【寸鐵的刷題筆記】樹、dfs、bfs、回溯、遞歸(一)
大家好 我是寸鐵👊
總結了一篇刷題關于樹、dfs、bfs、回溯、遞歸的文章?
喜歡的小伙伴可以點點關注 💝
105. 從前序與中序遍歷序列構造二叉樹
模擬分析圖
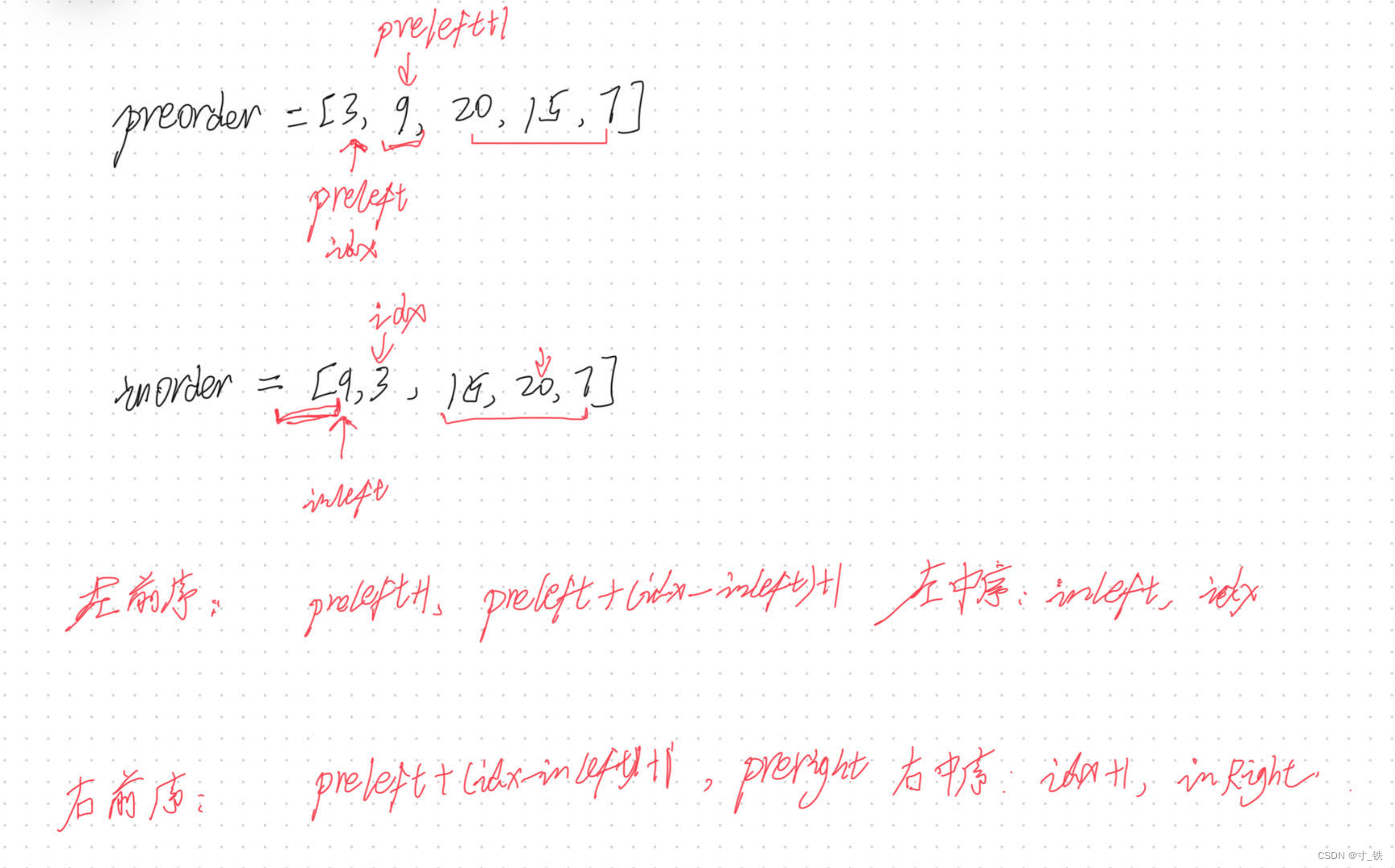
代碼實現
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {return buildTree1(preorder , 0 , preorder.length , inorder , 0 , inorder.length);}public TreeNode buildTree1(int []preorder , int preLeft, int preRight , int []inorder , int inLeft , int inRight){//遞歸終止條件//中序數組中右邊界-左邊界 < 1//返回nullif(inRight - inLeft < 1){return null;}//只有一個節點//則創建該值的節點返回出去即可if(inRight - inLeft == 1){return new TreeNode(inorder[inLeft]);}//前序遍歷中的第一個值為根節點的值int Val = preorder[preLeft];//記錄根節點的下標索引int rootIdx = 0;//在中序數組中查找到第一個值所在的下標//用于根據該下標進行數組的切割TreeNode root = new TreeNode(Val);for(int i = inLeft; i < inRight; i++){if(inorder[i] == Val){rootIdx = i;break;}}//遞歸根節點的左子樹和右子樹//注意: 編寫遞歸時要統一規范//由于上面寫的是i < inRight//這里需要不斷查找每個切分的數組的根節點進行切割。//區間是左閉右開的 要統一規范去寫//清楚是左閉右開后 編寫邏輯如下:root.left = buildTree1(preorder , preLeft + 1 , preLeft + 1 + (rootIdx - inLeft) , inorder , inLeft , rootIdx);root.right = buildTree1(preorder , preLeft+1+(rootIdx - inLeft) , preRight , inorder , rootIdx + 1 , inRight);//返回最后的根節點//每次遞歸時,向上返回該節點,接住該節點的是左孩子或者右孩子return root;}
}106. 從中序與后序遍歷序列構造二叉樹
模擬分析圖

