DXF文件格式理解
DXF文件格式是矢量圖形文件格式,其詳細說明了如何表示不同的圖形元素。
DXF是一個矢量圖形文件,它捕獲CAD圖形的所有元素,例如文本,線條和形狀。更重要的是,DXF是用于在CAD應用程序之間傳輸數據的圖形交換文件。
使用組代碼和值表示數據:
DXF文件中的每個變量都與一個組碼相關聯(組碼的范圍從1到1071)。
每個組代碼都在特定情況下使用,并包含特定類型的信息。
例如,組代碼2用于名稱,例如節的名稱或塊的名稱。
組代碼0表示實體的開頭或文件的結尾。
與每個變量關聯的值存儲為整數,浮點數或字符串。例如,線的長度存儲為整數,而點坐標存儲為浮點數。
DXF文件結構
DXF文件分為幾個部分:每個部分都由記錄組成,而記錄又由組代碼和關聯的數據值組成。
您可以按以下順序在DXF文件中找到以下部分:
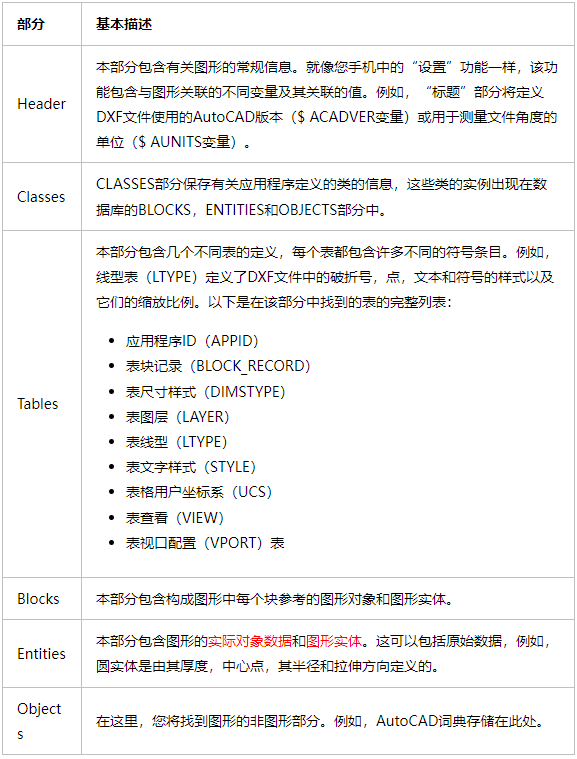
Drawing 類
在一個 DXF 文檔中,Drawing 類是一個核心的管理結構,它負責組織和管理整個繪圖的元素。Drawing 類提供了創建、修改和訪問DXF文件中不同部分的方法,如實體(entities)、塊(blocks)、圖層(layers)、樣式(styles)等。
Drawing 類充當了繪圖元素的容器,允許輕松地對繪圖元素進行操作和互動。它通常代表整個 DXF 文檔,并提供了與文檔內容有效交互的功能。
獲取DXF Drawing 對象:
doc = ezdxf.new()
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)
訪問DXF的各個部分:
import ezdxf,matplotlib
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\data\\褲子版dxf\\K009.dxf"
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)print(doc.header) # HeaderSection
print(doc.classes) # ClassesSection
print(doc.tables) # TablesSection
print(doc.blocks) # BlocksSection
print(doc.entities) # EntitySection
print(doc.objects) # ObjectsSection
提供了訪問Layouts的方法:
Drawing.modelspace()
Drawing.paperspace()
提供了訪問全局資源/屬性的方法:
Application ID Table: Drawing.appidsBlock Definition Table: Drawing.blocksDimension Style Table: Drawing.dimstylesLayer Table: Drawing.layersLinetype Table: Drawing.linetypesMLeader Style Table: Drawing.mleader_stylesMLine Style Table: Drawing.mline_stylesMaterial Table: Drawing.materialsText Style Table: Drawing.stylesUCS Table: Drawing.ucsVPort Table: Drawing.viewportsView Table: Drawing.viewsClasses Section: Drawing.classesObject Section: Drawing.objectsEntity Database: Drawing.entitydbEntity Groups: Drawing.groupsHeader Variables: Drawing.header
Header Section
Drawing的設置存儲在 HEADER 部分,可通過對象header的屬性訪問。具體key看這里。
0 <<< Begin HEADER section
SECTION
2
HEADER
9
$ACADVER <<< Header variable items go here
1
AC1009
...
