1.計算屬性
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>計算屬性</title><script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><div id="root">姓:<input type="text" v-model="firstName"><br><br>名:<input type="text" v-model="lastName"><br><br>姓名:<span>{{fullName}}</span></div><script>Vue.config.productionTip = false new Vue({el:'#root', data:{ firstName:'張',lastName:'三'},computed:{fullName:{get(){return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName},set(value){const arr = value.split('-')this.firstName = arr[0]this.lastName = arr[1]}}}})</script>
</body>
</html>
效果:

總結:
計算屬性:
????????定義:要用的屬性不存在,需要通過已有屬性計算得來。
????????原理:底層借助了Objcet.defineproperty()方法提供的getter和setter。
????????get函數什么時候執行?
????????????????初次讀取時會執行一次
????????????????當依賴的數據發生改變時會被再次調用
????????優勢:與methods實現相比,內部有緩存機制(復用),效率更高,調試方便
備注:
計算屬性最終會出現在vm上,直接讀取使用即可
如果計算屬性要被修改,那必須寫set函數去響應修改,且set中要引起計算時依賴的數據發生改變
如果計算屬性確定不考慮修改,可以使用計算屬性的簡寫形式
new Vue({el:'#root', data:{ firstName:'張',lastName:'三'},computed:{fullName(){return this.firstName + '-' + this.lastName}}
})
2.監視屬性
2.1 監視屬性基本用法
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>監視屬性</title><script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><div id="root"><h2>今天天氣好{{info}}!</h2><button @click="changeWeather">點擊切換天氣</button></div><script>Vue.config.productionTip = false new Vue({el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true,},computed:{info(){return this.isHot ? '炎熱' : '涼爽' }},methods:{changeWeather(){this.isHot = !this.isHot}},watch:{isHot:{immediate:true, //初始化時讓handler調用一下//handler什么時候調用?當isHot發生改變時handler(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue)}}}})</script>
</body>
</html>

