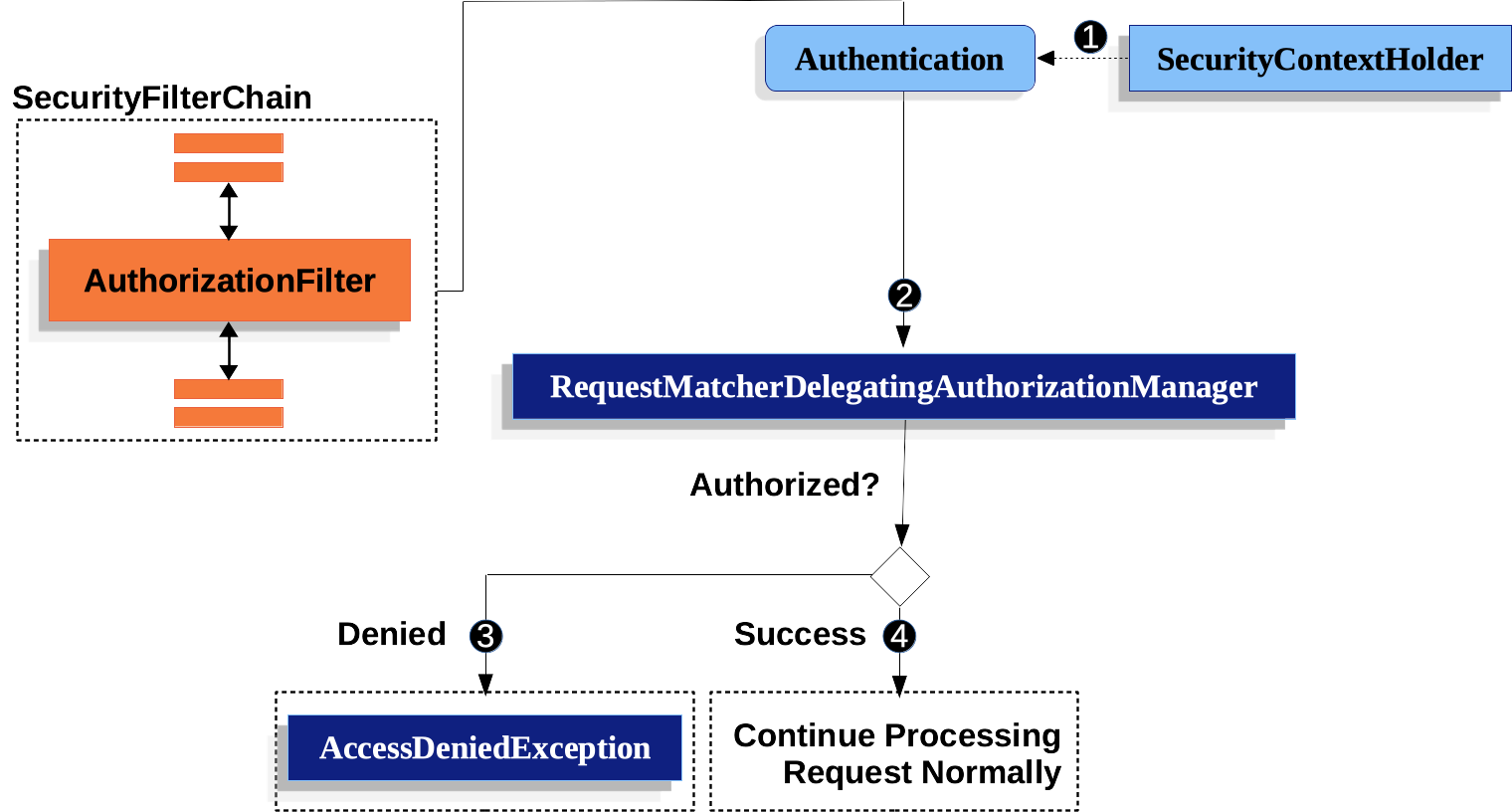
 首先,AuthorizationFilter 構建了一個 Supplier,用于從 SecurityContextHolder 檢索 Authentication。(First, the
首先,AuthorizationFilter 構建了一個 Supplier,用于從 SecurityContextHolder 檢索 Authentication。(First, the AuthorizationFilterconstructs aSupplierthat retrieves an Authentication from the SecurityContextHolder.) 第二,它將 Supplier 和 HttpServletRequest 傳遞給 AuthorizationManager。AuthorizationManager 將請求與 authorizeHttpRequests 中的模式進行匹配,并運行相應的規則。
第二,它將 Supplier 和 HttpServletRequest 傳遞給 AuthorizationManager。AuthorizationManager 將請求與 authorizeHttpRequests 中的模式進行匹配,并運行相應的規則。  如果授權被拒絕,將發布一個 AuthorizationDeniedEvent,并拋出一個 AccessDeniedException。在這種情況下,ExceptionTranslationFilter 將處理 AccessDeniedException。
如果授權被拒絕,將發布一個 AuthorizationDeniedEvent,并拋出一個 AccessDeniedException。在這種情況下,ExceptionTranslationFilter 將處理 AccessDeniedException。 如果授予訪問權限,則發布 AuthorizationGrantedEvent,AuthorizationFilter 繼續使用 FilterChain,它允許應用程序正常處理。
如果授予訪問權限,則發布 AuthorizationGrantedEvent,AuthorizationFilter 繼續使用 FilterChain,它允許應用程序正常處理。
AuthorizationFilter Is Last By Default
AuthorizationFilter 默認是 Spring Security 過濾器鏈中的最后一個。這意味著 Spring Security 的認證過濾器、漏洞保護以及其他過濾器集成不需要授權。如果您在 AuthorizationFilter 之前添加自己的過濾器,它們也不需要授權;否則,它們將需要授權。
一個典型的場景是當您添加 Spring MVC 端點時。因為它們由 DispatcherServlet 執行,這發生在 AuthorizationFilter 之后,所以您的端點需要被包含在 authorizeHttpRequests 中才能被允許。
All Dispatches Are Authorized
AuthorizationFilter 不僅在每次請求時運行,而且在每次分發時都會運行。這意味著 REQUEST 分發需要授權,但 FORWARD、ERROR 和 INCLUDE 也是如此。
例如,Spring MVC 可以將請求轉發到呈現 Thymeleaf 模板的視圖解析器,如下所示:
@Controller
public class MyController {@GetMapping("/endpoint")public String endpoint() {return "endpoint";}
}
在這種情況下,授權發生兩次; 一次用于授權/端點,一次用于轉發到 Thymeleaf 以呈現“端點”模板。
因此,您可能希望允許所有 FORWARD 分派。
這個原則的另一個例子是 SpringBoot 如何處理錯誤。如果容器捕獲到異常,則如下所示:
Sample Erroring Spring MVC Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {@GetMapping("/endpoint")public String endpoint() {throw new UnsupportedOperationException("unsupported");}
}
然后 Boot 會將其發送到 ERROR 調度。
在這種情況下,授權也會發生兩次: 一次用于授權/端點,一次用于分派錯誤。
因此,您可能希望允許所有 ERROR 分派。
Authentication Lookup is Deferred
記住 AuthorizationManager API 使用 Supplier < Authentication > 。
當請求總是被允許或總是被拒絕時,這與 AuthorizeHttpRequest 有關。在這些情況下,不會查詢身份驗證,從而使請求速度更快。
Authorizing an Endpoint
通過在優先順序中添加更多規則,可以將 Spring Security 配置為具有不同的規則。
如果您希望只有具有 USER 權限的最終用戶才能訪問該/端點,那么您可以這樣做:
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.requestMatchers("/endpoint").hasAuthority("USER").anyRequest().authenticated())// ...return http.build();
