1、線性表
2、線性鏈表
3、棧
4、隊列
5、串
6、數組
7、廣義表
8、樹和二叉樹
二叉樹:每個結點至多只有兩棵子樹(即二叉樹中不存在度大于2的結點),并且,二叉樹的子樹有左右之分,其次序不能任意顛倒。
二叉樹的性質:
性質1:在二叉樹的第?i?層上至多有2i-1個結點。
性質2:深度為k的二叉樹至多有2k-1個結點(k>=1)。
性質3:對任何一顆二叉樹T,如果其終端結點數為n0,度為2的結點數為n2,則n0=n2+1。
| 設n1為二叉樹T中度為1的節點數,因為二叉樹中所有結點的度均小于或等于2,所以其結點總數為:n=n0+n1+n2;再看二叉樹中的分支數,除了根節點外,其余結點都有一個分支進入,設B為分支數,則n=B+1;由于這些分支是由度為1或2的結點射出的,所以有B=n1+2*n2,于是得n=n1+2n2+1,所以n0=n2+1 |
滿二叉樹:一棵深度為k且有2k-1個結點的二叉樹。每一層上的結點數都是最大結點數。
完全二叉樹:如果對滿二叉樹的結點進行連續編號,約定編號從根結點起,自上而下,自左至右。深度為k的,有n個結點的二叉樹,當且僅當其每一個結點都與深度為k的滿二叉樹中編號從1至n的結點一一對應。
特點:(1)葉子結點只可能在層次最大的兩層上出現;(2)對任一結點,若其右分支下的子孫的最大層次為h,則其左分支下的子孫的最大層次必為lh+1。
性質4:具有n個結點的完全二叉樹的深度為log2n+1(2為下標,取log2n最小整數)。
性質5:如果對一棵有n個結點的完全二叉樹(其深度為log2n+1)(取log2n最小整數)的結點按層序編號(從第1層到第log2n+1層,每層從左到右),則對任一結點i(1<=i<=n),有:
(1)如果i=1,則結點i是二叉樹的根,無雙親;如果i>1,則其雙親PARENT(i)是結點i/2(取最小整數)。
(2)如果2i>n,則結點i無左孩子(結點i為葉子結點);否則其左孩子LCHILD(i)是結點2i。
(3)如果2i+1>n,則結點i無右孩子;否則其右孩子RCHILD(i)是結點2i+1。
最優二叉樹(赫夫曼樹):從樹中一個結點到另一個結點之間的分支構成這兩個結點之間的路徑,路徑上的分支數目稱為路徑長度。樹的路徑長度是從樹根到每一個結點的路徑長度之和。結點的帶權路徑長度為從該結點到樹根之間的路徑長度與結點上權的乘積。樹的帶權路徑長度為樹中所有葉子結點的帶權路徑長度之和。
二叉排序樹:或者是一棵空樹;或者是具有下列性質的二叉樹:(1)若它的左子樹不空,則左子樹上所有結點的值均小于它的根節點的值;(2)若它的右子樹上所有結點的值均大于它的根節點的值;(3)它的左、右子樹也分別為二叉排序樹。
平衡二叉樹:又稱AVL樹。它或者是一棵空樹,或者是具有下列性質的二叉樹。它的左子樹和右子樹都是平衡二叉樹,且左子樹和右子樹的深度只差的絕對值不超過1。若將二叉樹上結點的平衡因子BF定義為該結點的左子樹的深度減去它的右子樹的深度,則平衡二叉樹上所有結點的平衡因子只可能是-1、0和1。
紅黑樹:紅黑樹是一種自平衡排序二叉樹,樹中每個節點的值,都大于或等于在它的左子樹中的所有節點的值,并且小于或等于在它的右子樹中的所有節點的值,這確保紅黑樹運行時可以快速地在樹中查找和定位的所需節點。
- 性質 1:每個節點要么是紅色,要么是黑色。
- 性質 2:根節點永遠是黑色的。
- 性質 3:所有的葉節點都是空節點(即 null),并且是黑色的。
- 性質 4:每個紅色節點的兩個子節點都是黑色。(從每個葉子到根的路徑上不會有兩個連續的紅色節點)
- 性質 5:從任一節點到其子樹中每個葉子節點的路徑都包含相同數量的黑色節點。
Java 中實現的紅黑樹可能有如圖所示結構:
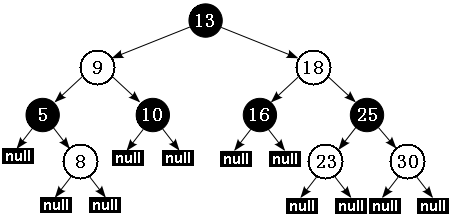
?
