Method Security
除了在請求級別進行建模授權之外,Spring Security 還支持在方法級別進行建模。
您可以在應用程序中激活它,方法是使用@EnableMethodSecurity 注釋任何@Configuration 類,或者將 < method-security > 添加到任何 XML 配置文件中,如下所示:
@EnableMethodSecurity
然后,您可以立即使用@PreAuthorize、@PostAuthorize、@PreFilter 和@PostFilter 對任何 Spring 管理的類或方法進行注釋,以授權方法調用,包括輸入參數和返回值。
SpringBootStarterSecurity 默認情況下不激活方法級授權。
Method Security 還支持許多其他用例,包括 AspectJ 支持、自定義注釋和幾個配置點。考慮學習以下用例:
- Migrating from
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity - Understanding how method security works and reasons to use it
- Comparing request-level and method-level authorization
- Authorizing methods with
@PreAuthorizeand@PostAuthorize - Providing fallback values when authorization is denied
- Filtering methods with
@PreFilterand@PostFilter - Authorizing methods with JSR-250 annotations
- Authorizing methods with AspectJ expressions
- Integrating with AspectJ byte-code weaving
- Coordinating with @Transactional and other AOP-based annotations
- Customizing SpEL expression handling
- Integrating with custom authorization systems
How Method Security Works
Spring Security 的方法授權支持在以下方面很方便:
- 提取細粒度授權邏輯;例如,當方法參數和返回值有助于授權決策時。
- 在服務層強制執行安全性
- 在風格上更傾向于基于注釋而非基于HttpSecurity的配置
由于Method Security是使用Spring AOP構建的,因此您可以訪問它的所有表達能力,以便根據需要覆蓋Spring Security的默認值。
如前所述,首先將@EnableMethodSecurity 添加到@Configuration 類或者在 Spring XML 配置文件中添加 < sec: method-security/> 。
這個注釋和 XML 元素分別取代了@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 和 < sec: global-method-security/> :
- 使用簡化的 AuthorizationManagerAPI 而不是元數據源、配置屬性、決策管理器和選民。
- 支持直接基于 bean 的配置,而不需要擴展 GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration 來定制 bean
- 使用原生 Spring AOP 構建,移除了抽象,并允許您使用 Spring AOP 構建塊來定制
- 檢查沖突注解,以確保明確的安全配置
- 符合 JSR-250
- 默認啟用 @PreAuthorize、@PostAuthorize、@PreFilter 和 @PostFilter
如果您正在使用@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 或 < global-method-security/> ,那么現在不推薦使用它們,并鼓勵您進行遷移。
方法授權是 before- and after-method授權的組合。考慮一個服務 bean,它的注釋方式如下:
@Service
public class MyCustomerService {@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('permission:read')")@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")public Customer readCustomer(String id) { ... }
}
當方法安全性被激活時,對 MyCustomerService # readCustomer 的給定調用可能類似于下面的內容:
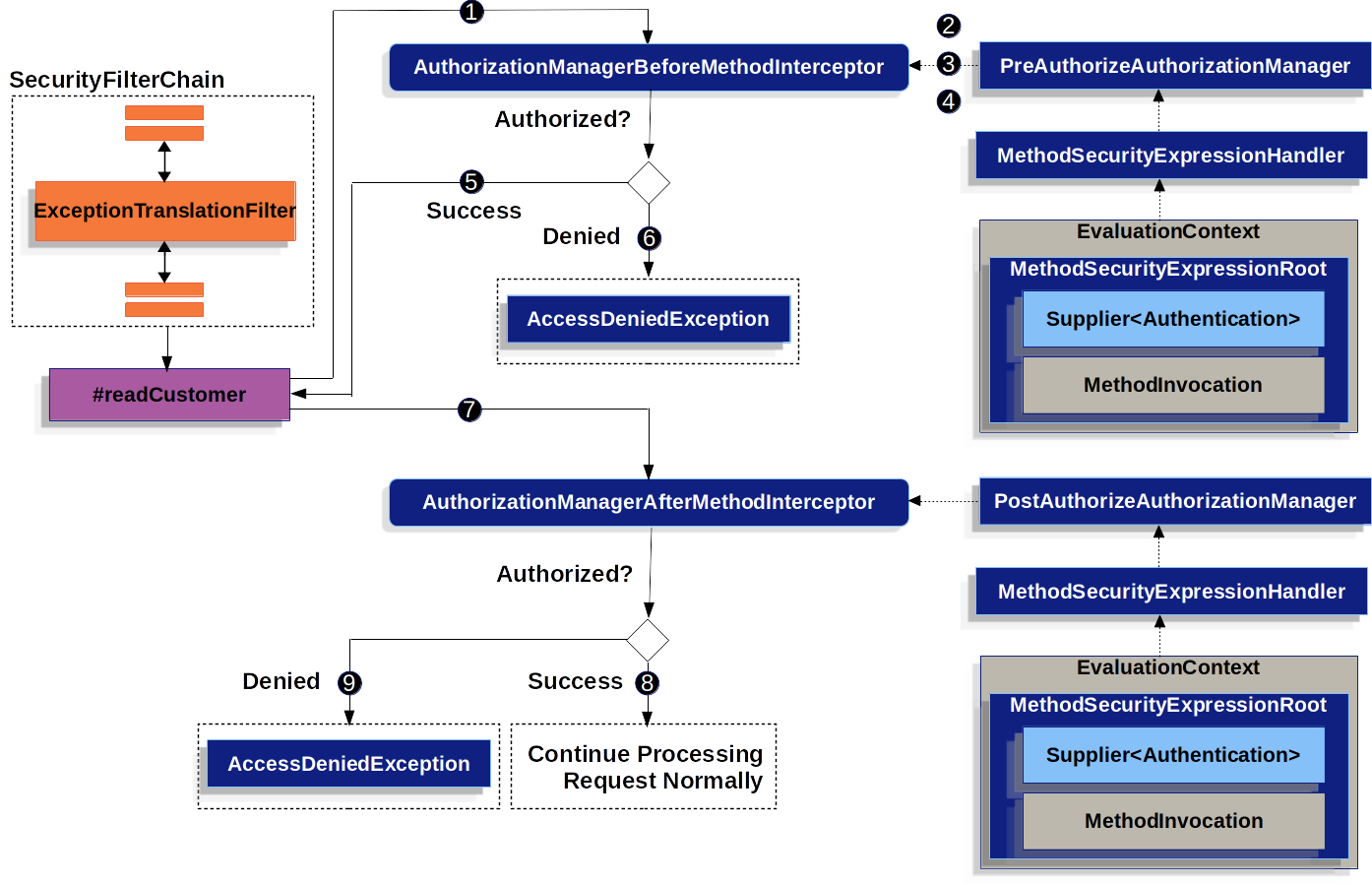
- Spring AOP 調用了其代理方法 readCustomer。在代理的其他顧問中,它調用了匹配 @PreAuthorize 切入點的方法 AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor。
- 攔截器調用了 PreAuthorizeAuthorizationManager#check。
- 授權管理器使用 MethodSecurityExpressionHandler 來解析注解的 SpEL 表達式,并從包含 Supplier 和 MethodInvocation 的 MethodSecurityExpressionRoot 構建相應的 EvaluationContext。
- 攔截器使用這個上下文來評估表達式;具體來說,它從 Supplier 中讀取 Authentication 并檢查它是否有權限:read 在其權限集合中。
- 如果評估通過,那么 Spring AOP 繼續調用方法。
- 如果沒有,攔截器發布一個 AuthorizationDeniedEvent 并拋出一個 AccessDeniedException,ExceptionTranslationFilter 捕獲并返回一個 403 狀態碼到響應。
- 方法返回后,Spring AOP 調用了匹配 @PostAuthorize 切入點的方法 AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor,其操作與上述相同,但使用 PostAuthorizeAuthorizationManager。
- 如果評估通過(在這種情況下,返回值屬于已登錄的用戶),則處理繼續正常。
- 如果沒有,攔截器發布一個 AuthorizationDeniedEvent 并拋出一個 AccessDeniedException,ExceptionTranslationFilter 捕獲并返回一個 403 狀態碼到響應。
如果沒有在 HTTP 請求的上下文中調用該方法,則可能需要自己處理 AccessDeniedException
Multiple Annotations Are Computed In Series
如上所述,如果一個方法調用涉及多個 Method Security 注釋,則每個注釋一次處理一個。這意味著它們可以被集體看作是“被捆綁在一起”的。換句話說,對于要授權的調用,所有的注釋檢查都需要通過授權。
Repeated Annotations Are Not Supported
也就是說,不支持在同一方法上重復相同的注釋。例如,不能在同一個方法上放置@PreAuthorize 兩次。
取而代之的是,使用 SpEL 的布爾支持或其對委托到單獨 bean 的支持。
Each Annotation Has Its Own Pointcut
每個注釋都有自己的切入點實例,它從方法及其封閉類開始,在整個對象層次結構中查找該注釋或其元注釋對應物。
您可以在 AuthorizationMethodPointcut 中看到這方面的詳細信息。
Each Annotation Has Its Own Method Interceptor
每個注解都有其自己的專用方法攔截器。這樣做的原因是使事情更具可組合性。例如,如果需要,您可以禁用 Spring Security 的默認行為,只發布 @PostAuthorize 方法攔截器。
方法攔截器如下:
- 對于 @PreAuthorize,Spring Security 使用 AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor#preAuthorize,進而使用 PreAuthorizeAuthorizationManager。
- 對于 @PostAuthorize,Spring Security 使用 AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor#postAuthorize,進而使用 PostAuthorizeAuthorizationManager。
- 對于 @PreFilter,Spring Security 使用 PreFilterAuthorizationMethodInterceptor。
- 對于 @PostFilter,Spring Security 使用 PostFilterAuthorizationMethodInterceptor。
- 對于 @Secured,Spring Security 使用 AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor#secured,進而使用 SecuredAuthorizationManager。
