目錄
1.簡介
2.安裝與集成
3.快速入門
4.完整示例
5.優勢與適用場景
1.簡介
????????continuable?是一個專注于?異步操作延續(continuation)?的現代 C++ 開源庫,旨在簡化異步編程流程,解決 “回調地獄” 問題,提供直觀、靈活的異步操作鏈式調用和組合能力。它的設計理念類似于 JavaScript 中的?Promise,但更貼合 C++ 語法特性和現代標準(C++11 及以上)。
????????異步編程中,多個依賴的異步操作(如網絡請求、文件 IO)常導致嵌套回調(“回調地獄”),代碼可讀性和維護性極差。continuable?通過?延續傳遞風格(Continuation-Passing Style)?封裝異步操作,允許將異步操作的 “后續處理邏輯”(延續)通過鏈式調用串聯,使異步流程更接近同步代碼的線性結構。
????????主要特性有:
- 鏈式延續:通過?
then()?方法串聯異步操作,前一個操作的結果自動傳遞給下一個延續。 - 錯誤處理:統一的錯誤傳播機制,通過?
catch_()?捕獲鏈中任意環節的錯誤。 - 操作組合:支持并行(
when_all())、串行(when_seq())等方式組合多個異步操作。 - 多范式兼容:可與回調函數、
std::future、協程(C++20)等多種異步模型集成。 - 輕量級:header-only 庫(僅需包含頭文件),無外部依賴,易于集成。
- 類型安全:通過模板推導自動處理參數類型,編譯期檢查類型匹配。
2.安裝與集成
continuable?是?header-only?庫,無需編譯,只需:
1.從?GitHub 倉庫?下載源碼或從網站下載壓縮包。
https://github.com/Naios/continuable
2.將?include?目錄添加到項目包含路徑。
3.包含核心頭文件?#include "continuable/continuable.hpp"?即可使用。
支持 C++11 及以上標準,兼容主流編譯器(GCC、Clang、MSVC)。
注意:continuable依賴asio和function2庫
asio庫源碼的下載地址:
Downloading Asio
function2的引用可參考:
function2:一個專注于函數對象包裝的現代 C++ 開源庫-CSDN博客
3.快速入門
1.通過make_continuable創建一個可延續對象,該對象在調用時會返回一個承諾:
auto http_request(std::string url) {return cti::make_continuable<std::string>([url = std::move(url)](auto&& promise) {// Perform the actual request through a different library,// resolve the promise upon completion of the task.promise.set_value("<html> ... </html>");// or: promise.set_exception(std::make_exception_ptr(std::exception("Some error")));// or: promise.set_canceled();});
}auto mysql_query(std::string query) {return cti::make_continuable<result_set, bool>([url = std::move(url)](auto&& promise) {// ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ multiple result types});
}auto do_sth() {return cti::make_continuable<void>([](auto&& promise) {// ^^^^ no result at all});
}auto run_it() {return async([] {// Directly start with a handler});
}continuable<> run_it() { // With type erasurereturn async([] {});
}2.通過then附加您的延續,支持多個結果和部分處理程序:
