


專欄:JavaEE初階起飛計劃
個人主頁:手握風云
目錄
一、JUC的常見類
1.1. Callable接口
1.2.?ReentrantLock?
1.3. 信號量Semaphore
1.4.?CountDownLatch
二、線程安全的集合類
2.1.?多線程環境使用 ArrayList?
2.2. 多線程環境使用哈希表
一、JUC的常見類
1.1. Callable接口
????????Callable是一個interface,類似于Runnable,把線程封裝了?個"返回值",方便程序員借助多線程的方式計算結果。
? ? ? ? 下面一個場景:創建線程計算1+2+3+4+……+100。
? ? ? ? 第一種寫法:通過Runnable的方案,需要借助成員變量sum,耦合性比較高。
public class Demo1 {private static int sum = 0;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {int ret = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {ret += i;}sum = ret;});t1.start();t1.join();System.out.println(sum);}
}? ? ? ? 第二種寫法:使用Callable版本。
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;public class Demo2 {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {Callable<Integer> callable = new Callable<>(){@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {int ret = 0;for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {ret += i;}return ret;}};FutureTask<Integer> task = new FutureTask<Integer>(callable);Thread t = new Thread(task);t.start();System.out.println(task.get());}
}? ? ? ? Callable帶有泛型參數,可以作為返回值計算結果。我們還需要重寫里面的call()方法來計算結果,再把callable利用FutureTask包裝一下,然后創建線程,將task傳入線程的構造方法中。在主線程中調用task.get(),能夠阻塞等待新線程計算完畢,并獲取到FutureTask中的結果。
????????對于FutureTask的理解,FutureTask是 Java 并發編程中異步任務與結果獲取的橋梁,通過封裝狀態管理、線程同步和異常處理,顯著簡化了異步編程模型。我們可以想象去吃麻辣燙,當餐點好后,后廚就開始做了,同時前臺會給你一張 "小票",這個小票就是FutureTask,后面我們可以隨時憑這張小票去查看自己的這份麻辣燙做出來了沒。
1.2.?ReentrantLock?
????????ReentrantLock也是可重入鎖,"Reentrant" 這個單詞的原意就是 "可重入"?。與synchronized定位類似,都是用來實現互斥效果,保證線程安全。
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;public class Demo3 {private static int count = 0;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {ReentrantLock locker = new ReentrantLock();Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 50_000; i++) {locker.lock();count++;locker.unlock();}});Thread t2 = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 50_000; i++) {locker.lock();count++;locker.unlock();}});t1.start();t2.start();t1.join();t2.join();System.out.println(count);}
}????????ReentrantLock和synchronized 的區別:
- synchronized 是一個關鍵字,是 JVM 內部實現的。ReentrantLock是標準庫的一個類, 在 JVM外實現的。
- synchronized使用時不需要手動釋放鎖,ReentrantLock 使用時需要手動釋放,使用起來更靈活,但是也容易遺漏unlock。
- synchronized 在申請鎖失敗時,會死等,ReentrantLock可以通過trylock的方式等待一段時間就放棄。
- synchronized是非公平鎖,ReentrantLock默認是非公平鎖。可以通過構造方法傳入一個true 開啟公平鎖模式。
- 更強大的喚醒機制,synchronized 是通過 Object 的 wait / notify 實現等待-喚醒. 每次喚醒的是一個隨機等待的線程。ReentrantLock 搭配 Condition 類實現等待-喚醒, 可以更精確控制喚醒某個指定的線程。
1.3. 信號量Semaphore
????????信號量,用來表示 "可用資源的個數",本質上就是一個計數器。我們申請資源(P操作),就會使計數器-1;釋放資源(V操作),就會使計數器+1。上述+1、-1的操作都是原子的。如果計數器為0,再去申請資源,就會造成阻塞。舉個例子,我們開車尋找停車場時,開進去,電子牌上的空閑車位就會-1,開出去,電子牌上的空閑車位就會+1。如果沒有空閑車位,就得停車等待或者尋找其他停車場。
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 初始許可數為3,也就是“可用資源”的個數Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);semaphore.acquire();System.out.println("執行P操作");semaphore.acquire();System.out.println("執行P操作");semaphore.acquire();System.out.println("執行P操作");semaphore.release();}
}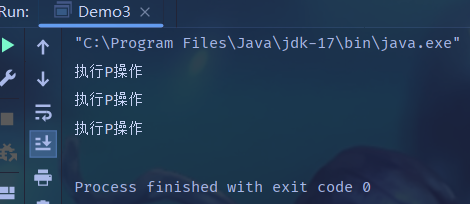
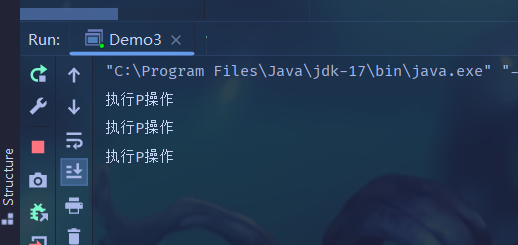
? ? ? ? 上面初始值設為3,當我們申請4次之后,就會產生阻塞。
