【力扣hot100】刷題筆記Day10
前言
- 一鼓作氣把鏈表給刷完!!中等題困難題沖沖沖啊啊啊!
25. K 個一組翻轉鏈表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
-
模擬
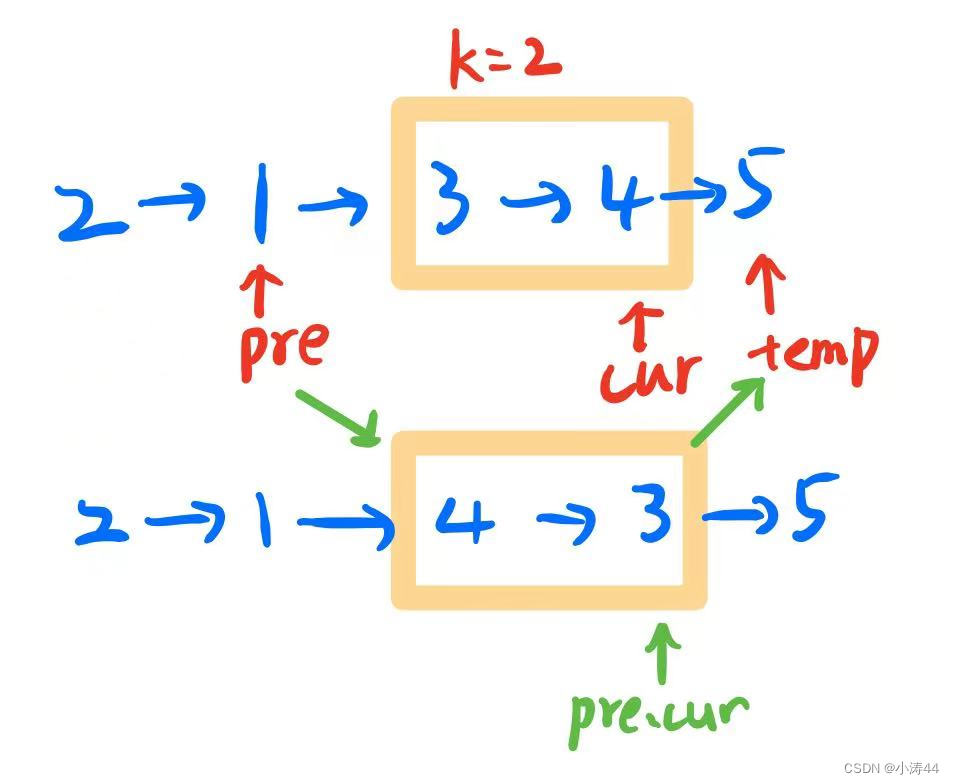
-
class Solution:def reverseKGroup(self, head: Optional[ListNode], k: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:# 翻轉鏈表前k項def reverse(head, k):pre, cur = None, headwhile cur and k:temp = cur.nextcur.next = prepre = curcur = tempk -= 1return pre, head # pre為頭,head為尾dummy = ListNode(0, head)pre = cur = dummycount = k # 用于重復計數while cur.next and count:count -= 1cur = cur.nextif count == 0:temp = cur.next # 存一下段后節點pre.next, cur = reverse(pre.next, k) # 連接段前+翻轉cur.next = temp # 連上段后節點pre = cur # 更新pre指針count = k # 恢復count繼續遍歷return dummy.next
?138. 隨機鏈表的復制 - 力扣(LeetCode)
- 路飛的題解真是太強啦!!優雅清晰簡潔
-
哈希表
-
"""
