目錄
- 作業介紹
- 環境光貼圖預計算
- 傳輸項的預計算
- Diffuse unshadowed
- Diffuse shadowed
- Diffuse Inter-reflection(bonus)
- 實時球諧光照計算
GitHub主頁:https://github.com/sdpyy1
作業實現:https://github.com/sdpyy1/CppLearn/tree/main/games202
作業介紹
物體在不同光照下的表現不同,PRT(Precomputed Radiance Transfer) 是一個計算物體在不同光照下表現的方法。光線在一個環境中,會經歷反射,折射,散射,甚至還會物體的內部進行散射。為了模擬具有真實感的渲染結果,傳統的Path Tracing 方法需要考慮來自各個方向的光線、所有可能的傳播形式并且收斂速度極慢。PRT 通過一種預計算方法,該方法在離線渲染的 Path Tracing 工具鏈中預計算 lighting 以及 light transport 并將它們用球諧函數擬合后儲存,這樣就將時間開銷轉移到了離線中。最后通過使用這些預計算好的數據,我們可以輕松達到實時渲染嚴苛的時間要求,同時渲染結果可以呈現出全局光照的效果。
PRT 方法存在的限制包括:
? 不能計算隨機動態場景的全局光照
? 場景中物體不可變動
本次作業的工作主要分為兩個部分:cpp 端的離線預計算部分以及在 WebGL框架上使用預計算數據部分
PRT課上最終得出的結論是對渲染方程的計算,可以先把光照和其余部分分別計算球諧展開后系數相乘(針對BRDF是diffuse的情況),所以我們只需要針對光照算球諧展開的系數,然后針對其余部分算一個球諧展開的系數,傳遞給頂點著色器后相乘就是頂點的著色
環境光貼圖預計算
要做的就是把L(wi)項用球諧函數表示,因為球諧函數都一樣,不一樣的只有系數,所以只需要預計算出系數,系數求法如下,針對球諧函數的任何一項求他的系數都是算一個積分

根據作業提示,需要完成函數,輸入為天空盒的6個面圖片
std::vector<Eigen::Array3f> PrecomputeCubemapSH(const std::vector<std::unique_ptr<float[]>> &images,const int &width, const int &height,const int &channel){
下面這一步是把6張貼圖每個像素的方向向量都存起來了
std::vector<Eigen::Vector3f> cubemapDirs;cubemapDirs.reserve(6 * width * height);for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){Eigen::Vector3f faceDirX = cubemapFaceDirections[i][0];Eigen::Vector3f faceDirY = cubemapFaceDirections[i][1];Eigen::Vector3f faceDirZ = cubemapFaceDirections[i][2];for (int y = 0; y < height; y++){for (int x = 0; x < width; x++){float u = 2 * ((x + 0.5) / width) - 1;float v = 2 * ((y + 0.5) / height) - 1;Eigen::Vector3f dir = (faceDirX * u + faceDirY * v + faceDirZ).normalized();cubemapDirs.push_back(dir);}}}
接著對系數數組初始化
// 表示球諧系數的個數constexpr int SHNum = (SHOrder + 1) * (SHOrder + 1);std::vector<Eigen::Array3f> SHCoeffiecents(SHNum);for (int i = 0; i < SHNum; i++)SHCoeffiecents[i] = Eigen::Array3f(0);
最后遍歷每個方向向量進行計算系數
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){for (int y = 0; y < height; y++){for (int x = 0; x < width; x++){// TODO: here you need to compute light sh of each face of cubemap of each pixel// TODO: 此處你需要計算每個像素下cubemap某個面的球諧系數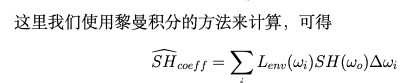Eigen::Vector3f dir = cubemapDirs[i * width * height + y * width + x];int index = (y * width + x) * channel;Eigen::Array3f Le(images[i][index + 0], images[i][index + 1],images[i][index + 2]);}}}