- 對于 JSR-250 注解,Spring Security 使用 AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor#jsr250,進而使用 Jsr250AuthorizationManager。
總的來說,您可以將以下列表視為添加 @EnableMethodSecurity 時 Spring Security 發布的攔截器的代表性示例。
@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor preAuthorizeMethodInterceptor() {return AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preAuthorize();
}@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor postAuthorizeMethodInterceptor() {return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postAuthorize();
}@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor preFilterMethodInterceptor() {return AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preFilter();
}@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor postFilterMethodInterceptor() {return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postFilter();
}
在復雜的 SpEL 表達式上優先授權
通常,引入一個復雜的 SpEL 表達式是很誘人的,如下所示:
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('permission:read') || hasRole('ADMIN')")
然而,您可以將權限:read 授予具有 ROLE_ADMIN 角色的人。一種方法是通過 RoleHierarchy 實現:
@Bean
static RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy() {return RoleHierarchyImpl.fromHierarchy("ROLE_ADMIN > permission:read");
}
然后在 MethodSecurityExpressionHandler 實例中設置它。這樣你就可以得到一個更簡單的@PreAuthorize 表達式,如下所示:
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('permission:read')")
或者,在可能的情況下,在登錄時將特定于應用程序的授權邏輯改編為授予的權限。
Comparing Request-level vs Method-level Authorization
您應該何時選擇方法級授權而不是請求級授權?這很大程度上取決于個人喜好;然而,考慮以下每種方式的優點列表,以幫助您做出決定。
| ** request-level** | request-level | method-level |
|---|---|---|
| authorization type | coarse-grained | fine-grained |
| configuration location | declared in a config class | local to method declaration |
| configuration style | DSL | Annotations |
| authorization definitions | programmatic | SpEL |
主要的折衷似乎是您希望授權規則存在于何處。
Authorizing with Annotations
Spring Security 支持方法級授權的主要方式是通過可以添加到方法、類和接口的注釋。
Authorizing Method Invocation with @PreAuthorize
當 Method Security 處于活動狀態時,可以使用@PreAuthorize 注釋對方法進行注釋,如下所示:
@Component
public class BankService {@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")public Account readAccount(Long id) {// ... is only invoked if the `Authentication` has the `ROLE_ADMIN` authority}
}
這意味著只有當提供的表達式 hasRole (‘ ADMIN’)通過時才能調用該方法。
然后,您可以測試該類,以確認它正在執行授權規則,如下所示:
@Autowired
BankService bankService;@WithMockUser(roles="ADMIN")
@Test
void readAccountWithAdminRoleThenInvokes() {Account account = this.bankService.readAccount("12345678");// ... assertions
}@WithMockUser(roles="WRONG")
@Test
void readAccountWithWrongRoleThenAccessDenied() {assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(() -> this.bankService.readAccount("12345678"));
}
雖然@PreAuthorize 對于聲明所需的權限非常有幫助,但是它也可以用來計算涉及方法參數的更復雜的表達式。
Authorization Method Results with @PostAuthorize
當 Method Security 處于活動狀態時,可以使用@PostAuthorize 注釋對方法進行注釋,如下所示:
@Component
public class BankService {@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")public Account readAccount(Long id) {// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user}
}
這意味著該方法只能在所提供的表達式 returObject.owner = = authentication.name 通過時才能返回值。ReturObject 表示要返回的 Account 對象。
然后,您可以測試該類,以確認它正在執行授權規則:
@Autowired
BankService bankService;@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
void readAccountWhenOwnedThenReturns() {Account account = this.bankService.readAccount("12345678");// ... assertions
}@WithMockUser(username="wrong")
@Test
void readAccountWhenNotOwnedThenAccessDenied() {assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(() -> this.bankService.readAccount("12345678"));
}
@ PostAuthorize 也可以是一個元注釋,在類或接口級別定義,并使用 SpEL Authorization Expressions。
@ PostAuthorize 在防御不安全的直接對象引用時特別有用。事實上,它可以定義為如下元注釋:
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PostAuthorize("returnObject.owner == authentication.name")
public @interface RequireOwnership {}
允許您以下列方式對服務進行注釋:
@Component
public class BankService {@RequireOwnershippublic Account readAccount(Long id) {// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user}
}
結果是,上述方法只有在其所有者屬性與登錄用戶的名稱匹配時才返回 Account。如果沒有,SpringSecurity 將拋出 AccessDeniedException 并返回403狀態代碼。
Filtering Method Parameters with @PreFilter
當 Method Security 處于活動狀態時,可以使用@PreFilter 注釋對方法進行注釋,如下所示:
@Component