# Definition for a Node.
class Node:def __init__(self, x: int, next: 'Node' = None, random: 'Node' = None):self.val = int(x)self.next = nextself.random = random
"""class Solution:def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':if not head: return Nonedic = {}# 1. 復制各節點,并建立 “原節點 -> 新節點” 的 Map 映射cur = headwhile cur:dic[cur] = Node(cur.val)cur = cur.next# 2. 構建新節點的 next 和 random 指向cur = headwhile cur:dic[cur].next = dic.get(cur.next)dic[cur].random = dic.get(cur.random)cur = cur.next# 3. 返回新鏈表的頭節點 return dic[head]
-
拼接 + 拆分
-
class Solution:def copyRandomList(self, head: 'Optional[Node]') -> 'Optional[Node]':if not head: return Nonedic = {}# 1. 復制各節點,并構建拼接鏈表cur = headwhile cur:temp = Node(cur.val)temp.next = cur.nextcur.next = tempcur = temp.next# 2. 構建各新節點的 random 指向cur = headwhile cur:if cur.random:cur.next.random = cur.random.nextcur = cur.next.next# 3. 拆分兩鏈表cur = newhead = head.nextpre = headwhile cur.next:pre.next = pre.next.nextcur.next = cur.next.nextpre = pre.nextcur = cur.nextpre.next = None # 單獨處理原鏈表尾節點return newhead # 返回新鏈表頭節點
148. 排序鏈表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
-
歸并排序(頂到底遞歸)
- 參考路飛題解
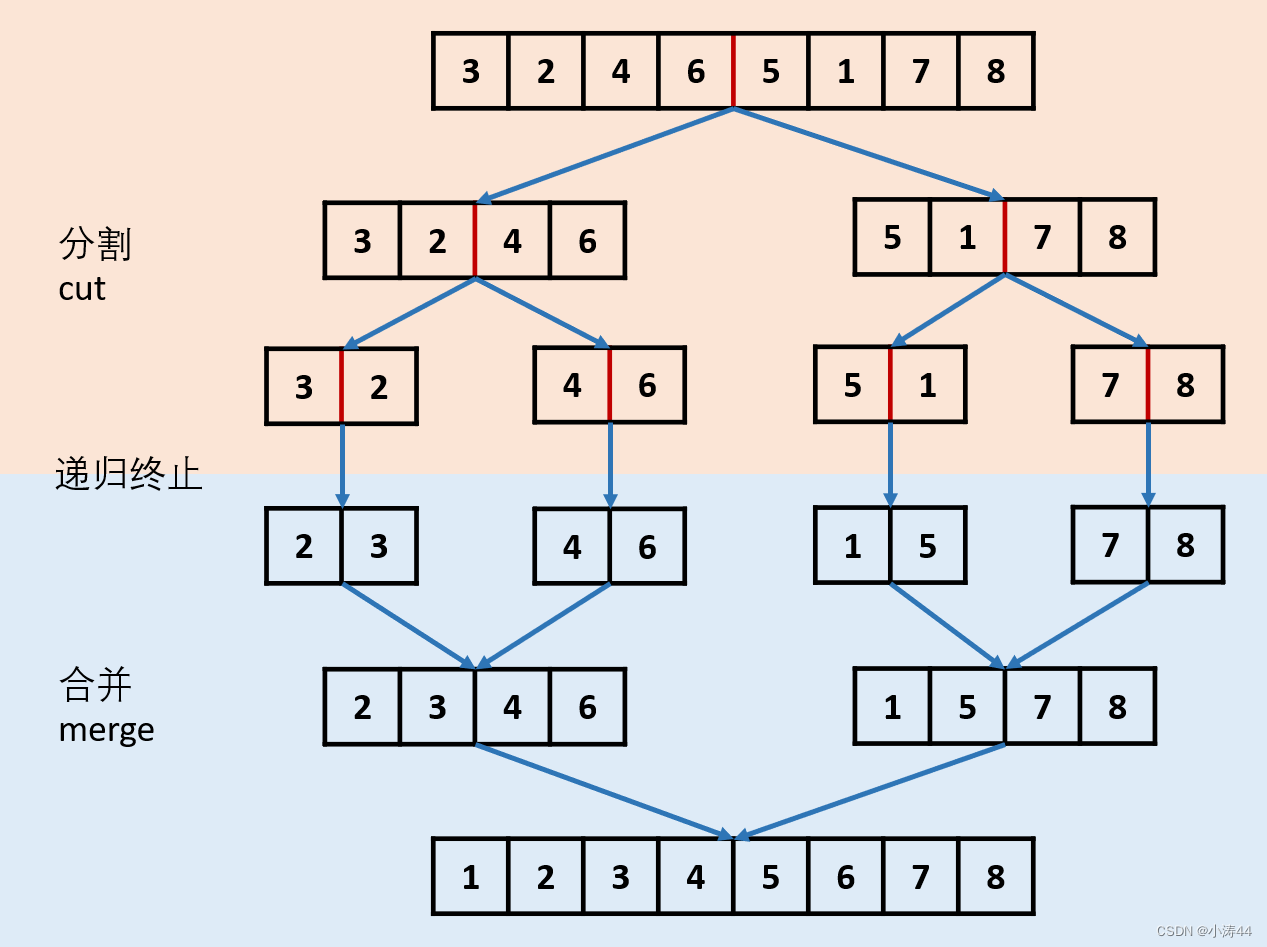
-