}
如您所見,聲明可以分解為pattern/rule對。
AuthorizationFilter 按列出的順序處理這些對,只將第一個匹配應用到請求上。這意味著,即使 /** 也會匹配 /endpoint,上述規則也不是問題。閱讀上述規則的方式是:“如果請求是 /endpoint,則需要 USER 權限;否則,只需認證”。
SpringSecurity 支持多種模式和多種規則; 您還可以通過編程方式創建自己的模式和規則。
一旦授權,您可以使用 Security 的測試支持以下方式對其進行測試:
Test Endpoint Authorization
@WithMockUser(authorities="USER")
@Test
void endpointWhenUserAuthorityThenAuthorized() {this.mvc.perform(get("/endpoint")).andExpect(status().isOk());
}@WithMockUser
@Test
void endpointWhenNotUserAuthorityThenForbidden() {this.mvc.perform(get("/endpoint")).andExpect(status().isForbidden());
}@Test
void anyWhenUnauthenticatedThenUnauthorized() {this.mvc.perform(get("/any")).andExpect(status().isUnauthorized());
}
Matching Requests
上面已經介紹了兩種匹配請求的方法。
您看到的第一個是最簡單的,即匹配任何請求。
第二種是通過 URI 模式進行匹配。Spring Security 支持兩種用于 URI 模式匹配的語言: Ant (如上所示)和正則表達式。
Matching Using Ant
Ant 是 Spring Security 用來匹配請求的默認語言。
您可以使用它來匹配單個端點或目錄,甚至可以捕獲占位符以供以后使用。您還可以對其進行細化以匹配一組特定的 HTTP 方法。
假設您不希望匹配/endpoint 端點,而是希望匹配/resource 目錄下的所有端點。在這種情況下,您可以執行以下操作:
Match with Ant
http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.requestMatchers("/resource/**").hasAuthority("USER").anyRequest().authenticated())
解讀方法是“如果請求是/resource 或某個子目錄,則需要 USER 權限; 否則,只需要身份驗證”
您還可以從請求中提取路徑值,如下所示:
Authorize and Extract
http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.requestMatchers("/resource/{name}").access(new WebExpressionAuthorizationManager("#name == authentication.name")).anyRequest().authenticated())
一旦授權,您可以使用 Security 的測試支持以下方式對其進行測試:
Test Directory Authorization
@WithMockUser(authorities="USER")
@Test
void endpointWhenUserAuthorityThenAuthorized() {this.mvc.perform(get("/endpoint/jon")).andExpect(status().isOk());
}@WithMockUser
@Test
void endpointWhenNotUserAuthorityThenForbidden() {this.mvc.perform(get("/endpoint/jon")).andExpect(status().isForbidden());
}@Test
void anyWhenUnauthenticatedThenUnauthorized() {this.mvc.perform(get("/any")).andExpect(status().isUnauthorized());
}
SpringSecurity 只匹配路徑。如果要匹配查詢參數,則需要一個自定義請求匹配器。
Matching Using Regular Expressions
SpringSecurity 支持將請求與正則表達式匹配。如果您想在子目錄上應用比 * * 更嚴格的匹配條件,這可能很方便。
例如,考慮一個包含用戶名的路徑和所有用戶名必須是字母數字的規則。您可以使用 RegexRequestMatcher 來遵守此規則,如下所示:
http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.requestMatchers(RegexRequestMatcher.regexMatcher("/resource/[A-Za-z0-9]+")).hasAuthority("USER").anyRequest().denyAll())