public class BankService {@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Account... accounts) {// ... `accounts` will only contain the accounts owned by the logged-in userreturn updated;}
}
這意味著從表達式 filterObject.owner = = authentication.name 失敗的帳戶中過濾出任何值。FilterObject 表示帳戶中的每個帳戶,用于測試每個帳戶。
然后,您可以用以下方式測試該類,以確認它正在執行授權規則:
@Autowired
BankService bankService;@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
void updateAccountsWhenOwnedThenReturns() {Account ownedBy = ...Account notOwnedBy = ...Collection<Account> updated = this.bankService.updateAccounts(ownedBy, notOwnedBy);assertThat(updated).containsOnly(ownedBy);
}
@ PreFilter 支持數組、集合、映射和流(只要流仍然打開)。
例如,上面的 updateAccount 聲明的功能與以下其他四個聲明的功能相同:
@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Account[] accounts)@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Collection<Account> accounts)@PreFilter("filterObject.value.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Map<String, Account> accounts)@PreFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Collection<Account> updateAccounts(Stream<Account> accounts)
結果是,上面的方法只有 Account 實例,其所有者屬性與登錄用戶的名稱匹配。
Filtering Method Results with @PostFilter
當 Method Security 處于活動狀態時,可以使用@PostFilter 注釋對方法進行注釋,如下所示:
@Component
public class BankService {@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")public Collection<Account> readAccounts(String... ids) {// ... the return value will be filtered to only contain the accounts owned by the logged-in userreturn accounts;}
}
這意味著從表達式 filterObject.owner = = authentication.name 失敗的返回值中過濾掉任何值。FilterObject 表示帳戶中的每個帳戶,用于測試每個帳戶。
然后,您可以像這樣測試該類,以確認它正在執行授權規則:
@Autowired
BankService bankService;@WithMockUser(username="owner")
@Test
void readAccountsWhenOwnedThenReturns() {Collection<Account> accounts = this.bankService.updateAccounts("owner", "not-owner");assertThat(accounts).hasSize(1);assertThat(accounts.get(0).getOwner()).isEqualTo("owner");
}
@ PostFilter 支持數組、集合、映射和流(只要流仍然打開)。
例如,上面的 readAccount 聲明的功能與以下其他三個聲明的功能相同:
@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Account[] readAccounts(String... ids)@PostFilter("filterObject.value.owner == authentication.name")
public Map<String, Account> readAccounts(String... ids)@PostFilter("filterObject.owner == authentication.name")
public Stream<Account> readAccounts(String... ids)
結果是,上面的方法將返回 Account 實例,其所有者屬性與登錄用戶的名稱匹配。
Authorizing Method Invocation with @Secured
@Secured 是授權調用的遺留選項。@PreAuthorize 取而代之,建議使用。
要使用@Secred 注釋,您應該首先更改您的 Method Security 聲明,以啟用它,如下所示:
@EnableMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
這將導致 Spring Security 發布相應的方法攔截器,該攔截器授權使用@Secure 注釋的方法、類和接口。
Authorizing Method Invocation with JSR-250 Annotations
如果您希望使用 JSR-250注釋,SpringSecurity 也支持這一點。@ PreAuthorize 具有更強的表達能力,因此推薦使用。
要使用 JSR-250注釋,您應該首先更改您的 Method Security 聲明,以便像下面這樣啟用它們:
@EnableMethodSecurity(jsr250Enabled = true)
這將導致 Spring Security 發布相應的方法攔截器,該攔截器授權使用@RolesAllows、@PermitAll 和@DenyAll 注釋的方法、類和接口。
Declaring Annotations at the Class or Interface Level
它還支持在類和接口級別使用 Method Security 注釋。
如果在類層面是這樣的:
@Controller
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_USER')")
public class MyController {@GetMapping("/endpoint")public String endpoint() { ... }
}
那么所有的方法都繼承了類級別的行為。
或者,如果它在類和方法級別都像下面這樣聲明:
@Controller
@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_USER')")
public class MyController {@GetMapping("/endpoint")@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('ROLE_ADMIN')")public String endpoint() { ... }
}
然后,聲明該注釋的方法將覆蓋類級注釋。
對于接口也是如此,但是如果一個類從兩個不同的接口繼承了注釋,那么啟動就會失敗。這是因為 SpringSecurity 無法判斷您想要使用哪一個。
在這種情況下,可以通過向具體方法添加注釋來解決歧義。
Using Meta Annotations
方法安全性支持元注釋。這意味著您可以使用任何注釋,并基于特定于應用程序的用例提高可讀性。
例如,您可以將@PreAuthorize (“ hasRole (‘ ADMIN’)”)簡化為@IsAdmin,如下所示:
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")
public @interface IsAdmin {}
其結果是,在你的安全方法,你現在可以做以下代替:
@Component
public class BankService {@IsAdminpublic Account readAccount(Long id) {// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user}
}
這會產生更易讀的方法定義。
Templating Meta-Annotation Expressions
您還可以選擇使用元注釋模板,它允許更強大的注釋定義。
首先,發布以下 bean:
@Bean
static PrePostTemplateDefaults prePostTemplateDefaults() {return new PrePostTemplateDefaults();
}
現在,您可以創建像@Hasrole 這樣功能更強大的程序,而不是@IsAdmin,如下所示:
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasRole('{value}')")