代碼實現
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public TreeNode buildTree(int[] inorder, int[] postorder) {//注:傳入的是中序和后序數組的長度//區間是左閉右開return buildTree1(inorder , 0 , inorder.length , postorder , 0 , postorder.length);}public TreeNode buildTree1(int []inorder , int inleft, int inRight , int[]postorder , int postLeft,int postRight){//對中序數組進行判斷//如果說中序數組的長度 - 起點下標 < 1 //則說明沒有元素 返回空// 0 - 0 = 0 < 1if(inRight - inleft < 1){return null;}//只有一個元素//則創建一個該元素的節點返回即可if(inRight - inleft == 1){return new TreeNode(inorder[inleft]);}//后序數組中的最后一個元素即為根起點int rootVal = postorder[postRight - 1];TreeNode root = new TreeNode(rootVal);int rootIndex = 0;//根據拿到的根節點root在中序數組中找到切割點for(int i = inleft; i < inRight; i++){if(inorder[i] == rootVal){rootIndex = i;}}//根據rootIndex在中、后序數組中劃分左右子樹//在中序中劃分root.left = buildTree1(inorder , inleft , rootIndex, postorder , postLeft , postLeft + (rootIndex - inleft));//在后序中劃分 root.right = buildTree1(inorder, rootIndex + 1, inRight , postorder , postLeft + (rootIndex - inleft) , postRight - 1); return root;}
}
112. 路徑總和
代碼實現
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {//如果說根節點為空 則無法得到目標和 直接返回falseif(root == null) return false;//采用的是減法 看最后targetSum 減少到最后是否為0//遞歸調用 傳入根節點 此時count和為targetSum - 當前根節點的值return traversal(root , targetSum - root.val);}public boolean traversal(TreeNode cur , int count){//如果說左子樹和右子樹都為空(此為葉子節點) 并且count等于0//則說明存在路徑使得節點之和為targetSum//返回trueif(cur.left == null && cur.right == null && count == 0)return true;//否則返回falseif(cur.left == null && cur.right == null && count == 0)return false;//遞歸邏輯//遞歸左子樹if(cur.left != null){//減去當前遍歷到的節點值count -= cur.left.val;//注意:這里需要向上返回布爾值//如果往左子樹遍歷的結果為true//則向上返回trueif(traversal(cur.left , count)){return true;}//回溯 把之前減去的節點值加上//再從另一個分支去尋找是否存在路徑count += cur.left.val;}//同理,遞歸右子樹if(cur.right != null){count -= cur.right.val;if(traversal(cur.right , count)){return true;}count += cur.right.val;}return false;}
}113. 路徑總和 II
相比較 112. 路徑總和
113. 路徑總和 II || 與下面的 129. 求根節點到葉節點數字之和
共同的邏輯都是需要遍歷一棵樹從根節點到所有葉子節點
這意味著需要一個數據結構(list)去存儲所有經過的路徑上的節點
也就意味著不需要返回值,但是由于需要遍歷所有的葉子節點
這里需要進行向上回溯,也就是怎么來的就怎么去(恢復現場)
代碼實現
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {//result隊列用于接收滿足條件的pathList<List<Integer>> result;//path用于接收每次搜索的結果//這里不用開啟全局變量//原因:path會遍歷到葉子節點會向上回溯 LinkedList<Integer> path;public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {result = new LinkedList<>();path = new LinkedList<>();travesal(root , targetSum);return result;}//這里由于有path接收搜索的結點//所以,這里不需要去返回值public void travesal(TreeNode root , int count){//如果說根節點為空 則直接結束if(root == null) return;//先把當前的節點值加入到path隊列中path.offer(root.val);//然后,更新當前的count 把當前添加入隊列的節點值減去count -= root.val;//接著,處理臨界條件,也就是遍歷到葉子節點對答案的判斷if(root.left == null && root.right == null && count == 0){//滿足條件則把當前遍歷的節點添加到path隊列中result.add(new LinkedList<>(path));}//向下遞歸,遍歷左子樹和右子樹//這里是直接往左子樹或者右子樹的某個方向能走的路走到底//無論是往右還是左走 走到底即可//走到底無路可走后再向上回溯 依次移除最后一個元素 再去搜索其他分支travesal(root.left , count);travesal(root.right , count);path.removeLast();}
}
debug