Matching By Http Method
還可以通過 HTTP 方法匹配規則。有一個地方很方便,那就是通過授予的權限進行授權,比如授予讀或寫權限。
為了要求所有 GET 都具有讀權限,并且所有 POST 都具有寫權限,您可以這樣做:
Match by HTTP Method
http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.requestMatchers(HttpMethod.GET).hasAuthority("read").requestMatchers(HttpMethod.POST).hasAuthority("write").anyRequest().denyAll())
這些授權規則的內容應該是: “如果請求是 GET,則需要讀權限; 否則,如果請求是 POST,則需要寫權限; 否則,拒絕請求”
默認情況下拒絕請求是一種健康的安全實踐,因為它將規則集轉換為允許列表。
一旦授權,您可以使用 Security 的測試支持以下方式對其進行測試:
Test Http Method Authorization
@WithMockUser(authorities="read")
@Test
void getWhenReadAuthorityThenAuthorized() {this.mvc.perform(get("/any")).andExpect(status().isOk());
}@WithMockUser
@Test
void getWhenNoReadAuthorityThenForbidden() {this.mvc.perform(get("/any")).andExpect(status().isForbidden());
}@WithMockUser(authorities="write")
@Test
void postWhenWriteAuthorityThenAuthorized() {this.mvc.perform(post("/any").with(csrf())).andExpect(status().isOk());
}@WithMockUser(authorities="read")
@Test
void postWhenNoWriteAuthorityThenForbidden() {this.mvc.perform(get("/any").with(csrf())).andExpect(status().isForbidden());
}
Matching By Dispatcher Type
XML 當前不支持此特性
如前所述,SpringSecurity 默認授權所有調度程序類型。而且,即使在 REQUEST 分派上建立的安全上下文將傳遞給后續分派,微妙的不匹配有時也會導致意外的 AccessDeniedException。
為了解決這個問題,您可以配置 Spring Security Java 配置,以允許 FORWARD 和 ERROR 等調度程序類型,如下所示:
http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.dispatcherTypeMatchers(DispatcherType.FORWARD, DispatcherType.ERROR).permitAll().requestMatchers("/endpoint").permitAll().anyRequest().denyAll())
Using an MvcRequestMatcher
一般來說,可以像上面演示的那樣使用 requestMatcher (String)。
但是,如果將 SpringMVC 映射到不同的 servlet 路徑,則需要在安全配置中考慮這一點。
例如,如果 Spring MVC 被映射到/Spring-MVC 而不是/(默認值) ,那么您可能有一個想要授權的端點,比如/Spring-MVC/my/controller。
您需要使用 MvcRequestMatcher 在配置中分割 servlet 路徑和控制器路徑,如下所示:
Example 2. Match by MvcRequestMatcher
@Bean
MvcRequestMatcher.Builder mvc(HandlerMappingIntrospector introspector) {return new MvcRequestMatcher.Builder(introspector).servletPath("/spring-mvc");
}@Bean
SecurityFilterChain appEndpoints(HttpSecurity http, MvcRequestMatcher.Builder mvc) {http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.requestMatchers(mvc.pattern("/my/controller/**")).hasAuthority("controller").anyRequest().authenticated());return http.build();
}
這種需要至少可以通過兩種不同的方式產生:
- 如果使用 spring.mvc.servlet.path Boot 屬性將默認路徑(/)更改為其他內容
- 如果您注冊了多個 Spring MVC DispatcherServlet (因此要求其中一個不是默認路徑)