public @interface HasRole {String value();
}
其結果是,在你的安全方法,你現在可以做以下代替:
@Component
public class BankService {@HasRole("ADMIN")public Account readAccount(Long id) {// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user}
}
請注意,這也適用于方法變量和所有注釋類型,但是您需要注意正確地處理引號,以便得到的 SpEL 表達式是正確的。
例如,考慮以下@HasAnyrole 注釋:
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@PreAuthorize("hasAnyRole({roles})")
public @interface HasAnyRole {String[] roles();
}
在這種情況下,您將注意到不應該在表達式中使用引號,而應該在參數值中使用,如下所示:
@Component
public class BankService {@HasAnyRole(roles = { "'USER'", "'ADMIN'" })public Account readAccount(Long id) {// ... is only returned if the `Account` belongs to the logged in user}
}
這樣,一旦替換,表達式就變成@PreAuthorize (“ hasAnyrole (‘ USER’,‘ ADMIN’)”)。
Enabling Certain Annotations
您可以關閉@EnableMethodSecurity 的預配置并將其替換為您自己的配置。如果要自定義 AuthorizationManager 或 Pointcut,可以選擇這樣做。或者您可能只想啟用特定的注釋,比如@PostAuthorize。
你可以這樣做:
Only @PostAuthorize Configuration
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = false)
class MethodSecurityConfig {@Bean@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)Advisor postAuthorize() {return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postAuthorize();}
}
上面的代碼片段通過首先禁用 Method Security 的預配置,然后發布@PostAuthorize 攔截器本身來實現這一點。
Authorizing with <intercept-methods>
雖然使用 Spring Security 的基于注釋的支持是方法安全的首選,但是您也可以使用 XML 來聲明 bean 授權規則。
如果需要在 XML 配置中聲明它,可以像下面這樣使用 < 攔截方法 > :
<bean class="org.mycompany.MyController"><intercept-methods><protect method="get*" access="hasAuthority('read')"/><protect method="*" access="hasAuthority('write')"/></intercept-methods>
</bean>
Authorizing Methods Programmatically
正如您已經看到的,有幾種方法可以使用 Method Security SpEL 表達式指定非常重要的授權規則。
有許多方法可以讓您的邏輯基于 Java 而不是基于 SpEL。這使得可以訪問整個 Java 語言,從而提高可測試性和流控制。
Using a Custom Bean in SpEL
以編程方式授權方法的第一種方法是兩步進程。
首先,聲明一個 bean,該 bean 具有一個接受 MethodSecurityExpressionOperations 實例的方法,如下所示:
@Component("authz")
public class AuthorizationLogic {public boolean decide(MethodSecurityExpressionOperations operations) {// ... authorization logic}
}
然后,按照以下方式在注釋中引用該 bean:
@Controller
public class MyController {@PreAuthorize("@authz.decide(#root)")@GetMapping("/endpoint")public String endpoint() {// ...}
}
SpringSecurity 將為每個方法調用調用該 bean 上的給定方法。
這樣做的好處是,所有的授權邏輯都在一個單獨的類中,可以獨立進行單元測試和驗證是否正確。它還可以訪問完整的 Java 語言。
如果您想要包含更多關于決策性質的信息,您可以像下面這樣返回一個自定義 AuthorizationDecision:
@Component("authz")
public class AuthorizationLogic {public AuthorizationDecision decide(MethodSecurityExpressionOperations operations) {// ... authorization logicreturn new MyAuthorizationDecision(false, details);}
}
或引發自定義 AuthorizationDeniedException 實例。但是請注意,最好是返回一個對象,因為這樣不會產生生成堆棧跟蹤的開銷。
然后,您可以在自定義如何處理授權結果時訪問自定義詳細信息。
Using a Custom Authorization Manager
以編程方式授權方法的第二種方法是創建自定義 AuthorizationManager。
首先,聲明一個授權管理器實例,比如:
@Component
public class MyAuthorizationManager implements AuthorizationManager<MethodInvocation>, AuthorizationManager<MethodInvocationResult> {@Overridepublic AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, MethodInvocation invocation) {// ... authorization logic}@Overridepublic AuthorizationDecision check(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, MethodInvocationResult invocation) {// ... authorization logic}
}
然后,使用切入點發布方法攔截器,該切入點對應于您希望 AuthorizationManager 運行的時間。例如,您可以將@PreAuthorize 和@PostAuthorize 的工作方式替換為:
@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = false)
class MethodSecurityConfig {@Bean@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)Advisor preAuthorize(MyAuthorizationManager manager) {return AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preAuthorize(manager);}@Bean@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)Advisor postAuthorize(MyAuthorizationManager manager) {return AuthorizationManagerAfterMethodInterceptor.postAuthorize(manager);}
}
Customizing Expression Handling
或者,第三,您可以自定義如何處理每個 SpEL 表達式。為此,可以公開自定義 MethodSecurityExpressionHandler,如下所示:
Custom MethodSecurityExpressionHandler
@Bean
static MethodSecurityExpressionHandler methodSecurityExpressionHandler(RoleHierarchy roleHierarchy) {DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler handler = new DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler();handler.setRoleHierarchy(roleHierarchy);return handler;
}
還可以繼承 DefaultMessageSecurityExpressionHandler,以在默認值之外添加自己的自定義授權表達式。
Authorizing with AspectJ
