目錄
1.ArrayList的缺陷
2. 鏈表
2.1 鏈表的概念及結構
2.2 鏈表結構
1.?單向或者雙向
2.帶頭或者不帶頭
3.循環或者非循環
2.3?鏈表的實現
1.完整代碼
2.圖解
?3.顯示方法
4.鏈表大小
5.?鏈表是否存在 key 值
6.頭插法
7.尾插法
8.中間插入
9.刪除key值節點
?10.刪除所有key值節點
11.clear
3.練習
3.1 刪除鏈表中等于給定值?val?的所有節點
3.2?反轉一個單鏈表
3.3?給定一個帶有頭結點 head 的非空單鏈表,返回鏈表的中間結點。如果有兩個中間結點,則返回第二個中間結點
3.4?輸入一個鏈表,輸出該鏈表中倒數第k個結點
?3.5?將兩個有序鏈表合并為一個新的有序鏈表并返回。新鏈表是通過拼接給定的兩個鏈表的所有節點組成的
3.6?編寫代碼,以給定值x為基準將鏈表分割成兩部分,所有小于x的結點排在大于或等于x的結點之前
?編輯
3.7 鏈表的回文結構
3.8?輸入兩個鏈表,找出它們的第一個公共結點
3.9 給定一個鏈表,判斷鏈表中是否有環
3.10 給定一個鏈表,返回鏈表開始入環的第一個節點。?如果鏈表無環,則返回?NULL
1.ArrayList的缺陷
通過篇章四,我們已經熟悉了ArrayList的使用,并且進行了簡單模擬實現。通過源碼知道,ArrayList底層使用數組來存儲元素。
那這樣會出現什么問題呢?
????????由于其底層是一段連續空間,當在ArrayList任意位置插入或者刪除元素時,就需要將后序元素整體往前或者往后搬移,時間復雜度為O(n),效率比較低。因此ArrayList不適合做任意位置插入和刪除比較多的場景。因此:java集合中又引入了LinkedList,即鏈表結構。
2. 鏈表
2.1 鏈表的概念及結構
鏈表是一種 物理存儲結構上非連續 存儲結構,數據元素的 邏輯順序 是通過鏈表中的 引用鏈接 次序實現的。

注意:
1.從上圖可看出,鏈式結構在邏輯上是連續的,但是在物理上不一定連續
2.現實中的結點一般都是從堆上申請出來的
3.從堆上申請的空間,是按照一定的策略來分配的,兩次申請的空間可能連續,也可能不連續
2.2 鏈表結構
實際中鏈表的結構非常多樣,以下情況組合起來就有8種鏈表結構:
1.?單向或者雙向

什么是雙向?

2.帶頭或者不帶頭
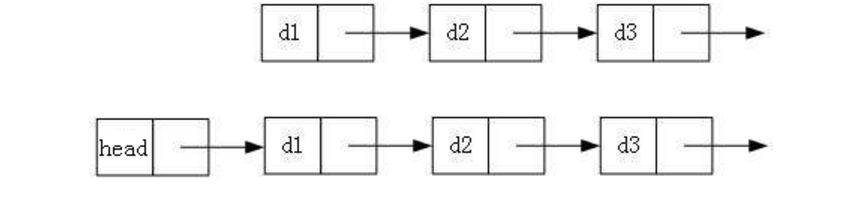
什么是帶頭?

什么是不帶頭?

3.循環或者非循環

什么是循環?

組合成的?8種鏈表結構:

雖然有這么多的鏈表的結構,但是我們重點掌握兩種:
1. 無頭單向非循環鏈表:結構簡單,一般不會單獨用來存數據。實際中更多是作為其他數據結構的子結構,如哈希桶、圖的鄰接表等等。

