
本文轉載于YivanLee知乎作者
專題目錄鏈接:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/67694999
這幾天研究了一下虛幻4的delegate,但是想要理解這個,還得從仿函數說起。下面是一段代碼例子:
class MyFunctor
{
public:
int operator()(int x) { return x * 2;}
}
MyFunctor doubler;
int x = doubler(5);The real advantage is that a functor can hold state.
class Matcher
{
int target;
public:
Matcher(int m) : target(m) {}
bool operator()(int x) { return x == target;}
}
Matcher Is5(5);
if (Is5(n)) // same as if (n == 5)
{ ....}現在還可以使用std::function
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class MyCharacter
{
public:
void BeHurt01(int hurtvalue)
{
cout << "hurt01" << hurtvalue << endl;
}
void BeHurt02(int hurtvalue)
{
cout << "hurt02" << hurtvalue << endl;
}
};
class OtherCharacter
{
public:
functionThisIsDelegate;
};
int main()
{
MyCharacter mycha;
OtherCharacter othecha;
othecha.ThisIsDelegate = bind(&MyCharacter::BeHurt01, &mycha, placeholders::_1);
othecha.ThisIsDelegate(19);
return 0;
}這樣做的好處就是實現延遲調用,比如我現在有個主角和一個怪物。因為需要完成動畫播放,主角的出招的特效播放之后才會執行怪物受傷扣血的邏輯。這時候可以先在主角出招的時候探測周圍的怪物然后給他們綁定上傷害函數。
相對于函數指針,std::function能綁定c++里的所有可調用對象,stdfunction相當于幫我們封裝了一個模板。
比如:
(1)首先我們建立一個第三人稱c++模板工程

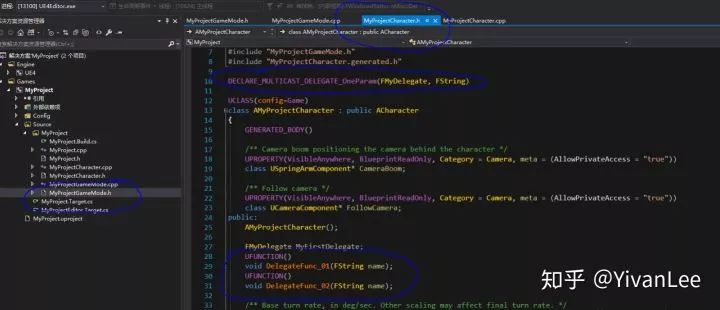
然后打開代碼,在MyProjectCharacter.h中聲明一個代理,兩個與之匹配的函數
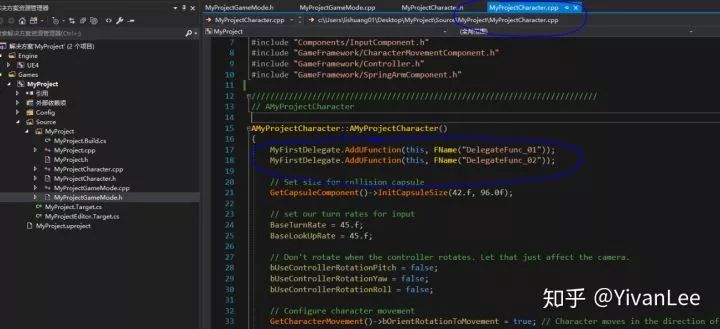
在構造函數中將函數和代理綁定

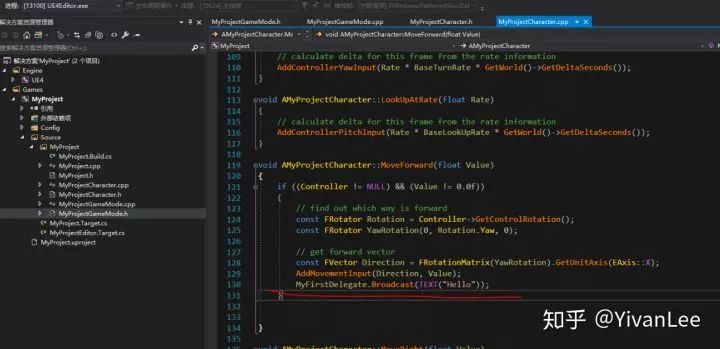
在MoveForward函數里執行這個代理
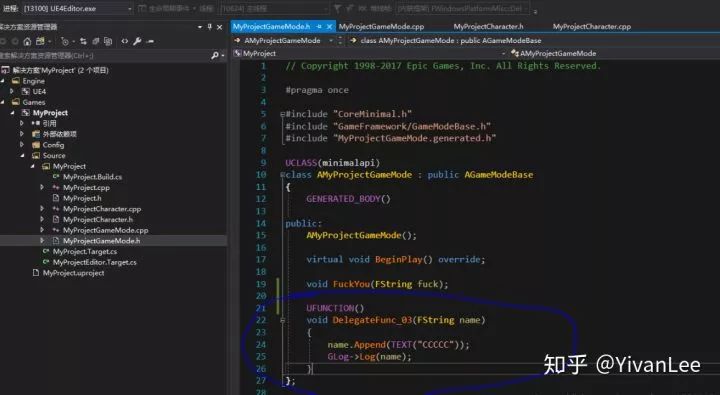
完成綁定工作后我們到gamemode類里做如下工作
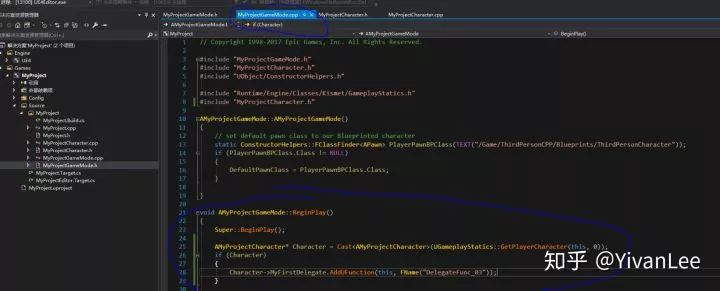
至此我們就可以在游戲執行后,按下w鍵之后的log里看到如下的輸出




與vw)





萬字長文,慎點。)