0
ENDSEC <<< End HEADER section
例如看header中CAD的版本:
import ezdxf
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\data\\褲子版dxf\\K009.dxf"
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)
print(doc.header['$ACADVER'])
Classes Section
DXF 文件中的 CLASSES 部分保存應用程序定義的類的信息,這些類的實例出現在Layout對象中。作為通常的包用戶,無需擔心類。
Tables Section
Tables Section是DXF 文檔的資源表,用于 圖層layers、線型linetypes、文本樣式和形狀文件 styles、尺寸樣式 dimstyles、唯一應用程序ID appids、用戶坐標系 ucs、msp視圖 views、psp視圖 viewports、塊記錄block_records等全局資源信息的table。
0
SECTION
2 <<< begin TABLES section
TABLES
0 <<< first TABLE
TABLE
2 <<< name of table "LTYPE"
LTYPE
5 <<< handle of the TABLE
8
330 <<< owner handle is always "0"
0
100 <<< subclass marker
AcDbSymbolTable
70 <<< count of table entries
4 <<< do not rely on this value!
0 <<< first table entry
LTYPE
...
0 <<< second table entry
LTYPE
...
0 <<< end of TABLE
ENDTAB
0 <<< next TABLE
TABLE
2 <<< name of table "LAYER"
LAYER
5 <<< handle of the TABLE
2
330 <<< owner handle is always "0"
0
100 <<< subclass marker
AcDbSymbolTable
70 <<< count of table entries
1
0 <<< first table entry
LAYER
...
0 <<< end of TABLE
ENDTAB
0 <<< end of SECTION
ENDSEC
import ezdxf
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\data\\褲子版dxf\\K009.dxf"
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)for i in doc.tables.appids:print(i)
for i in doc.tables.layers:print(i)
for i in doc.tables.linetypes:print(i)
for i in doc.tables.styles:print(i)
for i in doc.tables.dimstyles:print(i)
for i in doc.tables.ucs:print(i)
for i in doc.tables.views:print(i)
for i in doc.tables.viewports:print(i)
for i in doc.tables.block_records:print(i)
Blocks Section
Blocks Section是DXF 文檔的所有塊定義 ( BlockLayout ) 的所在地。除了INSERT 實體使用的正常可重用 BLOCKS 之外,所有布局(因為有MODEL_SPACE和所有PAPER_SPACE)在 BLOCKS 部分中至少有一個相應的 BLOCK 定義。模型空間 BLOCK 的名稱為“*Model_Space”,圖紙空間 BLOCK 的名稱為“*Paper_Space”。
import ezdxf
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\data\\褲子版dxf\\K009.dxf"
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)for i in doc.blocks:print(i.dxf.name)