Using a Custom Matcher
XML 當前不支持此特性
在 Java 配置中,您可以創建自己的 RequestMatcher 并將其提供給 DSL,如下所示:
Example 3. Authorize by Dispatcher Type
RequestMatcher printview = (request) -> request.getParameter("print") != null;
http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.requestMatchers(printview).hasAuthority("print").anyRequest().authenticated())
一旦授權,您可以使用 Security 的測試支持以下方式對其進行測試:
@WithMockUser(authorities="print")
@Test
void printWhenPrintAuthorityThenAuthorized() {this.mvc.perform(get("/any?print")).andExpect(status().isOk());
}@WithMockUser
@Test
void printWhenNoPrintAuthorityThenForbidden() {this.mvc.perform(get("/any?print")).andExpect(status().isForbidden());
}
Authorizing Requests
一旦匹配了一個請求,您可以通過幾種方式對其進行授權,如 permitAll、 denyAll 和 hasAuthority。
作為一個快速總結,以下是 DSL 中內置的授權規則:
- PermitAll-請求不需要授權,是一個公共端點; 請注意,在這種情況下,永遠不會從會話檢索 Authentication
- DenyAll-在任何情況下都不允許請求; 請注意,在這種情況下,永遠不會從會話檢索 Authentication
- HasAuthority ——該請求要求 Authentication 具有與給定值匹配的 GrantedAuthority
- HasRole-hasAuthority 的一個快捷方式,它將 ROLE _ 或其他配置為默認前綴的內容作為前綴
- HasAnyAuthority ——該請求要求 Authentication 具有與任何給定值匹配的 GrantedAuthority
- HasAnyrole-hasAnyAuthority 的一個快捷方式,它將 ROLE _ 或任何被配置為默認前綴的東西作為前綴
- Access-請求使用此自定義 AuthorizationManager 來確定訪問權限
現在已經了解了模式、規則以及如何將它們配對在一起,您應該能夠理解在這個更復雜的示例中發生了什么:
import static jakarta.servlet.DispatcherType.*;import static org.springframework.security.authorization.AuthorizationManagers.allOf;
import static org.springframework.security.authorization.AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasAuthority;
import static org.springframework.security.authorization.AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole;@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http// ....authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize (1).dispatcherTypeMatchers(FORWARD, ERROR).permitAll() (2).requestMatchers("/static/**", "/signup", "/about").permitAll() (3).requestMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN") (4).requestMatchers("/db/**").access(allOf(hasAuthority("db"), hasRole("ADMIN"))) (5).anyRequest().denyAll() (6));return http.build();
}
- 指定了多個授權規則。每個規則按其聲明的順序進行考慮。
- 分派 FORWARD 和 ERROR 允許 Spring MVC 呈現視圖,Spring Boot 呈現錯誤
- 我們指定了任何用戶都可以訪問的多個 URL 模式。具體來說,如果 URL 以“/static/”、等于“/signup”或等于“/about”開頭,則任何用戶都可以訪問請求。
- 任何以“/admin/”開頭的 URL 將僅限于具有“ ROLE _ ADMIN”角色的用戶。您會注意到,由于我們正在調用 hasRole 方法,因此不需要指定“ ROLE _”前綴。