mysql_query("SELECT `id`, `name` FROM `users`").then([](result_set users) {// Return the next continuable to process ...return mysql_query("SELECT `id` name FROM `sessions`");}).then([](result_set sessions) {// ... or pass multiple values to the next callback using tuples or pairs ...return std::make_tuple(std::move(sessions), true);}).then([](result_set sessions, bool is_ok) {// ... or pass a single value to the next callback ...return 10;}).then([](auto value) {// ^^^^ Templated callbacks are possible too})// ... you may even pass continuables to the `then` method directly:.then(mysql_query("SELECT * `statistics`")).then([](result_set result) {// ...return "Hi";}).then([] /*(std::string result) */ { // Handlers can accept a partial set of arguments{// ...});3.通過fail或next處理故障:
http_request("example.com").then([] {throw std::exception("Some error");}).fail([] (std::exception_ptr ptr) {if (ptr) {try {std::rethrow_exception(ptr);} catch(std::exception const& e) {// Handle the exception or error code here}}});4.通過特定的執行器調度延續(可能在不同的線程上或稍后)
auto executor = [](auto&& work) {// Dispatch the work here, store it for later invocation or move it to another thread.std::forward<decltype(work)>(work)();
};read_file("entries.csv").then([](Buffer buffer) {// ...}, executor);
// ^^^^^^^^5.通過when_all、when_any或when_seq連接可延續對象:
// `all` of connections:
(http_request("github.com") && http_request("example.com") && http_request("wikipedia.org")).then([](std::string github, std::string example, std::string wikipedia) {// The callback is called with the response of github,// example and wikipedia.});// `any` of connections:
(http_request("github.com") || http_request("example.com") || http_request("wikipedia.org")).then([](std::string github_or_example_or_wikipedia) {// The callback is called with the first response of either github,// example or wikipedia.});// `sequence` of connections:
(http_request("github.com") >> http_request("example.com") >> http_request("wikipedia.org")).then([](std::string github, std::string example, std::string wikipedia) {// The requests are invoked sequentially});// Mixed logical connections:
(http_request("github.com") && (http_request("example.com") || http_request("wikipedia.org"))).then([](std::string github, std::string example_or_wikipedia) {// The callback is called with the response of github for sure// and the second parameter represents the response of example or wikipedia.});// There are helper functions for connecting continuables:
auto all = cti::when_all(http_request("github.com"), http_request("example.com"));
auto any = cti::when_any(http_request("github.com"), http_request("example.com"));
auto seq = cti::when_seq(http_request("github.com"), http_request("example.com"));6.通過result處理多個結果變量,并通過recover從故障中恢復:
make_exceptional_continuable<void>(std::make_exception_ptr(std::exception("Some error")).fail([] (std::exception_ptr ptr) {return recover();}).then([] () -> result<> {// We recovered from the failure and proceeding normally// Will yield a default constructed exception type to signal cancellationreturn cancel();});7.對現有代碼進行“promisify”處理,或使用(asio)完成令牌集成:
// Promisification of your existing code that accepts callbacks
auto async_resolve(std::string host, std::string service) {return cti::promisify<asio::ip::udp::resolver::iterator>::from([&](auto&&... args) {resolver_.async_resolve(std::forward<decltype(args)>(args)...);},std::move(host), std::move(service));
}// (boost) asio completion token integration
asio::io_context io_context;
asio::steady_timer steady_timer(io_context);steady_timer.expires_after(std::chrono::seconds(5));
steady_timer.async_wait(cti::use_continuable).then([] {// Is called after 5s});4.完整示例
continuable?是一個?header-only?庫(僅需包含頭文件,無需編譯庫本身),因此使用 CMake 配置項目時,只需指定頭文件路徑和 C++ 標準即可。以下是詳細的 CMake 配置步驟和示例:
1.假設項目結構如下(將?continuable?作為第三方庫放在項目中):
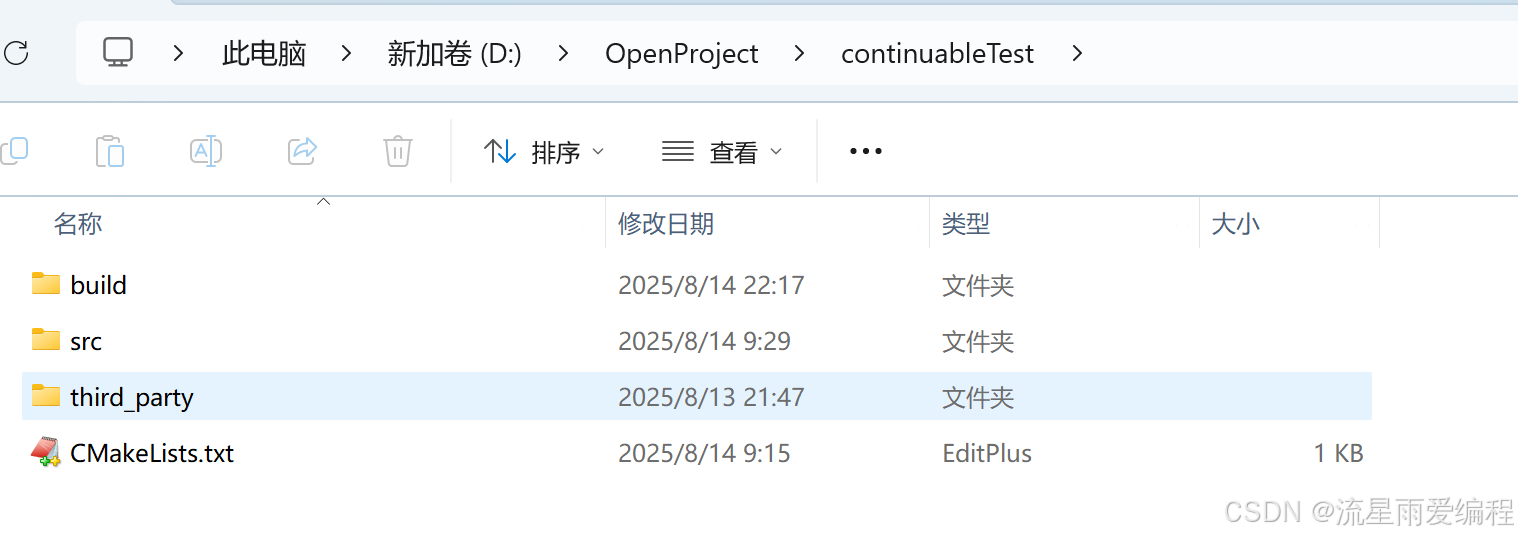
2.CMakeLists.txt 配置
核心配置包括:指定 C++ 標準(需 C++11 及以上)、添加?continuable?的頭文件路徑。
# 最低CMake版本要求
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10)# 項目名稱和版本
project(continuable_demo VERSION 1.0)# 指定C++標準(continuable需要C++11及以上)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11)
set(CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD_REQUIRED ON)
set(CMAKE_CXX_EXTENSIONS OFF) # 禁用編譯器擴展# 添加continuable的頭文件路徑
# 假設continuable放在third_party目錄下
#target_include_directories(continuable_demo