class Solution:def sortList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:if not head or not head.next: return head# 快慢指針分割鏈表slow, fast = head, head.nextwhile fast and fast.next:fast, slow = fast.next.next, slow.nextmid = slow.next # 右半部分的頭節點slow.next = None # 斷開兩部分# 遞歸進行歸并排序left = self.sortList(head)right = self.sortList(mid)# 合并左右兩個鏈表dummy = cur = ListNode(0)while left and right: # 根據大小依次插入新鏈表if left.val < right.val:cur.next = leftleft = left.nextelse:cur.next = rightright = right.nextcur = cur.nextcur.next = left if left else right # 接上剩下的return dummy.next
-
歸并排序(底到頂合并)?
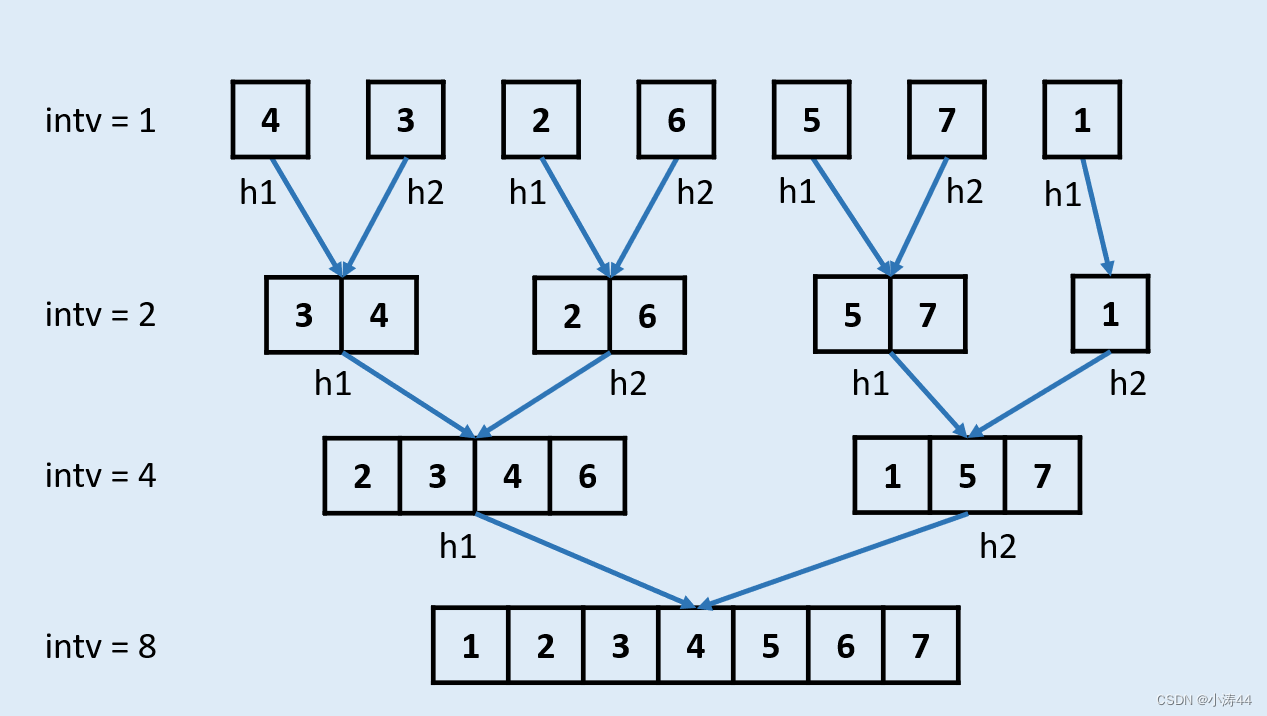
-
class Solution:def sortList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:# 合并兩個有序鏈表def merge(head1, head2):dummy = cur = ListNode(0)while head1 and head2:if head1.val < head2.val:cur.next = head1head1 = head1.nextelse:cur.next = head2head2 = head2.nextcur = cur.nextcur.next = head1 if head1 else head2return dummy.next# 如果只有一個節點直接返回headif not head: return head# 統計鏈表長度lenth = 0cur = headwhile cur:cur = cur.nextlenth += 1# 開始循環合并dummy = ListNode(0, head)sublenth = 1while sublenth < lenth:pre, cur = dummy, dummy.nextwhile cur:head1 = curfor i in range(1, sublenth):if cur.next:cur = cur.nextelse:break # 如果還沒找到head2說明不用合并,下一輪head2 = cur.nextif not head2: break # 空就不合并了cur.next = None # 斷開第一段后cur = head2for i in range(1, sublenth):if cur.next:cur = cur.nextelse:breaktemp = cur.next cur.next = None # 斷開第二段后cur = tempmerged = merge(head1, head2) # 合并pre.next = mergedwhile pre.next:pre = pre.next # pre更新到合并后鏈表的最后pre.next = temp # 重新連接第二段后# 下一輪合并sublenth *= 2return dummy.next
