一、基礎函數
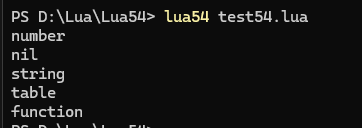
1.type(value)??
返回值的類型(如 "nil", "number", "string", "table", "function" 等)。
代碼測試:
a = 0
print(type(a))
a = nil
print(type(a))
a = "aaaaaaaa"
print(type(a))
a = {2,3,54}
print(type(a))
a = function() print("hello") end
print(type(a))?結果:
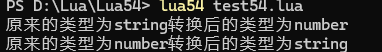
??2.tostring(value) / tonumber(value)??
類型轉換:將值轉為字符串或數字。
代碼測試:
a = "123"
b = tonumber(a)
print("原來的類型為"..type(a).."轉換后的類型為"..type(b))
a = 122321312
b = tostring(a)
print("原來的類型為"..type(a).."轉換后的類型為"..type(b))結果:
?
?注:lua輸出到控制臺亂碼時,需要將lua文件的編碼格式設置為GBK格式
![]()
3.??assert(condition, message)??
斷言:若條件為假,拋出錯誤并附帶消息。
代碼測試:
a = false
assert(a,"這是一個錯誤消息")結果:
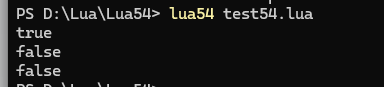
4.??rawequal(a, b)??
嚴格比較兩個值是否相等(忽略元表的 __eq 方法)。
代碼測試:
a = 10
b = 10
c = 11
d = "cccc"
print(rawequal(a,b))
print(rawequal(c,a))
print(rawequal(d,a))結果:
5.rawget??(table,key)
??作用??:直接獲取表中指定鍵的值,(忽略元表的 __index 方法)?。
代碼測試:
local t = {}
local mt = {__index = function() print("調用 __index 元方法")return "默認值"end
}
setmetatable(t, mt)print(t["不存在鍵"]) --> 輸出:"調用 __index 元方法" → "默認值"
print(rawget(t, "不存在鍵")) --> 輸出:nil(直接獲取表中的值,不觸發元方法)結果:?

6.rawset??(table,key,value)??
作用??:直接設置表中指定鍵的值,??(忽略元表的 __newindex方法)。
代碼測試:
local t = {}
local mt = {__newindex = function() print("調用 __newindex 元方法,拒絕寫入!")return -- 阻止寫入end
}
setmetatable(t, mt)t["新鍵"] = 10 --> 輸出:"調用 __newindex 元方法,拒絕寫入!"
print(t["新鍵"]) --> 輸出:nilrawset(t, "新鍵", 10) --> 繞過 __newindex,直接寫入表的底層存儲
print(t["新鍵"]) --> 輸出:10?結果:

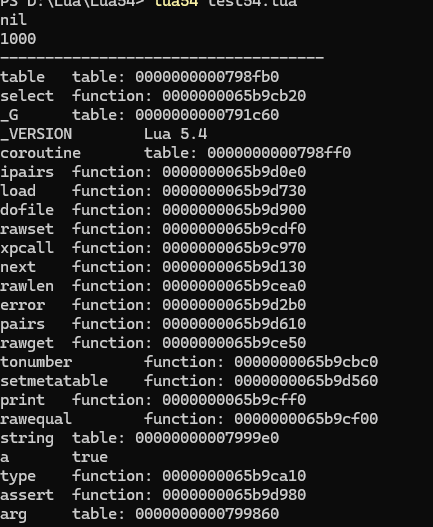
7.??_G??
全局變量表(直接讀寫全局變量)
測試代碼:
print(_G.myvalue)
_G.myvalue = 1000
print(_G.myvalue)print("------------------------------------") for key, value in pairs(_G) doprint(key, value)
end結果:
?
二、字符串處理
1.??string.sub(s, start, end)??
截取子字符串(支持負數索引)。
代碼測試:
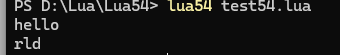
s = "hello world"
print(string.sub(s,1,5))
print(string.sub(s,-3,-1))結果:
注意:

使用負索引時,開始索引要設置為較小的負索引,結束索引使用較大的負索引
2.string.find(s, pattern)??
查找匹配模式的子串,返回起止位置。
代碼測試:
s = "hello world"
print(string.find(s,"world"))結果:
![]()
3.string.match(s, pattern)??
返回第一個匹配模式的子串(支持捕獲組)。
代碼測試:
s = "hello world"
print(string.match(s,"world1"))
print(string.match(s,"world"))
print(string.match(s,"llo wor"))結果:

4.??string.gsub(s, pattern, replace)??
全局替換匹配的子串(返回新字符串和替換次數)。
代碼測試:
s = "hello world"
print(string.gsub(s,"ll",2))結果:
![]()
5.string.format(format, ...)??
格式化字符串(類似 C 的 printf)。
代碼測試:
print(math.pi)
print(string.format("PI: %.2f", math.pi))結果:

三、表操作
1.??table.insert(t, [pos,] value)??
插入元素到數組末尾或指定位置。
代碼測試:
local t = {1, 2}
table.insert(t, 3) --> {1, 2, 3}
table.insert(t, 2, 99) --> {1, 99, 2, 3}for key, value in pairs(t) doprint(key, value)
end結果:

2.table.remove(t, [pos])??
刪除并返回數組末尾或指定位置的元素。
代碼測試:
local t = {1, 2, 3}
table.remove(t) --> 3,t 變為 {1, 2}for key, value in pairs(t) doprint(key, value)
end結果:?

3.table.concat(t, [sep], [i], [j])??
將數組元素連接為字符串(默認分隔符為空)。
代碼測試:
local t = {"a", "b", "c"}
print(table.concat(t, "-")) --> "a-b-c"結果:
![]()
4.table.sort(t, [comp_func])??
對數組排序(可自定義比較函數)。
代碼測試:
local t = {3, 1, 4}
table.sort(t) --> {1, 3, 4}
for key, value in pairs(t) doprint(key, value)
end結果:

5.??#t 操作符??
返回數組的連續部分長度(如果索引不連續則停止)。
代碼測試:
local t = {1, 2, [5] = 3,[6] = 4}
print("t len = "..#t) local t1 = {1, 2, ["3"] = 3,[7] = 4}
print("t1 len = "..#t1) local t2 = {1, 2, nil,3,[6] = 4}
print("t2 len = "..#t2) local t3 = {1, 2, nil,nil,4}
print("t3 len = "..#t3) local t4 = {["1"] = 1, ["xxx"] = 2, nil,nil,["ccc"] = 4}
print("t4 len = "..#t4) local t5 = {["1"] = 1, ["xxx"] = 2, nil,nil,["ccc"] = 4,1,2,3}
print("t5 len = "..#t5) local t6 = {["1"] = 1, ["xxx"] = 2, ["ccc"] = 4,1,2,3}
print("t6 len = "..#t6) 結果:
?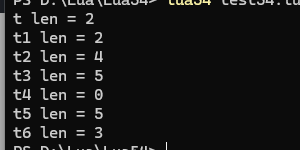
注:如果table中有顯示聲明為nil的元素且還有索引連續的元素,則#t會將顯示聲明為nil的元素數量也加會到返回的長度中,如果只有顯示聲明為nil的元素沒有索引連續的元素,則#t返回0,
四、模塊與包管理
1.require(modname)??
加載模塊(優先從 package.loaded 緩存中讀取)。
新建一個lua文件
 添加代碼:?
添加代碼:?
local M = {}
function M.say_hello()print("Hello from mymodule!")
end
return M測試代碼:?
print(require("testlua2"))結果:?
![]()
??2.package.loaded[modname]
已加載模塊的緩存表。
測試代碼:
require("testlua2")
print(package.loaded["testlua2"])結果:?
![]()
五、數學庫
1.math.floor(x) / math.ceil(x)??
向下/向上取整。
測試代碼:
print(math.floor(3.9)) --> 3
print(math.ceil(3.1)) --> 4結果:

2.math.random([m [, n]])??
生成隨機數(需先調用 math.randomseed)。
測試代碼:
math.randomseed(os.time())
print("生成的隨機數為:"math.random(1, 6)) -- 1~6 的隨機整數結果:?
![]()
3.math.abs(x) / math.max(x, ...) / math.min(x, ...)??
絕對值、最大值、最小值。
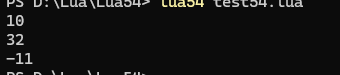
測試代碼:
print(math.abs(-10))
print(math.max(10, 20,-11,20,32))
print(math.min(10, 20,-11,20,32))結果:
?
??4.math.pi / math.sin(x) / math.cos(x)?? / math.tan(x)
數學常量及三角函數。
測試代碼:
print(math.pi)
print(math.sin(math.pi/2))
print(math.cos(math.pi/2))
print(math.tan(math.pi/2))結果:

六、操作系統庫
??1.os.time([table])??
返回當前時間戳或根據表生成時間戳。
測試代碼:
print(os.time())
print(os.time(os.date("*t", os.time())))結果:

2.??os.date([format [, time]])??
格式化時間戳為字符串(如 os.date("%Y-%m-%d"))。
測試代碼:
local time_table = os.date("*t", os.time()) -- 返回table格式時間
print(string.format("當前時間: %d年%d月%d日", time_table.year, time_table.month, time_table.day))????結果:

3.??os.execute(command)??
執行系統命令(如 os.execute("ls"))。
測試代碼:
--os.execute("sleep 1") -- Linux/macOS
os.execute("timeout 1") -- Windows
print("執行完成")結果:

4.??os.getenv(varname)??
獲取環境變量。
測試代碼:
local path = os.getenv("PATH")
print("系統PATH變量:", path)結果:

七、文件 I/O
1.io.open(filename, mode)??
打開文件,返回文件句柄(模式如 "r", "w", "a")。
測試代碼:
local file = io.open("data.txt", "r")
print(file)????結果:
![]()
注:
“r”:讀取模式(默認);
“w”:寫入模式;
“a”:附加模式;
“r+”: 更新模式,保留所有之前的數據;
“w+”:更新模式,之前的所有數據都被擦除;
“a+”:追加更新模式,保留之前的數據, 只允許在 file 末尾寫入。
2.?file:read(format)??
讀取文件內容(如 "*a" 讀取全部內容)。
新建一個data.txt文本文件,并在其中寫入一點文字

測試代碼:
local file = io.open("data.txt", "r")if file thenlocal data = file:read("*a")print(data)file:close()
end結果:
![]()
3.??file:write(...)??
寫入文件。
測試代碼:
io.write("Hello", " ", "World\n")結果:
![]()
4.??io.stdin / io.stdout / io.stderr??
標準輸入/輸出/錯誤流。
測試代碼:
-- 示例:讀取一行輸入
io.stdout:write("請輸入你的名字: ")
io.stdout:flush() -- 確保提示信息立即顯示
local name = io.stdin:read("*l") -- 讀取一行
if #name <= 3 thenio.stderr:write("錯誤:名字必須大于3個字符!\n")io.stderr:flush()return
end
print("你好," .. name)??????結果:

八、協程
1.coroutine.create(func)??
創建協程,返回線程對象。
2.??coroutine.resume(co, ...)??
啟動或恢復協程。
3.??coroutine.yield(...)??
掛起協程,返回參數給 resume。
測試代碼:
local co = coroutine.create(function()print("Start")coroutine.yield("Paused")print("End")
end)coroutine.resume(co) --> 輸出 "Start",返回 true, "Paused"
coroutine.resume(co) --> 輸出 "End",返回 true???????結果:

九、調試
1.debug.traceback ([thread,] [message [, level]])
獲取當前調用棧信息(常用于錯誤處理)。
測試代碼:
function risky_operation()error("模擬錯誤發生")
end-- 使用pcall包裹可能出錯的代碼
local success, err = pcall(risky_operation)
if not success thenprint("捕獲到錯誤:", err)print("錯誤堆棧:\n", debug.traceback())
end
-- 輸出包含錯誤信息和堆棧跟蹤???????結果:

2.??debug.getinfo ([thread,] f [, what])
獲取函數信息(如源碼位置、參數等)。
測試代碼:
function funcA()funcB()
endfunction funcB()print("調用堆棧:")-- 打印堆棧信息(層級從0開始)local level = 2 -- 跳過當前函數和debug.getinfo自身while true dolocal info = debug.getinfo(level, "nSl")if not info then break endprint(string.format("層級%d: 函數 %s (文件 %s 第%d行)", level-1, info.name or "匿名", info.short_src, info.currentline))level = level + 1end
endfuncA()???????結果:

十、元表與元方法
1.setmetatable(t, metatable)??
為表設置元表。
測試代碼:
local t = {}
setmetatable(t, { __index = { default = 42 } })
print(t.default) --> 42(通過元表 __index 獲取)???????結果:
![]()
2.??getmetatable(t)??
獲取表的元表。
測試代碼:
local t = {}
local mt = { __index = { default = 42 } }
setmetatable(t, mt)
print(getmetatable(t))
print(mt)???????結果:

??3.__index / __newindex / __call 等元方法??
Lua元表和元方法的使用_lua元方法有哪些-CSDN博客
十一、迭代器與遍歷
1.??pairs(t)??
遍歷表的鍵值對(包括非連續鍵),觸發 __pairs 元方法。
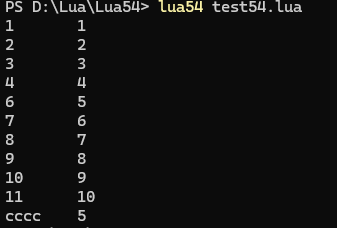
測試代碼:
local t = {1,2,3,4,["cccc"] = 5 ,nil,5,6,7,8,9,10}for key, value in pairs(t) doprint(key, value)
end結果:
?
2.??ipairs(t)??
遍歷數組部分的連續整數鍵(如 t[1], t[2],遇到 nil 停止)。
測試代碼:
local t = {1,2,3,4,["cccc"] = 5 ,nil,5,6,7,8,9,10}
for key, value in ipairs(t) doprint(key, value)
end
print("----------------------")
local t1 = {1,2,3,4,["cccc"] = 5,5,6,7,8,9,10}
for key, value in ipairs(t1) doprint(key, value)
end結果:
???????
3.??next(t, [key])??
直接調用底層迭代函數,返回下一個鍵值對。
測試代碼:
local t = {1,2,3,4,["cccc"] = 5 ,nil,5,6,7,8,9,10}print(next(t))
print(next(t, 5))
print(next(t, 11))
print(next(t, "cccc"))
結果:

十二、垃圾回收
1.collectgarbage("collect")??
手動觸發一次完整的垃圾回收。
測試例子可看弱表例子。
2.??collectgarbage("count")??
返回當前內存占用量(以 KB 為單位)。
測試代碼:
t = {["dddd"] = 123,1,2,3}
print(collectgarbage("count")) ???????結果:
![]()
3.??collectgarbage("step")??
分步執行垃圾回收(適合實時性要求高的場景)。
十三、弱表
1.??設置元表的 __mode 字段??
控制表鍵/值的弱引用(如 {__mode = "k"} 表示鍵是弱引用)。
測試代碼:
local weak_cache = setmetatable({}, { __mode = "v" })
weak_cache["data"] = true -- 當 data 無其他引用時自動清除for key, value in pairs(weak_cache) doprint(key, value)
end
print("-----------------------")
weak_cache["data"] = nil -- 手動清除 datacollectgarbage("collect") -- 強制垃圾回收for key, value in pairs(weak_cache) doprint(key, value)
end???????結果:
十四、錯誤處理
1.pcall(func, ...)??
安全調用函數,返回是否成功及結果/錯誤消息。
代碼測試:
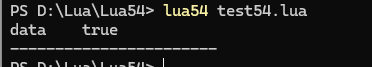
function pcallTest(msg)print("錯誤消息為:"..msg)
endlocal ok, result = pcall(pcallTest, "Oops!")
print(ok)
print(result) 結果:?

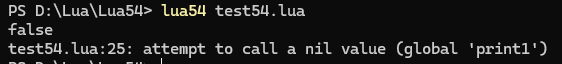
代碼測試:
function pcallTest(msg)print1("錯誤消息為:"..msg)
endlocal ok, result = pcall(pcallTest, "Oops!")
print(ok)
print(result) 結果:
2.xpcall(func, error_handler)??
類似 pcall,但可指定自定義錯誤處理函數。
代碼測試:
xpcall(function() print("xpcall測試") end, function(err) print("ERROR:", err) end)結果:?
![]()
代碼測試:?
xpcall(function() print1("xpcall測試") end, function(err) print("ERROR:", err) end)結果:![]() ?
?
4.??error(message)??
拋出錯誤。
代碼測試:
error("錯誤消息")結果:?
十五、二進制數據處理?
1.?位運算??
&, |, ~, <<, >> 等運算符(需整數類型)
測試代碼:
local a = 1 << 3;
local b = 1 << 4;
local c = 1 << 3;
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
print("------------------")
print(a & b)
print(a | b)
print(a ~ b)
print("------------------")
print(a & c)
print(a | c)
print(a ~ c)???????結果:

2.??string.pack(fmt, ...) / string.unpack(fmt, s)??
打包或解包二進制數據(類似 C 的結構體)。
測試代碼:
local packed = string.pack(">i4", 10234593) -- 大端序 4 字節整數
local num, offset = string.unpack(">i4", packed)
print(packed)
print(num) --> 12345
print(offset) --> 5 (跳過了 4 字節整數)???????結果:

十六、常用工具函數
1.select(index, ...)??
獲取可變參數的特定部分(select('#', ...)?返回參數數量)。
測試代碼:
local count = select("#", 1, "a", true) --> 3
print(count)
local second = select(2, 1, 2, 3) --> 1
print(second)???????結果:

2.??load(code) / loadfile(filename)??
動態加載代碼塊或文件(返回函數或錯誤)。
新建一個calc.lua文件
return function(a, b) return a + b end測試代碼:
--加載字符串代碼
local code = "return 1 + 2"
local func, err = load(code)
if func thenlocal result = func()print(result) -- 輸出: 3
elseprint("加載失敗:", err)
end-- 加載并執行文件中的代碼
local func, err = loadfile("testlua2.lua")
if func thenlocal m = func() -- 執行文件代碼,返回函數print(m.say_hello())
elseprint("加載失敗:", err)
end-- 加載并執行文件中的代碼
local func, err = loadfile("calc.lua")
if func thenlocal add = func() -- 執行文件代碼,返回函數print(add(2, 3)) -- 輸出: 5
elseprint("加載失敗:", err)
end???????結果:

十七、與C語言交互
在VS2022中使用Lua與c交互(二)_vs2022 lua d-CSDN博客
參考鏈接:
Lua 5.4 參考手冊








![[python]Prophet‘ object has no attribute ‘stan_backend‘解決方法](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[python]Prophet‘ object has no attribute ‘stan_backend‘解決方法)






與后臺數據庫進行交互時常用的兩種方式)



)