Matching Methods with Custom Pointcuts
在 SpringAOP 上構建,您可以聲明與注釋無關的模式,類似于請求級授權。這具有集中方法級授權規則的潛在優勢。
例如,您可以使用發布自己的 Advisor 或使用 < protected-pointcut > 將 AOP 表達式與服務層的授權規則匹配起來,如下所示:
import static org.springframework.security.authorization.AuthorityAuthorizationManager.hasRole@Bean
@Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE)
static Advisor protectServicePointcut() {AspectJExpressionPointcut pattern = new AspectJExpressionPointcut()pattern.setExpression("execution(* com.mycompany.*Service.*(..))")return new AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor(pattern, hasRole("USER"))
}
Integrate with AspectJ Byte-weaving
通過使用 AspectJ 將 Spring Security 通知編織到 bean 的字節代碼中,有時可以提高性能。
在設置 AspectJ 之后,您可以非常簡單地在@EnableMethodSecurity 注釋或 < method-security > 元素中聲明您正在使用 AspectJ:
@EnableMethodSecurity(mode=AdviceMode.ASPECTJ)
結果將是 Spring Security 將其advisors 作為 AspectJ 通知發布,以便它們可以相應地編入其中。
Specifying Order
如前所述,每個注釋都有一個 Spring AOP 方法攔截器,并且每個注釋都在 Spring AOP advisor 鏈中有一個位置。
也就是說,@PreFilter 方法攔截器的順序是100,@PreAuthorize 的順序是200,依此類推。
值得注意的是,還有其他基于 AOP 的注釋,如@EnableTransactionManagement,其順序為 Integer.MAX _ VALUE。換句話說,默認情況下,它們位于顧問鏈的末尾。
有時候,在 SpringSecurity 之前執行其他通知是很有價值的。例如,如果您有一個帶有@Transactional 和@PostAuthorize 注釋的方法,您可能希望在@PostAuthorize 運行時事務仍然處于打開狀態,以便 AccessDeniedException 將導致回滾。
要讓@EnableTransactionManagement 在方法授權通知運行之前打開事務,可以像下面這樣設置@EnableTransactionManagement 的順序:
@EnableTransactionManagement(order = 0)
由于最早的方法攔截器(@PreFilter)被設置為100的順序,如果設置為零,則意味著事務通知將在所有 Spring Security 通知之前運行。
Expressing Authorization with SpEL
您已經看到了幾個使用 SpEL 的示例,因此現在讓我們更深入地介紹一下 API。
SpringSecurity 將其所有授權字段和方法封裝在一組根對象中。最通用的根對象稱為 SecurityExpressionRoot,它是 MethodSecurityExpressionRoot 的基礎。當準備計算授權表達式時,SpringSecurity 將此根對象提供給 MethodSecurityevalationContext。
Using Authorization Expression Fields and Methods
它提供的第一件事是增強了 SpEL 表達式的授權字段和方法集。以下是最常用方法的簡要概述:
- PermitAll-該方法不需要調用任何授權; 注意,在這種情況下,永遠不會從會話檢索 Authentication
- DenyAll-在任何情況下都不允許使用該方法; 請注意,在這種情況下,永遠不會從會話檢索 Authentication
- HasAuthority ——該方法要求 Authentication 具有與給定值匹配的 GrantedAuthority
- HasRole-hasAuthority 的一個快捷方式,它將 ROLE _ 或其他配置為默認前綴的內容作為前綴
- HasAnyAuthority ——該方法要求 Authentication 具有與任何給定值匹配的 GrantedAuthority
- HasAnyrole-hasAnyAuthority 的一個快捷方式,它將 ROLE _ 或任何被配置為默認前綴的東西作為前綴
- HasPermission-一個連接到您的 Permisonevalator 實例的鉤子,用于執行對象級授權
以下是一些最常見的領域:
- Authentication ——與此方法調用關聯的 Authentication 實例
- principal-與此方法調用相關聯的 Authentication # getPrincipal
現在已經了解了模式、規則以及如何將它們配對在一起,您應該能夠理解在這個更復雜的示例中發生了什么:
@Component
public class MyService {@PreAuthorize("denyAll")MyResource myDeprecatedMethod(...);@PreAuthorize("hasRole('ADMIN')")MyResource writeResource(...)@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('db') and hasRole('ADMIN')")MyResource deleteResource(...)@PreAuthorize("principal.claims['aud'] == 'my-audience'")MyResource readResource(...);@PreAuthorize("@authz.check(authentication, #root)")MyResource shareResource(...);
}
- 由于任何原因,任何人都不能調用此方法
- 此方法只能由授予 ROLE _ ADMIN 權限的身份驗證調用
- 此方法只能由授予 db 和 ROLE _ ADMIN 權限的身份驗證調用
- 此方法只能由具有等于 “my-audience” 的 aud 聲明的主體調用。
- 此方法只能在 bean authz 的檢查方法返回 true 時調用。
Using Method Parameters
SpringSecurity 還支持包裝任何注釋了其方法安全性注釋的對象。
實現這一點的最簡單方法是使用@AuthorizeReturnObject 注釋標記任何返回您希望授權的對象的方法。
例如,考慮以下 User 類:
public class User {private String name;private String email;public User(String name, String email) {this.name = name;this.email = email;}public String getName() {return this.name;}@PreAuthorize("hasAuthority('user:read')")public String getEmail() {return this.email;}
}
給定一個像這樣的界面:
public class UserRepository {@AuthorizeReturnObjectOptional<User> findByName(String name) {// ...}
}
然后,從 findById 返回的任何 User 都將像其他 Spring Security 保護的組件一樣受到保護:
@Autowired
UserRepository users;@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {Optional<User> securedUser = users.findByName("name");assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(() -> securedUser.get().getEmail());
}
Using @AuthorizeReturnObject at the class level
@AuthorizeReturnObject可以放置在類級別。但是請注意,這意味著 Spring Security 將嘗試代理任何返回對象,包括 String、 Integer 和其他類型。這通常不是你想要做的.
如果您希望對方法返回值類型(如 int、 String、 Double 或這些類型的集合)的類或接口使用@AuthorizeReturnObject,那么您還應該發布適當的 AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory。目標訪問者如下:
@Bean
static Customizer<AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory> skipValueTypes() {return (factory) -> factory.setTargetVisitor(TargetVisitor.defaultsSkipValueTypes());
