昨天有位兄臺給我發了個文件,是下面這個樣子的:
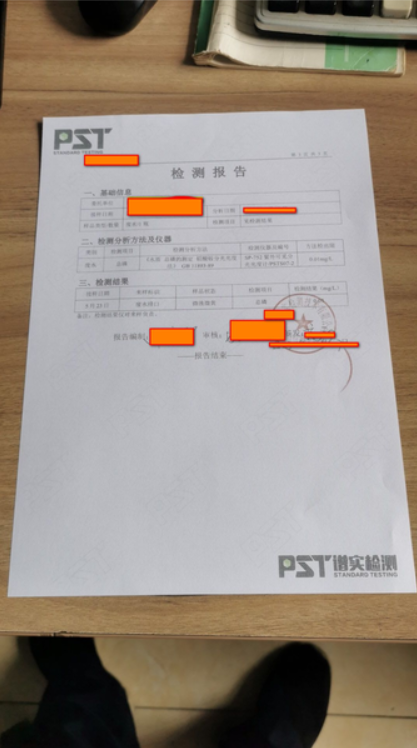
那一雙小腳既沒有裹成三寸金蓮,又沒有黑絲,這圖片肯定不符合我的要求。我要的是這個樣子的好不好:

讓他拿掃描儀重新給我規規矩矩掃一個發過來?他要能用掃描儀還用手機拍個這個東西給我?好在我有巨蟒與AI,對AI說:給我生成一個Python程序,可以打開一張圖片并顯示在圖片容器中,在圖片上點擊四個角點,對四個角點先按x位置升序排序,取前兩個點為右側點,后兩個點為左側點,再將左右側兩組點分別按y位置升序排序,前面的為上部點,后面的為下部點,將這四個點按【左上,右上,右下,左下】的秩序構造一個列表。求出這四個點的minX,maxX,minY,maxY,按照[[min_x,min_y],[max_x,min_y],[max_x,max_y],[min_x,max_y]]構造一個列表,將圖片中【左上,右上,右下,左下】四個點構成的四邊形范圍內的圖像進行透視變換,變換為由[[min_x,min_y],[max_x,min_y],[max_x,max_y],[min_x,max_y]]這四個點構成的矩形圖象。
幾乎任意一個AI都能夠給出一個基本能夠實現功能的代碼,然后可以繼續對AI增加要求,例如組裝出GUI界面、要求使用自己熟悉的工具庫、對圖片進行縮放顯示之類,試著運行一下,自己或者讓AI更正一下錯誤,還不到一小時就可以弄出下面的程序:(0728修改:增加微調角點位置功能)
# pip install pillow opencv-python numpy
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import filedialog, messagebox
from tkinter import ttkfrom PIL import Image, ImageTk
import cv2
import numpy as npclass ImageCorrectorApp:def __init__(self, root):self.root = rootself.root.title("圖片校正工具")self.img_canvas_size = 800 # 圖片顯示容器尺寸self.max_show_size = 800 # 校正后圖片最大顯示尺寸# 設置ttk主題和樣式style = ttk.Style()# 若系統支持clam/alt/vista/xpnative等主題可選themes = style.theme_names()if 'clam' in themes:style.theme_use('clam')style.configure('TFrame', background='#f8f9fa')style.configure('TLabel', background='#f8f9fa', font=('微軟雅黑', 11))style.configure('TButton', font=('微軟雅黑', 11, 'bold'), padding=6)style.configure('Warn.TLabel', foreground='#d9534f', font=('微軟雅黑', 10, 'bold'), background='#f8f9fa')# 圖片相關變量self.original_img = None # 原始PIL圖片self.display_img = None # 當前顯示的PIL圖片self.tk_img = None # Tkinter顯示用圖片self.scale = 1.0 # 當前縮放比例(放大/縮小按鈕用)self.display_scale = 1.0 # 打開圖片時的等比例縮放因子self.points = [] # 用戶點擊的點(用于校正)self.active_idx = None # 當前激活點下標self.corrected_img = None # 校正后的PIL圖片# 主framemain_frame = ttk.Frame(root, padding=10)main_frame.pack(padx=10, pady=10)# 圖片顯示區及滾動條img_frame = ttk.Frame(main_frame)img_frame.grid(row=0, column=0)self.canvas = tk.Canvas(img_frame, width=self.img_canvas_size, height=self.img_canvas_size, bg='#e9ecef', highlightthickness=2, highlightbackground='#adb5bd')self.canvas.grid(row=0, column=0, sticky='nsew')# 水平和垂直滾動條self.hbar = ttk.Scrollbar(img_frame, orient=tk.HORIZONTAL, command=self.canvas.xview)self.hbar.