- 任何以 “/db/” 開頭的 URL 都需要用戶同時擁有 “db” 權限以及 “ROLE_ADMIN” 角色。您會注意到,由于我們使用了 hasRole 表達式,因此不需要指定 “ROLE_” 前綴。
- 任何尚未匹配的 URL 都將被拒絕訪問。如果您不想意外地忘記更新授權規則,那么這是一個很好的策略。
Expressing Authorization with SpEL
雖然建議使用具體的 AuthorizationManager,但是在某些情況下需要使用表達式,比如使用 < stop-url > 或 JSP Taglibs。出于這個原因,本節將重點介紹來自這些域的示例。
既然如此,讓我們更深入地討論一下 Spring Security 的 Web 安全授權 SpEL API。
Spring Security 將其所有的授權字段和方法封裝在一個集合的根對象中。最通用的根對象稱為 SecurityExpressionRoot,它是 WebSecurityExpressionRoot 的基礎。當準備評估授權表達式時,Spring Security 將這個根對象提供給 StandardEvaluationContext。
Using Authorization Expression Fields and Methods
它提供的第一件事是增強了 SpEL 表達式的授權字段和方法集。以下是最常用方法的簡要概述:
-
permitAll - 請求不需要任何授權即可調用;注意,在這種情況下,Authentication 從未從會話中檢索
-
denyAll - 請求在任何情況下都不被允許;注意,在這種情況下,Authentication 從未從會話中檢索
-
hasAuthority - 請求需要 Authentication 具有與給定值匹配的 GrantedAuthority
-
hasRole - hasAuthority 的快捷方式,默認前綴為 ROLE_ 或配置的默認前綴
-
hasAnyAuthority - 請求需要 Authentication 具有與給定值中的任何一個匹配的 GrantedAuthority
-
hasAnyRole - hasAnyAuthority 的快捷方式,默認前綴為 ROLE_ 或配置的默認前綴
-
HasPermission-一個連接到您的 Permisonevalator 實例的鉤子,用于執行對象級授權
以下是一些最常見的領域:
-
authentication - 與本方法調用相關聯的 Authentication 實例
-
principal - 與本方法調用相關聯的 Authentication#getPrincipal
現在已經了解了模式、規則以及如何將它們配對在一起,您應該能夠理解在這個更復雜的示例中發生了什么:
Authorize Requests Using SpEL
<http><intercept-url pattern="/static/**" access="permitAll"/> (1)<intercept-url pattern="/admin/**" access="hasRole('ADMIN')"/>(2)<intercept-url pattern="/db/**" access="hasAuthority('db') and hasRole('ADMIN')"/>(3)<intercept-url pattern="/**" access="denyAll"/>(4)
</http>
- 我們指定了一個任何用戶都可以訪問的 URL 模式。具體來說,如果 URL 以“/static/”開頭,任何用戶都可以訪問請求。
- 任何以“/admin/”開頭的 URL 將僅限于具有“ ROLE _ ADMIN”角色的用戶。您會注意到,由于我們正在調用 hasRole 方法,因此不需要指定“ ROLE _”前綴。
- 任何以 “/db/” 開頭的 URL 都需要用戶同時擁有 “db” 權限以及 “ROLE_ADMIN” 角色。您會注意到,由于我們使用了 hasRole 表達式,因此不需要指定 “ROLE_” 前綴。
- 任何尚未匹配的 URL 都將被拒絕訪問。如果您不想意外地忘記更新授權規則,那么這是一個很好的策略。
Using Path Parameters
此外,Spring Security 提供了一種發現路徑參數的機制,因此也可以在 SpEL 表達式中訪問這些參數。
例如,您可以通過以下方式訪問 SpEL 表達式中的路徑參數:
Authorize Request using SpEL path variable
<http><intercept-url pattern="/resource/{name}" access="#name == authentication.name"/><intercept-url pattern="/**" access="authenticated"/>
</http>
這個表達式引用/resource/之后的 path 變量,并要求它等于 Authentication # getName。
Use an Authorization Database, Policy Agent, or Other Service
如果希望將 Spring Security 配置為使用單獨的服務進行授權,可以創建自己的 AuthorizationManager 并將其與 anyRequest 匹配。
首先,您的 AuthorizationManager 可能看起來像這樣:
Open Policy Agent Authorization Manager