Entities Section
Entities Section是Modelspace 和 active Paperspace中圖像實體的主頁。查看Modelspace 和 active Paperspace中entity的個數。
import ezdxf
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\data\\褲子版dxf\\K009.dxf"
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)print(len(doc.entities))
Objects Section
Objects Section 是 DXF 文檔中所有非圖形對象的主頁。
DXF Entities
DXF Entities 是存儲在 Modelspace, Paperspace 和 BlockLayout 三種Layouts中的 可見對象。它們代表構成 2D 或 3D 設計的各種形狀、線條和其他元素。
查看modelspace中各個實體的類型:CIRCLE、POLYLINE、LINE等
import ezdxf
doc = ezdxf.readfile("shapes.dxf")# iterate over all entities in modelspace
msp = doc.modelspace()
for e in msp:print(e.dxftype())
DXF 實體的一些常見類型包括:(所有DXF entity的基類ezdxf.entities.DXFEntity)
-
LINE和POLYLINE: 這些是 DXF 文件的基本構建塊。它們代表直線和曲線。 -
CIRCLE和ARC: 這些實體分別表示圓和圓的一部分。 -
TEXT和MTEXT:文本實體,可用于標記設計的各個部分或提供其他信息。 -
HATCH:填充圖案實體,用于填充具有特定圖案或紋理的區域。 -
DIMENSION:尺寸實體,它提供設計中各種元素的精確測量。 -
INSERT: BlockLayouts是一組實體,其中每個實體是 INSERT類型的重用實體,可用用于多次插入到其他layouts中,這使其成為重用設計元素的有用方法。
DXFEntity 和 DXFGraphic
DXFEntity是所有DXF實體的基類,查看DXFEntity的.dxf屬性命名空間:
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)
# iterate over all entities in modelspace
msp = doc.modelspace()
for e in msp:# dxf屬性命名空間if e.dxf.dxftype != 'TEXT':print(e.dxf.name, e.dxf.dxftype, e.dxf.layer)
DXFGraphic是所有圖像DXF實體的基類,繼承了DXFEntity,擁有眾多圖形實體的屬性:color, linetype, lineweight, true_color, transparency, ltscale ,invisible。graphic_properties方法會返回各種圖形實體的屬性。
msp = doc.modelspace()
for e in msp:if e.dxftype() == 'LINE':print(e.dxftype(), e.graphic_properties())
Graphical Entity Attributes 圖形實體屬性
所有圖形實體的屬性color, linetype, lineweight, true_color, transparency, ltscale ,invisible都可以通過.dxf屬性命名空間獲取:e.dxf.attribute。 除了true_color 和transparency是必須的,有默認值,其他屬性都是可選的。
不同DXF版本支持不同的屬性:

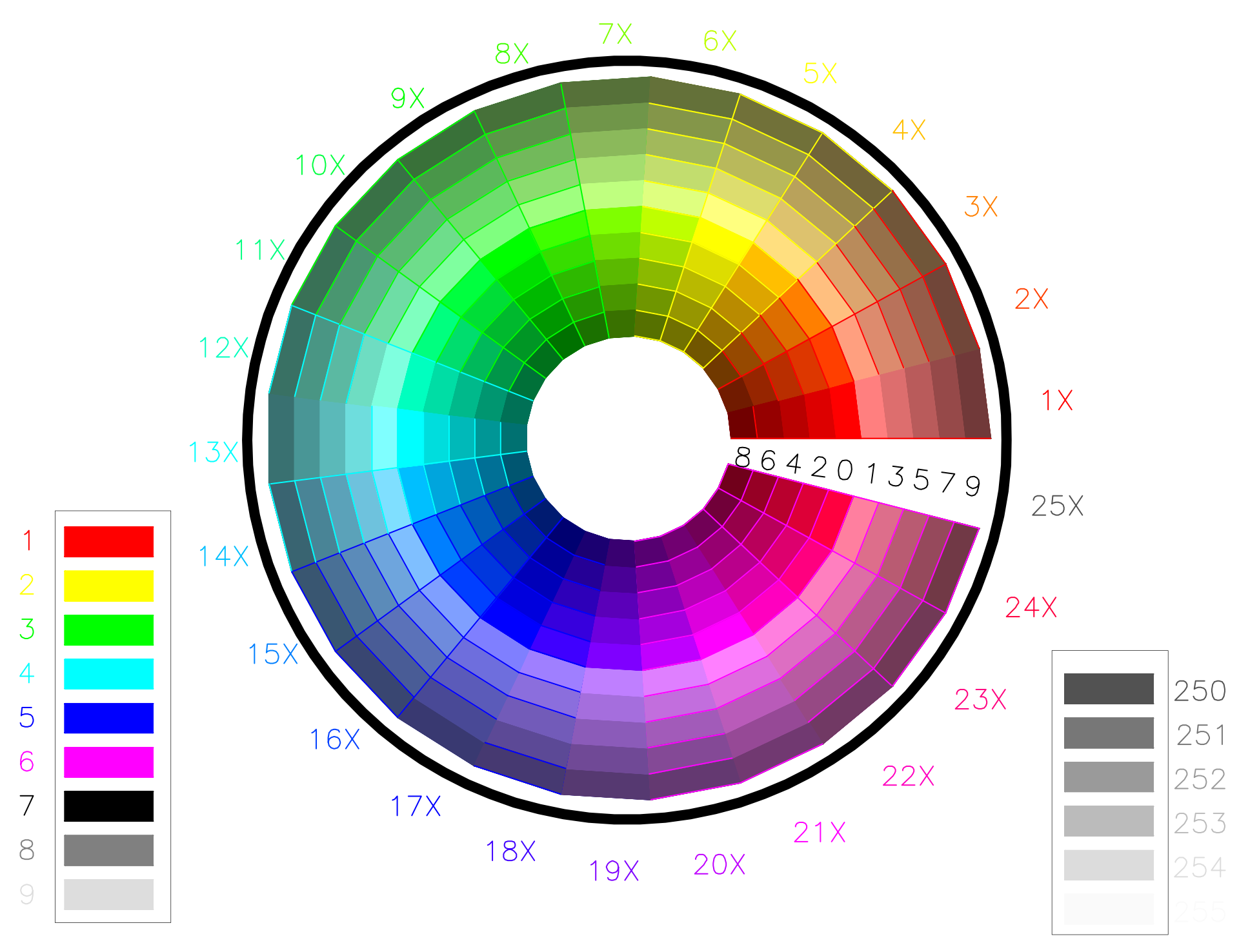
- AutoCAD 顏色索引 (ACI):該
e.dxf.color屬性表示ACI (AutoCAD 顏色索引)。該color屬性的默認值為 256,這意味著采用與實體關聯的layer定義的顏色。
msp = doc.modelspace()
for e in msp:if e.dxftype() == 'LINE':print(e.dxf.color)