計算方法就是遍歷每一個像素,通過黎曼積分的方法來說,每個像素點都對每個球諧函數的系數有貢獻
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++){for (int y = 0; y < height; y++){for (int x = 0; x < width; x++){// TODO: here you need to compute light sh of each face of cubemap of each pixel// TODO: 此處你需要計算每個像素下cubemap某個面的球諧系數Eigen::Vector3f dir = cubemapDirs[i * width * height + y * width + x];int index = (y * width + x) * channel;// 當前像素的RGB值Eigen::Array3f Le(images[i][index + 0], images[i][index + 1],images[i][index + 2]);// 計算當前像素的面積float delta_wi = CalcArea(x, y, width, height);Eigen::Vector3d _dir(Eigen::Vector3d(dir[0], dir[1], dir[2]).normalized());//這里dir要變成Eigen::Vector3d類型// 計算當前像素點對每個基函數系數的黎曼積分求法的貢獻for(int l = 0;l < SHNum; l++){for(int m = -l; m <= l; m++){SHCoeffiecents[sh::GetIndex(l,m)] += Le * sh::EvalSH(l,m,_dir)*delta_wi;}}}}}
對于作業提到的伽馬矯正,可以參考我之前的博客伽馬矯正
傳輸項的預計算
對于漫反射傳輸項來說,分為 unshadowed, shadowed, interreflection 三
種情況,我們將分別計算這三種情況的漫反射傳輸球諧系數。
Diffuse unshadowed
這種情況下渲染方程的BRDF項為常數,此時渲染方程為

Li項已經處理掉了,就剩下max()項了

作業中只需要寫出transport部分在給定一個方向時的值
if (m_Type == Type::Unshadowed){// TODO: here you need to calculate unshadowed transport term of a given direction// TODO: 此處你需要計算給定方向下的unshadowed傳輸項球諧函數值return 0;}
這里就只剩一個點乘和max了
float dot_product = wi.dot(n);if (m_Type == Type::Unshadowed){// TODO: here you need to calculate unshadowed transport term of a given direction// TODO: 此處你需要計算給定方向下的unshadowed傳輸項球諧函數值return dot_product > 0 ? dot_product : 0;}
Indoor的數據
0.518558 0.510921 0.498186
-0.0139227 -0.0198673 -0.0233177
-0.0229861 -0.0361469 -0.0237983
0.0263383 0.0681837 0.0585552
-0.0508792 -0.0607283 -0.0570984
0.0515054 0.035726 0.0207611
0.0147266 0.0112063 -0.026747
0.00411617 0.0257427 0.0428588
0.0642155 0.0399902 0.0190308
每一行代表一個基函數的參數,可以理解為把原光照函數投影到某一個基函數后的RGB分量分別為多少
Diffuse shadowed
相對于unshadowed,就多出來一項Visibility
// 從頂點位置發射一條光線,與場景相交說明被遮擋了if(dot_product > 0.0f && !scene->rayIntersect(Ray3f(v, wi.normalized()))){return dot_product;}else{return 0.0f;}
當定義好函數后調用了
auto shCoeff = sh::ProjectFunction(SHOrder, shFunc, m_SampleCount);
這行代碼根據SH的階數、被展開的函數、采樣數來得到展開后SH的系數
到這里 光照項和轉移項都分別計算了它們的SH展開的系數并存儲在txt文件中(通過跑該程序)
7905
0.213508 0.153329 0.206834 -0.0845127 -0.060769 0.144391 0.0588847 -0.0591535 -0.0178413
0.219123 0.147477 0.190788 -0.134417 -0.0519802 0.135719 0.0171978 -0.101493 0.0164001
0.206635 0.160885 0.201914 -0.0758193 -0.0472086 0.167402 0.0471802 -0.052247 -0.00859244
0.185821 0.153003 0.162114 -0.119748 -0.0931989 0.143295 0.00899377 -0.0984071 -0.0184536
0.206635 0.160885 0.201914 -0.0758193 -0.0472086 0.167402 0.0471802 -0.052247 -0.00859244
每一行代表一個頂點的球諧展開系數。因為T部分不僅與入射方向有關,也與頂點的具體位置有關,所以每固定一個頂點,球諧展開系數都是不一樣的
Diffuse Inter-reflection(bonus)
這里就需要考慮光線的多次彈射,渲染方程變成