?23. 合并 K 個升序鏈表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
-
依次合并
-
class Solution:def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[Optional[ListNode]]) -> Optional[ListNode]:# 合并兩個有序鏈表def merge(head1, head2):dummy = cur = ListNode(0)while head1 and head2:if head1.val < head2.val:cur.next = head1head1 = head1.nextelse:cur.next = head2head2 = head2.nextcur = cur.nextcur.next = head1 if head1 else head2return dummy.nextlenth = len(lists)if lenth == 0:return None# 每遍歷一個鏈表就合并掉dummyhead = ListNode(0)for i in range(0, len(lists)):dummyhead.next = merge(dummyhead.next, lists[i])return dummyhead.next
-
?分治合并
-
class Solution:def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:# 如果輸入為空,直接返回空if not lists:return # 獲取鏈表列表的長度n = len(lists)# 調用遞歸函數進行合并return self.merge(lists, 0, n-1)def merge(self, lists, left, right):# 當左右指針相等時,表示只有一個鏈表,直接返回該鏈表if left == right:return lists[left]# 計算中間位置mid = left + (right - left) // 2# 遞歸地合并左半部分和右半部分的鏈表l1 = self.merge(lists, left, mid)l2 = self.merge(lists, mid+1, right)# 調用合并兩個有序鏈表的函數return self.mergeTwoLists(l1, l2)def mergeTwoLists(self, l1, l2):# 若其中一個鏈表為空,則直接返回另一個鏈表if not l1:return l2if not l2:return l1# 比較兩個鏈表頭結點的大小,選擇較小的作為新鏈表的頭結點if l1.val < l2.val:l1.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2)return l1else:l2.next = self.mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next)return l2