備注:本文中所有關于紅黑樹中的示意圖采用白色代表紅色。黑色節點還是采用了黑色表示。
根據性質 5:紅黑樹從根節點到每個葉子節點的路徑都包含相同數量的黑色節點,因此從根節點到葉子節點的路徑中包含的黑色節點數被稱為樹的“黑色高度(black-height)”。
性質 4 則保證了從根節點到葉子節點的最長路徑的長度不會超過任何其他路徑的兩倍。假如有一棵黑色高度為 3 的紅黑樹:從根節點到葉節點的最短路徑長度是 2,該路徑上全是黑色節點(黑節點 - 黑節點 - 黑節點)。最長路徑也只可能為 4,在每個黑色節點之間插入一個紅色節點(黑節點 - 紅節點 - 黑節點 - 紅節點 - 黑節點),性質 4 保證絕不可能插入更多的紅色節點。由此可見,紅黑樹中最長路徑就是一條紅黑交替的路徑。
? ??
B-樹:B-數是一種平衡的多路查找樹,一棵m階B-樹,或為空樹,或為滿足下列特性的m叉樹:(m≥3)
? ??? ??(1)根結點只有1個,關鍵字字數的范圍[1,m-1],分支數量范圍[2,m];
? ??? ??(2)除根以外的非葉結點,每個結點包含分支數范圍[[m/2],m],即關鍵字字數的范圍是[[m/2]-1,m-1],其中[m/2]表示取大于m/2的最小整數;
? ??? ??(3)非葉結點是由葉結點分裂而來的,所以葉結點關鍵字個數也滿足[[m/2]-1,m-1];
? ??? ??(4)所有的非終端結點包含信息:(n,P0,K1,P1,K2,P2,……,Kn,Pn),
????其中Ki為關鍵字,Pi為指向子樹根結點的指針,并且Pi-1所指子樹中的關鍵字均小于Ki,而Pi所指的關鍵字均大于Ki(i=1,2,……,n),n+1表示B-樹的階,n表示關鍵字個數,即[ceil(m / 2)-1]<= n <= m-1;
? ??? ??(5)所有葉子結點都在同一層,并且指針域為空,具有如下性質:
根據B-樹定義,第一層為根有一個結點,至少兩個分支,第二層至少2個結點,i≥3時,每一層至少有2乘以([m/2])的i-2次方個結點([m/2]表示取大于m/2的最小整數)。若m階樹中共有N個結點,那么可以推導出N必然滿足N≥2*(([m/2])的h-1次方)-1 (h≥1),因此若查找成功,則高度h≤1+log[m/2](N+1)/2,h也是磁盤訪問次數(h≥1),保證了查找算法的高效率。
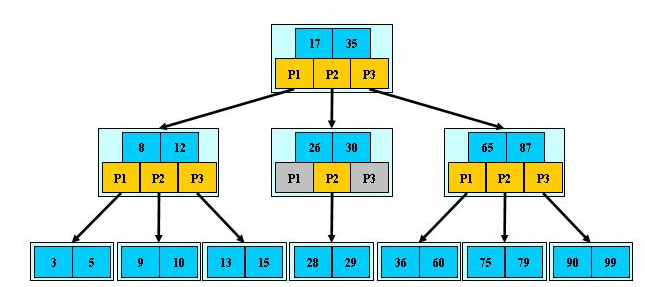
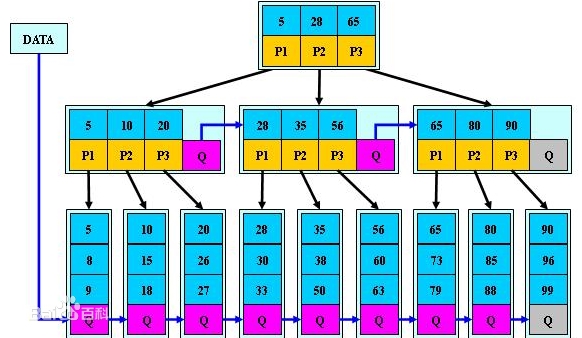
? ? ? ?1)非葉子結點的子樹指針與關鍵字個數相同;
? ? ? ?2)非葉子結點的子樹指針P[i],指向關鍵字值屬于[K[i], K[i+1])的子樹(B-樹是開區間);
? ? ? ?3)為所有葉子結點增加一個鏈指針;
? ? ? ?4)所有關鍵字都在葉子結點出現;
9、圖
?