總結:
監視屬性watch:
- 當被監視的屬性變化時,回調函數自動調用
- 監視的屬性必須存在,才能進行監視
- 監視有兩種寫法:
- 創建Vue時傳入watch配置
- 通過
vm.$watch監視
vm.$watch('isHot',{immediate:true,handler(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue)}
})
?2.2 深度監視
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>深度監視</title><script src="../js/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body><div id="root"><h3>a的值是:{{numbers.a}}</h3><button @click="numbers.a++">點我讓a+1</button><h3>b的值是:{{numbers.b}}</h3><button @click="numbers.b++">點我讓b+1</button></div><script>Vue.config.productionTip = false new Vue({el:'#root', data:{ isHot:true,numbers:{a:1,b:1,}},watch:{//監視多級結構中所有屬性的變化numbers:{deep:true,handler(){console.log('numbers改變了')}}//監視多級結構中某個屬性的變化/* 'numbers.a':{handler(){console.log('a被改變了')}} */}})</script>
</body>
</html>
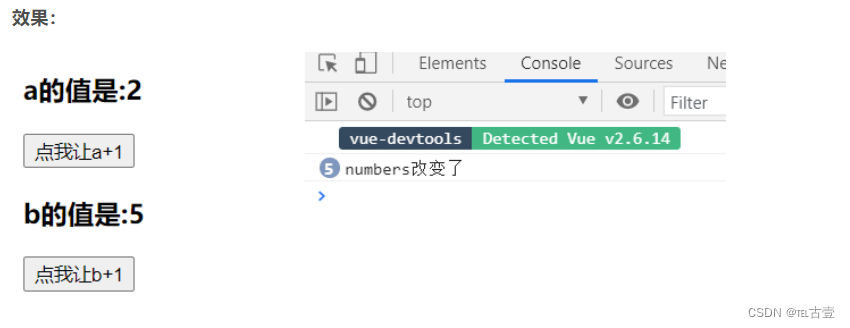
總結:
深度監視:
- Vue中的watch默認不監測對象內部值的改變(一層)
- 在watch中配置deep:true可以監測對象內部值的改變(多層)
備注:
- Vue自身可以監測對象內部值的改變,但Vue提供的watch默認不可以
- 使用watch時根據監視數據的具體結構,決定是否采用深度監視
?2.3 監視屬性簡寫
如果監視屬性除了handler沒有其他配置項的話,可以進行簡寫。
<script type="text/javascript">Vue.config.productionTip = false //阻止 vue 在啟動時生成生產提示。const vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{isHot:true,},computed:{info(){return this.isHot ? '炎熱' : '涼爽'}},methods: {changeWeather(){this.isHot = !this.isHot}},watch:{//正常寫法isHot:{handler(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue)}}, //簡寫isHot(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue,this)}}})//正常寫法vm.$watch('isHot',{handler(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue)}})//簡寫vm.$watch('isHot',function(newValue,oldValue){console.log('isHot被修改了',newValue,oldValue,this)})
</script>
2.4 監聽屬性VS計算屬性
總結:
computed和watch之間的區別:
- computed能完成的功能,watch都可以完成
- watch能完成的功能,computed不一定能完成,例如:watch可以進行異步操作
兩個重要的小原則:
- 所有被Vue管理的函數,最好寫成普通函數,這樣this的指向才是vm 或 組件實例對象
- 所有不被Vue所管理的函數(定時器的回調函數、ajax的回調函數等、Promise的回調函數),最好寫成箭頭函數,這樣this的指向才是vm 或 組件實例對象。
3. 綁定樣式
<style>.basic{width: 400px;height: 100px;border: 1px solid black;}.happy{border: 4px solid red;;background-color: rgba(255, 255, 0, 0.644);background: linear-gradient(30deg,yellow,pink,orange,yellow);}.sad{border: 4px dashed rgb(2, 197, 2);background-color: gray;}.normal{background-color: skyblue;}.atguigu1{background-color: yellowgreen;}.atguigu2{font-size: 30px;text-shadow:2px 2px 10px red;}.atguigu3{border-radius: 20px;}
</style>
<div id="root"><!-- 綁定class樣式--字符串寫法,適用于:樣式的類名不確定,需要動態指定 --><div class="basic" :class="mood" @click="changeMood">{{name}}</div> <br/><br/><!-- 綁定class樣式--數組寫法,適用于:要綁定的樣式個數不確定、名字也不確定 --><div class="basic" :class="classArr">{{name}}</div> <br/><br/><!-- 綁定class樣式--對象寫法,適用于:要綁定的樣式個數確定、名字也確定,但要動態決定用不用 --><div class="basic" :class="classObj">{{name}}</div> <br/><br/><!-- 綁定style樣式--對象寫法 --><div class="basic" :style="styleObj">{{name}}</div> <br/><br/><!-- 綁定style樣式--數組寫法 --><div class="basic" :style="styleArr">{{name}}</div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">Vue.config.productionTip = falseconst vm = new Vue({el:'#root',data:{name:'尚硅谷',mood:'normal',classArr:['atguigu1','atguigu2','atguigu3'],classObj:{atguigu1:false,atguigu2:false,},styleObj:{fontSize: '40px',color:'red',},styleObj2:{backgroundColor:'orange'},styleArr:[{fontSize: '40px',color:'blue',},{backgroundColor:'gray'}]},methods: {changeMood(){const arr = ['happy','sad','normal']const index = Math.floor(Math.random()*3)this.mood = arr[index]}},})
</script>
總結:
class樣式:
寫法:class="xxx",xxx可以是字符串、對象、數組
- 字符串寫法適用于:類名不確定,要動態獲取
- 對象寫法適用于:要綁定多個樣式,個數不確定,名字也不確定
- 數組寫法適用于:要綁定多個樣式,個數確定,名字也確定,但不確定用不用
style樣式:
- :style="{fontSize: xxx}"其中xxx是動態值
- :style="[a,b]"其中a、b是樣式對象
?



)
)
--樹形DP沒有上司的舞會)


)





)