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky='ew')self.vbar = ttk.Scrollbar(img_frame, orient=tk.VERTICAL, command=self.canvas.yview)self.vbar.grid(row=0, column=1, sticky='ns')self.canvas.config(xscrollcommand=self.hbar.set, yscrollcommand=self.vbar.set)self.canvas.bind("<Button-1>", self.on_canvas_click) # 綁定鼠標點擊事件self.root.bind("<Up>", self.on_key_press)self.root.bind("<Down>", self.on_key_press)self.root.bind("<Left>", self.on_key_press)self.root.bind("<Right>", self.on_key_press)# 右側按鈕區right_frame = ttk.Frame(main_frame)right_frame.grid(row=0, column=1, sticky='nw', padx=10, rowspan=2)# 用Canvas模擬綠色圓角矩形邊框的Labellabel_canvas = tk.Canvas(right_frame, width=110, height=190, bg='#f8f9fa', highlightthickness=0)label_canvas.pack(pady=8) # 畫綠色圓角矩形def draw_round_rect(canvas, x1, y1, x2, y2, radius=12, **kwargs):points = [x1+radius, y1,x2-radius, y1,x2, y1,x2, y1+radius,x2, y2-radius,x2, y2,x2-radius, y2,x1+radius, y2,x1, y2,x1, y2-radius,x1, y1+radius,x1, y1]return canvas.create_polygon(points, smooth=True, **kwargs)draw_round_rect(label_canvas, 2, 2, 108, 188, radius=14, outline='#28a745', width=2, fill='#f8f9fa')# 繪制文字label_canvas.create_text(10, 10, anchor='nw', text="打開圖片后點擊圖片選擇四個角點進行校正。 \可以使用上下左右箭頭對角點位置進行微調。", fill='#f00', font=('微軟雅黑', 12), width=90)ttk.Button(right_frame, text="撤銷最后選點", width=10, command=self.reset_point, style='TButton').pack(pady=8)ttk.Button(right_frame, text="放大圖片", width=10, command=self.zoom_in, style='TButton').pack(pady=8)ttk.Button(right_frame, text="縮小圖片", width=10, command=self.zoom_out, style='TButton').pack(pady=8)# 下方按鈕區bottom_frame = ttk.Frame(main_frame)bottom_frame.grid(row=1, column=0, sticky='sew', padx=10, pady=10)ttk.Button(bottom_frame, text="打開圖片", width=12, command=self.open_image, style='TButton').pack(side='left', expand=True, padx=8)ttk.Button(bottom_frame, text="校正圖片", width=12, command=self.correct_image, style='TButton').pack(side='left', expand=True, padx=8)ttk.Button(bottom_frame, text="保存圖片", width=12, command=self.save_image, style='TButton').pack(side='left', expand=True, padx=8)def