}
Programmatically Proxying
還可以通過編程方式代理給定對象。
為此,您可以自動連接提供的 AuthorizationProxyFactory 實例,該實例基于您配置的方法安全攔截器。如果您使用的是@EnableMethodSecurity,那么這意味著它默認擁有@PreAuthorize、@PostAuthorize、@PreFilter 和@PostFilter 的攔截器。
您可以通過以下方式代理用戶的實例:
@Autowired
AuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory;@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {User user = new User("name", "email");assertThat(user.getEmail()).isNotNull();User securedUser = proxyFactory.proxy(user);assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(securedUser::getEmail);
}
Manual Construction
如果需要不同于 Spring Security 默認值的東西,還可以定義自己的實例。
例如,如果像下面這樣定義 AuthorizationProxyFactory 實例:
import org.springframework.security.authorization.method.AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.TargetVisitor;
import static org.springframework.security.authorization.method.AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preAuthorize;
// ...AuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory = AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.withDefaults();
// and if needing to skip value types
proxyFactory.setTargetVisitor(TargetVisitor.defaultsSkipValueTypes());
然后您可以將 User 的任何實例包裝如下:
@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {AuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory = AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.withDefaults();User user = new User("name", "email");assertThat(user.getEmail()).isNotNull();User securedUser = proxyFactory.proxy(user);assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(securedUser::getEmail);
}
Proxying Collections
AuthorizationProxyFactory 通過代理元素類型和通過代理值類型映射來支持 Java 集合、流、數組、可選項和迭代器。
這意味著在代理 List 對象時,以下代碼也可以工作:
@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenAuthorizes() {AuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory = AuthorizationAdvisorProxyFactory.withDefaults();List<User> users = List.of(ada, albert, marie);List<User> securedUsers = proxyFactory.proxy(users);securedUsers.forEach((securedUser) ->assertThatExceptionOfType(AccessDeniedException.class).isThrownBy(securedUser::getEmail));
}
Proxying Classes
在有限的情況下,代理 Class 本身可能是有價值的,AuthorizationProxyFactory 也支持這一點。這大致相當于在 Spring 框架中調用 ProxyFactory # getProxyClass 以支持創建代理。
當您需要提前構造代理類(如 SpringAOT)時,這種方法非常方便。
Support for All Method Security Annotations
AuthorizationProxyFactory 支持應用程序中啟用的任何方法安全注釋。它基于作為 bean 發布的 AuthorizationAdvisor 類。
因為@EnableMethodSecurity 默認發布@PreAuthorize、@PostAuthorize、@PreFilter 和@PostFilter 顧問,所以通常不需要做任何事情來激活該能力。
Custom Advice
如果您有也希望應用的安全性建議,您可以像下面這樣發布您自己的 AuthorizationAdvisor:
@EnableMethodSecurity
class SecurityConfig {@Beanstatic AuthorizationAdvisor myAuthorizationAdvisor() {return new AuthorizationAdvisor();}
}
Spring Security 將把該顧問添加到 AuthorizationProxyFactory 在代理對象時添加的通知集中。
Working with Jackson
這個特性的一個強大用途是從控制器返回一個安全值,如下所示:
@RestController
public class UserController {@AutowiredAuthorizationProxyFactory proxyFactory;@GetMappingUser currentUser(@AuthenticationPrincipal User user) {return this.proxyFactory.proxy(user);}
}
但是,如果您正在使用 Jackson,這可能會導致一個序列化錯誤,如下所示:
com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.exc.InvalidDefinitionException: Direct self-reference leading to cycle
這是由于 Jackson 使用 CGLIB 代理的方式。為了解決這個問題,在 User 類的頂部添加以下注釋:
@JsonSerialize(as = User.class)
public class User {}
最后,您需要發布一個自定義攔截器來捕獲為每個字段拋出的 AccessDeniedException,您可以這樣做:
@Component
public class AccessDeniedExceptionInterceptor implements AuthorizationAdvisor {private final AuthorizationAdvisor advisor = AuthorizationManagerBeforeMethodInterceptor.preAuthorize();@Overridepublic Object invoke(MethodInvocation invocation) throws Throwable {try {return invocation.proceed();} catch (AccessDeniedException ex) {return null;}}@Overridepublic Pointcut getPointcut() {return this.advisor.getPointcut();}@Overridepublic Advice getAdvice() {return this;}@Overridepublic int getOrder() {return this.advisor.getOrder() - 1;}
}
然后,您將看到一個不同的基于用戶授權級別的 JSON 序列化。如果他們沒有user:read權限,那么他們會看到:
{"name" : "name","email" : null
}
如果他們真的有這個權限,他們會看到:
{"name" : "name","email" : "email"
}
Providing Fallback Values When Authorization is Denied
在某些情況下,您可能不希望在沒有所需權限的情況下調用方法時引發 AuthorizationDeniedException。相反,您可能希望返回一個后處理的結果,比如一個被屏蔽的結果,或者在調用方法之前拒絕授權的情況下返回一個默認值。