- 真彩色True Color:所有圖形實體都直接支持
e.true_color/e.rgb屬性來獲取和設置真彩色作為 (r, g, b) 元組,其中分量必須在 0 到 255 的范圍內。真實顏色值True Color的優先級高于AutoCAD 顏色索引 (ACI)值。
import ezdxfdoc = ezdxf.new()
msp = doc.modelspace()
line = msp.add_line((0, 0), (10, 0))
line.rgb = (255, 128, 32)
- 透明度Transparency:所有圖形實體都支持 transparency獲取和設置透明度的屬性,該
e.transparency屬性是一個介于 0.0 到 1.0 范圍內的浮點值,其中 0.0 表示不透明,1.0 表示完全透明:
import ezdxfdoc = ezdxf.new()
msp = doc.modelspace()
line = msp.add_line((0, 0), (10, 0))
line.transparency = 0.5
- 線型Linetypes:
e.dxf.linetype定義線性圖形實體(如 LINE、ARC、CIRCLE 等)的渲染模式。查看dxf文件中可用的線性及其描述。默認值為“BYLAYER”:ByLayer隨層,圖形對象的屬性使用它所在圖層的屬性。圖形對象的默認屬性是ByLayer,也就是將同類的很多圖形放到一個圖層上,通過圖層來控制圖形的屬性。未設置默認Cotinuous。
import ezdxf,matplotlib
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\data\\褲子版dxf\\K009.dxf"
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)# iterate over all entities in modelspace
msp = doc.modelspace()
for e in msp:if e.dxftype() == 'LINE':print(e.dxf.linetype)# iteration
print(f"There are {len(doc.linetypes)} available linetypes: ")
for lt in doc.linetypes:print(f"{lt.dxf.name}: {lt.dxf.description}")

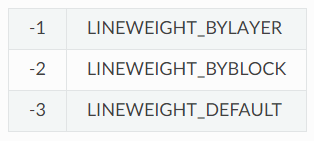
- 線寬Lineweights:
e.dxf.lineweight以毫米 * 100為單位的整數值,例如 0.25mm = 25,與 DXF 文檔中使用的單位系統無關。ByBlock:隨塊,圖形對象的屬性使用它所在圖塊的屬性。如果圖形對象屬性設置成ByBlock,但沒有被定義成塊,此對象將使用默認的屬性,顏色是白色、線寬為默認線寬、線型為實線。默認值為 -1。
msp = doc.modelspace()
for e in msp:if e.dxftype() == 'LINE':print(e.dxf.lineweight)
將 HEADER 變量設置$LWDISPLAY為 1,激活對在屏幕上顯示線寬的支持:
# activate on screen lineweight display
doc.header["$LWDISPLAY"] = 1

- 線型比例 ltscale:ltscale屬性通過浮點值縮放線型圖案,是可選的,默認值為 1.0
# iterate over all entities in modelspace
msp = doc.modelspace()
for e in msp:if e.dxftype() == 'LINE':print(e.dxf.ltscale )
- 不可見性invisible:invisible屬性是一個布爾值(0/1),定義實體是不可見還是可見。默認值為 0可見。
msp = doc.modelspace()
for e in msp:if e.dxftype() == 'LINE':print(e.dxf.invisible )
- 世界坐標系(WCS):世界坐標系——參考坐標系。所有其他坐標系都是相對于 WCS 定義的,永遠不會改變。
- 用戶坐標系(UCS): 用戶定義的工作坐標系,使繪圖任務更容易。