?
各種排序算法的比較:
?
?
一、插入排序
1、直接插入
穩定,平均和最壞都是O(n2)。它的工作原理是通過構建有序序列,對于未排序數據,在已排序序列中從后向前掃描,找到相應位置并插入。插入排序在實現上,通常采用in-place排序(即只需用到O(1)的額外空間的排序),因而在從后向前掃描過程中,需要反復把已排序元素逐步向后挪位,為最新元素提供插入空間。?
2、Shell排序
不穩定,平均O(n3/2),最壞O(n2)。它的基本思想是先取一個小于n的整數d1作為第一個增量,把文件的全部記錄分成d1個組。所有距離為dl的倍數的記錄放在同一個組中。先在各組內進行直接插人排序;然后,取第二個增量d2<d1重復上述的分組和排序,直至所取的增量dt=1(dt<dt-l<…<d2<d1),即所有記錄放在同一組中進行直接插入排序為止。該方法實質上是一種分組插入方法。
代碼實現:
?
package com.yyq;import java.util.Arrays;/*** Created by Administrator on 2015/9/9.*/
public class InsertSort {public static void insertDirectlySort(int a[]) {if (a == null) return;int len = a.length;try {for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {for (int j = i + 1; j < len && j > 0; j--) {if (a[j] < a[j - 1]) {int temp = a[j];a[j] = a[j - 1];a[j - 1] = temp;}}}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();}}public static void shellSort(int data[]) {if (data == null) return;int j = 0;int temp = 0;int len = data.length / 2;for (int increment = len; increment > 0; increment /= 2) {for (int i = increment; i < data.length; i++) {temp = data[i];for (j = i; j >= increment; j -= increment) {if(temp < data[j - increment]){data[j] = data[j - increment];}else{break;}}data[j] = temp;}}}public static void Test(int a[],int b[]) {System.out.println("The Source Secquence:");if (a == null) return;System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));insertDirectlySort(a);System.out.println("InsertDirectlySort Result: ");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));shellSort(b);System.out.println("ShellSort Result:");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args){int a1[] = null;int a2[] = {1};int a3[] = {3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4};int a4[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};int a5[] = {6, 9, 4, 8, -1};int a6[] = {9, 5, 4, 2, 1};int b1[] = null;int b2[] = {1};int b3[] = {3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4};int b4[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};int b5[] = {6, 9, 4, 8, -1};int b6[] = {9, 5, 4, 2, 1};Test(a1,b1);Test(a2,b2);Test(a3,b3);Test(a4,b4);Test(a5,b5);Test(a6,b6);} }
?