Spring Security 通過使用@HandleAuthorizationDenied 支持處理在方法調用時被拒絕的授權。該處理程序適用于在@PreAuthorize 和@PostAuthorize 注釋中發生的被拒絕的授權,以及從方法調用本身拋出的 AuthorizationDeniedException。
讓我們考慮一下上一節的例子,但是我們不創建 AccessDeniedExceptionInterceptor 來將 AccessDeniedException 轉換為 null 返回值,而是使用@HandleAuthorizationDenied 的 handlerClass 屬性:
public class NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler implements MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler {@Overridepublic Object handleDeniedInvocation(MethodInvocation methodInvocation, AuthorizationResult authorizationResult) {return null;}}@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {@Beanpublic NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler nullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler() {return new NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler();}}public class User {// ...@PreAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')")@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler.class)public String getEmail() {return this.email;}
}
- 創建返回空值的 MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler 的實現
- 將 NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler 注冊為 bean
- 用@HandleAuthorizationDenied 注釋該方法,并將 NullMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler 傳遞給 handlerClass 屬性
然后您可以驗證返回的是 null 值而不是 AccessDeniedException:
您還可以使用@Component 注釋類,而不用創建@Bean 方法
@Autowired
UserRepository users;@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenNullEmail() {Optional<User> securedUser = users.findByName("name");assertThat(securedUser.get().getEmail()).isNull();
}
Using the Denied Result From the Method Invocation
在某些情況下,您可能希望返回從被拒絕的結果派生的安全結果。例如,如果用戶未被授權查看電子郵件地址,您可能希望對原始電子郵件地址應用一些屏蔽,即 useremail@example.com 將成為 use * * * *@example.com。
對于這些場景,可以重寫 MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler 中的 handleDeniedInvocationResult,該 Handler 將 MethodInvocationResult 作為參數。讓我們繼續前面的例子,但是不返回 null,我們將返回一個電子郵件的屏蔽值:
public class EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler implements MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler {@Overridepublic Object handleDeniedInvocation(MethodInvocation methodInvocation, AuthorizationResult authorizationResult) {return "***";}@Overridepublic Object handleDeniedInvocationResult(MethodInvocationResult methodInvocationResult, AuthorizationResult authorizationResult) {String email = (String) methodInvocationResult.getResult();return email.replaceAll("(^[^@]{3}|(?!^)\\G)[^@]", "$1*");}}@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {@Beanpublic EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler emailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler() {return new EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler();}}public class User {// ...@PostAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')")@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler.class)public String getEmail() {return this.email;}
}
- 創建 MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler 的實現,該實現返回未授權結果值的屏蔽值
- 將 EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler 注冊為 bean
- 用@HandleAuthorizationDenied 注釋該方法,并將 EmailMaskingMethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler 傳遞給 handlerClass 屬性
然后您可以驗證是否返回了一封蒙蔽的電子郵件,而不是一個 AccessDeniedException:
@Autowired
UserRepository users;@Test
void getEmailWhenProxiedThenMaskedEmail() {Optional<User> securedUser = users.findByName("name");// email is useremail@example.comassertThat(securedUser.get().getEmail()).isEqualTo("use******@example.com");
}
在實現 MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler 時,您可以選擇返回的類型:
- 空值。
- 一個非空值,與方法的返回類型相關。
- 拋出異常,通常是 AuthorizationDeniedException 的實例。這是默認行為。
- 用于反應應用的 Mono 型。
注意,由于處理程序必須在應用程序上下文中注冊為 bean,因此如果需要更復雜的邏輯,可以向它們注入依賴項。除此之外,您還可以使用 MethodInvation 或 MethodInvocationResult,以及 AuthorizationResult 獲取與授權決策相關的更多細節。
Deciding What to Return Based on Available Parameters
考慮一個場景,不同的方法可能有多個掩碼值,如果我們必須為每個方法創建一個處理程序,那么效率就會降低,盡管這樣做完全沒問題。在這種情況下,我們可以使用通過參數傳遞的信息來決定做什么。例如,我們可以創建一個自定義@Mask 注釋和一個檢測該注釋的處理程序,以決定返回什么掩碼值:
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Mask {String value();}public class MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler implements MethodAuthorizationDeniedHandler {@Overridepublic Object handleDeniedInvocation(MethodInvocation methodInvocation, AuthorizationResult authorizationResult) {Mask mask = AnnotationUtils.getAnnotation(methodInvocation.getMethod(), Mask.class);return mask.value();}}@Configuration