2. 無頭雙向非循環鏈表:在Java的集合框架庫中LinkedList底層實現就是無頭雙向循環鏈表。
2.3?鏈表的實現
1.完整代碼
/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA* Description 無頭單向非循環鏈表實現* User: 王杰* Date: 2025-05-26* Time: 20:33*/
public class MySingleList implements IList{static class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}public ListNode head;// 創建鏈表public void createList() {ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);ListNode node2 = new ListNode(23);ListNode node3 = new ListNode(34);ListNode node4 = new ListNode(45);ListNode node5 = new ListNode(56);node1.next = node2;node2.next = node3;node3.next = node4;node4.next = node5;this.head = node1;}// 顯示方法@Overridepublic void display() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}}// 鏈表大小@Overridepublic int size() {int len = 0;ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {len++;cur = cur.next;}return len;}// 鏈表是否存在 key 值@Overridepublic boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}// 頭插法@Overridepublic void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);node.next = head;head = node;}// 尾插法@Overridepublic void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);// 一個節點都沒有if (head == null) {head = node;return;}// 找尾巴ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.next == null) {cur.next = node;return;}cur = cur.next;}}//中間插入@Overridepublic void addIndex(int index, int data) {int len = size();if (index < 0 || index > len) {System.out.println("index位置不存在");return;}if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}if (index == len) {addLast(data);return;}// 中間插入ListNode cur = head;if (index - 1 != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}ListNode node = new ListNode(data);// 所有的插入 優先 綁定后邊node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;}// 刪除 key值 節點@Overridepublic void remove(int key) {if (head == null) {return;}// 刪除頭節點if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;return;}ListNode cur = findNodeOfKey(key);if (cur == null) {return;}ListNode del = cur.next;cur.next = del.next;}private ListNode findNodeOfKey(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur.next != null) {if (cur.next.val == key) {return cur;}cur = cur.next;}return null;}// 刪除 所有key值 節點@Overridepublic void removeAllKey(int key) {if (head == null) {return;}ListNode prev = head;ListNode cur = head.next;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;}}@Overridepublic void clear() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = null;cur = curNext;}head = null;}}
2.圖解
單向不帶頭非循環鏈表:

?3.顯示方法

// 顯示方法
@Override
public void display() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}
}4.鏈表大小

// 鏈表大小@Overridepublic int size() {int len = 0;ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {len++;cur = cur.next;}return len;}實現到這里,我們需要掌握的是:
1.ListNode cur = head;?
????????此處申請了臨時變量,因為數據存儲在堆空間,而且 cur 也指向鏈表,所以改變有效。同時 此處也是為了不改變 head 的位置,因為后續要用head找到該鏈表,如果head位置變動了,就找不到該鏈表了。
2.cur != null;
? ? ? ? 此處最后一個節點,是會運算的。最后,cur指向的是最后一個節點的下一個節點,也就是 null;
3.cur.next?!= null;
? ? ? ? 此處最后一個節點,是不會運算的。最后,cur指向的是最后一個節點。
5.?鏈表是否存在 key 值

// 鏈表是否存在 key 值@Overridepublic boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}6.頭插法

// 頭插法@Overridepublic void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);node.next = head;head = node;}7.尾插法

// 尾插法@Overridepublic void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);// 一個節點都沒有if (head == null) {head = node;return;}// 找尾巴ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.next == null) {cur.next = node;return;}cur = cur.next;}}8.中間插入

//中間插入@Overridepublic void addIndex(int index, int data) {int len = size();if (index < 0 || index > len) {System.out.println("index位置不存在");return;}if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}if (index == len) {addLast(data);}// 中間插入ListNode cur = head;if (index - 1 != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}ListNode node = new ListNode(data);// 所有的插入 優先 綁定后邊node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;}注意:
1.此處中間插入,關鍵是找到 要 插入的位置 的 前一個位置。
2.要牢記 所有的插入 優先 綁定后邊
9.刪除key值節點

// 刪除 key值 節點@Overridepublic void remove(int key) {if (head == null) {return;}// 刪除頭節點if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;return;}ListNode cur = findNodeOfKey(key);if (cur == null) {return;}ListNode del = cur.next;cur.next = del.next;}private ListNode findNodeOfKey(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur.next != null) {if (cur.next.val == key) {return cur;}cur = cur.next;}return null;}注意:
????????找到 要刪除的節點 的前一個節點
這一思路在單鏈表中很關鍵
?10.刪除所有key值節點

// 刪除 所有key值 節點@Overridepublic void removeAllKey(int key) {if (head == null) {return;}ListNode prev = head;ListNode cur = head.next;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;}}11.clear