@Component
public final class OpenPolicyAgentAuthorizationManager implements AuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> {@Overridepublic AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, RequestAuthorizationContext context) {// make request to Open Policy Agent}
}
然后,您可以通過以下方式將其連接到 Spring Security:
Any Request Goes to Remote Service
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http, AuthorizationManager<RequestAuthorizationContext> authz) throws Exception {http// ....authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.anyRequest().access(authz));return http.build();
}
Favor permitAll over ignoring
當您擁有靜態資源時,很容易將篩選器鏈配置為忽略這些值。一個更安全的方法是允許他們使用 permitAll like so:
Example 4. Permit Static Resources
http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.requestMatchers("/css/**").permitAll().anyRequest().authenticated())
它更加安全,因為即使使用靜態資源,編寫安全頭文件也很重要,如果忽略請求,Spring Security 就無法做到這一點。
在過去,這帶來了性能折衷,因為 Spring Security 在每次請求時都會咨詢會話。但是,從 SpringSecurity6開始,除非授權規則要求,否則不再 ping 會話。由于現在已經解決了性能影響問題,SpringSecurity 建議對所有請求至少使用 permitAll。
Migrating from authorizeRequests
AuthorizationFilter 為 HttpServletRequest 提供授權。它作為安全篩選器之一插入到 FilterChainProxy 中。
您可以在聲明 SecurityFilterChain 時覆蓋默認值:
@Bean
SecurityFilterChain web(HttpSecurity http) throws AuthenticationException {http.authorizeHttpRequests((authorize) -> authorize.anyRequest().authenticated();)// ...return http.build();
}
這在若干方面改進了 AuthorizeRequest:
- 使用簡化的 AuthorizationManager API 而不是元數據源、配置屬性、決策管理器和投票者metadata sources, config attributes, decision managers, and voters.。這簡化了重用和自定義。
- 延遲 Authentication 查找。而不是為每個請求都查找 Authentication,只有在需要授權決策時才會查找。
- 支持基于 Bean 的配置。
如果使用 AuthorizeHttpRequest 代替 AuthorizeRequest,則使用 AuthorizationFilter 代替 FilterSecurityInterceptor。
Migrating Expressions
在可能的情況下,建議使用類型安全授權管理器而不是 SpEL。對于 Java 配置,WebExpressionAuthorizationManager 可用于幫助遷移遺留的 SpEL。
要使用 WebExpressionAuthorizationManager,您可以使用試圖遷移的表達式構造一個表達式,如下所示:
.requestMatchers("/test/**").access(new WebExpressionAuthorizationManager("hasRole('ADMIN') && hasRole('USER')"))
如果您在表達式中引用一個 bean,例如:@webSecurity.check(authentication, request),建議您直接調用 bean,它看起來會像這樣:
.requestMatchers("/test/**").access((authentication, context) ->new AuthorizationDecision(webSecurity.check(authentication.get(), context.getRequest())))
對于包含 bean 引用和其他表達式的復雜指令,建議更改這些指令以實現 AuthorizationManager,并通過調用.access(AuthorizationManager).