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;public class Demo3 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {// 初始許可數為3,也就是“可用資源”的個數Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(3);semaphore.acquire();System.out.println("執行P操作");semaphore.acquire();System.out.println("執行P操作");semaphore.acquire();System.out.println("執行P操作");semaphore.acquire();System.out.println("執行P操作");semaphore.release();}
}
? ? ? ? 信號量相當于鎖概念的延伸。換句話說,鎖也可以看作時初始值為1的特殊信號量。如果我們想要編寫的多線程代碼不允許使用鎖,也可以使用信號量保證線程安全。
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;public class Demo4 {private static int count = 0;public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1);// 創建一個線程t1,該線程執行的任務是:循環50_000次,每次執行時獲取semaphore的許可,然后count加1,最后釋放semaphore的許可Thread t1 = new Thread(() ->{for (int i = 0; i < 50_000; i++) {try {// 獲取semaphore的許可semaphore.acquire();// count加1count++;// 釋放semaphore的許可semaphore.release();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}});Thread t2 = new Thread(() ->{for (int i = 0; i < 50_000; i++) {try {semaphore.acquire();count++;semaphore.release();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}});t1.start();t2.start();t1.join();t2.join();System.out.println(count);}
}1.4.?CountDownLatch
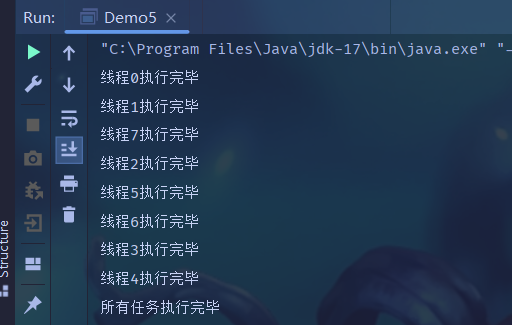
? ? ? ? CountDownLatch是Java 并發包中的同步輔助工具,用于協調多個線程的執行順序,同時等待多個任務執行結束。比如在跑步?賽中,8個選?依次就位,哨聲響才同時出發;所有選?都通過終點,才能公布成績。
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;public class Demo5 {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(8);for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {int id = i;Thread t = new Thread(() -> {// 通過sleep模擬try {Thread.sleep(1_000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("線程" + id + "執行完畢");// 計數器減一,相當于一個運動員到達終點latch.countDown();});t.start();}// 主線程通過await()方法等待所有線程結束latch.await();System.out.println("所有任務執行完畢");}
}
? ? ? ? CountDownLatch通常用于一些特場景:在開發工作中,把一個大任務拆分成多個子任務,通過多線程并發執行,把所有任務完成之后才能進入下一階段。
二、線程安全的集合類
2.1.?多線程環境使用 ArrayList?
- 自己使用同步機制 (synchronized 或者 ReentrantLock)?
- Collections.synchronizedList(new ArrayList)。synchronizedList 是標準庫提供的一個基于 synchronized 進行線程同步的 List. synchronizedList 的關鍵操作上都帶有 synchronized?。
2.2. 多線程環境使用哈希表
????????HashMap 本身不是線程安全的,在多線程環境下可以使用Hashtable?或者ConcurrentHashMap。而Hashtable類似于Vector,在方法名上加上synchronized修飾,所以不推薦使用。
import java.util.Hashtable;public class Demo6 {public static void main(String[] args) {Hashtable<String, String> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();hashtable.put("111","aaa");hashtable.get("111");}
}public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {……
}public synchronized V get(Object key) {……
}? ? ? ? ConcurrentHashMap最大的調整就是針對鎖的粒度進行可優化。對于Hashtable來說,針對this加鎖,任何線程,只要操作這個哈希表都可能觸發鎖競爭。
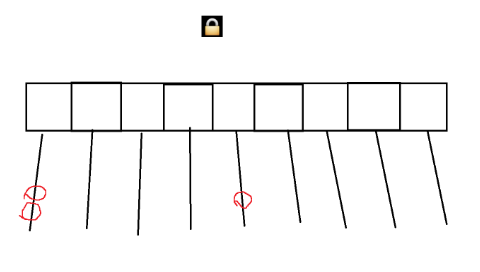
? ? ? ? 兩個線程針對同一變量進行修改才會引發線程安全,所以針對哈希表來說,如果兩個線程的修改是在不同鏈表上,線程就是安全的。針對同一鏈表時,才引入阻塞。在ConcurrentHashMap中,每個鏈表都有一把鎖,稱為“鎖桶”。由于是不同的鎖對象,出發鎖競爭的概率就會降低。
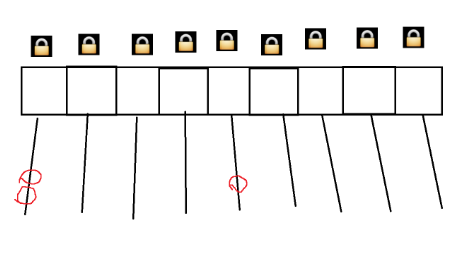
? ? ? ? 在實際中,一個哈希表的桶的個數非常多,針對哈希表的操作,大部分是分布在不同桶上,觸發鎖競爭的概率可以忽略不計。
? ? ? ? ConcurrentHashMap擴容的時候,采取“化整為零”的方案。因為如果哈希表原來的元素很多,擴容會造成很大的開銷。為了保證線程安全,必須得加鎖,如果全部進行搬運,持有鎖的時間比較長,其他線程就無法正常使用哈希表了。










畫刷 QBrush:刷子只涉及填充顏色,線型,填充圖片,以及變換矩陣這幾個屬性,附源代碼帶注釋。)







![[硬件電路-123]:模擬電路 - 信號處理電路 - 常見的高速運放芯片、典型電路、電路實施注意事項](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[硬件電路-123]:模擬電路 - 信號處理電路 - 常見的高速運放芯片、典型電路、電路實施注意事項)
