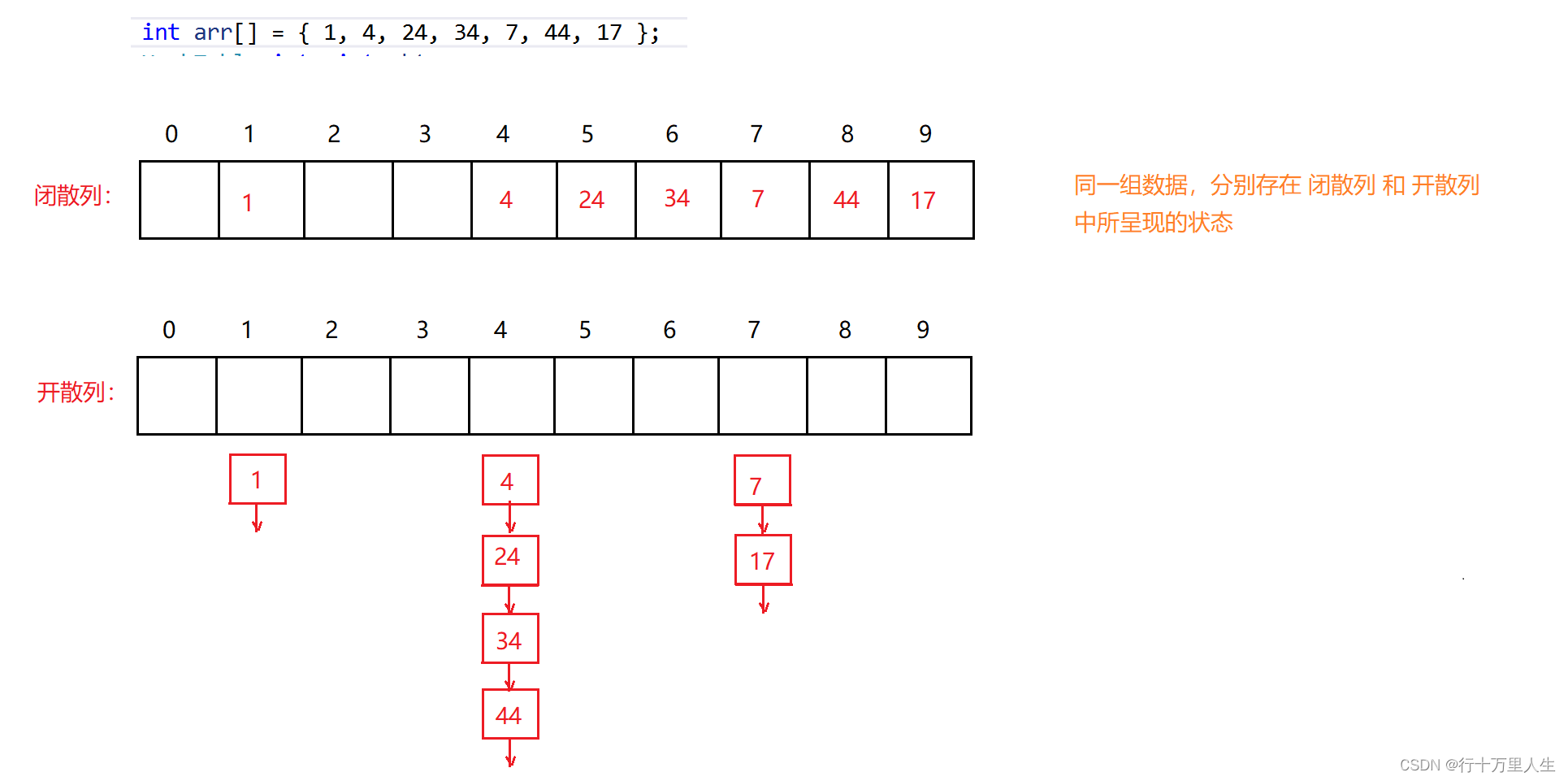
通過上面這幅圖,讀者應該能較為直觀地理解何為開散列,以及閉散列與開散列的區別在哪里 —— 數據的存儲形式不同,至于其他的,如確定每個元素的哈希地址等一概相同。
與閉散列相比,開散列能夠更好地處理發生沖突的元素 —— 假使我們要在上述閉散列中再插入 5 ,會因為 24 的先插入而導致 5 必須往后尋找空位置,進而影響 6 的插入等。
1. 什么是桶?