DXF 文件中存儲的所有坐標都是 WCS 或 OCS,而不是 UCS。 - 對象坐標系 (OCS):對象坐標系是相對于對象本身的坐標。OCS 的主要目標是將 2D 元素放置在 3D 空間中,OCS 由實體的擠壓向量定義。只要擠壓矢量為 (0, 0, 1)
(WCS z 軸),OCS 就與 WCS 重合,這意味著 OCS 坐標等于 WCS 坐標,大多數情況下對于 2D 實體來說都是如此。- 以下
3D實體不位于特定平面內。所有點均以世界坐標表示。在這些實體中,只能擠出線和點。它們的擠出方向可能與世界 z 軸不同:Line、Point、3DFace、Polyline(3D)、Vertex(3D)、Polymesh、Polyface、Viewport。 - 以下
2D實體本質上是平面的。所有點均以對象坐標表示。所有這些實體都可以被擠壓。它們的擠出方向可能與世界 z 軸不同:Circle、Arc、Solid、Trace、Text、Attrib、Attdef、Shape、Insert、Polyline(二維)、Vertex(二維)、LWPolyline、Hatch、Image。
- 以下
if (abs(Az.x) < 1/64.) and (abs(Az.y) < 1/64.):Ax = Vec3(0, 1, 0).cross(Az).normalize() # the cross-product operator
else:Ax = Vec3(0, 0, 1).cross(Az).normalize() # the cross-product operator
Ay = Az.cross(Ax).normalize()
Az = Vec3(entity.dxf.extrusion).normalize() # normal (extrusion) vectordef wcs_to_ocs(point):px, py, pz = Vec3(point) # point in WCSx = px * Ax.x + py * Ax.y + pz * Ax.zy = px * Ay.x + py * Ay.y + pz * Ay.zz = px * Az.x + py * Az.y + pz * Az.zreturn Vec3(x, y, z)Wx = wcs_to_ocs((1, 0, 0))
Wy = wcs_to_ocs((0, 1, 0))
Wz = wcs_to_ocs((0, 0, 1))def ocs_to_wcs(point):px, py, pz = Vec3(point) # point in OCSx = px * Wx.x + py * Wx.y + pz * Wx.zy = px * Wy.x + py * Wy.y + pz * Wy.zz = px * Wz.x + py * Wz.y + pz * Wz.zreturn Vec3(x, y, z)
- 圖層Layers:Layers是一種
entity屬性的集合屬性。每個對象都有一個Layers作為其屬性之一。layer 然后通過將傳遞Layers name字符串,將這些Layers 的屬性分配給其他 DXF 實體。如實體可以通過使用字符串’BYLAYER’作為線型字符串、256顏色或-1線寬,從名稱為’BYLAYER’的Layers繼承此屬性,所有這些值都是新實體的默認值。
import ezdxfdoc = ezdxf.new(setup=True) # setup required line types
msp = doc.modelspace()
doc.layers.add(name="MyLines", color=7, linetype="DASHED")
# 新entity繼承名為"MyLines"的layers的屬性
msp.add_line((0, 0), (10, 0), dxfattribs={"layer": "MyLines"})
# 靈活切換layers
# move the entity to layer "OtherLayer"
line.dxf.layer = "OtherLayer"# 查看dxf文件中的所有layers
import ezdxf,matplotlib
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\data\\褲子版dxf\\K009.dxf"
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)
for l in doc.layers:print(l.dxf.name)
Point,LINE,Circle,Arc,Ellipse,Text