@Overridepublic void clear() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = null;cur = curNext;}head = null;}注意:
? ? ? ? ?此處最后 head 也要置空
3.練習
3.1 刪除鏈表中等于給定值?val?的所有節點
203. 移除鏈表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {if (head == null) {return head;}ListNode prev = head;ListNode cur = head.next;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == val) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if (head.val == val) {head = head.next;}return head;}
}203. 移除鏈表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode) 此處和 2.3 中的 10.刪除所有key節點 一樣
3.2?反轉一個單鏈表
OJ鏈接
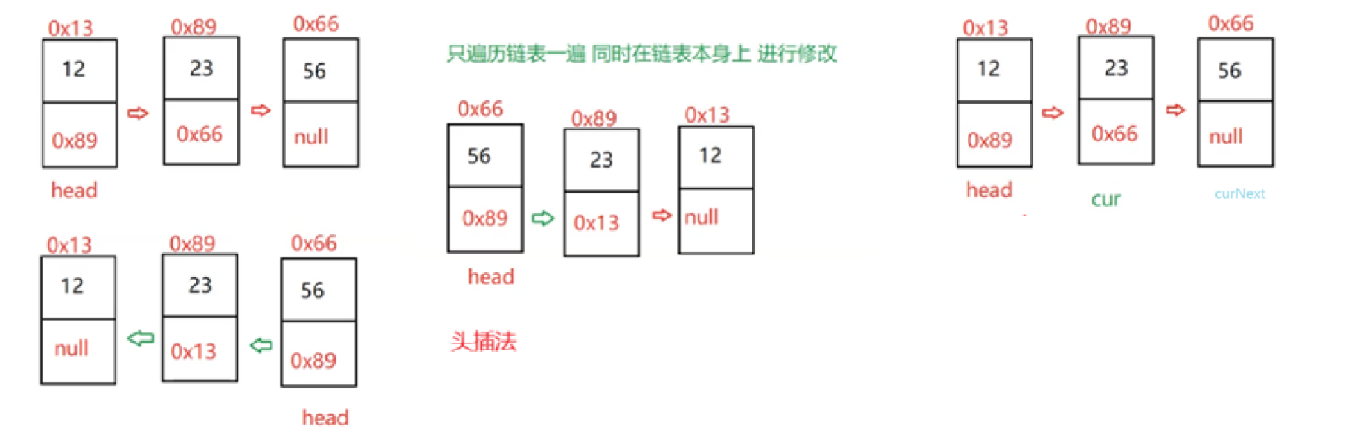
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return head;}ListNode cur = head.next;head.next = null;while(cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = head;head = cur;cur = curNext;}return head;}
}3.3?給定一個帶有頭結點 head 的非空單鏈表,返回鏈表的中間結點。如果有兩個中間結點,則返回第二個中間結點
OJ鏈接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/class Solution {public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return null;}ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;} return slow; }}注意:
? ? ? ? 做這些練習的時候,要考慮 空鏈表 的情況,也就是 head == null?
3.4?輸入一個鏈表,輸出該鏈表中倒數第k個結點
OJ鏈接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {if(head == null) {return -1;}ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;// fast 走 k - 1 步int count = 0; while(count != k - 1) {fast = fast.next;count++;}while(fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}return slow.val;}
}注意:
1. fast.next != null;
? ? ? ? 此處 fast 走到最后一個節點即可,不必走到 null
2.此處 k 值,不確定是否合法,一般題目中會設置范圍,但是沒設置的話就需要補充上k值合法性的校驗
補充:驗證 k 的合法性

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {if(head == null) {return -1;}if(k <= 0) {return -1;}ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;// fast 走 k - 1 步int count = 0; while(count != k - 1) {fast = fast.next;if(fast == null) {return -1;}count++;}while(fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}return slow.val;}
}?3.5?將兩個有序鏈表合并為一個新的有序鏈表并返回。新鏈表是通過拼接給定的兩個鏈表的所有節點組成的
OJ鏈接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {ListNode newHead = new ListNode();ListNode cur = newHead;while(list1 != null && list2 != null) {if(list1.val > list2.val) {cur.next = list2;list2 = list2.next;cur = cur.next;}else {cur.next = list1;list1 = list1.next;cur = cur.next;}}if(list1 != null) {cur.next = list1;}if(list2 != null) {cur.next = list2;}return newHead.next;}}3.6?編寫代碼,以給定值x為基準將鏈表分割成兩部分,所有小于x的結點排在大于或等于x的結點之前
OJ鏈接
import java.util.*;/*
public class ListNode {int val;ListNode next = null;ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}*/
public class Partition {public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {ListNode cur = pHead;ListNode beforStart = null;ListNode beforEnd = null;ListNode afterStart = null;ListNode afterEnd = null;while(cur != null) {if(cur.val < x) {if(beforStart == null) {beforStart = cur;beforEnd = cur;}else {beforEnd.next = cur;beforEnd = beforEnd.next;}cur = cur.next;}else {if(afterStart == null) {afterStart = cur;afterEnd = cur;}else {afterEnd.next = cur;afterEnd = afterEnd.next;}cur = cur.next;} }if(beforStart == null) {return afterStart;}// 置空 afterEnd.nextif(afterStart != null) {afterEnd.next = null;}beforEnd.next = afterStart;return beforStart;}
}注意:
此處思路:是把 大于x 和 小于x 的值分為兩個鏈表。
但是:注意特殊情況,比如大于x的鏈表為空 和 小于x的鏈表為空。
而且:要注意,在 小于x的鏈表不為空時, 置空?afterEnd.next
3.7 鏈表的回文結構
OJ鏈接