@EnableMethodSecurity
public class SecurityConfig {@Beanpublic MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler maskAnnotationDeniedHandler() {return new MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler();}}@Component
public class MyService {@PreAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')")@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler.class)@Mask("***")public String foo() {return "foo";}@PreAuthorize(value = "hasAuthority('user:read')")@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler.class)@Mask("???")public String bar() {return "bar";}}
現在,拒絕訪問時的返回值將根據@Mask 注釋來決定:
@Autowired
MyService myService;@Test
void fooWhenDeniedThenReturnStars() {String value = this.myService.foo();assertThat(value).isEqualTo("***");
}@Test
void barWhenDeniedThenReturnQuestionMarks() {String value = this.myService.foo();assertThat(value).isEqualTo("???");
}
Combining with Meta Annotation Support
還可以將@HandleAuthorizationDenied 與其他注釋組合起來,以減少和簡化方法中的注釋。讓我們考慮一下上一節中的例子,并將@HandleAuthorizationDenied 與@Mask 合并:
@Target({ ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE })
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@HandleAuthorizationDenied(handlerClass = MaskAnnotationDeniedHandler.class)
public @interface Mask {String value();}@Mask("***")
public String myMethod() {// ...
}
現在,當需要在方法中添加掩碼行為時,您不必記得添加這兩個注釋。請務必閱讀元注釋支持部分了解更多關于用法的詳細信息。
Migrating from @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity
如果使用@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity,則應該遷移到@EnableMethodSecurity。
Replace global method security with method security
如果使用@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity,則應該遷移到@EnableMethodSecurity。
Replace global method security with method security
@ EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 和 < global-method-security > 分別不推薦使用@EnableMethodSecurity 和 < method-security > 。默認情況下,新的注釋和 XML 元素激活 Spring 的事后注釋,并在內部使用 AuthorizationManager。
這意味著以下兩個清單在功能上是等價的:
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
@EnableMethodSecurity
對于不使用 pre-post注釋的應用程序,請確保將其關閉,以避免激活不必要的行為。
例如:
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
應該改為:
@EnableMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true, prePostEnabled = false)
Use a Custom @Bean instead of subclassing DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler
作為性能優化,MethodSecurityExpressionHandler 引入了一個新方法,該方法采用 Supplier < Authentication > 而不是 Authentication。
這允許 Spring Security 延遲身份驗證的查找,并且當您使用@EnableMethodSecurity 而不是@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity 時會自動利用這一點。
但是,假設您的代碼擴展了 DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler 并重寫了 createSecurityExpressionRoot (Authentication,MethodInvation)以返回自定義的 SecurityExpressionRoot 實例。這將不再起作用,因為@EnableMethodSecurity 設置的安排改為調用 createevalationContext (Supplier < Authentication > ,MethodInvocation)。
令人高興的是,這種級別的定制通常是不必要的。相反,您可以使用所需的授權方法創建自定義 bean。
或者,假設您想要一個@PostAuthorize (“ hasAuthority (‘ ADMIN’)”)的自定義計算。你可以創建一個像這樣的自定義@Bean:
class MyAuthorizer {boolean isAdmin(MethodSecurityExpressionOperations root) {boolean decision = root.hasAuthority("ADMIN");// custom work ...return decision;}
}
然后在注釋中引用如下:
@PreAuthorize("@authz.isAdmin(#root)")
I’d still prefer to subclass DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler我仍然希望繼承 DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler 類
如果您必須繼續子類化 DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler,您仍然可以這樣做:
@Component
class MyExpressionHandler extends DefaultMethodSecurityExpressionHandler {@Overridepublic EvaluationContext createEvaluationContext(Supplier<Authentication> authentication, MethodInvocation mi) {StandardEvaluationContext context = (StandardEvaluationContext) super.createEvaluationContext(authentication, mi);MethodSecurityExpressionOperations delegate = (MethodSecurityExpressionOperations) context.getRootObject().getValue();MySecurityExpressionRoot root = new MySecurityExpressionRoot(delegate);context.setRootObject(root);return context;}
}
Further Reading
現在您已經保護了應用程序的請求,如果您還沒有保護它的請求,請保護它。您還可以進一步閱讀關于測試應用程序或將 Spring Security 與應用程序的其他方面(如數據層或跟蹤和度量)集成的內容。



















)