以下示例中的圖元始終放置在 WCS 的 xy 平面(即 2D 繪圖空間)中。 其中一些實體只能放置在 3D 空間的 xy 平面之外 利用 OCS,這里沒用涉及。
Point 在 WCS 中標記一個 3D 點:
import ezdxf
from ezdxf.gfxattribs import GfxAttribs
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\shapes.dxf"
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)
msp = doc.modelspace()point = msp.add_point((10, 10))
p = msp.query('POINT')[0]
print(p.dxf.location, p.dxf.angle)
# (10.0, 10.0, 0.0) 0
Line 包含 start 和 end Point 在世界坐標系WCS:
import ezdxf
from ezdxf.gfxattribs import GfxAttribs
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\shapes.dxf"
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)
msp = doc.modelspace()line = msp.add_line((0, 0), (10, 10))
l = msp.query('LINE')[0]
# 起點,終點,粗細,縮放拉伸
print(l.dxf.start, l.dxf.end, l.dxf.thickness, l.dxf.extrusion)
# (0.0, 0.0, 0.0) (10.0, 10.0, 0.0) 0 (0.0, 0.0, 1.0)
Circle包含在OCS中的 中心點center point 和 半徑radius:
import ezdxf
from ezdxf.gfxattribs import GfxAttribs
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\shapes.dxf"
# doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)
doc = ezdxf.new()
msp = doc.modelspace()circle = msp.add_circle((10, 10), radius=3)c = msp.query('CIRCLE')[0]
# 圓心,半徑
print(c.dxf.center, c.dxf.radius)
# (10.0, 10.0, 0.0) 3.0
Arc圓弧 包括 中心點center point, radius半徑, 起始角 start angl,結束角 end angle(以度為單位):
import ezdxf
from ezdxf.gfxattribs import GfxAttribs
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\shapes.dxf"
# doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)
doc = ezdxf.new()
msp = doc.modelspace()arc = msp.add_arc((10, 10), radius=3, start_angle=30, end_angle=120,)a = msp.query('ARC')[0]
# 圓心,半徑,起始角度,終止角度
print(a.dxf.center, a.dxf.radius, a.dxf.start_angle, a.dxf.end_angle)
# (10.0, 10.0, 0.0) 3.0 30.0 120.0
Ellipse橢圓 需要 DXF R2000 或更高版本,并且是 真正的 WCS 實體。橢圓包括 中心點,長軸major axis,長軸和短軸之間的比率ratio,起點start_param和終點end_param (以弧度為單位):
import ezdxf
import math
from ezdxf.gfxattribs import GfxAttribs
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\shapes.dxf"
# doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)
doc = ezdxf.new()
msp = doc.modelspace()ellipse = msp.add_ellipse((10, 10), major_axis=(5, 0), ratio=0.5, start_param=0, end_param=math.pi )
e = msp.query('ELLIPSE')[0]
print(e.dxf.center, e.dxf.major_axis, e.dxf.ratio, e.dxf.start_param, e.dxf.end_param)
# (10.0, 10.0, 0.0) (5.0, 0.0, 0.0) 0.5 0.0 3.141592653589793
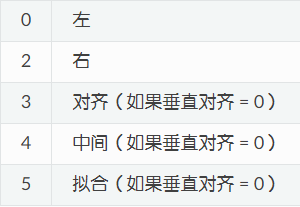
TEXT 實體 表示一行文本。t.dxf.text表示文本內容字符串, t.dxf.insert表示 第一個LEFT, ALIGNED 和 FIT對齊的2D/3D Point in OCS, t.dxf.align_point表示主對齊點非LEFT對齊或者ALIGNED和FIT對齊的第二個對齊點, t.dxf.halign水平對齊標志作為 int 值默認0, t.dxf.valign垂直對齊標志作為 int 值默認0, t.dxf.height文本高度為浮點值,默認值為 1, t.dxf.width寬度比例因子作為浮點值,默認值為 1, t.dxf.rotation文本旋轉(以度為單位)作為浮點值,默認值為 0, t.dxf.style表示Textstyle的名字默認Standard。
水平對齊標志:
垂直對齊標志:
doc = ezdxf.new()
msp = doc.modelspace()# Use method set_placement() to define the TEXT alignment, because the
# relations between the DXF attributes 'halign', 'valign', 'insert' and
# 'align_point' are tricky.
msp.add_text("A Simple Text").set_placement((2, 3), align=TextEntityAlignment.MIDDLE_RIGHT)# Using a predefined text style:
msp.add_text("Text Style Example: Liberation Serif", height=0.35, dxfattribs={"style": "LiberationSerif"}).set_placement((2, 6), align=TextEntityAlignment.LEFT)t = msp.query('TEXT')[0]
print(t.dxf.text, t.dxf.insert, t.dxf.align_point, t.dxf.halign, t.dxf.valign, t.dxf.height, t.dxf.width, t.dxf.rotation, t.dxf.style)
# A Simple Text (2.0, 3.0, 0.0) (2.0, 3.0, 0.0) 2 2 2.5 1 0 Standard
DXF Objects
DXF Objects 是非圖形實體,沒有視覺表示,它們存儲管理數據、圖紙空間布局定義、多種實體類型的樣式定義、自定義數據和對象。DXF 文件中的 OBJECTS 部分充當這些非圖形對象的容器。
DXF 對象的一些常見 DXF 類型包括:
-
DICTIONARY:字典對象由一系列<名稱-值 >對組成,其中名稱是標識字典中特定對象的字符串,值是對該對象的引用。對象本身可以是任何類型的 DXF 實體或 DXF 文件中定義的自定義對象。 -
XRECORD 實體用于將自定義應用程序數據存儲在 DXF 文件中。 -
LAYOUT 實體是一個 DXF 實體,表示 DXF 文件中的單個圖紙空間布局。圖紙空間是 CAD 繪圖中的區域,表示將在其上繪制或打印設計的紙張或其他物理介質。 -
MATERIAL、MLINESTYLE、MLEADERSTYLE定義存儲在某些 DICTIONARY 對象中。 -
GROUP 實體包含引用繪圖中其他 DXF 實體的句柄列表。組中的實體可以是任何類型,包括來自模型空間或圖紙空間布局的實體。
TagStorage