輸出結果:
| The Source Secquence: The Source Secquence: [1] InsertDirectlySort Result:? [1] ShellSort Result: [1] ? The Source Secquence: [3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4] InsertDirectlySort Result:? [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9] ShellSort Result: [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] InsertDirectlySort Result:? [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] ShellSort Result: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [6, 9, 4, 8, -1] InsertDirectlySort Result:? [-1, 4, 6, 8, 9] ShellSort Result: [-1, 4, 6, 8, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [9, 5, 4, 2, 1] InsertDirectlySort Result:? [1, 2, 4, 5, 9] ShellSort Result: [1, 2, 4, 5, 9] |
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
二、選擇排序
1、直接選擇
不穩定,平均和最壞都是O(n2)。是一種簡單直觀的排序算法。它的工作原理如下。首先在未排序序列中找到最小元素,存放到排序序列的起始位置,然后,再從剩余未排序元素中繼續尋找最小元素,然后放到排序序列末尾(目前已被排序的序列)。以此類推,直到所有元素均排序完畢。
2、堆排序
不穩定,平均和最壞都是O(nlogn),輔助存儲O(1)。利用堆這種數據結構所設計的一種排序算法。堆是一個近似完全二叉樹的結構,并同時滿足堆性質:即子結點的鍵值或索引總是小于(或者大于)它的父節點。
package com.yyq;import java.util.Arrays;/*** Created by Administrator on 2015/9/9.*/ public class SelectSort {public static void selectDirectlySort(int[] a) {if (a == null) return;int min = 0;int i = 0;int j = 0;int index = 0;int len = a.length;for (i = 0; i < len - 1; i++) {min = a[i];index = i;for (j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {if (a[j] < min) {min = a[j];index = j;}}a[index] = a[i];a[i] = min;}}public static void heapSort(int[] array) {if (array == null) return;buildHeap(array);//構建堆int n = array.length;int i = 0;for (i = n - 1; i >= 1; i--) {swap(array, 0, i);heapify(array, 0, i);}}//構建public static void buildHeap(int[] array) {int n = array.length;//數組中元素的個數for (int i = n / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)heapify(array, i, n);}public static void heapify(int[] A, int idx, int max) {int left = 2 * idx + 1;// 左孩子的下標(如果存在的話)int right = 2 * idx + 2;// 左孩子的下標(如果存在的話)int largest = 0;//尋找3個節點中最大值節點的下標if (left < max && A[left] > A[idx])largest = left;elselargest = idx;if (right < max && A[right] > A[largest])largest = right;if (largest != idx) {swap(A, largest, idx);heapify(A, largest, max);}}public static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j) {int temp = 0;temp = array[i];array[i] = array[j];array[j] = temp;}public static void Test(int a[], int b[]) {System.out.println("The Source Secquence:");if (a == null) return;System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));selectDirectlySort(a);System.out.println("BubbleSort Result: ");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));heapSort(b);System.out.println("QuickSort Result:");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) {int a1[] = null;int a2[] = {1};int a3[] = {3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4};int a4[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};int a5[] = {6, 9, 4, 8, -1};int a6[] = {9, 5, 4, 2, 1};int b1[] = null;int b2[] = {1};int b3[] = {3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4};int b4[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};int b5[] = {6, 9, 4, 8, -1};int b6[] = {9, 5, 4, 2, 1};Test(a1, b1);Test(a2, b2);Test(a3, b3);Test(a4, b4);Test(a5, b5);Test(a6, b6);} }
輸出結果:
| The Source Secquence: The Source Secquence: [1] BubbleSort Result:? [1] QuickSort Result: [1] ? The Source Secquence: [3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4] BubbleSort Result:? [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9] QuickSort Result: [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] BubbleSort Result:? [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] QuickSort Result: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [6, 9, 4, 8, -1] BubbleSort Result:? [-1, 4, 6, 8, 9] QuickSort Result: [-1, 4, 6, 8, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [9, 5, 4, 2, 1] BubbleSort Result:? [1, 2, 4, 5, 9] QuickSort Result: [1, 2, 4, 5, 9] |