open_image(self):# 打開圖片文件,按容器等比例縮放顯示file_path = filedialog.askopenfilename(filetypes=[("Image files", "*.jpg *.png *.jpeg")])if not file_path:returnself.original_img = Image.open(file_path).convert("RGB")w, h = self.original_img.sizescale = min(self.img_canvas_size / w, self.img_canvas_size / h, 1.0)self.display_scale = scaleif scale < 1.0:self.display_img = self.original_img.resize((int(w * scale), int(h * scale)), Image.LANCZOS)else:self.display_img = self.original_img.copy()self.scale = 1.0self.points.clear()self.corrected_img = Noneself.show_image()def reset_point(self):if self.original_img is None:returnif len(self.points) > 0:# 清除保存的最后一個角點self.points.pop()self.show_image()def show_image(self):# 在canvas上顯示圖片,并繪制用戶點擊的點和線if self.display_img is None:returnw, h = self.display_img.sizeself.tk_img = ImageTk.PhotoImage(self.display_img)self.canvas.config(scrollregion=(0, 0, w, h))self.canvas.delete("all")self.canvas.create_image(0, 0, anchor='nw', image=self.tk_img)# 自動檢測角點并用黃色圓圈標記。經試驗,這個功能作用不大,取消# img_np = np.array(self.display_img)# if img_np.ndim == 3 and img_np.shape[2] == 3:# gray = cv2.cvtColor(img_np, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)# else:# gray = img_np# corners = cv2.goodFeaturesToTrack(gray, maxCorners=100, qualityLevel=0.01, minDistance=10)# if corners is not None:# for pt in corners:# x, y = pt.ravel()# self.canvas.create_oval(x-4, y-4, x+4, y+4, outline='yellow', width=2)# 繪制點和線for i, (x, y) in enumerate(self.points):if self.active_idx is not None and i == self.active_idx:# 激活點用藍色邊框高亮self.canvas.create_oval(x-7, y-7, x+7, y+7, outline='blue', width=3)# 繪制角點self.canvas.create_oval(x-5, y-5, x+5, y+5, fill='red', outline='red')if i > 0:x0, y0 = self.points[i-1]# 繪制新選擇的角點與前一個角點之間的連線self.canvas.create_line(x0, y0, x, y, fill='red', width=2)if len(self.points) == 4:# 繪制最后一個角點與第一個角點之間的連線x0, y0 = self.points[0]x3, y3 = self.points[3]self.canvas.create_line(x3, y3, x0, y0, fill='red', width=2)def zoom_in(self):# 放大圖片,每次放大10%if self.display_img is None:returnself.scale *= 1.1w, h = self.original_img.sizescale = self.display_scale * self.scaleself.display_img = self.original_img.resize((int(w * scale), int(h * scale)), Image.LANCZOS)# 點坐標同步放大self.points = [(int(x*1.1), int(y*1.1)) for (x, y) in self.points]self.show_image()def zoom_out(self):# 縮小圖片,每次縮小10%if self.display_img is None:returnself.scale /= 1.1w, h = self.original_img.sizescale = self.display_scale * self.scaleself.display_img = self.original_img.resize((int(w * scale), int(h * scale)), Image.LANCZOS)# 點坐標同步縮小self.points = [(int(x/1.1), int(y/1.1)) for (x, y) in self.points]self.show_image()def on_key_press(self, event):# 方向鍵移動激活點if self.active_idx is None or not self.points:returnx, y = self.points[self.active_idx]if event.keysym == 'Up':y = max(0, y - 1)elif event.keysym == 'Down':y = y + 1elif event.keysym == 'Left':x = max(0, x - 1)elif event.keysym == 'Right':x = x + 1self.points[self.active_idx] = (x, y)self.show_image()def on_canvas_click(self, event):# 支持激活點和點選邏輯if self.display_img is None:returnx = self.canvas.canvasx(event.x)y = self.canvas.canvasy(event.y)click = (int(x), int(y))# 判斷是否點擊到已有點idx_near = Nonefor idx, (px, py) in enumerate(self.points): # 計算點擊位置與已有角點之間的距離dist = ((px - click[0]) ** 2 + (py - click[1]) ** 2) ** 0.5if dist < 8: # 距離在8像素內算點擊到角點idx_near = idx# 點中了已有角點if idx_near is not None:self.active_idx = idx_nearself.show_image()return# 未點中已有角點,若點數<4,新增點并激活if len(self.points) < 4:self.points.append(click)self.active_idx = len(self.points) - 1self.show_image()return# 點數已滿4,且未點中已有點,不做操作def correct_image(self):# 校正圖片,將四邊形區域映射為矩形if self.original_img is None or len(self.points) != 4:messagebox.showwarning("提示", "請先選擇圖片并點擊4個點")return# 將顯示坐標還原為原圖坐標pts = np.array(self.points, dtype=np.float32) / (self.display_scale * self.scale)# 1. 按x排序,分左右兩組idx = np.argsort(pts[:, 0])left_pts = pts[idx[:2]]right_pts = pts[idx[2:]]# 2. 左右組分別按y排序left_pts = left_pts[np.argsort(left_pts[:, 1])]right_pts = right_pts[np.argsort(right_pts[:, 1])]# 3. 按左上、右上、右下、左下排列原始點位ordered_src = np.array([left_pts[0], # 左上right_pts[0], # 右上right_pts[1], # 右下left_pts[1], # 左下], dtype=np.float32)# 4. 