簡介
ConcurrentHashMap是線程安全的HashMap實現,這里主要研究JDK8后的ConcurrentHashMap,下面是ConcurrentHashMap的簡單結構: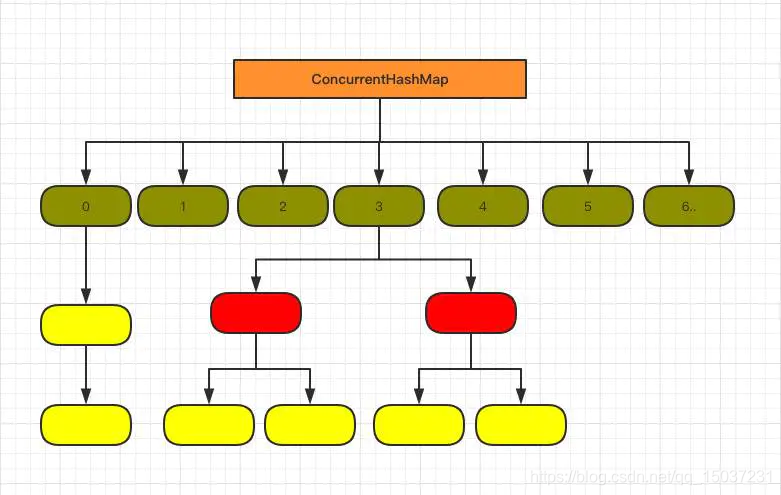
ConcurrentHashMap基于HashMap的基本邏輯,通過CAS + synchronized 來保證并發安全性。ConcurrentHashMap使用的數組及數組的每個節點都為volatile類型,通過CAS進行更新刪除操作,而所有的鏈表操作都需要通過synchronized鎖定鏈表的頭節點,然后進行操作。
/*** The array of bins. Lazily initialized upon first insertion.* Size is always a power of two. Accessed directly by iterators.*/transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;/*** Key-value entry. This class is never exported out as a* user-mutable Map.Entry (i.e., one supporting setValue; see* MapEntry below), but can be used for read-only traversals used* in bulk tasks. Subclasses of Node with a negative hash field* are special, and contain null keys and values (but are never* exported). Otherwise, keys and vals are never null.*/static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {final int hash;final K key;volatile V val;volatile Node<K,V> next;}
核心方法
1.put方法
final V putVal(K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {if (key == null || value == null) throw new NullPointerException();int hash = spread(key.hashCode());int binCount = 0;for (Node<K,V>[] tab = table;;) {Node<K,V> f; int n, i, fh;if (tab == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)tab = initTable();else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i = (n - 1) & hash)) == null) {if (casTabAt(tab, i, null,new Node<K,V>(hash, key, value, null)))break; // no lock when adding to empty bin}else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)tab = helpTransfer(tab, f);else {V oldVal = null;synchronized (f) {if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {if (fh >= 0) {binCount = 1;for (Node<K,V> e = f;; ++binCount) {K ek;if (e.hash == hash &&((ek = e.key) == key ||(ek != null && key.equals(ek)))) {oldVal = e.val;if (!onlyIfAbsent)e.val = value;break;}Node<K,V> pred = e;if ((e = e.next) == null) {pred.next = new Node<K,V>(hash, key,value, null);break;}}}else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {Node<K,V> p;binCount = 2;if ((p = ((TreeBin<K,V>)f).putTreeVal(hash, key,value)) != null) {oldVal = p.val;if (!onlyIfAbsent)p.val = value;}}}}if (binCount != 0) {if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD)treeifyBin(tab, i);if (oldVal != null)return oldVal;break;}}}addCount(1L, binCount);return null;}
我們可以看到put是通過一個死循環來實現,在循環邏輯內:
- 首先檢查核心的Node<K,V>[] table是否已經初始化,如果沒有初始化,則利用CAS將sizeCtl的值置為-1進行初始化。
- 通過CAS查詢key相應的槽位是否為 null,若為null直接通過CAS將鍵值對放入槽位。
- 如果相應的槽位已經有節點,并且其hash值為-1,則表示正在進行擴容,則當前線程幫忙進行擴容。
- 否則通過synchronized鎖住槽位內的節點即鏈表的頭結點,然后遍歷鏈表,尋找是否有hash值及key值相同的節點,若有則將value設置進去,否者創建新的節點加入鏈表。
- 通過addCount函數更新ConcurrentHashMap鍵值對的數量。
2.get方法