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
三、交換排序
1、冒泡排序
穩定,平均和最壞都是O(n2)。是一種簡單的排序算法。它重復地走訪過要排序的數列,一次比較兩個元素,如果他們的順序錯誤就把他們交換過來。走訪數列的工作是重復地進行直到沒有再需要交換,也就是說該數列已經排序完成。這個算法的名字由來是因為越小的元素會經由交換慢慢“浮”到數列的頂端。
2、快速排序
不穩定,平均O(nlogn),最壞O(n2),輔助存儲O(logn)。基本思想是:通過一趟排序將要排序的數據分割成獨立的兩部分,其中一部分的所有數據都比另外一部分的所有數據都要小,然后再按此方法對這兩部分數據分別進行快速排序,整個排序過程可以遞歸進行,以此達到整個數據變成有序序列。
package com.yyq;import java.util.Arrays;/*** Created by Administrator on 2015/9/10.*/ public class ChangeSort {public static void swap(int[] array, int i, int j){int temp = array[i];array[i] = array[j];array[j] = temp;}public static void bubbleSort(int[] array){if (array == null) return;int len = array.length;;for(int i = 0; i < len-1; i++){for (int j = len-1; j > i; j--){if (array[j] < array[j-1] ){swap(array,j,j-1);}}}}public static void quickSort(int[] array, int low, int high){if (array == null || low < 0 || high < 0 || low >= array.length) return;int pivotloc = partition(array, low, high);if(low < high){quickSort(array, low, pivotloc-1);quickSort(array,pivotloc+1,high);}}public static int partition(int[] array, int low, int high){int pivokey = array[low];while(low < high){while(low < high && array[high] >= pivokey){high--;}array[low] = array[high];while(low < high && array[low] <= pivokey){low++;}array[high] = array[low];}array[low] = pivokey;return low;}public static void Test(int a[],int b[]) {System.out.println("The Source Secquence:");if (a == null) return;System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));bubbleSort(a);System.out.println("BubbleSort Result: ");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));quickSort(b, 0, b.length-1);System.out.println("QuickSort Result:");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b));System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args){int a1[] = null;int a2[] = {1};int a3[] = {3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4};int a4[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};int a5[] = {6, 9, 4, 8, -1};int a6[] = {9, 5, 4, 2, 1};int b1[] = null;int b2[] = {1};int b3[] = {3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4};int b4[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};int b5[] = {6, 9, 4, 8, -1};int b6[] = {9, 5, 4, 2, 1};Test(a1,b1);Test(a2,b2);Test(a3,b3);Test(a4,b4);Test(a5,b5);Test(a6,b6);} }
輸出結果:
| The Source Secquence: The Source Secquence: [1] BubbleSort Result:? [1] QuickSort Result: [1] ? The Source Secquence: [3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4] BubbleSort Result:? [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9] QuickSort Result: [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] BubbleSort Result:? [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] QuickSort Result: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [6, 9, 4, 8, -1] BubbleSort Result:? [-1, 4, 6, 8, 9] QuickSort Result: [-1, 4, 6, 8, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [9, 5, 4, 2, 1] BubbleSort Result:? [1, 2, 4, 5, 9] QuickSort Result: [1, 2, 4, 5, 9] |
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
四、歸并排序(臺灣譯作:合并排序):
穩定,平均和最壞都是O(nlogn),輔助存儲O(n)。是建立在歸并操作上的一種有效的排序算法。將兩個(或兩個以上)有序表合并成一個新的有序表?即把待排序序列分為若干個子序列,每個子序列是有序的。然后再把有序子序列合并為整體有序序列。
package com.yyq;import java.util.Arrays;/*** Created by Administrator on 2015/9/10.*/ public class MergingSort {public static void Test(int a[]) {System.out.println("The Source Secquence:");if (a == null) return;System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));mergeSort(a,0,a.length-1);System.out.println("MergeSort Result: ");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args){int a1[] = null;int a2[] = {1};int a3[] = {3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4};int a4[] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};int a5[] = {6, 9, 4, 8, -1};int a6[] = {9, 5, 4, 2, 1};Test(a1);Test(a2);Test(a3);Test(a4);Test(a5);Test(a6);}public static int[] mergeSort(int[] nums, int