目標點直接用x/y的min/max,按左上、右上、右下、左下排列min_x = np.min(pts[:, 0])max_x = np.max(pts[:, 0])min_y = np.min(pts[:, 1])max_y = np.max(pts[:, 1])ordered_dst = np.array([[min_x, min_y], # 左上[max_x, min_y], # 右上[max_x, max_y], # 右下[min_x, max_y], # 左下], dtype=np.float32)# 透視變換img_cv = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(self.original_img), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)# 計算透視變換矩陣M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(ordered_src, ordered_dst)# 應用透視變換warped = cv2.warpPerspective(img_cv, M, (self.original_img.width, self.original_img.height))# 裁剪到目標矩形區域cropped = warped[int(min_y):int(max_y), int(min_x):int(max_x)]warped_pil = Image.fromarray(cv2.cvtColor(cropped, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB))self.corrected_img = warped_pil# 校正結果縮放顯示show_w, show_h = warped_pil.sizescale = min(self.max_show_size / show_w, self.max_show_size / show_h, 1.0)if scale < 1.0:warped_pil = warped_pil.resize((int(show_w * scale), int(show_h * scale)), Image.LANCZOS)# 彈窗顯示校正后圖片win = tk.Toplevel(self.root)win.title("校正后圖片")tk_img = ImageTk.PhotoImage(warped_pil)label = tk.Label(win, image=tk_img)label.image = tk_imglabel.pack()def save_image(self):# 保存校正后的圖片if self.corrected_img is None:messagebox.showwarning("提示", "沒有可保存的校正圖片")returnfile_path = filedialog.asksaveasfilename(defaultextension=".png", filetypes=[("PNG文件", "*.png")])if file_path:self.corrected_img.save(file_path, "PNG")messagebox.showinfo("保存成功", f"圖片已保存到\n{file_path}")if __name__ == "__main__":root = tk.Tk()# 設置窗體初始位置居中,距上100pxscreen_w = root.winfo_screenwidth()screen_h = root.winfo_screenheight()win_w = 980win_h = 900x = (screen_w - win_w) // 2y = 50root.geometry(f"{win_w}x{win_h}+{x}+{y}")app = ImageCorrectorApp(root)root.mainloop()AI為代碼生成了注釋,其實最關鍵的就是提示詞里提到的構造出原始四邊形與目標圖像矩形的角點一一映射的思路,至于透視變換的矩陣運算,可以直接調用OpenCV的API接口。程序運行界面如下:
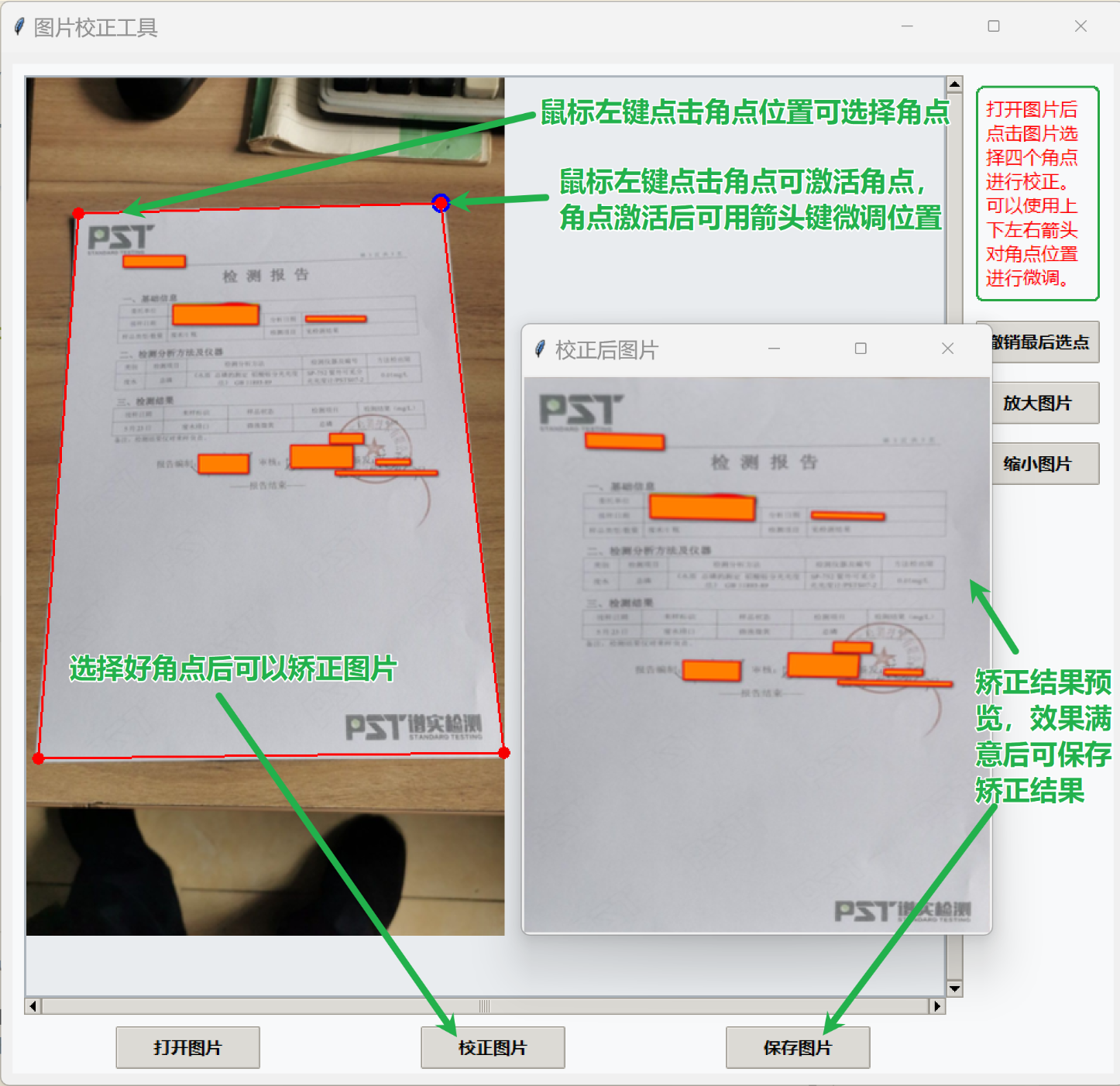
AI時代就是好,真正做到了讓人基本上只負責構思與理解AI代碼的邏輯以及修改一些小錯誤,敲字和記憶知識都由AI負責,沒有AI上面的程序恐怕要花掉我半天還不一定有這么完善。
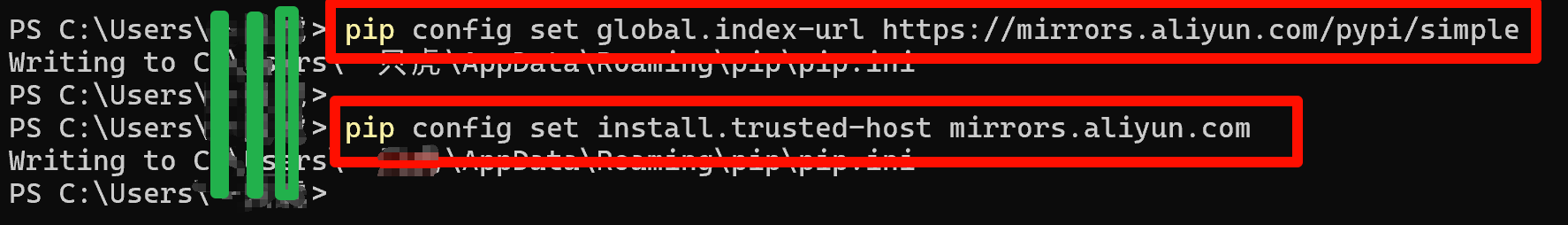
附:使用命令行將pip安裝源設置為阿里云鏡像:
pip config set global.index-url https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple?
pip config set install.trusted-host mirrors.aliyun.com





)

 安卓虛擬機 Android模擬器 的救命稻草(下載安裝指南))
)







)


行為型:中介者模式詳解)