如果不能這樣做,可以使用 bean 解析器配置 DefaultHttpSecurityExpressionHandler,并將其提供給 WebExpressionAuthorizationManager # setExpressionHandler。
Security Matchers
RequestMatcher 接口用于確定請求是否與給定的規則匹配。我們使用 securityMatchers 來確定給定的 HttpSecurity 是否應該應用于給定的請求。同樣,我們可以使用 requestMatchers 來確定應該應用于給定請求的授權規則。請看以下示例:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {@Beanpublic SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.securityMatcher("/api/**").authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize.requestMatchers("/user/**").hasRole("USER").requestMatchers("/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN").anyRequest().authenticated()).formLogin(withDefaults());return http.build();}
}
- 將 HttpSecurity 配置為僅應用于以/api/開頭的 URL
- 允許具有 USER 角色的用戶訪問以
/user/開頭的 URL - 允許具有
ADMIN角色的用戶訪問以/admin/開頭的 URL - 任何其他與上述規則不匹配的請求都將需要身份驗證
SecurityMatcher (s)和 requestMatcher (s)方法將決定哪個 RequestMatcher 實現最適合您的應用程序: 如果 Spring MVC 在類路徑中,那么將使用 MvcRequestMatcher,否則將使用 AntPathRequestMatcher。您可以在這里了解更多關于 Spring MVC 集成的信息。
如果您想使用一個特定的 RequestMatcher,只需將一個實現傳遞給 securityMatcher 和/或 requestMatcher 方法:
import static org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.AntPathRequestMatcher.antMatcher; (1)
import static org.springframework.security.web.util.matcher.RegexRequestMatcher.regexMatcher;@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {@Beanpublic SecurityFilterChain securityFilterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {http.securityMatcher(antMatcher("/api/**")) (2).authorizeHttpRequests(authorize -> authorize.requestMatchers(antMatcher("/user/**")).hasRole("USER") (3).requestMatchers(regexMatcher("/admin/.*")).hasRole("ADMIN") (4).requestMatchers(new MyCustomRequestMatcher()).hasRole("SUPERVISOR") (5).anyRequest().authenticated()).formLogin(withDefaults());return http.build();}
}public class MyCustomRequestMatcher implements RequestMatcher {@Overridepublic boolean matches(HttpServletRequest request) {// ...}
}
- 從 AntPathRequestMatcher 和 RegexRequestMatcher 導入靜態工廠方法以創建 RequestMatcher 實例。
- 使用 AntPathRequestMatcher 將 HttpSecurity 配置為僅應用于以/api/開頭的 URL
- 允許使用 AntPathRequestMatcher 訪問以/USER/開頭的 URL 到具有 USER 角色的用戶
- 允許使用 RegexRequestMatcher 對具有 ADMIN 角色的用戶訪問以/ADMIN/開頭的 URL
- 允許使用自定義 RequestMatcher 訪問與具有 SUPERVISOR 角色的用戶匹配的 MyCustomRequestMatcher 的 URL
Further Reading
既然已經保護了應用程序的請求,那么就考慮保護它的方法。您還可以進一步閱讀關于測試應用程序或將 Spring Security 與應用程序的其他方面(如數據層或跟蹤和度量)集成的內容。

)





)









- 行業挑戰與 TiDB 的應對之道)