public V get(Object key) {Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> e, p; int n, eh; K ek;int h = spread(key.hashCode());if ((tab = table) != null && (n = tab.length) > 0 &&(e = tabAt(tab, (n - 1) & h)) != null) {if ((eh = e.hash) == h) {if ((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek)))return e.val;}else if (eh < 0)return (p = e.find(h, key)) != null ? p.val : null;while ((e = e.next) != null) {if (e.hash == h &&((ek = e.key) == key || (ek != null && key.equals(ek))))return e.val;}}return null;}
get方法實現的邏輯比較簡單:
- 利用key通過cas的方式獲取其對應槽位的節點,若該節點就是想要查詢的節點,那就直接返回value。
- 如果槽位內節點的hash值小于0則說明正在進行擴容,則通過ForwardingNode的find函數去新的數組nextTable中進行查找。
- 以上都不符合的話,就直接遍歷節點,匹配就返回,否則最后就返回null。
3.擴容方法
/*** Helps transfer if a resize is in progress.*/final Node<K,V>[] helpTransfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V> f) {Node<K,V>[] nextTab; int sc;if (tab != null && (f instanceof ForwardingNode) &&(nextTab = ((ForwardingNode<K,V>)f).nextTable) != null) {int rs = resizeStamp(tab.length);while (nextTab == nextTable && table == tab &&(sc = sizeCtl) < 0) {if ((sc >>> RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT) != rs || sc == rs + 1 ||sc == rs + MAX_RESIZERS || transferIndex <= 0)break;if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc, sc + 1)) {transfer(tab, nextTab);break;}}return nextTab;}return table;}/*** Moves and/or copies the nodes in each bin to new table. See* above for explanation.*/private final void transfer(Node<K,V>[] tab, Node<K,V>[] nextTab) {int n = tab.length, stride;if ((stride = (NCPU > 1) ? (n >>> 3) / NCPU : n) < MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE)stride = MIN_TRANSFER_STRIDE; // subdivide rangeif (nextTab == null) { // initiatingtry {@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")Node<K,V>[] nt = (Node<K,V>[])new Node<?,?>[n << 1];nextTab = nt;} catch (Throwable ex) { // try to cope with OOMEsizeCtl = Integer.MAX_VALUE;return;}nextTable = nextTab;transferIndex = n;}int nextn = nextTab.length;ForwardingNode<K,V> fwd = new ForwardingNode<K,V>(nextTab);boolean advance = true;boolean finishing = false; // to ensure sweep before committing nextTabfor (int i = 0, bound = 0;;) {Node<K,V> f; int fh;while (advance) {int nextIndex, nextBound;if (--i >= bound || finishing)advance = false;else if ((nextIndex = transferIndex) <= 0) {i = -1;advance = false;}else if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, TRANSFERINDEX, nextIndex,nextBound = (nextIndex > stride ?nextIndex - stride : 0))) {bound = nextBound;i = nextIndex - 1;advance = false;}}if (i < 0 || i >= n || i + n >= nextn) {int sc;if (finishing) {nextTable = null;table = nextTab;sizeCtl = (n << 1) - (n >>> 1);return;}if (U.compareAndSwapInt(this, SIZECTL, sc = sizeCtl, sc - 1)) {if ((sc - 2) != resizeStamp(n) << RESIZE_STAMP_SHIFT)return;finishing = advance = true;i = n; // recheck before commit}}else if ((f = tabAt(tab, i)) == null)advance = casTabAt(tab, i, null, fwd);else if ((fh = f.hash) == MOVED)advance = true; // already processedelse {synchronized (f) {if (tabAt(tab, i) == f) {Node<K,V> ln, hn;if (fh >= 0) {int runBit = fh & n;Node<K,V> lastRun = f;for (Node<K,V> p = f.next; p != null; p = p.next) {int b = p.hash & n;if (b != runBit) {runBit = b;lastRun = p;}}if (runBit == 0) {ln = lastRun;hn = null;}else {hn = lastRun;ln = null;}for (Node<K,V> p = f; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {int ph = p.hash; K pk = p.key; V pv = p.val;if ((ph & n) == 0)ln = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, ln);elsehn = new Node<K,V>(ph, pk, pv, hn);}setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);advance = true;}else if (f instanceof TreeBin) {TreeBin<K,V> t = (TreeBin<K,V>)f;TreeNode<K,V> lo = null, loTail = null;TreeNode<K,V> hi = null, hiTail = null;int lc = 0, hc = 0;for (Node<K,V> e = t.first; e != null; e = e.next) {int h = e.hash;TreeNode<K,V> p = new TreeNode<K,V>(h, e.key, e.val, null, null);if ((h & n) == 0) {if ((p.prev = loTail) == null)lo = p;elseloTail.next = p;loTail = p;++lc;}else {if ((p.prev = hiTail) == null)hi = p;elsehiTail.next = p;hiTail = p;++hc;}}ln = (lc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(lo) :(hc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(lo) : t;hn = (hc <= UNTREEIFY_THRESHOLD) ? untreeify(hi) :(lc != 0) ? new TreeBin<K,V>(hi) : t;setTabAt(nextTab, i, ln);setTabAt(nextTab, i + n, hn);setTabAt(tab, i, fwd);advance = true;}}}}}}
擴容的邏輯比較復雜,如果擴容時有多個線程,那么每個線程都可以通過helpTransfer函數幫忙進行擴容:
- 首先新建一個兩倍長度的數組nextTable。
- 初始化ForwardingNode節點,其中保存了新數組nextTable的引用,在處理完每個槽位節點后當做占位節點,表示該槽位已經處理過了。
- 通過for循環處理每個槽位中的鏈表元素,處理完后在這個槽位內通過CAS插入初始化的ForwardingNode節點,用于告訴其它線程該槽位已經處理過了。
- 如果某個槽位已經被線程A處理了,那么線程B處理到這個節點時,取到該節點的hash值應該為MOVED,值為-1,則直接跳過,繼續處理下一個槽位內的節點。
4.計數方法
/*** {@inheritDoc}*/public int size() {long n = sumCount();return ((n < 0L) ? 0 :(n > (long)Integer.MAX_VALUE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE :(int)n);}/*** A padded cell for distributing counts. Adapted from LongAdder* and Striped64. See their internal docs for explanation.*/@sun.misc.Contended static final class CounterCell {volatile long value;CounterCell(long x) { value = x; }}final long sumCount() {CounterCell[] as = counterCells; CounterCell a;long sum = baseCount;if (as != null) {for (int i = 0; i < as.length; ++i) {if ((a = as[i]) != null)sum += a.value;}}return sum;}
代碼里的變量baseCount用于在無競爭環境下記錄元素的個數,每當插入元素或刪除元素時都會利用CAS更新鍵值對個數。
當有線程競爭時,會使用CounterCell數組來計數,每個ConuterCell都是一個獨立的計數單元。線程可以通過ThreadLocalRandom.getProbe() & m找到屬于它的CounterCell進行計數。這種方法能夠降低線程的競爭,相比所有線程對一個共享變量不停進行CAS操作性能上要好很多。這里的CounterCell數組初始容量為2,最大容量是機器的CPU數。
注意這里有個@sun.misc.Contended,這個注解用于解決偽共享問題。所謂偽共享,就是在同一緩存行cache line(CPU緩存的基本單位)中連續存儲了多個變量,當其中一個變量被修改時,會導致其他變量也失效,會降低計算機cache的緩存命中率并且導致內存總線流量大增。


)









)



![[Python] 程序結構與控制流](http://pic.xiahunao.cn/[Python] 程序結構與控制流)


:RecyclerView增刪item)