通過 HashFunc 計算每個元素的哈希地址,哈希地址相同的元素所組成的子集稱為 哈希桶 ,這些元素通過單鏈表鏈接在一起。
如:4 % 10 == 24 % 10 == 34 % 10 == 44 % 10 == 4 。
開散列的每個桶中存的都是發生哈希沖突的元素。
2. 開散列框架搭建
- HashFunc
template<class K> struct HashFunc {size_t operator()(const K& key){size_t ret = key;return ret;} };// 為 string 寫一個特化版本 template<> struct HashFunc<string> {size_t operator()(const string& s){size_t hash = 0;for (auto& e : s){hash = hash * 131 + e; // 131 是前輩用大量數據測試得到的值,可以盡大程度避免哈希沖突}return hash;} };
- HashNode
template<class K, class V>struct HashNode{HashNode* _next;pair<K, V> _kv;HashNode(const pair<K, V>& kv):_next(nullptr),_kv(kv){}};
- HashTable
template<class K, class V, class Hash = HashFunc<K>>class HashTable{typedef HashNode<K, V> Node;public:HashTable(){_tables.resize(10);}private:vector<Node*> _tables;size_t _n = 0;};
3. Insert()
bool Insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){if (Find(kv.first)) // 未實現的 Find,已存在則返回該元素哈希位置的指針,不存在則返回空return false;Hash hs;// 擴容 if (_n == _tables.size()) // STL 庫中,開散列的負載因子設為 1{// ...}// 插入size_t hashi = hs(kv.first) % _tables.size();Node* newNode = new Node(kv);newNode->_next = _tables[hashi];_tables[hashi] = newNode;// 頭插++_n;return true;}
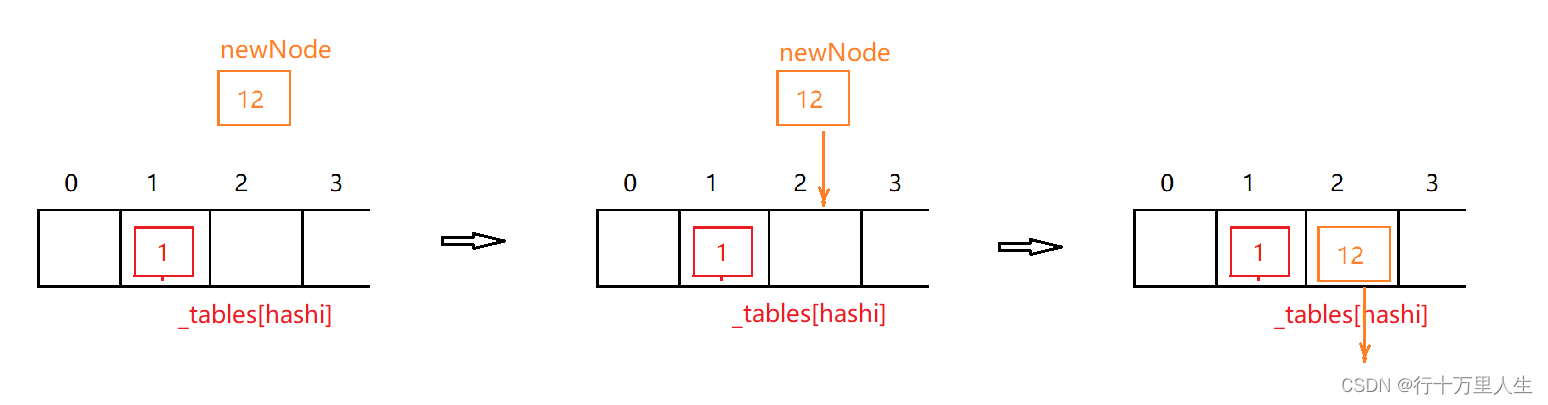
再來聊一聊擴容邏輯。
與閉散列不同,我們不準備復用 Insert() 完成數據的拷貝 —— 假設哈希桶中已經存在 1000, 000 個元素,需要重新拷貝 1000, 000 個元素,再將原表中的元素一一釋放。
更好的辦法是,直接將原表中的節點 掛到 新表對應的哈希位置上。
// 擴容部分if (_n == _tables.size()){vector<Node*> newTable(2 * _tables.size(), nullptr);for (size_t i = 0; i < _tables.size(); i++){Node* cur = _tables[i];while (cur){Node* next = cur->_next;size_t hashi = hs(cur->_kv.first) % newTable.size();cur->_next = newTable[hashi];newTable[hashi] = cur;cur = next;}_tables[i] = nullptr;// 將原表置空}_tables.swap(newTable);// 不需要手動將 newTable delete[],編譯器會自動調用 vector 的析構函數,// 且 swap 后,newTable 里全為空,不需要擔心內存泄露的問題}
4. Find() 和 Erase()
- Find()
Node* Find(const K& key){Hash hs;size_t hashi = hs(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];while (cur){if (cur->_kv.first == key){break;}cur = cur->_next;}if (cur && cur->_kv.first == key)return cur;else return nullptr;}
- Erase()
開散列的 Erase() 不能像閉散列那樣,Find() 后直接刪除。
調用 Find() 能得到 key 對應的 HashData 的指針,但無法得到前一個節點的指針,會造成一系列問題。
bool Erase(const K& key){Hash hs;size_t hashi = hs(key) % _tables.size();Node* cur = _tables[hashi];Node* prev = nullptr; // prev 為前一個節點指針while (cur){if (cur->_kv.fisrt == key) // 找到了{if (prev) // prev 不為空,說明 cur 為中間節點{prev->_next = cur->_next;}else // prev 為空,說明 cur 為 _tables[hashi]{_tables[hashi] = cur->_next;}delete cur;--_n;return true;}prev = cur;cur = cur->_next;}return false;}
)











)
)

)