# PRIVATE
# ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/third_party/continuable/include
#)message(STATUS "continuable directories: ${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}")include_directories(${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/third_party/include${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/third_party/include/dep/function2/include
)# 添加源文件
add_executable(continuable_demosrc/main.cpp
)3.示例代碼(src/main.cpp)
編寫一個簡單的異步操作示例,驗證配置是否正確:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
// 引入continuable頭文件
#include "continuable/continuable.hpp"// 模擬異步操作:1秒后返回一個整數
auto async_operation(int value) {return cti::make_continuable<int>([value](auto&& promise) {// 在新線程中執行異步操作std::thread([value, promise = std::forward<decltype(promise)>(promise)]() mutable {std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(1)); // 模擬耗時操作promise.set_value(value * 2); // 異步操作結果}).detach();});
}int main() {std::cout << "開始異步操作..." << std::endl;// 鏈式調用異步操作async_operation(5).then([](int result) {std::cout << "第一步結果: " << result << "(5*2)" << std::endl;return async_operation(result); // 傳遞結果到下一個異步操作}).then([](int result) {std::cout << "第二步結果: " << result << "(10*2)" << std::endl;})/*.catch_([](const std::exception& e) {std::cerr << "錯誤: " << e.what() << std::endl;})*/;// 等待異步操作完成(實際項目中用事件循環替代)std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::seconds(3));return 0;
}4.編譯步驟
mkdir build && cd build
cmake .. # 生成Makefile
cmake --build . --config Debug # 編譯項目
.\Debug\continuable_demo # 運行程序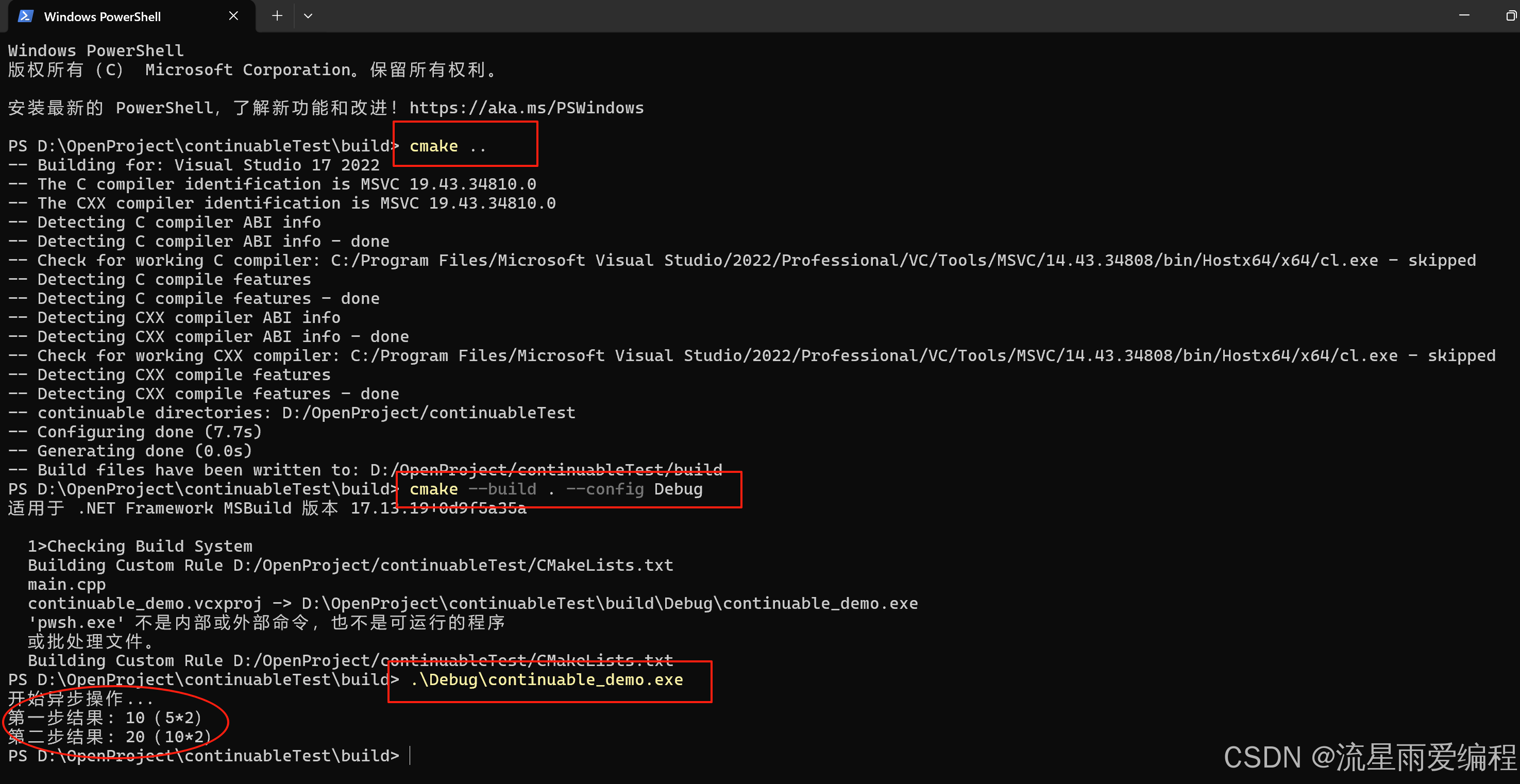
5.關鍵說明
1)header-only 特性
continuable?無需編譯為靜態庫或動態庫,只需在 CMake 中通過?target_include_directories?指定其頭文件路徑即可。
2)C++ 標準:
必須指定?CMAKE_CXX_STANDARD 11?或更高(如 C++14、C++17),否則會因語法不兼容導致編譯錯誤。
3)跨平臺兼容性
上述配置兼容 Windows(MSVC)、Linux(GCC/Clang)、macOS,只需確保編譯器支持 C++11 及以上標準。
6.完整源碼下載地址
通過網盤分享的文件:continuableTest.zip
鏈接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1MkrlvYChgIWr2boGnwD4_g?pwd=1234 提取碼: 1234
5.優勢與適用場景
- 簡化異步流程:將嵌套回調轉為線性鏈式調用,代碼更易讀、維護。
- 靈活組合:支持串行、并行等復雜異步工作流,滿足多任務依賴場景。
- 現代 C++ 友好:充分利用模板、lambda、移動語義等特性,類型安全且高效。
適用于需要處理大量異步操作的場景:網絡編程(如 HTTP 請求、RPC 調用)、文件 IO、異步數據庫操作等。
)

)




詳解)

)
)






)