計算一個頂點的系數時,不僅考慮到來自環境光的光照,還考慮來自別的地方彈射過來的光的影響,仿照光線追蹤的寫法,從著色點射出采樣光線,若擊中物體,則把光線反過來求出它對著色點的貢獻(如果遞歸的寫就可以求出擊中物體的值,遞歸到最后一層就是本身著色點的值)
std::unique_ptr<std::vector<double>> computeInterreflectionSH(Eigen::MatrixXf* directTSHCoeffs, const Point3f& pos, const Normal3f& normal, const Scene* scene, int bounces)
{std::unique_ptr<std::vector<double>> coeffs(new std::vector<double>());coeffs->assign(SHCoeffLength, 0.0);if (bounces > m_Bounce)return coeffs;const int sample_side = static_cast<int>(floor(sqrt(m_SampleCount)));std::random_device rd;std::mt19937 gen(rd());std::uniform_real_distribution<> rng(0.0, 1.0);for (int t = 0; t < sample_side; t++) {for (int p = 0; p < sample_side; p++) {double alpha = (t + rng(gen)) / sample_side;double beta = (p + rng(gen)) / sample_side;double phi = 2.0 * M_PI * beta;double theta = acos(2.0 * alpha - 1.0);//這邊模仿ProjectFunction函數寫Eigen::Array3d d = sh::ToVector(phi, theta);const auto wi = Vector3f(d.x(), d.y(), d.z());double H = wi.normalized().dot(normal);Intersection its;if (H > 0.0 && scene->rayIntersect(Ray3f(pos, wi.normalized()), its)){MatrixXf normals = its.mesh->getVertexNormals();Point3f idx = its.tri_index;Point3f hitPos = its.p;Vector3f bary = its.bary;Normal3f hitNormal =Normal3f(normals.col(idx.x()).normalized() * bary.x() +normals.col(idx.y()).normalized() * bary.y() +normals.col(idx.z()).normalized() * bary.z()).normalized();auto nextBouncesCoeffs = computeInterreflectionSH(directTSHCoeffs, hitPos, hitNormal, scene, bounces + 1);for (int i = 0; i < SHCoeffLength; i++){auto interpolateSH = (directTSHCoeffs->col(idx.x()).coeffRef(i) * bary.x() +directTSHCoeffs->col(idx.y()).coeffRef(i) * bary.y() +directTSHCoeffs->col(idx.z()).coeffRef(i) * bary.z());(*coeffs)[i] += (interpolateSH + (*nextBouncesCoeffs)[i]) * H;}}}}for (unsigned int i = 0; i < coeffs->size(); i++) {(*coeffs)[i] /= sample_side * sample_side;}return coeffs;
}
for (int i = 0; i < mesh->getVertexCount(); i++){const Point3f& v = mesh->getVertexPositions().col(i);const Normal3f& n = mesh->getVertexNormals().col(i).normalized();auto indirectCoeffs = computeInterreflectionSH(&m_TransportSHCoeffs, v, n, scene, 1);for (int j = 0; j < SHCoeffLength; j++){m_TransportSHCoeffs.col(i).coeffRef(j) += (*indirectCoeffs)[j];}std::cout << "computing interreflection light sh coeffs, current vertex idx: " << i << " total vertex idx: " << mesh->getVertexCount() << std::endl;}
實時球諧光照計算
這里我不展示如何跑通代碼,只展示主要的邏輯點。跑通代碼可以參考博客:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/596050050
對于預計算數據使用就是在頂點著色器中,要求一個頂點的著色,就要把光照項的每一個系數與T項對應的系數相乘后相加即可
從下面代碼可以看出,三個顏色通道單獨計算
//prtVertex.glslattribute vec3 aVertexPosition;
attribute vec3 aNormalPosition;
attribute mat3 aPrecomputeLT;uniform mat4 uModelMatrix;
uniform mat4 uViewMatrix;
uniform mat4 uProjectionMatrix;
uniform mat3 uPrecomputeL[3];varying highp vec3 vNormal;
varying highp mat3 vPrecomputeLT;
varying highp vec3 vColor;float L_dot_LT(mat3 PrecomputeL, mat3 PrecomputeLT) {vec3 L_0 = PrecomputeL[0];vec3 L_1 = PrecomputeL[1];vec3 L_2 = PrecomputeL[2];vec3 LT_0 = PrecomputeLT[0];vec3 LT_1 = PrecomputeLT[1];vec3 LT_2 = PrecomputeLT[2];return dot(L_0, LT_0) + dot(L_1, LT_1) + dot(L_2, LT_2);
}void main(void) {// 無實際作用,避免aNormalPosition被優化后產生警告vNormal = (uModelMatrix * vec4(aNormalPosition, 0.0)).xyz;for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++){vColor[i] = L_dot_LT(aPrecomputeLT, uPrecomputeL[i]);}gl_Position = uProjectionMatrix * uViewMatrix * uModelMatrix * vec4(aVertexPosition, 1.0);
}
以R通道舉例


一行(頂點的系數)乘一列(環境光貼圖系數的R通道)結果作為著色點的R通道值



至于還有一個作業要做旋轉。
我的理解是如果環境光貼圖進行了旋轉,其實修改的就只是環境光貼圖的球諧展開的系數,其他的不會變,而且因為球諧函數的特性,很容易就能求旋轉后的系數。先理解了就行
---java版)









)
 ---- EGL)



阻止了未簽名的原生模塊(bcrypt_lib.node)加載)