ezdxf包支持許多但不是所有實體類型,所有這些不支持的類型都存儲為實例,以便在通過ezdxf TagStorage導出編輯的 DXF 內容時保留其數據。
Layouts
作為存儲DXF entities的容器,如LINE, CIRCLE, TEXT 等等。每個 DXF entity只能駐留在一個Layouts中。
共有三種不同的Layouts類型:(DXF文件由一個Modelspace和至少一個Paperspace組成,且所有Layouts對象都是可迭代對象)
-
Modelspace:模型空間是 DXF 文件中用來表示實際繪圖內容的部分。在模型空間中,用戶可以繪制和編輯實際的圖形元素,比如線條、圓形、多邊形等。模型空間通常用于表示實際的設計內容。 -
Paperspace:紙張空間用來表示圖紙的布局和顯示方式,通常用于設置圖紙的打印布局、視圖窗口等。在紙張空間中,用戶可以安排模型空間的內容,設置視圖窗口的大小和位置,以便在打印或顯示時呈現出所需的效果。 -
BlockLayout:塊是 DXF 文件中的可重用圖形元素,類似于 CAD 軟件中的符號庫。塊可以包含線條、弧線、文本等元素,并被定義為一個單獨的對象。這使得用戶可以多次插入相同的塊,而不必重復繪制相同的圖形元素。
Modelspace
Modelspace始終存在且無法刪除。
import ezdxf
doc = ezdxf.readfile("shapes.dxf")
msp = doc.modelspace()
Modelspace可以具有一個或多個稱為Modelspace Viewport的矩形區域。Modelspace Viewport可用于從Modelspace的不同觀察方向顯示Modelspace的不同視圖。重要的是要知道Modelspace Viewport ( VPort) 與Paperspace Viewport(Viewport) 不同。
Paperspace
Paperspace 是為了 2D 輸出而組裝和組織模型空間繪圖內容的地方,例如打印在一張紙上,或作為數字文檔(例如 PDF 文件)。
import ezdxf
doc = ezdxf.readfile("shapes.dxf")
psp = doc.paperspace("Layout1")
每個 DXF 文檔可以有一個或多個Paperspace ,但 DXF 版本 R12 僅支持一種Paperspace ,因此不建議依賴 DXF 版本 R12 中的Paperspace 。
BlockLayout
BlockLayout只是另一種Entity集合空間,它可以通過 INSERT 實體多次重用,插入到其他Layouts和BlockLayout中,也稱為塊引用,這是 DXF 格式的一個非常強大且重要的概念。塊參考 (INSERT) 可以旋轉、縮放、通過OCS放置在 3D 空間中并以類似網格的方式排列,每個INSERT實體可以塊屬性(Attrib)附加單獨的屬性 。
通過block name 獲取BlockLayout:
import ezdxf
doc = ezdxf.readfile("shapes.dxf")
blk = doc.blocks.get("NAME")
查看msp中所有INSERT的實體及其屬性:
import ezdxf
file_path = "E:\\7創業\\AI+Clothes\\data\\褲子版dxf\\K009.dxf"
doc = ezdxf.readfile(file_path)blockrefs = msp.query('INSERT')
print(len(blockrefs))
for be in blockrefs:print(be.dxftype(), be.dxf.name)print(be.get_attrib('diameter'), be.get_attrib('color'), be.get_attrib("rgb"))











![[出錯]-RuntimeError: “slow_conv_transpose2d_out_cpu“ not implemented for ‘Byte‘](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[出錯]-RuntimeError: “slow_conv_transpose2d_out_cpu“ not implemented for ‘Byte‘)

)



解碼)
![[動態規劃]---part1](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[動態規劃]---part1)