low, int high) {if (nums == null || low < 0 || low > nums.length-1 || high < 0) return nums;int mid = (low + high) / 2;if (low < high) {// 左邊 mergeSort(nums, low, mid);// 右邊mergeSort(nums, mid + 1, high);// 左右歸并 merge(nums, low, mid, high);}return nums;}public static void merge(int[] nums, int low, int mid, int high) {int[] temp = new int[high - low + 1];int i = low;// 左指針int j = mid + 1;// 右指針int k = 0;// 把較小的數先移到新數組中while (i <= mid && j <= high) {if (nums[i] < nums[j]) {temp[k++] = nums[i++];} else {temp[k++] = nums[j++];}}// 把左邊剩余的數移入數組while (i <= mid) {temp[k++] = nums[i++];}// 把右邊邊剩余的數移入數組while (j <= high) {temp[k++] = nums[j++];}// 把新數組中的數覆蓋nums數組for (int k2 = 0; k2 < temp.length; k2++) {nums[k2 + low] = temp[k2];}} }
輸出結果:
| The Source Secquence: The Source Secquence: [1] MergeSort Result:? [1] ? The Source Secquence: [3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4] MergeSort Result:? [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] MergeSort Result:? [1, 3, 5, 7, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [6, 9, 4, 8, -1] MergeSort Result:? [-1, 4, 6, 8, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [9, 5, 4, 2, 1] MergeSort Result:? [1, 2, 4, 5, 9] |
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
五、基數排序又稱“桶子法”:
穩定,平均和最壞都是O(d(n+rd)),對于n個記錄,每個記錄含d個關鍵字(即位數),每個關鍵字的取值范圍為rd個值。它是透過鍵值的部份資訊,將要排序的元素分配至某些“桶”中,藉以達到排序的作用。
package com.yyq;import java.util.Arrays;/*** Created by Administrator on 2015/9/10.*/ public class RadixSort {public static void radixSort(int[] array, int num, int radix) {if (array == null) return;int k = 0;int n = 1;int index = 1;int len = array.length;//分成nums.length個桶int[][] radixArray = new int[radix][radix];//每個桶放的個數組成的數組int[] tempArray = new int[radix];for (int i = 0; i < tempArray.length; i++){tempArray[i] = 0;}//還在位數內while (index <= num) {for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {//個,十,百,千...int temp = (array[i] / n) % 10;//存入特定桶的特定位置radixArray[temp][tempArray[temp]] = array[i];tempArray[temp] = tempArray[temp] + 1;}for (int i = 0; i < radix; i++) {if (tempArray[i] != 0) {for (int j = 0; j < tempArray[i]; j++) {//數組重組array[k] = radixArray[i][j];k++;}//重置,以防下次循環時數據出錯tempArray[i] = 0;}}//重置,以防下次循環時數據出錯k = 0;//進位n *= 10;index++;}}// 基數排序的實現public static void Test(int a[]) {System.out.println("The Source Secquence:");if (a == null) return;System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));int num = 0;int max_num = num;for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++){int temp = a[i];while(temp != 0){num++;temp = temp / 10;}if (num > max_num){max_num = num;}num = 0;}System.out.println("The largest number'length is:"+max_num);radixSort(a, max_num,10);System.out.println("RadixSort Result: ");System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a));System.out.println();}public static void main(String[] args) {int a1[] = null;int a2[] = {1};int a3[] = {3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4};int a4[] = {110, 35, 4855, 2726,562599};int a5[] = {278, 109, 930, 184, 505, 269, 800, 831};int a6[] = {9, 35, 4, 2, 1};Test(a1);Test(a2);Test(a3);Test(a4);Test(a5);Test(a6);} }
輸出結果:
| The Source Secquence: The Source Secquence: [1] The largest number'length is:1 RadixSort Result:? [1] ? The Source Secquence: [3, 6, 1, 8, 2, 9, 4] The largest number'length is:1 RadixSort Result:? [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 9] ? The Source Secquence: [110, 35, 4855, 2726, 562599] The largest number'length is:6 RadixSort Result:? [35, 110, 2726, 4855, 562599] ? The Source Secquence: [278, 109, 930, 184, 505, 269, 800, 831] The largest number'length is:3 RadixSort Result:? [109, 184, 269, 278, 505, 800, 831, 930] ? The Source Secquence: [9, 35, 4, 2, 1] The largest number'length is:2 RadixSort Result:? [1, 2, 4, 9, 35] |

CONDITION(條件)實現線程同步通信)




![20180601]函數與標量子查詢2.txt](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/20180601]函數與標量子查詢2.txt)



)








