?日志用于記錄程序的執行記錄包括程序的出錯記錄,程序致命退出原因,程序的正常執行記錄。這樣我們就可以很快的察覺程序的錯誤原因、執行狀況等等,因此管理日志信息是非常重要的。
日志一般由以下部分組合:
日志時間、日志等級、日志內容、日志文件的名稱
日志等級分為5個:Info:常規信息、Warning:報警信息、Error:發生錯誤,需要立即處理、Fatal:致命信息、Debug:調試信息
學習一下多參數函數相關的c接口:
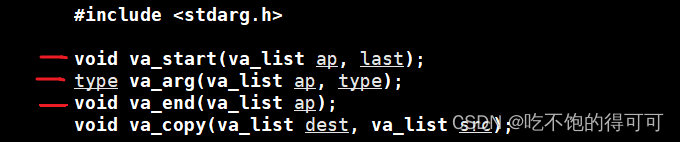
#include <iostream>
#include <stdarg.h>
int argfunc(int n, ...)//n是要相加的元素個數,...代表要傳入的參數
{va_list s;//s相當于一個int*類型的指針va_start(s, n);//s=&n+1int sum=0;while(n--){sum += va_arg(s, int);}va_end(s);//將s置為空return sum;
}
int main()
{int a= argfunc(3,1,2,3);std::cout<<a<<std::endl;return 0;
}?vsnprintf函數

利用多參數相關接口,就可以實現對函數進行動態參數傳參!
time函數

localtime函數
![]()
localtime函數的返回值是一個struct tm結構體類型的指針,struct tm結構體里儲存了對應時間戳的年月日時分秒,如下就是struct tm結構體:

具體代碼實現如下:
log.hpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <ctime>
#include <cstdio>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>#define Screen 1 // 表示向顯示器上打印日志信息
#define Onefile 2 // 表示向logtxt日志文件里寫日志信息(沒有該日志文件open函數會自動創建)
#define Classfile 3 // 對向指定等級的日志文件寫內容,比如:Fatal等級的日志信息寫到logtxt.Fatal日志文件中#define Size 1024
#define Logfile "log.txt"class Log
{
public:Log(int n = 1): printmethod(n), path("./log/"){}void printLogtxt(const std::string &s, const char *logtxt){switch (printmethod){case Screen:std::cout << logtxt;break;case Onefile:printOneFile(Logfile, logtxt);break;case Classfile:printClassFile(s, logtxt);break;default:break;}}void printOneFile(const std::string &Logname, const std::string& logtxt){std::string _s = path + Logname; // 給logtxt文件加上我們路徑,方便我們以后再該路徑里管理日志文件int fd = open(_s.c_str(), O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_APPEND, 0666);if (fd < 0){perror("open");return;}write(fd, logtxt.c_str(), logtxt.size());close(fd);}void printClassFile(const std::string &s, const char *logtxt){std::string _s(Logfile);_s+= ".";_s+= s;printOneFile(_s, logtxt);}void operator()(const std::string &str, const char *format, ...){time_t t = time(nullptr);struct tm *ctime = localtime(&t);char str1[Size] = {0};snprintf(str1, sizeof(str1), "[%s][%d-%d-%d:%d:%d:%d]", str.c_str(), ctime->tm_year + 1900,ctime->tm_mon + 1, ctime->tm_mday,ctime->tm_hour, ctime->tm_min, ctime->tm_sec);va_list s;va_start(s, format);char str2[Size] = {0};vsnprintf(str2, sizeof(str2), format, s); // format是格式字符串 s是多參數...的第一個字符串地址va_end(s);char logtxt[2 * Size] = {0};snprintf(logtxt, sizeof(logtxt), "%s %s\n", str1, str2);printLogtxt(str, logtxt);}private:int printmethod;std::string path; // 日志文件將來被創建時所在的路徑,更有利于我們管理日志文件
};testlog.cpp
#include "log.hpp"
#include <errno.h>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
int main()
{Log log(3);log("Info", "向%s日志文件里寫入內容成功!", "log.txt.Info");std::vector<int> v = {1,2};if(!v.empty())log("Debug", "v.size() is %d", v.size());return 0;
}
在log目錄下生成的log.txt.Info文件:

在log目錄下生成的log.txt.Debug文件:

)


:JVM虛擬機內存模型)
 報錯問題)





![[go-zero] 簡單微服務調用](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[go-zero] 簡單微服務調用)



)


)