import java.util.*;/*
public class ListNode {int val;ListNode next = null;ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}*/
public class PalindromeList {public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {if(A == null) {return true;}ListNode fast = A;ListNode slow = A;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}ListNode cur = slow.next;while(cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = slow;slow = cur;cur =curNext;} while(A != slow) {if(A.val != slow.val) {return false;}// 偶數情況if(A.next == slow) {return true;}A = A.next;slow = slow.next;}return true;}
}注意:
1.??三步走:找中間節點,反轉中間節點后的鏈表,比較前半部分和后半部分鏈表的val值
2. 偶數情況:
? ? ? ? ? ? if(A.next == slow) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? return true;
? ? ? ? ? ? }
3.8?輸入兩個鏈表,找出它們的第一個公共結點
OJ鏈接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode pLong = headA;ListNode pShort = headB;// 先求兩個鏈表的長度int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;while(pLong != null) {lenA++;pLong = pLong.next;}while(pShort != null) {lenB++;pShort = pShort.next;}pLong = headApShort = headB// 求差值int len = lenA - lenB;if(len < 0) {pLong = lenB;pShort = lenA;len = lenB - lenA;}// 走完上述兩步 pLong 一定指向最長的鏈表 pShort 一定指向最短的鏈表// 接下來的操作 只需要操作 pLong 和 pShort 就行了// 讓最長的鏈表走 len 步while(len != 0) {pLong = pLong.next;len--;}// 兩個引用同時走 直到他們相遇while(pLong != pShort) {pLong = pLong.next;pShort = pShort.next;}if(pLong == null) {return null; // 不相交}return pLong;}
}注意:
1.主要思路就是:走兩個鏈表長度的差值步
2. 此處注意還原 pLong 和 pShort ,因為算長度,他們的位置發生了改變,要還原,否則影響下面代碼
????????pLong = headA
? ? ? ? pShort = headB3.注意不相交的情況:
????????if(pLong == null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? return null; // 不相交
? ? ? ? }
3.9 給定一個鏈表,判斷鏈表中是否有環
OJ鏈接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return false;}if(head.next == null) {return false;}ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if(fast == slow) {return true;}}return false;}
}【思路】
????????快慢指針,即慢指針一次走一步,快指針一次走兩步,兩個指針從鏈表起始位置開始運行,如果鏈表帶環則一定會在環中相遇,否則快指針率先走到鏈表的末尾。比如:陪女朋友到操作跑步減肥。
【擴展問題】
-
為什么快指針每次走兩步,慢指針走一步可以?
假設鏈表帶環,兩個指針最后都會進入環,快指針先進環,慢指針后進環。當慢指針剛進環時,可能就和快
指針相遇了,最差情況下兩個指針之間的距離剛好就是環的長度。此時,兩個指針每移動一次,之間的距離就縮小一步,不會出現每次剛好是套圈的情況,因此:在慢指針走到一圈之前,快指針肯定是可以追上慢指針的,即相遇。
-
快指針一次走3步,走4步,...n步行嗎?

?注意:
1.鏈表為空,和只有一個節點的情況是不存在環的
????????if(head == null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? return false;
? ? ? ? }? ? ? ? if(head.next == null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? return false;
? ? ? ? }2.快慢指針的步數問題:
? ? ? ? 快 2 慢 2:會相遇
? ? ? ? 快3 慢 1 :永不相遇
可見:并不是快指針比慢指針快就行,還得注意步數問題。
3.10 給定一個鏈表,返回鏈表開始入環的第一個節點。?如果鏈表無環,則返回?NULL
OJ鏈接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;if(head == null) {return null;}if(head.next == null) {return null;}while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if(fast == slow) {break;}}if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {return null; // 沒有環}slow = head;while(slow != fast) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}
}【結論】
????????讓一個指針從鏈表起始位置開始遍歷鏈表,同時讓一個指針從判環時相遇點的位置開始繞環運行,兩個指針都是每次均走一步,最終肯定會在入口點的位置相遇。
【證明】

?注意:
1.鏈表為空,和只有一個節點的情況是不存在環的
????????if(head == null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? return false;
? ? ? ? }? ? ? ? if(head.next == null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? return false;
? ? ? ? }2.相遇時出循環:
????????while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? fast = fast.next.next;
? ? ? ? ? ? slow = slow.next;
? ? ? ? ? ? if(fast == slow) {
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? break;
? ? ? ? ? ? }
? ? ? ? }3.去除沒有環的情況:
????????if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {
? ? ? ? ? ? return null; // 沒有環
? ? ? ? }4.關鍵:讓慢指針回到鏈表開頭,然后慢指針與快指針以相同的速度走
????????slow = head;
? ? ? ? while(slow != fast) {
? ? ? ? ? ? fast = fast.next;
? ? ? ? ? ? slow = slow.next;
? ? ? ? }5.證明:此處最關鍵的是,fast的路程是slow路程的二倍,建立等式,計算,取極端情況 得出關系,寫代碼。


)
)
)






 ----- Python的函數定義及其使用)




)