-
?最小堆
-
"""
假設有3個有序鏈表分別是:1->4->5, 1->3->4, 2->6。
初始時,最小堆為空。我們依次將(1,0),(1,1),(2,2)加入最小堆。
然后不斷彈出最小值(1,0),(1,1),(2,2),加入到結果鏈表中,
并將對應鏈表的下一個節點值和索引加入最小堆,直到最小堆為空。
最終得到的合并后的鏈表為1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
"""
class Solution:def mergeKLists(self, lists: List[ListNode]) -> ListNode:import heapq# 創建虛擬節點dummy = ListNode(0)p = dummyhead = []# 遍歷鏈表數組for i in range(len(lists)):if lists[i] :# 將每個鏈表的頭結點值和索引加入到最小堆中heapq.heappush(head, (lists[i].val, i))lists[i] = lists[i].nextwhile head:# 彈出最小堆中的值和對應的索引val, idx = heapq.heappop(head)# 創建新節點并連接到結果鏈表上p.next = ListNode(val)p = p.next# 如果該鏈表還有剩余節點,則將下一個節點的值和索引加入到最小堆中if lists[idx]:heapq.heappush(head, (lists[idx].val, idx))lists[idx] = lists[idx].next# 返回合并后的鏈表return dummy.next
146. LRU 緩存 - 力扣(LeetCode)
-
哈希 + 雙向鏈表
- 借用靈神題解的圖,really good
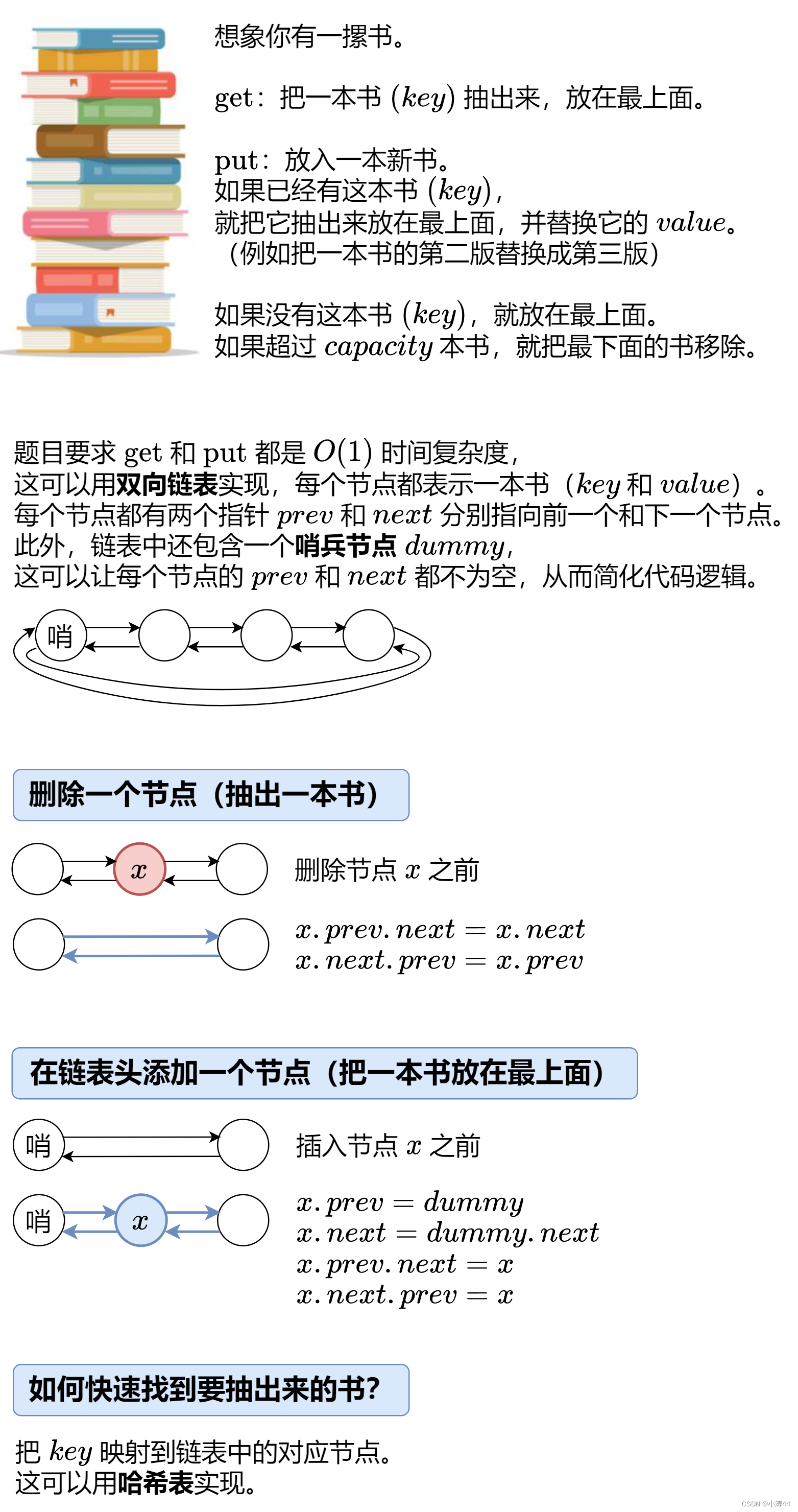
-
class Node:# 提高訪問屬性的速度,并節省內存__slots__ = 'prev', 'next', 'key', 'value'def __init__(self, key=0, value=0):# self.prev = None# self.next = Noneself.key = keyself.value = valueclass LRUCache:def __init__(self, capacity: int):self.capacity = capacityself.dummy = Node() # 哨兵節點self.dummy.prev = self.dummyself.dummy.next = self.dummyself.key_to_node = dict()def get_node(self, key: int) -> Optional[Node]:if key not in self.key_to_node: # 沒有這本書return Nonenode = self.key_to_node[key] # 有這本書self.remove(node) # 把這本書抽出來self.push_front(node) # 放在最上面return nodedef get(self, key: int) -> int:node = self.get_node(key)return node.value if node else -1def put(self, key: int, value: int) -> None:node = self.get_node(key)if node: # 有這本書node.value = value # 更新 valuereturnself.key_to_node[key] = node = Node(key, value) # 新書self.push_front(node) # 放在最上面if len(self.key_to_node) > self.capacity: # 書太多了back_node = self.dummy.prevdel self.key_to_node[back_node.key]self.remove(back_node) # 去掉最后一本書# 刪除一個節點(抽出一本書)def remove(self, x: Node) -> None:x.prev.next = x.nextx.next.prev = x.prev# 在鏈表頭添加一個節點(把一本書放在最上面)def push_front(self, x: Node) -> None:x.prev = self.dummyx.next = self.dummy.nextx.prev.next = xx.next.prev = x# Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = LRUCache(capacity)
# param_1 = obj.get(key)
# obj.put(key,value)
后言
- 鏈表終于結束了!后面這幾道真是難到我了,基本都是CV寫出來的,還是得多沉淀啊?!休息一下,晚上干點活了,不然新學期要被老板罵罵
本文來自互聯網用戶投稿,該文觀點僅代表作者本人,不代表本站立場。本站僅提供信息存儲空間服務,不擁有所有權,不承擔相關法律責任。
如若轉載,請注明出處:http://www.pswp.cn/news/697369.shtml
繁體地址,請注明出處:http://hk.pswp.cn/news/697369.shtml
英文地址,請注明出處:http://en.pswp.cn/news/697369.shtml
如若內容造成侵權/違法違規/事實不符,請聯系多彩編程網進行投訴反饋email:809451989@qq.com,一經查實,立即刪除!




--兩個多項式的和)


)

----生命周期事件)


)




查詢)