class Solution {List<List<Integer>> result;LinkedList <Integer> path;public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {result = new LinkedList<>();path = new LinkedList<>();travesal(root , targetSum);return result;}public void travesal(TreeNode root , int count){if(root == null)return;path.offer(root.val);count -= root.val;System.out.println("111111111");System.out.println(path);if(root.left == null && root.right == null && count == 0){//打印出來去看path的變化過程System.out.println("22222222");System.out.println(path);result.add(new LinkedList<>(path));}travesal(root.left , count);System.out.println("leftleftleftleftleftleft");System.out.println(path);travesal(root.right , count);System.out.println("333333333333");System.out.println(path);//依次移除掉最后一個節點,向上回溯//直至移除到最后一個根節點path.removeLast();}
}
129. 求根節點到葉節點數字之和
代碼實現
/*** Definition for a binary tree node.* public class TreeNode {* int val;* TreeNode left;* TreeNode right;* TreeNode() {}* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {* this.val = val;* this.left = left;* this.right = right;* }* }*/
class Solution {//path存儲dfs到的節點List<Integer>path = new LinkedList<>();//記錄最終求和的結果int res = 0;public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {//如果root為null 則返回0if(root == null)return 0;//如果root不為null 則把根節點添加到path中path.add(root.val);travesal(root);return res;}public void travesal(TreeNode root){//遍歷到葉子節點則對當前的path的值求和if(root.left == null && root.right == null){res += listToInt(path);}//遍歷左子樹if(root.left != null){//先添加左子樹節點的值path.add(root.left.val);//再繼續遞歸到下一層travesal(root.left);//移除掉當前隊列中的最后一個元素 向上回溯path.remove(path.size() - 1);}//遍歷右子樹if(root.right != null){path.add(root.right.val);travesal(root.right);path.remove(path.size() - 1);}}//對path中存儲的節點值進行求和public int listToInt(List<Integer> path){int sum = 0;//這里由于list是隊列 先進先出//在原來的sum基礎上乘10 再加上最后一個元素即可for(Integer s : path){sum = sum * 10 + s;}return sum;}}
總結
大邏輯其實還是最核心的三個點,一個是根節點,一個是左孩子 ,一個是右孩子。
可以把遞歸函數看成是一個整體部分,整體的去對左子樹進行處理,整體
的去對右子樹進行處理,然后返回結果或者說記錄結果,不必去深究遞歸里面的細節,會讓整個的解題思路變得十分復制混亂,就是理解為遞歸函數去幫助你進行處理,最后返回一個結果或者將結果存起來就好了!
看到這里的小伙伴,恭喜你又掌握了一個技能👊
希望大家能取得勝利,堅持就是勝利💪
我是寸鐵!我們下期再見💕
往期好文💕
保姆級教程
【保姆級教程】Windows11下go-zero的etcd安裝與初步使用
【保姆級教程】Windows11安裝go-zero代碼生成工具goctl、protoc、go-zero
【Go-Zero】手把手帶你在goland中創建api文件并設置高亮
報錯解決
【Go-Zero】Error: user.api 27:9 syntax error: expected ‘:‘ | ‘IDENT‘ | ‘INT‘, got ‘(‘ 報錯解決方案及api路由注意事項
【Go-Zero】Error: only one service expected goctl一鍵轉換生成rpc服務錯誤解決方案
【Go-Zero】【error】 failed to initialize database, got error Error 1045 (28000):報錯解決方案
【Go-Zero】Error 1045 (28000): Access denied for user ‘root‘@‘localhost‘ (using password: YES)報錯解決方案
【Go-Zero】type mismatch for field “Auth.AccessSecret“, expect “string“, actual “number“報錯解決方案
【Go-Zero】Error: user.api 30:2 syntax error: expected ‘)‘ | ‘KEY‘, got ‘IDENT‘報錯解決方案
【Go-Zero】Windows啟動rpc服務報錯panic:context deadline exceeded解決方案
Go面試向
【Go面試向】defer與time.sleep初探
【Go面試向】defer與return的執行順序初探
【Go面試向】Go程序的執行順序
【Go面試向】rune和byte類型的認識與使用
【Go面試向】實現map穩定的有序遍歷的方式








)
)

)


)


![[newstarctf2023] --RE wp](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[newstarctf2023] --RE wp)
)
